SpringBoot详解
文章目录
- 第一个SpringBoot程序
- 原理
- yaml
-
- 给属性赋值的几种方法
- JSR303校验
- 多环境切换
-
- 多配置文件
- yaml的多文档块
- 配置文件加载位置
- 分析自动配置原理
-
- 精髓
- SpringBoot Web开发
-
- 静态资源导入
- 首页如何定制
- Thymeleaf
- 扩展使用SpringMVC
- 全面接管SpringMVC
- 员工管理系统
-
- 首页实现
- 页面国际化
- 登录功能
- 展示员工列表
- 增加员工
- 修改员工
- 删除员工
- 404
- 回顾
- 整合JDBC
-
- 整合Druid数据源
- 配置数据源
- 配置Druid数据源监控
- 整合Mybatis框架
- SpringSecurity
-
- 认识SpringSecurity
- 实战测试
-
- 实验环境搭建
- 认证和授权
- 权限控制和注销
- 记住我
- 定制登录页
- Swagger
-
- SpringBoot集成Swagger
- 配置Swagger
- Swagger配置扫描接口
- 配置API文档分组
- 加注释
- 测试
- 总结
- 任务
-
- 异步任务
-
- 开启多线程的异步方法
- 使用Spring
- 邮件任务
- 定时任务
- 分布式Dubbo+Zookeeper
-
- RPC 远程过程调用
- Dubbo
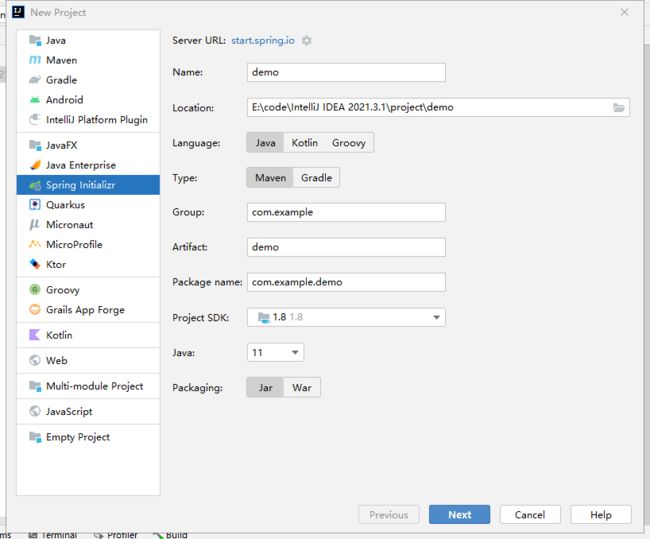
第一个SpringBoot程序
jdk1.8
maven3.6.1
SpringBoot最新
IDEA
官方:提供了一个快速生成的网站,IDEA集成了这个网站(首选)
https://start.spring.io/
原理
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/hzRwZvjYSX-dy-9Drz94aQ
pom.xml
- spring-boot-dependencies:核心依赖在父工程中
- 我们在写入或者引入一些SpringBoot依赖时,不需要指定版本,就是因为有这些版本仓库
启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starterartifactId>
dependency>
SpringBoot的启动场景,比如spring-boot-starter-web,就会自动导入web环境所有依赖
SpringBoot会将所有场景都变成启动器
需要什么功能,找到对应的启动器就可以
主程序
//标注这个类是一个SpringBoot的应用
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot01HelloworldApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将SpringBoot启动
SpringApplication.run(Springboot01HelloworldApplication.class, args);
}
}
注解
@SpringBootConfiguration:SpringBoot的配置
@Configuration:spring配置类
@Component:说明是个spring组件
@EnableAutoConfiguration:自动配置
@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包
@Import({Registrar.class)}:注册
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}):自动配置导入选择
SpringApplication
这个类主要做了以下四件事情:
1、推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是Web项目
2、查找并加载所有可用初始化器 , 设置到initializers属性中
3、找出所有的应用程序监听器,设置到listeners属性中
4、推断并设置main方法的定义类,找到运行的主类
yaml
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件 , 配置文件名称是固定的
-
application.properties
-
- 语法结构 :key=value
-
application.yml
-
- 语法结构 :key:空格 value
#普通的key-value
name: cc
#对象
student:
name: cc
age: 3
#行内写法
student2: {name: cc,age: 3}
#数组
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
pets2: [cat,dog,pig]
给属性赋值的几种方法
用@value给实体类每个字段赋值,或者用properties文件关联,或者yaml文件关联:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
1.实体类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person”):和配置文件赋值的对象绑定(给属性赋值)
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
}
2.application.yaml
person:
name: cc
age: 3
happy: false
birth: 2022/02/12
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- code
- girl
- music
dog:
name: 旺财
age: 3
3.测试
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot02ConfigApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
JSR303校验
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validationartifactId> <version>2.6.3version>dependency>
@Validatedpublic class Person { @Email(message="邮箱格式错误") private String name;
多环境切换
多配置文件
我们在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml , 用来指定多个环境版本;
例如:
application-test.properties 代表测试环境配置
application-dev.properties 代表开发环境配置
但是Springboot并不会直接启动这些配置文件,它默认使用application.properties主配置文件;
我们需要通过一个配置来选择需要激活的环境:
spring.profiles.active=dev#比如在配置文件中指定使用dev环境,我们可以通过设置不同的端口号进行测试;
我们启动SpringBoot,就可以看到已经切换到dev下的配置了;
yaml的多文档块
和properties配置文件中一样,但是使用yml去实现不需要创建多个配置文件,更加方便了 !
server: port: 8081 spring: profiles: active: prod #选择要激活那个环境块---server: port: 8083spring: profiles: dev #配置环境的名称---server: port: 8084spring: profiles: prod #配置环境的名称
注意:如果yml和properties同时都配置了端口,并且没有激活其他环境 , 默认会使用properties配置文件的!
