RNA-seq数据分析
一、数据收集
1.NCBI GEO数据库收集相关RNA-seq数据

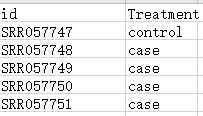
样本信息以及引用文献可以点击对应链接查看
2.SRA Run Selector 查看数据单双端类型(SINGLE or PAIRED)及分组信息
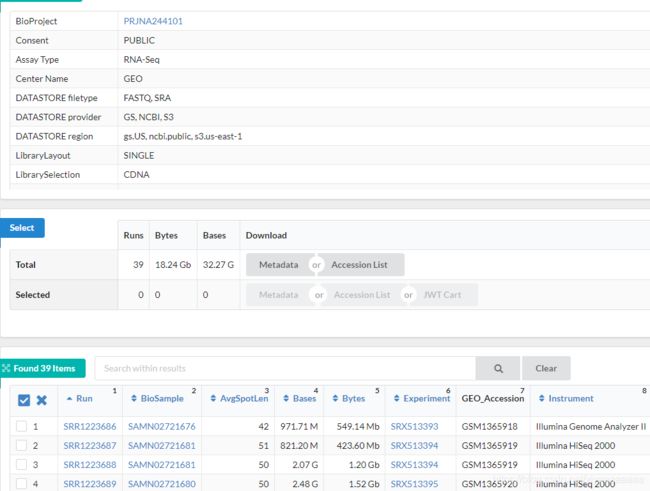
可以点击Accession List下载对应的SRR_Acc_List.txt
二、RNA-seq 处理流程
使用HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown处理流程
<一>下载并解压SRA文件
1.根据下载的SRR_Acc_List.txt下载原始sra文件至SRR文件夹
prefetch -O SRR/ --option-file SRR_Acc_List.txt
2.解压sra文件生成对应的fastq文件至fastq文件夹
for i in SRR/SRR*/*.sra; do echo $i ; fasterq-dump -O fastq/ -e 16 --split-3 $i; done
#--split-3, 会把双端sra文件拆分成两个文件,但是单端并不会保存成两个文件
<二>对数据进行质量控制
fastqc进行质控,multiqc合并质控结果
#fastqc
#fastqc质控
for i in fastq/*.fastq; do echo $i ; fastqc -t 20 -o fastq/quality $i; done
#multiqc
multiqc fastq/quality/ -n before_report.html -o fastq/
<三> 数据裁剪
1.fastp使用
#单端测序数据(single-end,SE)
fastp -i in.fq -o out.fq
#双端测序数据(paired-end,PE)
fastp -i in.R1.fq -o out.R1.fq -I in.R2.fq -O out.R2.fq
2.参数详解
#单端数据
for filename in fastq/*.fastq
do
base=$(basename $filename .fastq)
echo $base
fastp -i fastq/${base}.fastq -o fastq/deal/${base}.fastq -w 16 -x --trim_poly_x --poly_x_min_len 20 -q 20 -u 40 -n 5 -3 -W 4 -M 25
done
#-w 16 线程数
#-x --trim_poly_x --poly_x_min_len 20 切除polyx尾巴,尾巴长度设置为20
#-q 20 -u 40 表示一个 read 最多只能有 40%的碱基的质量值低于Q20,否则会被扔掉
#-n 5 过滤N碱基过多的reads
#-3 -W 4 -M 25 从3'开始移动滑动窗口,滑窗大小为4, 平均质量低于25被切
#双端数据
for filename in fastq/*_1.fastq
do
base=$(basename $filename _1.fastq)
echo $base
fastp -i fastq/${base}_1.fastq -I fastq/${base}_2.fastq -o fastq/deal/${base}_1.fastq -O fastq/deal/${base}_2.fastq -w 16 -x --trim_poly_x --poly_x_min_len 20 -q 20 -u 40 -n 5 -3 -W 4 -M 25 -c --overlap_len_require 30 --overlap_diff_limit 5 --overlap_diff_percent_limit 20
done
#-c, --correction 对PE碱基校正,使用该参数是基于检测overlap。
#--overlap_len_require overlap的长度要求,默认是30,即默认overlap区域的长度不低于30bp;
#--overlap_diff_limit overlap中最大错配数,默认是5,即默认overlap时最多有5个错配;
#--overlap_diff_percent_limit overlap中最大错配数在重叠区的占比,默认是20,即默认最大错配数的碱基占比不高于20%;否则认为无overlap。`
<四>检查数据质量
#fastqc
#fastqc质控
for i in fastq/deal/*.fastq; do echo $i ; fastqc -t 20 -o fastq/deal/quality $i; done
#multiqc
multiqc fastq/deal/quality/ -n after_report.html -o fastq/
<五>Hisat比对
1.参考基因组及对应注释文件(gtf)下载
参考基因组与注释文件要对应,否则比对率很低且下游分析比较麻烦
iGenomes
2.Hisat2索引
hisat2-build -p 16 genome.fa genome
#genome.fa 为对应的参考基因组
#genome 为建立的索引名称
3.mapping到参考基因组
#单端文件比对
for filename in fastq/deal/*.fastq
do
base=$(basename $filename .fastq)
echo $base
hisat2 -t -p 16 --dta -x /lustre/home/acct-clsdqw/clsdqw-user1/Desktop/RNA-seq/E.coli/reference/hisat2/genome \
-U fastq/deal/${base}.fastq -S process/sam/${base}.sam
