SpringCloud-Ribbon、负载均衡、自定义负载均衡算法
SpringCloud-Ribbon、负载均衡、自定义负载均衡算法
- 前言
-
- 什么是Ribbon
- Ribbon能做什么
- 负载均衡简单分类
- 集成Ribbon
-
- 导入依赖
- 编写配置
- 修改配置类
- 修改Controller
- 启动类
- 使用Ribbon实现负载均衡
-
- 创建三个数据库
- 运行客户端
- 总结
- 自定义负载均衡算法
-
- 分析
- 使用随机算法
- 自定义编写配置类
-
- 自定义算法
- 使用自定义算法
- 配置启动类
前言
什么是Ribbon
SpringCloud-Ribbon是基于Netflix Ribbon实现的一套客户端负载均衡的工具
主要功能是提供客户端的软件负载均衡算法,例如连接超时、重试等等,Ribbon会自动的帮助你基于某种规则(简单轮询、随机连接)去连接这些机器,我们也可以使用Ribbon实现自定义的负载均衡算法!
Ribbon能做什么
- 负载均衡(LB-LoadBalance)
- 自定义负载均衡算法
- 常用的负载均衡软件有Nginx、Lvs、Apache+Tomcat等等
负载均衡简单分类
- 集中式LB
即在服务的消费方和提供方之间使用独立的LB设施,如Nginx:反向代理服务器,由该设施负责把访问请求通过某种策略转发至服务的提供方 - 进程式LB
将LB逻辑集成到消费方,消费方从服务注册中心获知哪些地址可用,然后自己再从这些地址中选出一个合适的服务器
Ribbon就属于进程式LB,它只是一个类库,集成与消费方进程,消费方通过它来获取服务提供方的地址
集成Ribbon
由于Ribbon是集成在消费方的,因此我们只需要在消费方配置上Ribbon即可
导入依赖
<!--Ribbon-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-ribbon</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--eureka-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
编写配置
server:
port: 80
#Eureka配置
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false #不向eureka注册自己
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/,http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://localhost:7003/eureka/
修改配置类
我们客户端是通过 RestTemplate来访问服务的,而Ribbon是集成在客户端的,所以我们要在我们的配置类上绑定我们的Ribbon,只需要加一个注解即可@LoadBalanced
package com.cjh.springcloud.config;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@Configuration
public class ConfigBean {
//配置负载均衡实现RestTemplate
@LoadBalanced //Ribbon
@Bean
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
修改Controller
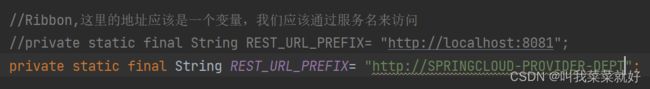
我们在初次使用Springcloud的时候,客户端获取服务是通过Rest来获取的,通过访问url来获取服务,这里的url是写死的,而Ribbon是需要负载均衡算法判断访问哪一个服务器的,因此这里的地址应该是一个变量,我们应该通过服务名来访问。
package com.cjh.springcloud.controller;
import com.cjh.springcloud.pojo.Dept;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class DeptConsumerController {
//理解:消费者,不应该有service层
//RestTemplate
//(url,实体:Map,Class<T> responseType)
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate; //提供多种便捷访问远程http服务的方法,简单的restful服务模板
//Ribbon,这里的地址应该是一个变量,我们应该通过服务名来访问
//private static final String REST_URL_PREFIX= "http://localhost:8081";
private static final String REST_URL_PREFIX= "http://SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT";
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/add")
public boolean add(Dept dept){
return restTemplate.postForObject(REST_URL_PREFIX+"/dept/add",dept,Boolean.class);
}
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/list")
public List<Dept> list(){
return restTemplate.getForObject(REST_URL_PREFIX+"/dept/list",List.class);
}
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/get/{id}")
public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
return restTemplate.getForObject(REST_URL_PREFIX+"/dept/get/"+id,Dept.class);
}
}
启动类
在启动类上加上注解@EnableEurekaClient
package com.cjh.springcloud;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class DeptConsumer_80 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeptConsumer_80.class,args);