配置文件加载位置
springboot 启动会扫描以下位置的application.properties或者application.yml文件作为Spring boot的默认配置文件:
优先级1:项目路径下的config文件夹配置文件优先级2:项目路径下配置文件优先级3:资源路径下的config文件夹配置文件优先级4:资源路径下配置文件
优先级由高到底,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置;
SpringBoot会从这四个位置全部加载主配置文件;互补配置;
分析自动配置原理
我们以**HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)**为例解释自动配置原理;
//表示这是一个配置类,和以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件;@Configuration //启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能; //进入这个HttpProperties查看,将配置文件中对应的值和HttpProperties绑定起来; //并把HttpProperties加入到ioc容器中@EnableConfigurationProperties({HttpProperties.class}) //Spring底层@Conditional注解 //根据不同的条件判断,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效; //这里的意思就是判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效@ConditionalOnWebApplication( type = Type.SERVLET)//判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器;@ConditionalOnClass({CharacterEncodingFilter.class})//判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置:spring.http.encoding.enabled; //如果不存在,判断也是成立的 //即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的;@ConditionalOnProperty( prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = {"enabled"}, matchIfMissing = true)public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration { //他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了 private final Encoding properties; //只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿 public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpProperties properties) { this.properties = properties.getEncoding(); } //给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBean //判断容器没有这个组件?public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() { CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter(); filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name()); filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpProperties.Encoding.Type.REQUEST)); filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpProperties.Encoding.Type.RESPONSE)); return filter;}//。。。。。。。}
一句话总结 :根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效!
- 一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;
- 这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
- 所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装着;
- 配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类
精髓
1、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2、我们看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中;
3、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件存在在其中,我们就不需要再手动配置了)
4、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们只需要在配置文件中指定这些属性的值即可;
**xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类;**给容器中添加组件
xxxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性;
SpringBoot Web开发
静态资源导入
1、在SpringBoot中可以使用以下方式处理静态资源:
- webjars 访问方式:localhost:8080/webjars/
- public,static,/**,resources 访问方式:localhost:8080/
2、优先级
resources > static(默认)> public
首页如何定制
新建一个 index.html ,在我们上面的3个目录中任意一个
Thymeleaf
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>dependency>
我们首先得按照SpringBoot的自动配置原理看一下我们这个Thymeleaf的自动配置规则,在按照那个规则,我们进行使用。
我们去找一下Thymeleaf的自动配置类:ThymeleafProperties
@ConfigurationProperties( prefix = "spring.thymeleaf")public class ThymeleafProperties { private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING; public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/"; public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html"; private boolean checkTemplate = true; private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true; private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/"; private String suffix = ".html"; private String mode = "HTML"; private Charset encoding;}
我们可以在其中看到默认的前缀和后缀!
我们只需要把我们的html页面放在类路径下的templates下,thymeleaf就可以帮我们自动渲染了。
使用thymeleaf什么都不需要配置,只需要将他放在指定的文件夹下即可!
@RequestMapping("/t1")public String test1(Model model){ //存入数据 model.addAttribute("msg","Hello,Thymeleaf"); //classpath:/templates/test.html return "test";}
DOCTYPE html><html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle>head><body><div th:text="${msg}">div>body>html>
注意命名空间:
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
扩展使用SpringMVC
我们要做的就是编写一个@Configuration注解类,并且类型要为WebMvcConfigurer,还不能标注@EnableWebMvc注解;我们去自己写一个;我们新建一个包叫config,写一个类MyMvcConfig;
//应为类型要求为WebMvcConfigurer,所以我们实现其接口//可以使用自定义类扩展MVC的功能@Configurationpublic class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { // 浏览器发送/test , 就会跳转到test页面; registry.addViewController("/test").setViewName("test"); }}
全面接管SpringMVC
官方文档:
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVCyou can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
全面接管即:SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不需要了,所有都是我们自己去配置!
只需在我们的配置类中要加一个@EnableWebMvc。
我们发现所有的SpringMVC自动配置都失效了!回归到了最初的样子;
当然,我们开发中,不推荐使用全面接管SpringMVC
总结一句话:@EnableWebMvc将WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来了;
而导入的WebMvcConfigurationSupport只是SpringMVC最基本的功能!
