GDAL 读取和保存 Grd 文件
文章目录
- GDAL 读取和保存 Grd 文件
-
- Sufer 6 Binary 文件格式
- 读取 Grd 文件
-
- Grd 文件和 GDAL tiff 文件的区别
- 手动实现读取 Grd 文件
- 使用GDAL直接读取Grd文件
- 保存为 grd 文件
- 测试
-
- 测试结果
- 测试代码
GDAL 读取和保存 Grd 文件
绘图软件 Golden Surfer 的网格文件(Grd)主要有三种存储格式:
- Sufer 6 Text
- Sufer 6 Binary
- Sufer 7
其中,Sufer 6 Text 格式以 ASCII 码存储,可以直接用文本编辑查看。另外两种是以二进制格式存储的,需要按一定的规则进行读取。
具体的文件格式可以参考:Grd文件格式说明_地球屋里老师的博客-CSDN博客_.grd文件
GDAL是可以直接支持读写 Golden Surfer 的 grd 文件,对应的格式字符串如下:
要实现和其他图像格式的转换也非常的简单,直接在对应的驱动下 createcopy 即可。
这里主要介绍下 Sufer 6 Binary Grd 文件的读取。
Sufer 6 Binary 文件格式
文件样式:
DSBB
nx ny
xmin xmax
ymin ymax
zmin zmax
z11 z12 ... z1nx
z21 z22 ... z2nx
⁝ ⁝ ⁝
zny1 zny2 ... znynx
数据说明:
| 行号 | 变量名 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | id | unsigned char[4] × \times × 4 bytes |
格式标识符,‘DSBB’ |
| 2 | nx | unsigend short × \times × 2 bytes |
x 方向的点数(列数) |
| ny | unsigend short × \times × 2 bytes |
y 方向的点数(行数) | |
| 3 | xmin | double × \times × 8 bytes |
x 地理坐标的最小值 |
| xmax | double × \times × 8 bytes |
x 地理坐标的最大值 | |
| 4 | ymin | double × \times × 8 bytes |
y 地理坐标的最小值 |
| ymax | double × \times × 8 bytes |
y 地理坐标的最大值 | |
| 5 | zmin | double × \times × 8 bytes |
数据 z 中的最小值(不含白化点 nodata) |
| zmax | double × \times × 8 bytes |
数据 z 中的最大值(不含白化点 nodata) | |
| 6 | z(i,j) | float × \times × 4 bytes |
对应位置的数据 z (等于nodata表示该点无效) |
| ⋯ \cdots ⋯ |
读取 Grd 文件
Grd 文件和 GDAL tiff 文件的区别
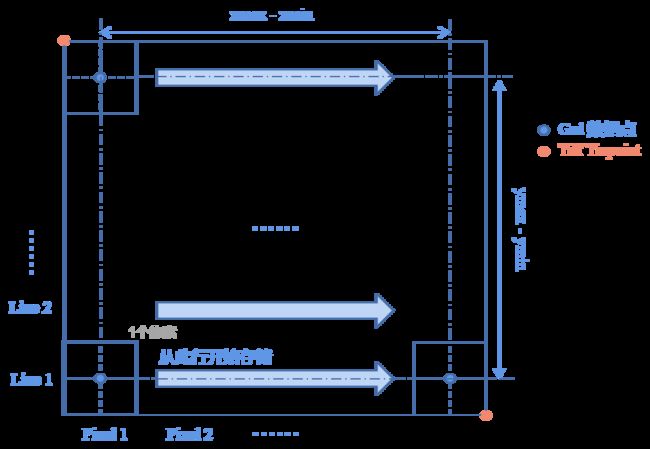
- 坐标原点不同
Grd 文件的坐标原点在图像的西南角,而 tiff 的坐标原点在西北角。Grd 的行的顺序是从南向北的,tiff 的行顺序则是从北向南的。因此 grd 文件 存储的数据其实是按 从南向北,由西向东 的顺序存储。 - 数据的锚点的不同
Grd 的数据锚点是在像素块的中心位置,而 tiff 的数据锚点是在像素块的左上角(西北角)。Tiff 还有 tie point 的概念,分别在图像的西北角和东南角,这两个 tie point 界定了 tiff 图像的地理范围。
根据 grd 的数据计算 tiff 的信息:
- 分辨率的计算
Δ x = x max − x min N x − 1 Δ y = y min − y max N y − 1 \begin{split} \Delta x &= \frac{x_{\max} - x_{\min}}{N_x-1}\\ \Delta y &= \frac{y_{\min} - y_{\max}}{N_y-1}\\ \end{split} ΔxΔy=Nx−1xmax−xmin=Ny−1ymin−ymax
这里 y 方向分辨率为负值,和 GDAL 中的一致。
- Tie point 的计算
{ X W N = x min − 0.5 Δ x Y W N = y max − 0.5 Δ y \begin{cases} X_{_{WN}} = x_{\min} - 0.5 \Delta x\\ Y_{_{WN}} = y_{\max} - 0.5 \Delta y \end{cases} {XWN=xmin−0.5ΔxYWN=ymax−0.5Δy
tiff 的仿射系数 geotrans[6] 就可以确定了,即