}
}
使用Ribbon实现负载均衡
我们用图解看看我们要做什么事情:
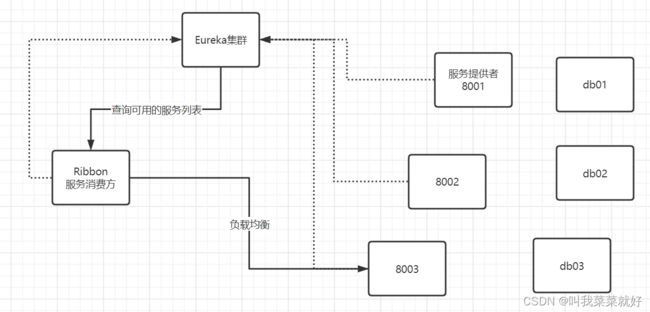
我们的Ribbon就是从服务注册中心查询服务列表,并通过负载均衡算法来判断哪一个服务最合适,实线部分就是Ribbon在做的事情。
创建三个数据库
我们把db01的内容备份并复制为db02和db03,共三个数据库,模拟多个服务多个数据库。
/*
Navicat MySQL Data Transfer
Source Server : 本地mysql
Source Server Version : 50520
Source Host : localhost:3306
Source Database : db01
Target Server Type : MYSQL
Target Server Version : 50520
File Encoding : 65001
Date: 2022-05-04 12:05:32
*/
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for dept
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `dept`;
CREATE TABLE `dept` (
`deptno` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`dname` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
`db_source` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`deptno`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='部门表';
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of dept
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `dept` VALUES ('1', '开发部', 'db01');
INSERT INTO `dept` VALUES ('2', '人事部', 'db01');
INSERT INTO `dept` VALUES ('3', '财务部', 'db01');
INSERT INTO `dept` VALUES ('4', '市场部', 'db01');
INSERT INTO `dept` VALUES ('5', '运维部', 'db01');

我们现在数据相同,但是数据源不同,这样就可以知道客户端从哪个服务中获取数据的。
接着我们创建多个服务提供者,只是连接数据库不同,具体过程就不再演示。
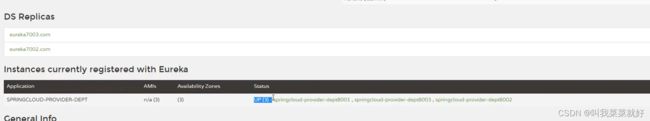
然后我们分别启动之后就可以在注册中心中发现我们的服务提供者有3个。
运行客户端
我们启动客户端,看看客户端会从注册中心中获取哪一个服务,通过负载均衡来判断,默认是轮询算法,每一次的刷新我们可以看到我们获取数据源都是轮询来获取的,接下来我们来自定义算法。
总结
使用Ribbon负载均衡只需要在客户端的启动类中绑定上Ribbon的LB即可,这样在启动客户端之后,会自动根据负载均衡判断哪一个服务最优,默认是轮询算法
自定义负载均衡算法
分析
我们来看Ribbon的注解@LoadBalanced做了什么,它的核心接口其实是IRule.Class,那么IRule.class有哪些对象呢
IRule.class

这个接口非常简单,首先是选择、然后是设置负载均衡
然后我们可以看到他的继承类:

我们要自定义的前提就是看别人是怎么写的,然后进行自定义修改。
首先是AvailabilityFilteringRule ,它的功能就是会先过滤掉跳闸的、访问故障的服务,对剩下的进行轮询
其实是RoundRobinRule,它的功能是轮询
然后是RandomRule,它的功能是随机
RetryRule:它的功能是重试,它会按照轮询获取服务,如果服务获取失败则会在指定的时间内进行重试
我们发现,这些方法都继承了AbstractLoadBalancerRule,所以我们写自定义算法,就是继承AbstractLoadBalancerRule即可
我们就选一个最经典的轮询算法来自定义我们的轮询算法。
我们来分析源码,其实最核心的算法就是这一段:
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
log.warn("no load balancer");
return null;
} else {
Server server = null;
int count = 0;
while(true) {
if (server == null && count++ < 10) {
List<Server> reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers();
List<Server> allServers = lb.getAllServers();
int upCount = reachableServers.size();
int serverCount = allServers.size();
if (upCount != 0 && serverCount != 0) {
int nextServerIndex = this.incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount);
server = (Server)allServers.get(nextServerIndex);
if (server == null) {
Thread.yield();
} else {
if (server.isAlive() && server.isReadyToServe()) {
return server;
}
server = null;
}
continue;
}
log.warn("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb);
return null;
}
if (count >= 10) {
log.warn("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: " + lb);
}
return server;
}
}
}
- 这里的lb就是从父类直接获取的,首先判断,如果lb是空的,那么默认没有负载均衡,返回空。