在SpringBoot中会有非常多的扩展配置,只要看见了这个,我们就应该多留心注意~
员工管理系统
首页实现
1、config包下编写MyMvcConfig类
@Configurationpublic class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index"); registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("index"); }}
2、静态资源用thymeleaf接管
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
3、application.properties
#关闭模板引擎的缓存spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
页面国际化
1、编写Login bundle
在resources文件夹下建i18n文件夹
可视化编写
2、静态资源用thymeleaf接管
th:text="#{login.tip}"
[[#{login.remember}]]
<body class="text-center"> <form class="form-signin" action="dashboard.html"> <img class="mb-4" th:src="@{/img/bootstrap-solid.svg}" alt="" width="72" height="72"> <h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal" th:text="#{login.tip}">Please sign inh1> <input type="text" class="form-control" th:placeholder="#{login.username}" required="" autofocus=""> <input type="password" class="form-control"th:placeholder="#{login.password}" required=""> <div class="checkbox mb-3"> <label> <input type="checkbox" value="remember-me"> [[#{login.remember}]] label> div> <button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit" th:text="#{login.btn}">Sign inbutton> <p class="mt-5 mb-3 text-muted">© 2017-2018p> <a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(l='zh_CN')}">中文a> <a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(l='en_US')}">Englisha> form>body>
3、给中英文按钮增加链接
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(l='zh_CN')}">中文a><a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(l='en_US')}">Englisha>
4、自定义国际化组件LocaleResolver
public class MyLocalResolver implements LocaleResolver { //解析请求 @Override public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) { //获取请求中的语言参数 String language = request.getParameter("l"); Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();//如果没有就使用默认 //如果请求的链接携带了国际化的参数 if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(language)){ String[] split = language.split("_"); locale = new Locale(split[0], split[1]); } return locale; } @Override public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) { }}
5、将组件配置到容器中(@Bean)
@Configurationpublic class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index"); registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("index"); } //自定义国际化组件生效了 @Bean public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){ return new MyLocalResolver(); }}
登录功能
编写控制类
@Controllerpublic class LoginController { @RequestMapping("/user/login") public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password, Model model) { //具体的业务 if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(username)&&"123456".equals(password)){ return "redirect:/main.html"; }else { model.addAttribute("msg","用户名或者密码错误!"); return "index"; } }}
MyMvcConfig中添加视图解析
registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard");
登录拦截:
public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { Object loginUser = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser"); if(loginUser==null){ request.setAttribute("msg","没有权限,请先登录"); request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request,response); return false; }else { return true; } }}
配置拦截器: MyMvcConfig重写addInterceptors
@Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**").excludePathPatterns("/index.html","/","/user/login", "/css/**","/js/**","/img/**"); }
展示员工列表
1、提取公共页面
th:fragment=“sidebar”
th:replace="~{common/commons::sidebar}"
如果要传递参数,可以直接使用()传参,接收判断即可
2、列表循环展示
@RequestMapping("/emps")public String list(Model model){ Collection<Employee> employees = employeeDao.getAll(); model.addAttribute("emps",employees); return "emp/list";}
增加员工
@GetMapping("/emp")public String toAddpage(Model model){ //查出所有部门信息 Collection departments = departmentDao.getDepartments(); model.addAttribute("departments",departments); return "emp/add";}@PostMapping("/emp")public String addEmp(Employee employee){ employeeDao.save(employee);//保存员工 return "redirect:/emps";}
#时间日期格式化spring.mvc.format.date=yyyy-MM-dd
<form th:action="@{/emp}" method="post"> <div class="form-group"> <label>LastNamelabel> <input type="text" name="lastName" class="form-control" placeholder="海绵宝宝"> div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Emaillabel> <input type="email" name="email" class="form-control" placeholder="[email protected]"> div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Genderlabel><br> <div class="form-check form-check-inline"> <input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gender" value="1"> <label class="form-check-label">男label> div> <div class="form-check form-check-inline"> <input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gender" value="0"> <label class="form-check-label">女label> div> div> <div class="form-group"> <label>departmentlabel> <select class="form-control" name="department.id"> <option th:each="dept:${departments}" th:text="${dept.getDepartmentName()}" th:value="${dept.getId()}">option> select> div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Birthlabel> <input type="text" name="birth" class="form-control" placeholder="2022-2-14"> div> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">添加button>form>
修改员工
隐藏域:
<input type="hidden" name="id" th:value="${emp.getId()}">
//去员工修改页面@GetMapping("/emp/{id}")public String toUpdateEmp(@PathVariable("id")Integer id, Model model){ //查出原来数据 Employee employee = employeeDao.getEmployeeById(id); model.addAttribute("emp",employee); Collection departments = departmentDao.getDepartments(); model.addAttribute("departments",departments); return "emp/update";}//修改@PostMapping("/updateEmp")public String updateEmp(Employee employee){ employeeDao.save(employee); return "redirect:/emps";}
<a class="btn btn-sm btn-primary" th:href="@{/emp/}+${emp.id}">编辑a>
删除员工
