torch.max()、expand()、expand_as()使用讲解
在分类问题中,通常需要使用max()函数对softmax函数的输出值进行操作,求出预测值索引,然后与标签进行比对,计算准确率。下面讲解一下torch.max()函数的输入及输出值都是什么,便于我们理解该函数。函数主要用来求 tensor 的最大值
1. torch.max(input, dim,keepdim) 函数
output = torch.max(input, dim)
输入
input是softmax函数输出的一个tensordim是max函数索引的维度0/1,0是每列的最大值,1是每行的最大值
输出
- 函数会返回两个
tensor,第一个tensor是每行的最大值;第二个tensor是每行最大值的索引。
在多分类任务中我们并不需要知道各类别的预测概率,所以返回值的第一个tensor对分类任务没有帮助,而第二个tensor包含了预测最大概率的索引,所以在实际使用中我们仅获取第二个tensor即可。
-
keepdim(bool)– 保持输出的维度 :
当keepdim=False时,输出比输入少一个维度(就是指定的dim求范数的维度)<即输出时,可能只需要输出对应维度上的最大值,形成一维数组输出>。而keepdim=True时,输出与输入维度相同,仅仅是输出在求范数的维度上元素个数变为1<即输出时,输出对应维度上的最大值,形成与输入tensor数组相同尺寸大小输出>。
c # 三行两列
#tensor([[2, 2],
# [3, 3],
# [4, 4]])
torch.max(c,1,keepdim=True)[0] # 在列方向上,out tensor 与 input tensor维度一致
#tensor([[2],
# [3],
# [4]])
torch.max(c,1,keepdim=False)[0] # 在列方向上,out tensor 与 input tensor维度不一致
#tensor([2, 3, 4])参考博客:
torch.max(output, 2, keepdim=True)[1]_踏实写代码,认真搞学术的小研的博客-CSDN博客
-
dim: index,第二个参数为一个整数[-2-1]
dim=0表示计算每列的最大值,dim=1表示每行的最大值
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
input = torch.randn(2,2,3)
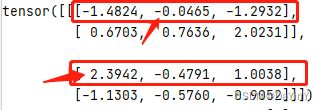
print(input)输出:
tensor([[[-1.4824, -0.0465, -1.2932],
[ 0.6703, 0.7636, 2.0231]],
[[ 2.3942, -0.4791, 1.0038],
[-1.1303, -0.5760, -0.9052]]])当dim=0时:
a = torch.max(input, dim = 0)输出:
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([[ 2.3942, -0.0465, 1.0038],
[ 0.6703, 0.7636, 2.0231]]),
indices=tensor([[1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0]]))当dim=1时:
b = torch.max(input, dim = 1)输出:
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([[ 0.6703, 0.7636, 2.0231],
[ 2.3942, -0.4791, 1.0038]]),
indices=tensor([[1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0]]))
a = torch.max(input, dim = 0)当dim=-1时:
c = torch.max(input, dim = -1)输出:
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([[-0.0465, 2.0231],
[ 2.3942, -0.5760]]),
indices=tensor([[1, 2],
[0, 1]]))当dim=2时:(dim=-1和dim=2的结果是一样的)
d = torch.max(input, dim = 2)输出:
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([[-0.0465, 2.0231],
[ 2.3942, -0.5760]]),
indices=tensor([[1, 2],
[0, 1]]))总结(dim)
![]()
参考博客:
pytorch: torch.max() 使用与理解_让机器看懂世界的博客
pytorch中tf.nn.functional.softmax(x,dim = -1)对参数dim的理解
-
函数的用法(示例)
import torch
a = torch.tensor([[1,5,62,54], [2,6,2,6], [2,65,2,6]])
print(a)
输出:
tensor([[ 1, 5, 62, 54],
[ 2, 6, 2, 6],
[ 2, 65, 2, 6]])
- 索引每行的最大值:
torch.max(a, 1)
输出:
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([62, 6, 65]), # value值
indices=tensor([2, 3, 1])) # 对应的索引
- 在计算准确率时第一个tensor
values是不需要的,所以我们只需提取第二个tensor,并将tensor格式的数据转换成array格式。