{ g e o t r a n s [ 0 ] = X W N g e o t r a n s [ 1 ] = Δ x g e o t r a n s [ 2 ] = 0.0 g e o t r a n s [ 3 ] = Y W N g e o t r a n s [ 4 ] = 0.0 g e o t r a n s [ 5 ] = Δ y \begin{cases} geotrans[0] = X_{_{WN}}\\ geotrans[1] = \Delta x\\ geotrans[2] = 0.0\\ geotrans[3] = Y_{_{WN}}\\ geotrans[4] = 0.0\\ geotrans[5] = \Delta y\\ \end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧geotrans[0]=XWNgeotrans[1]=Δxgeotrans[2]=0.0geotrans[3]=YWNgeotrans[4]=0.0geotrans[5]=Δy
手动实现读取 Grd 文件
根据 [[#Sufer 6 Binary 文件格式]] 定义一个抬头结构体:
typedef unsigned char byte;
typedef unsigned char DT_8U;
typedef unsigned short DT_16U;
typedef short DT_16S;
typedef unsigned int DT_32U;
typedef int DT_32S;
typedef float DT_32F;
typedef double DT_64F;
typedef struct {
DT_8U id[4];
DT_16U sizex;
DT_16U sizey;
DT_64F xmin;
DT_64F xmax;
DT_64F ymin;
DT_64F ymax;
DT_64F zmin;
DT_64F zmax;
} DSBBHeader;
使用 fread 直接读取即可,注意写入数据的时候,需要从最后一行开始写起。
参考代码如下:
GDALDataset* grd2gdal_manual(const char* pszSrcFile, const char* pszDstFile, const char* pFormat, DT_32F* pNodata = NULL)
{
FILE* fout = NULL;
// fout = fopen(pszSrcFile, "rb");
fopen_s(&fout, pszSrcFile, "rb");
if (fout == NULL) {
printf("无法打开文件: %s\n", pszSrcFile);
return NULL;
}
// 读取文件抬头信息
DSBBHeader header;
fread(&header, sizeof(DSBBHeader), 1, fout);
// 读取数据部分
DT_32F* pdata = new DT_32F[header.sizex * header.sizey];
fread(pdata, sizeof(DT_32F), header.sizex * header.sizey, fout);
// 创建输出文件
GDALAllRegister();
GDALDriver* pDriver = GetGDALDriverManager()->GetDriverByName(pFormat);
if (pDriver == NULL) {
printf("不支持格式: %s\n", pFormat);
fclose(fout);
return NULL;
}
GDALDataset* pDstDS = pDriver->Create(pszDstFile, header.sizex, header.sizey, 1, GDT_Float32, NULL);
if (pDstDS == NULL) {
printf("创建失败!\n");
fclose(fout);
return NULL;
}
// 设置nodata
if (pNodata) {
pDstDS->GetRasterBand(1)->SetNoDataValue(*pNodata);
}
// 计算仿射参数
double adftrans[6] = { 0.0 };
adftrans[1] = (header.xmax - header.xmin) / static_cast<double>(header.sizex - 1);
adftrans[5] = (header.ymin - header.ymax) / static_cast<double>(header.sizey - 1);
adftrans[0] = header.xmin - 0.5 * adftrans[0];
adftrans[3] = header.ymax - 0.5 * adftrans[5];
pDstDS->SetGeoTransform(adftrans);
// 从最后一行开始写入数据
for (int y = header.sizey - 1; y >= 0; --y) {