//删除@GetMapping("/delemp/{id}")public String deleteEmp(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){ employeeDao.delete(id); return "redirect:/emps";}
404
templates文件夹下建error文件夹,新建404.html,自动跳转
x-admin 后台模板
回顾
整合JDBC
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/2gO3010iV34uGUs4FCGvmA
1、我去新建一个项目测试:springboot-data-jdbc ; 引入相应的模块!基础模块
2、项目建好之后,发现自动帮我们导入了如下的启动器:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbcartifactId>dependency><dependency> <groupId>mysqlgroupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId> <scope>runtimescope>dependency>
3、编写yaml配置文件连接数据库;
spring: datasource: username: root password: 123456 #时区报错,就增加一个时区配置 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&useSSL=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
4、配置完这一些东西后,我们就可以直接去使用了,因为SpringBoot已经默认帮我们进行了自动配置;去测试一下
@RestControllerpublic class JDBCController { @Autowired JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; //查询数据库的所有信息 @GetMapping("/userList") public List> userList(){ String sql = "select * from mybatis.user"; List> list_maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql); return list_maps; }}
整合Druid数据源
配置数据源
1、添加上 Druid 数据源依赖。
<dependency> <groupId>com.alibabagroupId> <artifactId>druidartifactId> <version>1.2.8version>dependency>
2、切换数据源;之前已经说过 Spring Boot 2.0 以上默认使用 com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource 数据源,但可以 通过 spring.datasource.type 指定数据源。
spring: datasource: username: root password: 123456 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource # 自定义数据源
3、可以设置数据源连接初始化大小、最大连接数、等待时间、最小连接数 等设置项;
spring: datasource: username: root password: 123456 #?serverTimezone=UTC解决时区的报错 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource #Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定 #druid 数据源专有配置 initialSize: 5 minIdle: 5 maxActive: 20 maxWait: 60000 timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000 minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000 validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL testWhileIdle: true testOnBorrow: false testOnReturn: false poolPreparedStatements: true #配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入 #如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority #则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j filters: stat,wall,log4j maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20 useGlobalDataSourceStat: true connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
4、导入Log4j 的依赖
5、现在需要程序员自己为 DruidDataSource 绑定全局配置文件中的参数,再添加到容器中,而不再使用 Spring Boot 的自动生成了;我们需要 自己添加 DruidDataSource 组件到容器中,并绑定属性;
@Configurationpublic class DruidConfig { /* 将自定义的 Druid数据源添加到容器中(类比beans.xml),不再让 Spring Boot 自动创建 绑定全局配置文件中的 druid 数据源属性注入到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource从而让它们生效(给属性赋值) @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource"):作用就是将 全局配置文件中 前缀为 spring.datasource的属性值注入到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 的同名参数中 */ @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") @Bean public DataSource druidDataSource() { return new DruidDataSource(); }}
配置Druid数据源监控
Druid 数据源具有监控的功能,并提供了一个 web 界面方便用户查看,类似安装 路由器 时,人家也提供了一个默认的 web 页面。
所以第一步需要设置 Druid 的后台管理页面,比如 登录账号、密码 等;配置后台管理;
@Configurationpublic class DruidConfig { @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") @Bean public DataSource druidDataSource() { return new DruidDataSource(); } //后台监控 //因为SpringBoot内置了servlet容器,所以没有web.xml,替代方法ServletRegistrationBean @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet(){ ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean<>(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*"); //后台需要有人登录,账号密码配置 HashMap initParameters = new HashMap<>(); initParameters.put("loginUsername","admin");//key是固定的 initParameters.put("loginPassword","123456"); //允许谁可以访问 initParameters.put("allow",""); bean.setInitParameters(initParameters); return bean; } //filter 配置 Druid web 监控 filter 过滤器 @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter(){ FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>(); bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter()); //可以过滤哪些请求 Map initParameters = new HashMap<>(); //这些东西不进行统计 initParameters.put("exclusions","*.js,*.css,/druid/*"); bean.setInitParameters(initParameters); return bean; }}
整合Mybatis框架
1、导入 MyBatis 所需要的依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId> <version>2.2.2version>dependency>
2、配置数据库连接信息
spring.datasource.username=rootspring.datasource.password=123456spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&useSSL=true&characterEncoding=utf-8spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver#整合mybatismybatis.type-aliases-package=com.cc.pojomybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
3、测试数据库是否连接成功!
4、创建实体类,导入 Lombok!
5、创建mapper目录以及对应的 Mapper 接口
@Mapper//这个注解表示这是一个mybatis的mapper类,或者@MapperScan("com.cc.mapper")@Repositorypublic interface UserMapper { List queryUserList(); User queryUserById(int id); int addUser(User user); int updateUser(User user); int deleteUser(int id);}
6、对应的Mapper映射文件
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="com.cc.mapper.UserMapper"> <select id="queryUserList" resultType="User"> select * from mybatis.user select> <select id="queryUserById" resultType="User"> select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id} select> <insert id="addUser" parameterType="User"> insert into mybatis.user(id, name, pwd) values (#{id},#{name},#{psw}); insert> <update id="updateUser" parameterType="User"> update mybatis.user set name = #{name},pwd=#{pwd} where id = #{id}; update> <delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="int"> delete from mybatis.user where id = #{id}; delete>mapper>
7、maven配置资源过滤问题
<resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/javadirectory> <includes> <include>**/*.xmlinclude> includes> <filtering>truefiltering> resource>resources>
8、编写Controller 进行测试!
