遗传算法(Python)
一、遗传算法
1、遗传算法的定义
遗传算法是一种现代优化算法。根据自然界适者生存的法则,种群中优秀个体的基因进行遗传。每个个体的染色体通过选择、交叉和变异等过程产生新的适应度更大的染色体,其中适应度越大的个体越优秀,种群得到优化,得到的解逼近最优解,种群重复迭代不断优化最终得到目标问题的最优解。
2、遗传算法的特点
优点
① 具有良好的全局搜索能力,求解时不易陷入局部最优解
② 搜索过程中具有潜在的并行性
缺点
① 局部搜索能力较差,往往只能得到次优解
3、遗传算法的主要步骤
① 编码解码
② 确定初始种群
③ 确定适应度函数
④ 选择
⑤ 交叉
⑥ 变异
⑦ 搜索最优解
二、遗传算法基本模型
(以求解 ![]() 的最小值为例)
的最小值为例)
1、编码解码
常见的编码方法有二进制编码、整数编码、格雷编码、浮点数编码等。
以二进制编码为例
① 计算所需二进制编码位数
#[start,end]为取值范围,precision为精度,即小数点后的位数
def get_binary_bit(start, end, precision):
numbers = (end - start) * pow(10, precision) + 1
if int(math.log(numbers, 2)) == math.log(numbers, 2):
return int(math.log(numbers, 2))
else:
return int(math.log(numbers, 2)) + 1② 编码
#decimal为未编码的十进制数
def binary_encode(decimal, start, end, precision):
bit = get_binary_bit(start, end, precision)
#将十进制数转为对应的二进制编码
binary = bin(int((decimal - start) * pow(10, precision)))
#由于bin()生成的是0bxxxxx的形式,因此切片
binary = str(binary)[2:]
#补齐位数
while len(binary) < bit:
binary = '0' + binary
#返回二进制编码
return binary③ 解码
#binary为二进制编码
def binary_decode(binary, start, precision):
#将二进制编码转为标准形式0bxxxxx
binary = '0b' + binary
#将二进制编码转为十进制编码
decimal = int(binary, 2)
#将十进制编码转为对应的十进制数
decimal = start + decimal / pow(10, precision)
return decimal2、确定初始种群
① 随机生成初始种群
#population为种群大小
def initialization(population, start, end, precision):
initialized = []
for i in range(population):
#随机生成指定范围和精度的小数,并转为二进制编码
random_float = random.uniform(start, end)
random_float_precision = round(random_float, precision)
random_binary = binary_encode(random_float_precision, start, end, precision)
initialized.append(random_binary)
#返回初始化种群
return initialized② 在确定初始种群之前,尽量进行一个大概率的区间估计,以免初始种群分布在远离全局最优解的编码空间,导致遗传算法的搜索范围受到限制,同时也为算法减轻负担。
以该函数为例,可以先画出函数在定义域内的图像,进行大致的区间估计
x = np.linspace(-1.57, 20.18, 200)
y = x ** 3 * np.cos(x)
plt.plot(x, y, color='red')
plt.show()如图所示,可以大致估计出函数的区间在[15,17],因此可以使用收缩的初始化种群
#[optimize_start, optimize_end]为大致的估计区间
def initialization(population, start, end, precision, optimize_start, optimize_end):
initialized = []
for i in range(population):
random_float = random.uniform(optimize_start, optimize_end)
random_float_precision = round(random_float, precision)
random_binary = binary_encode(random_float_precision, start, end, precision)
initialized.append(random_binary)
return initialized3、确定适应度函数
适应度函数用来判断染色体的优劣,适应度函数的确认与目标函数密切相关,当目标函数是非负的情况下,可以作为适应度函数;当目标函数是负数的情况下,需要通过变形成为正数,再作为适应度函数,适应度越高种群的优良性越好,遗传给下一代的可能性越大,此时的解越接近最优解。
该例中,如图所示目标函数可能为负数,因此需要加一个参数使之为正数;由于需要求目标函数最小值,因此取倒数,目标函数值越小,适应度函数越大。
def fitness(binary, start, precision):
decimal = binary_decode(binary, start, precision)
fit = 1 / (pow(decimal, 3) * math.cos(decimal) + 4500)
return fit4、选择
选择通常使用轮盘赌法。轮盘赌法根据将个体的适应度函数值与所有个体适应度值相加的比值,作为个体被选择的概率,这种随机选择的方法,可以大概率地选到适应度大的个体,进行复制产生适应度更高的个体,提高种群的适应度。
#generation为该代待选择的种群
def select(generation, population, start, precision):
#计算所有个体的适应度
all_fitness = []
for binary in generation:
fit = fitness(binary, start, precision)
all_fitness.append(fit)
fitness_array = np.array(all_fitness)
#将适应度归一化,作为概率进行选择
fitness_array = fitness_array / fitness_array.sum()
selected_index = np.random.choice(list(range(population)), size=population, p=fitness_array)
selected_index = selected_index.tolist()
#将选择到的个体加入选择后的种群
selected = []
for index in selected_index:
selected.append(generation[index])
#返回被选择之后的种群
return selected5、交叉
① 确定二进制编码是否在定义域内
def in_range(binary, start, end, precision):
if start <= binary_decode(binary, start, precision) <= end:
return True
else:
return False② 交叉
遗传算法的交叉算子主要有单点交叉、双点交叉、多点交叉、均匀交叉等。单点交叉是指在交叉的染色体中设置一个交叉点,在交叉的位置将两个父代基因串进行截断重新组合形成新的两个基因串。单点交叉容易操作、效率高,是使用最多的一种算子。
#selected为被选择之后的种群,probability为交叉概率
def cross(selected, population, probability, start, end, precision):
crossed = selected[:]
bit = get_binary_bit(start, end, precision)
#numbers为进行交叉的次数
numbers = population * probability
count = 0
i = 0
while i < population - 1 and count < numbers:
#随机选取分割点
position = random.randrange(1, bit)
#将两个父二进制编码分别截成两个部分
binary11 = selected[i][:position]
binary12 = selected[i][position:]
binary21 = selected[i + 1][:position]
binary22 = selected[i + 1][position:]
#将二进制编码切片重组形成新的两个子二进制编码
binary1 = binary11 + binary22
binary2 = binary21 + binary12
#判断新生成的二进制编码是否在自定义范围内,在则加入交叉之后的种群;否则,重新交叉
if in_range(binary1, start, end, precision) and in_range(binary2, start, end, precision):
crossed[i] = binary1
crossed[i + 1] = binary2
count += 1
i += 2
#返回交叉之后的种群
return crossed6、变异
① 取反
def reverse(string, position):
string = list(string)
if string[position] == '0':
string[position] = '1'
else:
string[position] = '0'
return ''.join(string)② 变异
变异的方式有很多种包括单点变异、互换变异、逆序变异、插入变异、高斯变异等。在实际应用中,主要采用单点变异,也叫位变异,即只需要对基因序列中某一个位进行变异,以二进制编码为例,即0变为1,而1变为0。
#crossed为交叉之后的种群,probability为变异的概率
def mutation(crossed, population, probability, start, end, precision):
mutated = crossed[:]
bit = get_binary_bit(start, end, precision)
for i in range(population):
#随机生成一个0-1之间的数,判断该二进制编码是否突变
whether_mutated = True if random.random() < probability else False
if whether_mutated:
#随机生成一个变异位,将该位进行取反
position = random.randrange(0, bit)
mutated_binary = reverse(crossed[i], position)
#若生成的新二进制编码不在定义域内,则重复生成直至符合条件
while not in_range(mutated_binary, start, end, precision):
position = random.randrange(0, bit)
mutated_binary = reverse(crossed[i], position)
mutated[i] = mutated_binary
#返回变异后的种群
return mutated7、搜索最优解
在最后一代种群中,搜索适应度最大的二进制编码,即为遗传算法的最优解
#final_generation为最后一代种群
def search(final_generation, start, precision):
#计算所有个体的适应度,找到适应度最高的个体
all_fitness = []
for binary in final_generation:
fit = fitness(binary, start, precision)
all_fitness.append(fit)
index = all_fitness.index(max(all_fitness))
#解码,返回最优解
return binary_decode(final_generation[index], start, precision)8、主函数
#population为种群大小;generations为进化代数,cross_probabilit为交叉概率
#mutation_probability为变异概率,[start,end]为定义域,precision为精度
