Eigen库:(二)密集线性问题和分解
1. 线性代数和分解
1.1 线性方程组求解
求解线性方程组Ax=b,b可以是向量,也可以是矩阵。
#include 上面的例子是列主元的QR分解,速度很快,是求解线性方程组的一个很折中的选择。colPivHouseholderQr()返回的是A的ColPivHouseholderQR对象,完成对A的QR分解,然后solve()方法返回Ax=b的一个解,如果解存在的话。上面倒数第二句可以用下面两句来代替:
ColPivHouseholderQR<Matrix3f> dec(A);
Vector3f x = dec.solve(b);
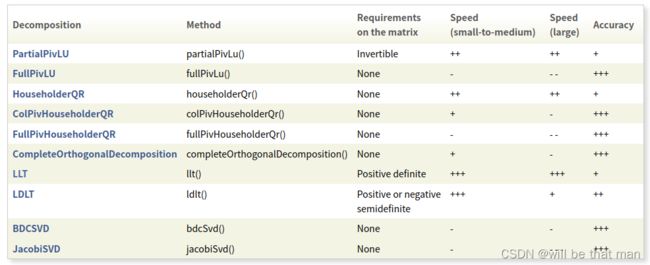
下面给出各种分解的表:
1.2 检查相对误差
#include 1.3 特征值和特征向量
SelfAdjointEigenSolver类是自伴随矩阵的特征分解类,可以用于对一般矩阵和复数矩阵的特征分解。
EigenSolver类是一般矩阵的特征分解类。
ComplexEigenSolver是复数矩阵的特征分解类。
因此SelfAdjointEigenSolver类是包含了EigenSolver和ComplexEigenSolver的所有功能。
#include 1.4 矩阵的逆和行列式
求矩阵的逆运算比较复杂,一般我们在求解线性方程组都是用矩阵分解solve()来做,因为更加高效。下面给出矩阵求逆和行列式的方法。
A.determinant()
A.inverse()
1.5 最小二乘解
最精确的最小二乘求解方法是SVD分解,还有其他的方法,第二章会说。Eigen提供了两种实现:
BDCSVD类(推荐),适用于大问题,在较小问题上自动回退到JacobiSVD类。JacobiSVD类,适用于小问题。
#include 上述的bdcSvd()内的参数不清楚有什么用,但我们需要指定,可选参数为ComputeFullU, ComputeThinU, ComputeFullV, ComputeThinV。
1.6 利用构造器来分解计算
所有的分解都有一个默认构造器,我们对构造器模板指定数据类型后,就可以利用构造器的compute()方法进行分解,利用solve()方法求解。这样能够避免对象的重新创建。
#include 我们还可以在创建构造器对象时指定矩阵的大小,这样,对同样大小的矩阵时,就不需要再进行动态内存分配了,节省计算资源。
HouseholderQR<MatrixXf> qr(50,50);
MatrixXf A = MatrixXf::Random(50,50);
qr.compute(A); // no dynamic memory allocation
1.7 秩揭示分解
有些方法是提供了计算秩的方法和计算零空间和列空间的方法。
#include 2. 线性最小二乘问题
一个过定方程组,比如Ax = b,没有解。在这种情况下,寻找最接近解的向量x是有意义的,即Ax - b的差值尽可能小。这个x称为最小二乘解(如果使用欧几里德范数)。
下面提供三种方法:
- SVD分解:最准确但最慢
- 正规方程:最快但最不准确
- QR分解:两者之间
2.1 SVD分解
#include 2.2 QR分解
QR分解有三个类:
- HouseholderQR (no pivoting,
so fast but unstable) - ColPivHouseholderQR (column pivoting, thus
a bit slower but more accurate) - FullPivHouseholderQR (full pivoting,
so slowest and most stable).
MatrixXf A = MatrixXf::Random(3, 2);
VectorXf b = VectorXf::Random(3);
cout << "The solution using the QR decomposition is:\n"
<< A.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(b) << endl;
2.3 正规方程
基于正规方程:
A T A x = A T b A^TAx = A^Tb ATAx=ATb
MatrixXf A = MatrixXf::Random(3, 2);
VectorXf b = VectorXf::Random(3);
cout << "The solution using normal equations is:\n"
<< (A.transpose() * A).ldlt().solve(A.transpose() * b) << endl;