@RestControllerpublic class UserController { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @GetMapping("/queryUserList") public List<User> queryUserList(){ List<User> userList = userMapper.queryUserList(); return userList; }
SpringSecurity
shiro SpringSecurity
认识SpringSecurity
Spring Security 是针对Spring项目的安全框架,也是Spring Boot底层安全模块默认的技术选型,他可以实现强大的Web安全控制,对于安全控制,我们仅需要引入 spring-boot-starter-security 模块,进行少量的配置,即可实现强大的安全管理!
记住几个类:
- WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter:自定义Security策略
- AuthenticationManagerBuilder:自定义认证策略
- @EnableWebSecurity:开启WebSecurity模式
Spring Security的两个主要目标是 “认证” 和 “授权”(访问控制)。
“认证”(Authentication)
身份验证是关于验证您的凭据,如用户名/用户ID和密码,以验证您的身份。
身份验证通常通过用户名和密码完成,有时与身份验证因素结合使用。
“授权” (Authorization)
授权发生在系统成功验证您的身份后,最终会授予您访问资源(如信息,文件,数据库,资金,位置,几乎任何内容)的完全权限。
这个概念是通用的,而不是只在Spring Security 中存在。
实战测试
实验环境搭建
1、新建一个初始的springboot项目web模块,thymeleaf模块
2、导入静态资源
3、controller跳转
@Controllerpublic class RouterController { @RequestMapping({"/","/index"}) public String index(){ return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/toLogin") public String toLogin(){ return "views/login"; } @RequestMapping("/level1/{id}") public String level1(@PathVariable("id") int id){ return "views/level1/"+id; } @RequestMapping("/level2/{id}") public String level2(@PathVariable("id") int id){ return "views/level2/"+id; } @RequestMapping("/level3/{id}") public String level3(@PathVariable("id") int id){ return "views/level3/"+id; }}
4、测试实验环境是否OK!
认证和授权
1、引入 Spring Security 模块
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId>dependency>
2、编写 Spring Security 配置类
参考官网:https://spring.io/projects/spring-security
查看我们自己项目中的版本,找到对应的帮助文档:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.3.0.RELEASE/reference/html5 #servlet-applications 8.16.4
3、定制请求的授权规则
4、在configure()方法中加入以下配置,开启自动配置的登录功能!
5、定义认证规则,重写configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)方法
6、测试,发现会报错!
There is no PasswordEncoder mapped for the id “null”
7、原因,我们要将前端传过来的密码进行某种方式加密,否则就无法登录,修改代码
//AOP:拦截器@EnableWebSecuritypublic class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { //授权 //链式编程 @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { //首页所有人可以访问,功能页只有对应有权限的人才能访问 //请求授权的规则 http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/").permitAll() .antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1") .antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2") .antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3"); //没有权限会默认到登录页,需要开启登录页面 http.formLogin(); } //认证 //密码编码:PasswordEncoder //在SpringSecurity5.0+新增了很多加密方法 @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { //这些数据正常应该从数据库读 auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder()) .withUser("cc").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip2","vip3") .and() .withUser("root").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2","vip3") .and() .withUser("guest").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1"); }}
权限控制和注销
1、开启自动配置的注销的功能
//定制请求的授权规则@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { //.... //开启自动配置的注销的功能 // /logout 注销请求 http.logout();}
2、我们在前端,增加一个注销的按钮,index.html 导航栏中
<a class="item" th:href="@{/logout}"> <i class="address card icon">i> 注销a>
3、我们可以去测试一下,登录成功后点击注销,发现注销完毕会跳转到登录页面!
4、但是,我们想让他注销成功后,依旧可以跳转到首页,该怎么处理呢?
//logoutSuccessUrl("/"); 注销成功来到首页http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/");
5、测试,注销完毕后,发现跳转到首页OK
6、我们现在又来一个需求:用户没有登录的时候,导航栏上只显示登录按钮,用户登录之后,导航栏可以显示登录的用户信息及注销按钮!还有就是,比如kuangshen这个用户,它只有 vip2,vip3功能,那么登录则只显示这两个功能,而vip1的功能菜单不显示!这个就是真实的网站情况了!该如何做呢?
我们需要结合thymeleaf中的一些功能
sec:authorize=“isAuthenticated()”:是否认证登录!来显示不同的页面
Maven依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.thymeleaf.extrasgroupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5artifactId> <version>3.0.4.RELEASEversion>dependency>
7、修改我们的 前端页面
导入命名空间
xmlns:sec=“http://www.thymeleaf.org/extras/spring-security”
修改导航栏,增加认证判断
<div class="right menu"> <div sec:authorize="!isAuthenticated()"> <a class="item" th:href="@{/toLogin}"> <i class="address card icon">i> 登录 a> div> <div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()"> <a class="item"> 用户名:<span sec:authentication="name">span> 角色:<span sec:authentication="authorities">span> a> div> <div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()"> <a class="item" th:href="@{/logout}"> <i class="sign-out icon">i> 注销 a> div>
8、重启测试,我们可以登录试试看,登录成功后确实,显示了我们想要的页面;
9、如果注销404了,就是因为它默认防止csrf跨站请求伪造,因为会产生安全问题,我们可以将请求改为post表单提交,或者在spring security中关闭csrf功能;我们试试:在 配置中增加 http.csrf().disable();
//开启了注销功能,跳到首页http.logout().disable();//关闭csrf功能(springsecurity5不用手动关闭)http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/");
10、我们继续将下面的角色功能块认证完成!