def main(population, generations, cross_probability, mutation_probability, start, end, precision):
#确定初始化种群(如图所示大致区间为[15,17]
generation = initialization(population, start, end, precision, 15, 17)
for i in range(generations):
#选择
generation = select(generation, population, start, precision)
#交叉
generation = cross(generation, population, cross_probability, start, end, precision)
#变异
generation = mutation(generation, population, mutation_probability, start, end, precision)
#搜索最优解,打印结果
best = search(generation, start, precision)
print(round(best, precision), round(pow(best, 3) * math.cos(best), precision))
9、问题求解
main(60, 300, 0.7, 0.05, -1.57, 20.18, 3)注意,遗传算法有4个参数需要提前设定,一般在以下范围内进行设置:
① 种群大小:20~100
② 进化代数:100~500
③ 交叉概率:0.4~0.99
④ 变异概率:0.0001~0.1
输出结果如下
15.893 -3945.845
三、遗传算法求解TSP模型
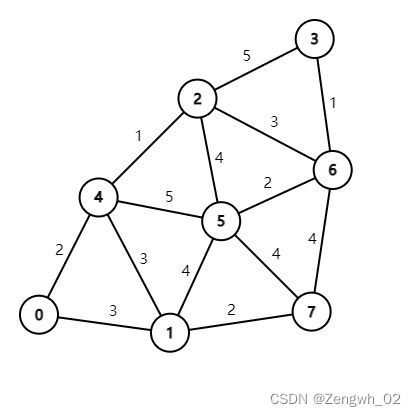
以下图为例,求从0号城市出发访问每一座城市并回到0号城市的最短回路
1、基本模型
① 编码
求解TSP模型采用自然数编码,0节点代表初始城市,1-7节点表示其他7座城市。如 1,7,6,3,2,5,4 表示从0出发依次经过城市1、7、6、3、2、5、4最后回到0
② 生成初始种群
随机生成种群大小为60的种群。其中每个个体都是由数字1-7各出现一次的数列。
③ 适应度函数
TSP模型以最短路径为目标函数,因此以路径长度的倒数为适应度函数。
④ 选择算子
采用轮盘赌法,据将个体的适应度函数值与所有个体适应度值相加的比值,作为个体被选择的概率。
⑤ 交叉算子
采用双点交叉,即对配对的染色体随机设置两个交叉点,然后进行交叉运算,改变染色体基因序列。交叉概率设置为0.7。双点交叉操作如下:假设两条父染色体为A=1,4,5,2,3,6,7和B=4,2,3,6,5,7,1,随机生成两个交叉点2和6,那么A=1|4,5,2,3,6|7,B=4|2,3,6,5,7|1,A1=4,5,2,3,6,B1=2,3,6,5,7;删除A中与B1重复的基因,再把 B1 全部添加到 A 相应的片段中,即生成了新的A。例如A=1|4,5,2,3,6|7,B1=2,3,6,5,7,删除后A为1,4,把B1全部添加到A后A=1,2,3,6,5,7,4。B同理。
⑥ 变异算子
采用逆转变异,即对一条染色体设置两个点,然后染色体基因在这两点中发生逆转,改变染色体基因序列。变异概率设置为0.05。逆转变异操作如下:假设染色体为A=1,4,5,2,3,6,7,随机生成两个点2和6,那么A1=4,5,2,3,6,逆转后A1=6,3,2,5,4,A=1,6,3,2,5,4,7。
⑦搜索最优解
选择迭代300代,停止运算后搜索遗传算法最优解。由于遗传算法局部搜索能力较弱,因此循环运行10次遗传算法,取得模型最优解
2、代码求解
① 确定初始种群
#population为种群中路径数目,city_numbers为需要经过的其他城市的数量
def initialization(population, city_numbers):
initialized = []
for i in range(population):
random_path_array = np.random.choice(list(range(1, city_numbers + 1)), replace=False, size=city_numbers)
random_path_list = random_path_array.tolist()
initialized.append(random_path_list)
return initialized② 确定适应度函数
#length_mat为各个节点之间的最短距离
def fitness(path, length_mat):
path_numbers = len(path) - 1
all_length = 0
#求相邻两城市的距离
for i in range(path_numbers):
src = path[i]
dest = path[i + 1]
all_length += length_mat[src][dest]
#加上从0点出发和回到0点的距离
all_length += length_mat[0][path[0]]
all_length += length_mat[path[-1]][0]
#路径长度取倒数即为适应度函数
fit = 1 / all_length
return fit③ 选择
def select(generation, population, length_mat):
all_fitness = []
for path in generation:
fit = fitness(path, length_mat)
all_fitness.append(fit)
fitness_array = np.array(all_fitness)
fitness_array = fitness_array / fitness_array.sum()
selected_index = np.random.choice(list(range(population)), size=population, p=fitness_array)
selected = []
for index in selected_index:
selected.append(generation[index])
return selected④ 交叉
def cross(selected, population, probability, city_numbers):
#内层嵌套需要深拷贝才能开辟新的内存空间