- 接着定义两个变量,一个用来计数,一个用来存储当前的服务
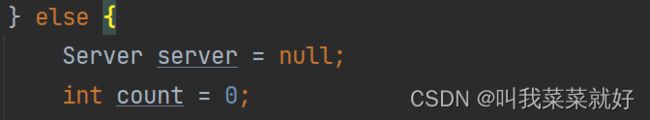
- 接着通过循环获取可以获取到的服务,从lb中获取,如果存在多个,就返回一个list
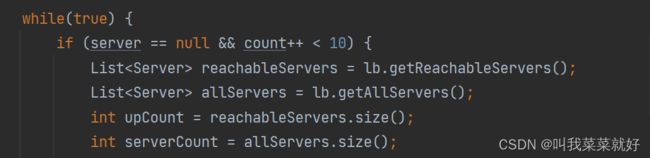
- 如果为0,说明没有可用的,返回No up servers,如果不为0,就获取下一个节点,进行轮询,如果线程为空,那么就礼让一下,如果线程还活着,就返回当前这个线程,否则就返回为空
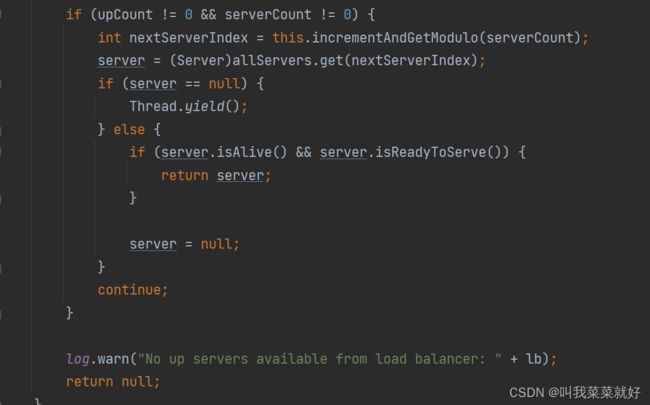
- 如果数量大于10,就说明没有可以用的线程,最后把服务放回去。
使用随机算法
这里我们先尝试使用它的随机算法,Ribbon默认是轮询算法,我们来体验一下随机算法。
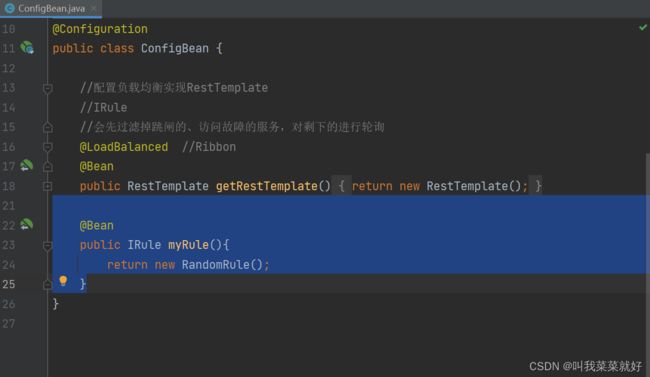
把随机算法注册进Bean中
@Bean
public IRule myRule(){
return new RandomRule();
}
这仅仅是测试一下,正常情况下我们应该在别的路径下创建配置类,下面就介绍这种方式。
自定义编写配置类
自定义算法
我们现在自己定义一个随机算法,参考RandomRule,我们写一个 CjhRandomRule
package com.cjh.myrule;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import com.netflix.client.config.IClientConfig;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.AbstractLoadBalancerRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.ILoadBalancer;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.IRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.Server;
public class CjhRandomRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
//每个服务,访问5次,换一下个服务(总共3个服务)
//total=0,默认=0.如果=5,我们就指向下一个节点
//index=0,默认=0,如果total=5,那么index应该加1,index如果大于3,就要把自身重置为0
private int total =0 ;//被调用的次数
private int currentIndex = 0;//当前是谁在提供服务
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
return null;
}
Server server = null;
while (server == null) {//当所有服务器死光才停止
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
return null;
}
List<Server> upList = lb.getReachableServers();//活着的server
List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers();//所有server
int serverCount = allList.size();
if (serverCount == 0) {
return null;
}
//自定义代码
if(total<5) {
server = upList.get(currentIndex);//访问当前服务器
total ++;//访问次数增加
}else {
total = 0;
currentIndex++;//五次后切换另一台服务器
if(currentIndex>=upList.size()) { //大于活着的数量
currentIndex = 0;//所有可用服务器循环完毕后再次循环
}
server = upList.get(currentIndex); //从活着的服务中获取指定的服务来进行操作
}
if (server == null) {
Thread.yield();
continue;
}
if (server.isAlive()) {
return (server);
}
server = null;
Thread.yield();
}
return server;
}
@Override
public Server choose(Object key) {
return choose(getLoadBalancer(), key);
}
@Override
public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
使用自定义算法
CjhRule
package com.cjh.myrule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.IRule;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class CjhRule {
@Bean
public IRule myRule(){
return new CjhRandomRule(); //自定义负载均衡算法
}
}
配置启动类
DeptConsumer_80
package com.cjh.springcloud;
import com.cjh.myrule.CjhRule;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@RibbonClient(name = "SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT",configuration = CjhRule.class)
public class DeptConsumer_80 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeptConsumer_80.class,args);
}
}
我们需要在启动类中加上注解@RibbonClient(name = "SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT",configuration = CjhRule.class)
它的功能就负责哪一个服务的负载均衡,指定是哪一个配置类,在启动的时候就去判定。