<div class="column" sec:authorize="hasRole('vip1')"> <div class="ui raised segment"> <div class="ui"> <div class="content"> <h5 class="content">Level 1h5> <hr> <div><a th:href="@{/level1/1}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-1-1a>div> <div><a th:href="@{/level1/2}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-1-2a>div> <div><a th:href="@{/level1/3}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-1-3a>div> div> div> div>div><div class="column" sec:authorize="hasRole('vip2')"> <div class="ui raised segment"> <div class="ui"> <div class="content"> <h5 class="content">Level 2h5> <hr> <div><a th:href="@{/level2/1}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-2-1a>div> <div><a th:href="@{/level2/2}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-2-2a>div> <div><a th:href="@{/level2/3}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-2-3a>div> div> div> div>div><div class="column" sec:authorize="hasRole('vip3')"> <div class="ui raised segment"> <div class="ui"> <div class="content"> <h5 class="content">Level 3h5> <hr> <div><a th:href="@{/level3/1}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-3-1a>div> <div><a th:href="@{/level3/2}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-3-2a>div> <div><a th:href="@{/level3/3}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-3-3a>div> div> div> div>
11、测试一下!
12、权限控制和注销搞定!
记住我
现在的情况,我们只要登录之后,关闭浏览器,再登录,就会让我们重新登录,但是很多网站的情况,就是有一个记住密码的功能,这个该如何实现呢?很简单
1、开启记住我功能
//定制请求的授权规则@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {//。。。。。。。。。。。 //记住我 http.rememberMe();}
2、我们再次启动项目测试一下,发现登录页多了一个记住我功能,我们登录之后关闭 浏览器,然后重新打开浏览器访问,发现用户依旧存在!
思考:如何实现的呢?其实非常简单
我们可以查看浏览器的cookie
3、我们点击注销的时候,可以发现,spring security 帮我们自动删除了这个 cookie
4、结论:登录成功后,将cookie发送给浏览器保存,以后登录带上这个cookie,只要通过检查就可以免登录了。如果点击注销,则会删除这个cookie,具体的原理我们在JavaWeb阶段都讲过了,这里就不在多说了!
定制登录页
现在这个登录页面都是spring security 默认的,怎么样可以使用我们自己写的Login界面呢?
1、在刚才的登录页配置后面指定 loginpage
http.formLogin().loginPage("/toLogin");
2、然后前端也需要指向我们自己定义的 login请求
<a class="item" th:href="@{/toLogin}"> <i class="address card icon">i> 登录a>
3、我们登录,需要将这些信息发送到哪里,我们也需要配置,login.html 配置提交请求及方式,方式必须为post:
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post"> <div class="field"> <label>Usernamelabel> <div class="ui left icon input"> <input type="text" placeholder="Username" name="username"> <i class="user icon">i> div> div> <div class="field"> <label>Passwordlabel> <div class="ui left icon input"> <input type="password" name="password"> <i class="lock icon">i> div> div> <div class="field"> <input type="checkbox" name="remember">记住我 div>
4、这个请求提交上来,我们还需要验证处理,怎么做呢?我们可以查看formLogin()方法的源码!我们配置接收登录的用户名和密码的参数!
http.formLogin() .usernameParameter("username") .passwordParameter("password") .loginPage("/toLogin") .loginProcessingUrl("/login"); // 登陆表单提交请求
5、在登录页增加记住我的多选框
<input type="checkbox" name="remember"> 记住我
6、后端验证处理!
//定制记住我的参数!http.rememberMe().rememberMeParameter("remember");
Swagger
- 号称世界上最流行的API框架
- RestFul API文档在线自动生成工具=>API文档与API定义同步更新
- 直接运行,可以在线测试API接口
- 支持多种语言:(Java、PHP…)
在项目中使用Swagger需要springfox
SpringBoot集成Swagger
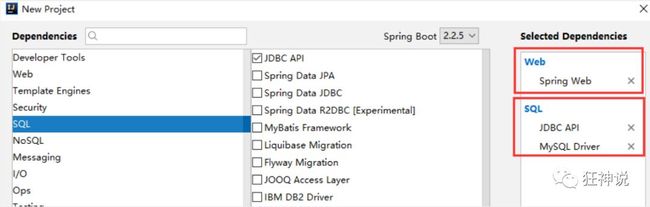
1、新建SpringBoot-web项目
2、导入相关依赖
<dependency> <groupId>io.springfoxgroupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger2artifactId> <version>2.9.2version>dependency><dependency> <groupId>io.springfoxgroupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger-uiartifactId> <version>2.9.2version>dependency>
3、编写一个hello工程
4、配置swagger==>Confige
@Configuration@EnableSwagger2//开启swagger2public class SwaggerConfig {}
5、测试运行 http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
配置Swagger
Swagger的bean实例docket
@EnableSwagger2//开启swagger2public class SwaggerConfig { @Bean public Docket docket(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()); } //配置swagger信息=apiinfo private ApiInfo apiInfo(){ //作者信息 Contact contact =new Contact("cc","","[email protected]"); return new ApiInfo("cc的Api Documentation", "Api Documentation", "1.0", "urn:tos", contact, "Apache 2.0", "http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0", new ArrayList()); }}
Swagger配置扫描接口
Docket.select()
@Beanpublic Docket docket(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .enable(false) .select() //指定要扫描的包:basePackage() 扫描全部:any() 不扫描:none() 扫描注解上的类:withClassAnnotation() 扫描方法上的注解withMethodAnnotation() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.cc.controller"))//RequestHandlerSelectors配置要扫描接口的方式 .paths(PathSelectors.ant("/cc/**"))//过滤什么路径 .build();}
配置是否启动Swagger
.enable(false)
如果为false,则Swagger不能在浏览器中访问
只希望我的Swagger在生产环境中使用,在发布的时候不使用?