crossed = copy.deepcopy(selected)
frequency = population * probability
count = 0
i = 0
while i < population - 1 and count < frequency:
#随机生成两个交叉点
position1 = random.randrange(0, int(city_numbers / 2))
position2 = random.randrange(int(city_numbers / 2), city_numbers)
#截取交叉片段
crossed1 = selected[i].copy()
crossed2 = selected[i + 1].copy()
crossed12 = crossed1[position1:position2 + 1]
crossed22 = crossed2[position1:position2 + 1]
#交叉生成染色体1
for city in crossed22:
crossed1.remove(city)
result1 = crossed1[:position1]
result1.extend(crossed22)
result1.extend(crossed1[position1:])
#交叉生成染色体2
for city in crossed12:
crossed2.remove(city)
result2 = crossed2[:position1]
result2.extend(crossed12)
result2.extend(crossed2[position1:])
crossed[i] = result1
crossed[i + 1] = result2
count += 1
i += 2
return crossed⑤ 变异
def mutation(crossed, population, probability, city_numbers):
#内层嵌套需要深拷贝才能开辟新的内存空间
mutated = copy.deepcopy(crossed)
for i in range(population):
whether_mutated = True if random.random() < probability else False
if whether_mutated:
#随机生成两个点
position1 = random.randrange(0, int(city_numbers / 2))
position2 = random.randrange(int(city_numbers / 2), city_numbers)、
#将中间染色体逆转
mid_reversed = crossed[i][position1: position2 + 1]
mid_reversed.reverse()
#拼接生成变异后染色体
result = crossed[i][:position1]
result.extend(mid_reversed)
result.extend(crossed[i][position2 + 1:])
mutated[i] = result
return mutated⑥ 搜索最优解
def search(final_generation, length_mat):
all_fitness = []
for path in final_generation:
fit = fitness(path, length_mat)
all_fitness.append(fit)
index = all_fitness.index(max(all_fitness))
return final_generation[index]⑦ 遗传算法
def ga(population, generations, cross_probability, mutation_probability, length_mat, city_numbers):
generation = initialization(population, city_numbers)
for i in range(generations):
generation = select(generation, population, length_mat)
generation = cross(generation, population, cross_probability, city_numbers)
generation = mutation(generation, population, mutation_probability, city_numbers)
best = search(generation, length_mat)
return best, round(1 / fitness(best, length_mat))⑧ 主程序
先通过Floyd算法求每个节点之间的最短路径
graph = nx.Graph()
graph.add_nodes_from(range(0, 8))
edges = [(0, 1, 3), (0, 4, 2),
(1, 4, 3), (1, 5, 4), (1, 7, 2),
(2, 3, 5), (2, 4, 1), (2, 5, 4), (2, 6, 3),
(3, 6, 1),
(4, 5, 5),
(5, 6, 2), (5, 7, 4),
(6, 7, 4)]
graph.add_weighted_edges_from(edges)
shortest_length = dict(nx.shortest_path_length(graph, weight='weight'))
length_mat = []
for i in range(0, 8):
i_j = []
for j in range(0, 8):
i_j.append(shortest_length[i][j])
length_mat.append(i_j)(图论详见(23条消息) 图论(Python networkx)_Zengwh_02的博客-CSDN博客)
再调用10次遗传算法求最优解
best_value = 0xffff
best_path = []
for i in range(10):
path, value = ga(60, 300, 0.7, 0.05, length_mat, 7)
if value < best_value:
best_value = value
best_path = path
print(best_path, best_value)3、输出结果
[1, 7, 5, 6, 3, 2, 4] 19