#双端文件比对
for filename in fastq/deal/*_1.fastq
do
base=$(basename $filename _1.fastq)
echo $base
hisat2 -t -p 20 -x /lustre/home/acct-clsdqw/clsdqw-user1/Desktop/RNA-seq/code/Yeast/reference/hisat2/genome \
-1 fastq/deal/${base}_1.fastq -2 fastq/deal/${base}_2.fastq -S process/sam/${base}.sam
-x 要写到对应的索引名称
<六>samtools进行格式转换并排序
1.view: 将sam文件与bam文件互换
bam文件优点:bam文件为二进制文件,占用的磁盘空间比sam文本文件小;利用bam二进制文件的运算速度快。
2.sort: 对bam文件进行排序(sort)
这些操作是对bam文件进行的,因而当输入为sam文件的时候,不能进行该操作
samtools view -@ 16 -S process/sam/${base}.sam -b > process/bam/${base}.bam
samtools sort -@ 16 process/bam/${base}.bam -o process/bam_sort/${base}.bam
<七>得到转录本并进行组装
#获得gtf
for filename in process/bam_sort/*.bam
do
base=$(basename $filename .bam)
echo $base
stringtie -p 16 process/bam_sort/${base}.bam -G /lustre/home/acct-clsdqw/clsdqw-user1/Desktop/RNA-seq/E.coli/reference/E.coli.gtf -o process/gtf/${base}.gtf
done
#获得strimerge.gtf
for filename in process/gtf/*.gtf
do
base=$(basename $filename .gtf)
echo process/gtf/${base}.gtf >> process/gtf/mergelist.txt
done
stringtie --merge -p 16 -G /lustre/home/acct-clsdqw/clsdqw-user1/Desktop/RNA-seq/E.coli/reference/E.coli.gtf -o process/gtf/strimerge.gtf process/gtf/mergelist.txt
<八>Ballgown获得所有转录本及其丰度
#ballgown
for filename in process/bam_sort/*.bam
do
base=$(basename $filename .bam)
echo $base
stringtie -e -B -p 16 -G process/gtf/strimerge.gtf -o ballgown/${base}/${base}.gtf process/bam_sort/${base}.bam
done
三、下游分析
1.使用R语言进行差异表达基因筛选,GO KEGG富集分析并绘图
my_DEG_analysis <-function(gse_name,phenodata,ballgownfile,smallprotein,logfc,pvalue)
{
library(ballgown)
library(genefilter)
library(dplyr)
library(devtools)
library(ggplot2)
library(GSEABase)
###指定分组信息
sampleGroup <- read.csv(phenodata, header = TRUE)
#DESeq2说明清楚哪个因子level对应的control,避免后面解释数据遇到麻烦(你不知道到底logFC是以谁做参照的,希望是以control作为参照,这样logFC>1就表示实验组表达大于对照组;但是R不知道,R默认按字母顺序排列因子顺序,所以要对这个因子顺序set一下:
#factor levels,写在前面的level作为参照
sampleGroup$Treatment <- factor(sampleGroup$Treatment, levels = c("control", "case"))
###读入数据
bg_chrX=ballgown(dataDir =ballgownfile,samplePattern = "SRR", meas='all',pData=sampleGroup)
whole_tx_table=texpr(bg_chrX, 'all')
transcript_fpkm=texpr(bg_chrX, 'FPKM')
colnames(transcript_fpkm)<-substring(colnames(transcript_fpkm), 6)
rownames(transcript_fpkm)<-whole_tx_table$gene_name
###提取fpkm矩阵
data<-transcript_fpkm
group_list <- sampleGroup$Treatment
expMatrix <- data
fpkmToTpm <- function(fpkm)
{
exp(log(fpkm) - log(sum(fpkm)) + log(1e6))
}
tpms <- apply(expMatrix,2,fpkmToTpm)
tpms[1:3,]
colSums(tpms)
exprSet <- tpms
#limma 对数据进行归一化处理
library(limma)
exprSet2=normalizeBetweenArrays(exprSet)