- 判断是不是生产环境 flag=false
- 注入enable(flag)
@Beanpublic Docket docket(Environment environment){ //设置要显示的Swagger环境 Profiles profiles = Profiles.of("dev","test"); //通过environment.acceptsProfiles判断是否处在自己设定的环境 boolean flag = environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles); return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .enable(flag) .select() //指定要扫描的包:basePackage() 扫描全部:any() 不扫描:none() 扫描注解上的类:withClassAnnotation() 扫描方法上的注解withMethodAnnotation() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.cc.controller"))//RequestHandlerSelectors配置要扫描接口的方式 .build();}
配置API文档分组
.groupName("cc")
如何配置多个分组:多个Docket实例即可
@Beanpublic Docket docket1(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("A");}@Beanpublic Docket docket2(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("B");}@Beanpublic Docket docket3(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("C");}
加注释
实体类
//只要接口返回值中存在实体类,他就会被扫描到swagger中@PostMapping("/user")public User user(){ return new User();}
//给类和字段加注释//@Api(注释)@ApiModel("用户实体类")public class User { @ApiModelProperty("用户名") public String username; @ApiModelProperty("密码") public String password;}
接口方法:
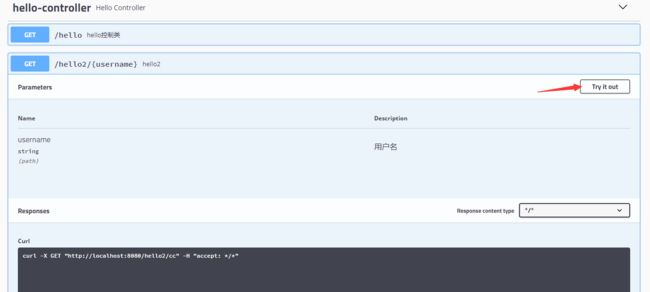
@ApiOperation("hello控制类")@GetMapping("/hello")public String hello(){ return "hello";}
参数
@GetMapping("/hello")public String hello(@ApiParam("用户名") String username){ return "hello"+username;}
测试
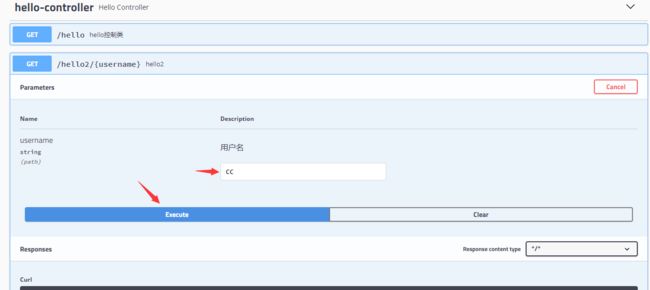
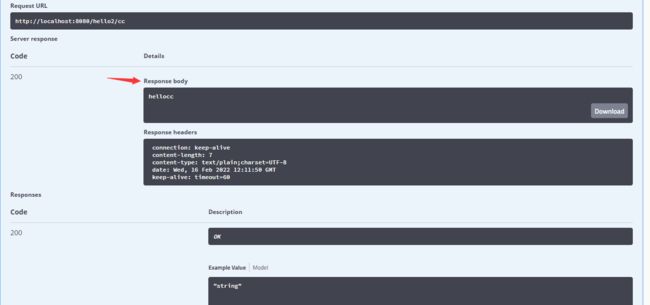
restful风格传值
@GetMapping("/hello2/{username}")public String hello2(@ApiParam("用户名") @PathVariable("username") String username){ return "hello"+username;}
总结
通过Swagger给一些难理解的属性或接口增加注释信息
接口文档实时更新
可以在线测试
【注意点】在正式发布时候关闭Swagger(出于安全考虑)而且节省运行内存
任务
异步任务
1、写一个service,线程停止三秒
@Servicepublic class AsyncService { public void hello(){ try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("数据正在处理"); }}
2、写一个controller,调用业务
@RestControllerpublic class AsyncController { @Autowired AsyncService asyncService; @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ asyncService.hello();//停止三秒 return "ok"; }}
3、测试
发现服务器请求三秒后返回ok
开启多线程的异步方法
业务实现runnable接口重写run方法,controller创建线程对象代理接口实现类对象,调用start()开启线程
@Servicepublic class AsyncService implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("数据正在处理"); }}
@RestControllerpublic class AsyncController { @Autowired AsyncService asyncService; @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ Thread thread = new Thread(asyncService); thread.start(); return "ok"; }}
