用python将dataframe将中的两列处理成行索引和列索引
目录
-
- 1. 操作案例
- 2. 函数讲解
-
- statck(堆叠)
- unstack(拆堆)
1. 操作案例
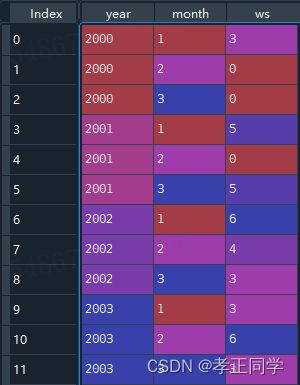
构建dataframe,dataframe 设为 frame,其中三列分别为 year,month,ws。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = {'year': [2000,2000,2000, 2001,2001,2001, 2002,2002,2002, 2003,2003,2003],
'month': [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3,],
'ws':np.random.randint(7, size=12)}
frame = pd.DataFrame(data)
frame2 = frame.set_index(['year', 'month'])
frame2 = frame2.unstack()
frame2.columns = frame.month.unique().tolist()
2. 函数讲解
statck(堆叠)
该操作会“旋转”或将列中的数据透视到行。
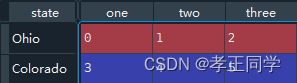
我将通过一系列的例子来说明这些操作。考虑一个带有字符串数组作为行和列索引的小型DataFrame:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(6).reshape((2, 3)),
index=pd.Index(['Ohio', 'Colorado'], name='state'),
columns=pd.Index(['one', 'two', 'three'],
name='number'))
data
Out[2]:
number one two three
state
Ohio 0 1 2
Colorado 3 4 5

在这份数据上使用stack方法会将列透视到行,产生一个新的Series:
result = data.stack() #得到一个 Series
result
Out[4]:
state number
Ohio one 0
two 1
three 2
Colorado one 3
two 4
three 5
dtype: int32
unstack(拆堆)
该操作会将行中的数据透视到列。
从一个多层索引序列中,你可以使用 unstack 方法将数据重排列后放入一个DataFrame中:
result.unstack()# 恢复到 stack 前的状态
Out[5]:
number one two three
state
Ohio 0 1 2
Colorado 3 4 5
默认情况下,最内层是已拆堆的(与stack方法一样)。你可以传入一个层级序号或名称来拆分一个不同的层级:
result.unstack(0)
Out[7]:
state Ohio Colorado
number
one 0 3
two 1 4
three 2 5
result.unstack('state') #解开 'state'列
Out[8]:
state Ohio Colorado
number
one 0 3
two 1 4
three 2 5