#boxplot(exprSet2,outline=FALSE, notch=T,col=group_list, las=2)
#判断数据是否需要转换
exprSet3 <- log2(exprSet2+1)
###主成分分析图
dat <- t(exprSet2)#画PCA图时要求是行名时样本名,列名时探针名,因此此时需要转换
dat <- as.data.frame(dat)#将matrix转换为data.frame
dat <- cbind(dat,group_list) #cbind横向追加,即将分组信息追加到最后一列
#dat[1:5,1:5]
#BiocManager::install("FactoMineR")
#BiocManager::install("factoextra")
library("FactoMineR")
library("factoextra")
# before PCA analysis
dat.pca <- PCA(dat[,-ncol(dat)], graph = FALSE)#现在dat最后一列是group_list,需要重新赋值给一个dat.pca,这个矩阵是不含有分组信息的
fviz_pca_ind(dat.pca,
geom.ind = "point", # show points only (nbut not "text")
col.ind = dat$group_list, # color by groups
# palette = c("#00AFBB", "#E7B800"),
addEllipses = TRUE, # Concentration ellipses
legend.title = "Groups"
)
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"all_samples_PCA.png"))
###差异分析
dat <- exprSet3
#design <- model.matrix(~0+factor(group_list))
design=model.matrix(~factor( group_list ))
fit=lmFit(dat,design)
fit=eBayes(fit)
options(digits = 4)
topTable(fit,coef=2,adjust='BH')
degene=topTable(fit,coef=2,adjust='BH',number = Inf)
head(degene)
write.csv(degene,paste(gse_name,"gene_results.csv") ,row.names=FALSE)
###筛选差异表达小蛋白
library(ggrepel)
smallp<-read.csv(smallprotein,header = F)
deg<-subset(degene,degene$ID %in% smallp$V1)
write.csv(deg, paste(gse_name,"smallprotein_results.csv"),row.names=FALSE)
deg$g=ifelse(deg$P.Value<pvalue & abs(deg$logFC) >logfc,
ifelse(deg$P.Value<pvalue & deg$logFC > logfc,'UP','DOWN'),'STABLE')
table(deg$g)
data<-deg
data$threshold = as.factor(deg$g)
data$label <- ifelse(data$P.Value < pvalue & abs(data$logFC) >= logfc,data$ID,"")
p<-ggplot(data, aes(logFC, -log10(P.Value),col = threshold)) +
ggtitle("Differential genes") +
geom_point(alpha=0.3, size=2) +
scale_color_manual(values=c("blue", "grey","red")) +
labs(x="logFC",y="-log10 (p-value)") +
theme_bw()+
geom_hline(yintercept = -log10(as.numeric(pvalue)), lty=4,col="grey",lwd=0.6) +
geom_vline(xintercept = c(-1, 1), lty=4,col="grey",lwd=0.6) +
theme(plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5),
panel.grid=element_blank(),
axis.title = element_text(size = 12),
axis.text = element_text(size = 12))
p
p+geom_text_repel(data = data, aes(x = logFC, y = -log10(P.Value), label = label),
size = 3,box.padding = unit(0.5, "lines"),
point.padding = unit(0.8, "lines"),
segment.color = "black",
show.legend = FALSE)
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"VolcanoSP.png"),width = 7, height = 7)
###差异基因注释分析
library(ggstatsplot)
library(cowplot)
library(clusterProfiler)
library(enrichplot)
library(ReactomePA)