torch.max(a, 1)[1].numpy()
输出:
array([2, 3, 1], dtype=int64)
这样,我们就可以与标签值进行比对,计算模型预测准确率。
*注:在有的地方我们会看到torch.max(a, 1).data.numpy()的写法,这是因为在早期的pytorch的版本中,variable变量和tenosr是不一样的数据格式,variable可以进行反向传播,tensor不可以,需要将variable转变成tensor再转变成numpy。现在的版本已经将variable和tenosr合并,所以只用torch.max(a,1).numpy()就可以了。
2.准确率的计算
pred_y = torch.max(predict, 1)[1].numpy()
label_y = torch.max(label, 1)[1].data.numpy()
accuracy = (pred_y == label_y).sum() / len(label_y)
predict - softmax函数输出label - 样本标签,这里假设它是one-hot编码
参考博客:
torch.max()使用讲解 - 简书
3、expand()函数:
(1)函数功能:
expand()函数的功能是用来扩展张量中某维数据的尺寸,它返回输入张量在某维扩展为更大尺寸后的张量。
扩展张量不会分配新的内存,只是在存在的张量上创建一个新的视图(关于张量的视图可以参考博文:由浅入深地分析张量),而且原始tensor和处理后的tensor是不共享内存的。
expand()函数括号中的输入参数为指定经过维度尺寸扩展后的张量的size。
(2)应用举例:
1)# 在行上更改
import torch
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) # C:一行三列
c = a.expand(2, 3) # 将C进行扩为:两行三列
print(a)
print(c)
# 输出信息:
tensor([1, 2, 3])
tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3]]
2)
import torch
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) # C:一行三列
c = a.expand(3, 3) # 将C进行扩为:三行三列
print(a)
print(c)
# 输出信息:
tensor([1, 2, 3])
tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3]])
3) # 在列上更改
import torch
a = torch.tensor([[1], [2], [3]]) # C:三行一列
print(a.size())
c = a.expand(3, 3) # 将C进行扩为:三行三列
print(a)
print(c)
# 输出信息:
torch.Size([3, 1])
tensor([[1],
[2],
[3]])
tensor([[1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3]])
4)
import torch
a = torch.tensor([[1], [2], [3]]) # C:三行一列
print(a.size())
c = a.expand(3, 4) # 将C进行扩为:三行四列
print(a)
print(c)
# 输出信息:
torch.Size([3, 1])
tensor([[1],
[2],
[3]])
tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2, 2],(3)注意事项:
expand()函数只能将size=1的维度扩展到更大的尺寸,如果扩展其他size()的维度会报错。
4、expand_as()函数:
(1)函数功能:
expand_as()函数与expand()函数类似,功能都是用来扩展张量中某维数据的尺寸,区别是它括号内的输入参数是另一个张量,作用是将输入tensor的维度扩展为与指定tensor相同的size。
(2)应用举例:
1) # 不使用另一个张量的值,只是参考张量的尺寸
import torch
a = torch.tensor([[2], [3], [4]]) # 三行一列
print(a)
b = torch.tensor([[2, 2], [3, 3], [5, 5]]) # 三行两列
print(b.size())
c = a.expand_as(b) # 三行两列
print(c)
print(c.size())
# 输出信息:
tensor([[2],
[3],
[4]])
torch.Size([3, 2])
tensor([[2, 2],
[3, 3],
[4, 4]])
torch.Size([3, 2])
2)
import torch
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) # 一行三列
print(a)
b = torch.tensor([[2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 3]]) # 两行三列
print(b.size())
c = a.expand_as(b) # 两行三列
print(c)
print(c.size())
# 输出信息:
tensor([1, 2, 3])
torch.Size([2, 3])
tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3]])
torch.Size([2, 3])
参考博客:
pytorch中的expand()和expand_as()函数_小娜美要努力努力的博客-CSDN博客_expand_as