测试:
发现浏览器迅速显示ok,但控制台的"数据正在处理"仍然需要三秒才输出。
使用Spring
@Async @EnableAsync
@Servicepublic class AsyncService { //告诉Spring这是一个异步方法 @Async public void hello(){ try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("数据正在处理"); }}
//开启异步注解功能@EnableAsync@SpringBootApplicationpublic class Springboot09TestApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Springboot09TestApplication.class, args); }}
邮件任务
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mailartifactId>dependency>
spring.mail.username=xxx你的邮箱地址spring.mail.password=xxxx授权码spring.mail.host=smtp.qq.com#开启加密验证spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.ssl.enable=true
@SpringBootTestclass Springboot09TestApplicationTests { @Autowired JavaMailSenderImpl mailSender; @Test void contextLoads() { //一个简单的邮件 SimpleMailMessage mailMessage = new SimpleMailMessage(); mailMessage.setSubject("通知");//主题 mailMessage.setText("谢谢");//文本 mailMessage.setTo("[email protected]"); mailMessage.setFrom("[email protected]"); mailSender.send(mailMessage); }}
@Testvoid contextLoads2() throws MessagingException { //一个复杂的邮件 MimeMessage mimeMessage = mailSender.createMimeMessage(); //组装 MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage,true); helper.setSubject("通知2"); helper.setText("谢谢
",true); //附件 helper.addAttachment("1.jpg",new File("C:\\Users\\ASUS\\Pictures\\1.jpg")); helper.setTo("[email protected]"); helper.setFrom("[email protected]"); mailSender.send(mimeMessage);}
定时任务
TaskScheduler 任务调度者
TaskExecutor 任务执行者
@EnableScheduling 开启定时功能的注解
@Scheduled 什么时候执行
Cron表达式:
30 15 10 * * ? 每天10点15分30秒执行一次
30 0/5 10,18 * * ? 每天10点和18点,每隔5分钟执行一次
0 15 10 ? * 1-6 每个月周一到周六10点15分执行一次
@Servicepublic class ScheduledService { //在特定时间执行该方法 //cron表达式 秒 分 时 日 月 星期 @Scheduled(cron="0 42 16 * * 0-7") public void hello(){ System.out.println("hello,你被执行了"); }}
分布式Dubbo+Zookeeper
RPC 远程过程调用
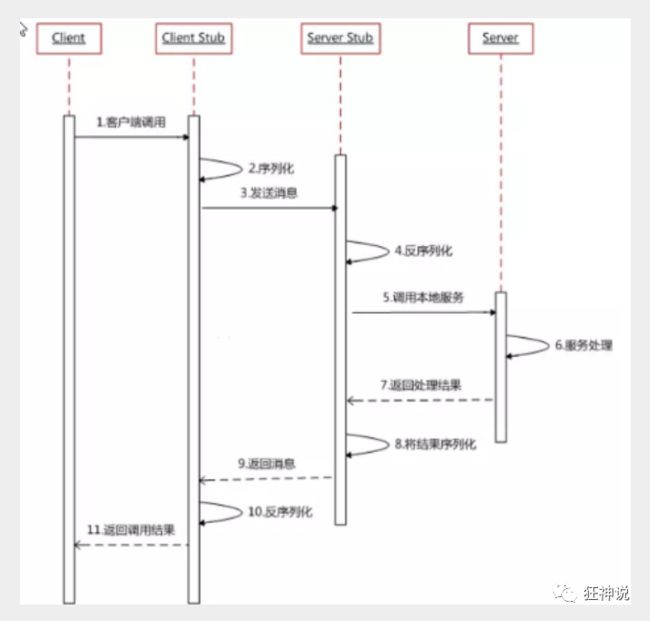
RPC【Remote Procedure Call】是指远程过程调用,是一种进程间通信方式,他是一种技术的思想,而不是规范。它允许程序调用另一个地址空间(通常是共享网络的另一台机器上)的过程或函数,而不用程序员显式编码这个远程调用的细节。即程序员无论是调用本地的还是远程的函数,本质上编写的调用代码基本相同。
RPC两个核心模块:通讯,序列化。
Dubbo
Apache Dubbo |ˈdʌbəʊ| 是一款高性能、轻量级的开源Java RPC框架,它提供了三大核心能力:面向接口的远程方法调用,智能容错和负载均衡,以及服务自动注册和发现。
dubbo官网 http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/index.html
环境搭建:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/sKu9-vH7NEpUd8tbxLRLVQ
Dubbo-admin是一个监控管理后台,查看注册了哪些服务,哪些服务被消费了
Dubbo:jar包