library(stringr)
library(tidyr)
library(org.Sc.sgd.db)
degene$ENSEMBL=degene$ID
df <- bitr(unique(degene$ENSEMBL), fromType = "ENSEMBL",
toType = c("ENTREZID","GENENAME"),
OrgDb = org.Sc.sgd.db)
#head(df)
DEG=degene
#head(DEG)
DEG$g=ifelse(DEG$P.Value<pvalue & abs(DEG$logFC) >logfc,
ifelse( DEG$P.Value<pvalue & DEG$logFC > logfc,'UP','DOWN'),'STABLE')
DEG=merge(DEG,df,by='ENSEMBL')
head(DEG)
save(DEG,file = 'anno_DEG.Rdata')
DEG_diff=DEG[DEG$g == 'UP' | DEG$g == 'DOWN',]
gene_diff=DEG_diff$ENSEMBL
###通路与基因之间的关系可视化
###制作genlist三部曲:
## 1.获取基因logFC
geneList <- as.numeric(DEG$logFC)
## 2.命名
names(geneList) = as.character(DEG$ENSEMBL)
## 3.排序很重要
geneList = sort(geneList, decreasing = TRUE)
geneList = na.omit(geneList)
head(geneList)
geneListgo <- as.numeric(DEG$logFC)
names(geneListgo) = as.character(DEG$ENTREZID)
geneListgo = sort(geneListgo, decreasing = T)
geneListgo <- geneListgo[!is.na(geneListgo)]
head(geneListgo)
###GO分析
library(DOSE)
library(ggnewscale)
library(topGO)
GO<-enrichGO(DEG_diff$ENSEMBL, OrgDb = "org.Sc.sgd.db", keyType = "ENSEMBL",ont = "all", pvalueCutoff = 0.5,
pAdjustMethod = "BH", qvalueCutoff = 0.5, minGSSize = 10,
maxGSSize = 500, readable = FALSE, pool = FALSE)
write.csv(GO, paste(gse_name,"GO_results.csv"),row.names=FALSE)
if (length(GO$ID) > 0){
dotplot(GO, split="ONTOLOGY") + facet_grid(ONTOLOGY~., scale="free")
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"GO_dotplot.png"))
barplot(GO, split="ONTOLOGY")+facet_grid(ONTOLOGY~., scale="free")
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"GO_barplot.png"))
enrichplot::cnetplot(GO,circular=FALSE,colorEdge = TRUE)
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"GO_gene_pathway.png"))
enrichplot::heatplot(GO,foldChange=geneListgo,showCategory = 50)
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"GO_gene_pathway_heatmap.png"))
}
###KEGG
enrichKK <- enrichKEGG(gene = as.character(gene_diff),
organism = 'sce',
keyType = "kegg",
#universe = gene_all,
pvalueCutoff = 0.5,
qvalueCutoff = 0.5)
write.csv(enrichKK, paste(gse_name,"KEGG_results.csv"),row.names=FALSE)
print(enrichKK)
#head(enrichKK)[,1:6]
#气泡图
if (length(enrichKK$ID) > 0){
dotplot(enrichKK)
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"KEGG_dotplot.png"))
##最基础的条形图和点图
#条带图
barplot(enrichKK,showCategory=20)
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"KEGG_barplot.png"))
enrichplot::cnetplot(enrichKK,circular=FALSE,colorEdge = TRUE)#circluar为指定是否环化,基因过多时建议设置为FALSE
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"KEGG_gene_pathway.png"))
enrichplot::heatplot(enrichKK,foldChange=geneList,showCategory = 50)
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"KEGG_gene_pathway_heatmap.png"))
}
GSEA_KEGG <- gseKEGG(geneList, organism = 'sce', nPerm = 1000, minGSSize = 10, maxGSSize = 500, pvalueCutoff = 1)
if (length(GSEA_KEGG$ID) > 0){
ridgeplot(GSEA_KEGG)
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"enrichKEGG_ridgeplot.png"))
if(length(GSEA_KEGG$ID) < 5){
enrichplot::gseaplot2(GSEA_KEGG,1:as.numeric(dim(GSEA_KEGG)[1]))
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"enrichKEGG_gseaplot.png"))
}else{
enrichplot::gseaplot2(GSEA_KEGG,1:5)
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"enrichKEGG_gseaplot.png"))
}
}
GSEA_GO <- gseGO(geneList = geneListgo ,
OrgDb = org.Sc.sgd.db,
keyType = "ENTREZID",
ont = "all",
nPerm = 1000, ## 排列数
minGSSize = 5,
maxGSSize = 500,
pvalueCutoff = 0.95,
verbose = TRUE)
print(GSEA_GO)
if (length(GSEA_GO$ID) > 0){
ridgeplot(GSEA_GO)
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"enrichGO_ridgeplot.png"))
if(length(GSEA_GO$ID) < 5){
enrichplot::gseaplot2(GSEA_GO,1:as.numeric(dim(GSEA_GO)[1]))
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"enrichGO_gseaplot.png"))
}else{
enrichplot::gseaplot2(GSEA_GO,1:5)
ggsave(file=paste(gse_name,"enrichGO_gseaplot.png"))
}
}
}
#my_DEG_analysis("GSE63516","phenodata.csv","ballgown","smallprotein.csv",1.5,0.05)
args = commandArgs(trailingOnly=TRUE)
gse_name<-args[1]
phenodata<-args[2]
ballgownfile<-args[3]
smallprotein<-args[4]
logfc<-args[5]
pvalue<-args[6]
my_DEG_analysis(gse_name,phenodata,ballgownfile,smallprotein,logfc,pvalue)
2.服务器调用sh文件
#!/bin/bash
mkdir jobid
#传入用户上传的phenodata.csv
mkdir jobid_yeast/ballgown
#copy指定SRR的表达文件
awk -F"," '{if (NR>1)print$1}' jobid_yeast/phenodata.csv | while read input;do cp -r /home/qzhao/database/Saccharomyces_cerevisiae/GSE/GSE56622/ballgown/$input jobid_yeast/ballgown;done
cd jobid_yeast
source activate R3.6
Rscript /home/qzhao/database/Saccharomyces_cerevisiae/reference/DEG_function.R jobid phenodata.csv ballgown /home/qzhao/database/Saccharomyces_cerevisiae/reference/sp.csv 1 0.05
3.结果说明
Figure1. all_samples_PCA
Each sample represents a sample of GSE data.
Figure2. VolcanoSP
Volcano plot shows fold change and p-value for a particular comparison (case versus control). The y-axis represents the p-value of genes. The x-axis represents the logFC of genes. The gray dashed line shows selected fold change and p-value cutoff. Small proteins at the selected logFC and P-value threshold are highlighted in red (indicate upregulation) and blue(indicate downregulation) separately.
Figure3. GO_barplot.
The y-axis represents GO-enriched terms. The x-axis represents the genes’ number. The size of the bar represents the number of genes under a specific GO term. The BP(biological processes), CC(cellular component), MF(molecular function) GO terms are colored by the adjusted p-values.
Figure4. GO_dotplot.
The y-axis represents GO-enriched terms. The x-axis represents the GeneRatio. The size of dots represents the number of genes under a specific term. The color of the dots represents the adjusted P-value.
Figure5. GO_gene_pathway_heatmap
The y-axis represents GO-enriched terms. The x-axis represents the gene name. The color represents the fold change.
Figure6. GO_gene_pathway
The nodes represent the significantly regulated DEGs. The edges represent the interaction of significantly regulated DEGs. DEGs, differentially expressed genes.
Figure7. KEGG_barplot.
The y-axis represents KEGG-enriched terms. The x-axis represents the genes’ number. The size of the bar represents the number of genes under a specific term. The KEGG terms are colored by the adjusted p-values.
Figure8. KEGG_dotplot.
The y-axis represents KEGG-enriched terms. The x-axis represents the GeneRatio. The size of dots represents the number of genes under a specific term. The color of the dots represents the adjusted P-value.
Figure9. KEGG_gene_pathway_heatmap.
The y-axis represents KEGG-enriched terms. The x-axis represents the gene name. The color represents the fold changes.
Figure10. KEGG_gene_pathway
The nodes represent the significantly regulated DEGs. The edges represent the interaction of significantly regulated DEGs. DEGs, differentially expressed genes.
Figure11. enrichGO_gseaplot
Each line representing one particular gene set with unique color and the display limit is 5. Only gene sets with FDR q < 0.05 were considered significant.
Figure12.enrichGO_ ridgeplot.
Grouped by gene set, density plots are generated by using the frequency of fold change values per gene within each set.
Figure13. enrichKEGG_ridgeplot.
Grouped by gene set, density plots are generated by using the frequency of fold change values per gene within each set.
Figure14. enrichKEGG_gseaplot
Each line representing one particular gene set with unique color and the display limit is 5. Only gene sets with FDR q < 0.05 were considered significant.
Table 1. smallprotein_results
ID: the small protein gene names
LogFC: estimate of the log2-fold-change corresponding to the contrast(case vs control)
AveExpr: average log2-expression for the sample
t: moderated t-statistic
P.Value: raw p-value
B: log-odds that the gene is differentially expressed
Table 2. GO_results
ONTOLOGY: Three categories of functions subordinate to GO (MF: molecular function, CC: cellular component, BP: biological process)
ID: enriched GO terms
Description: GO function description
GeneRatio: The ratio of the number of genes annotated to the corresponding GO to the total number of genes with GO annotations
BgRatio: The ratio of the number of genes related to the Term among all (bg) genes to all (bg) genes.
pvalue: statistically significant level of enrichment analysis, under normal circumstances, P-value <0.05 this function is an enrichment item
p.adjust: adjust corrected P-Value
qvalue: the q value for statistical testing of the p-value
geneID: the gene names annotated to the corresponding GO term
Cout: the number of genes annotated to the corresponding GO term
Table 3. KEGG_results
ID: enriched KEGG terms
Description: KEGG function description
GeneRatio: The ratio of the number of genes annotated to the corresponding KEGG to the total number of genes with KEGG annotations
BgRatio: The ratio of the number of genes related to the Term among all (bg) genes to all (bg) genes.
pvalue: statistically significant level of enrichment analysis, under normal circumstances, P-value <0.05 this function is an enrichment item
p.adjust: adjust corrected P-Value
qvalue: the q value for statistical testing of the p-value
geneID: the gene names annotated to the corresponding KEGG term
Cout: the number of genes annotated to the corresponding KEGG term