pDstDS->GetRasterBand(1)->RasterIO(GF_Write, 0, y, header.sizex, 1,
pdata + header.sizex * (header.sizey - 1 - y), header.sizex, 1, GDT_Float32, 0, 0, 0);
}
fclose(fout);
return pDstDS;
}
使用GDAL直接读取Grd文件
GDAL 可以直接读取 Grd 文件,并且会自动进行仿射系数的计算,自动进行数据读取的翻转。
GDALDataset* grd2gdal(const char *pszSrcFile, const char *pszDstFile, const char *pFormat, DT_32F *pNodata = NULL)
{
GDALAllRegister();
GDALDataset* pSrcDS = (GDALDataset*)GDALOpen(pszSrcFile, GA_ReadOnly);
if (pSrcDS == NULL) {
printf("无法打开: %s\n", pszSrcFile);
return NULL;
}
GDALDriver* pDriver = GetGDALDriverManager()->GetDriverByName(pFormat);
if (pDriver == NULL) {
printf("不支持格式: %s\n", pFormat);
GDALClose(pSrcDS);
return NULL;
}
GDALDataset* pDstDS = pDriver->CreateCopy(pszDstFile, pSrcDS, false, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (pDstDS == NULL) {
printf("创建失败!\n");
GDALClose(pDstDS);
return NULL;
}
if (pNodata) {
pDstDS->GetRasterBand(1)->SetNoDataValue(*pNodata);
}
GDALClose(pSrcDS);
return pDstDS;
}
保存为 grd 文件
手动实现保存为 grd 文件,参考代码如下:
bool gdal2grd(GDALDataset *pSrcDS, const char *pGrdFile)
{
if (pSrcDS == NULL) {
printf("数据指针为空!\n");
return false;
}
DSBBHeader header;
int sizex = pSrcDS->GetRasterXSize();
int sizey = pSrcDS->GetRasterYSize();
double adftrans[6];
if (pSrcDS->GetGeoTransform(adftrans) != CE_None) {
printf("图像无仿射系数!\n");
GDALClose(pSrcDS);
return false;
}
GDALRasterBand* pband = pSrcDS->GetRasterBand(1);
if (pband->GetRasterDataType() != GDT_Float32) {
printf("图像数据类型不是 float!\n");
GDALClose(pSrcDS);
return false;
}
int hasNodata = 0;
DT_32F nodata = pband->GetNoDataValue(&hasNodata);
header.id[0] = 'D';
header.id[1] = 'S';
header.id[2] = 'B';
header.id[3] = 'B';
header.sizex = sizex;
header.sizey = sizey;
header.xmin = adftrans[0] + adftrans[1] / 2;
header.ymax = adftrans[3] + adftrans[5] / 2;
header.xmax = header.xmin + (static_cast<double>(sizex) - 1.0) * adftrans[1];
header.ymin = header.ymax + (static_cast<double>(sizey) - 1.0) * adftrans[5];
FILE* fout = NULL;
fopen_s(&fout, pGrdFile, "wb");
if (fout == NULL) {
printf("文件创建失败!\n");
GDALClose(pSrcDS);
return false;
}
fwrite(&header, sizeof(DSBBHeader), 1, fout);
DT_64F maxv = -1.0;
DT_64F minv = 99999.0;
DT_32F* pdata = new DT_32F[sizex];
for (int y = sizey - 1; y >= 0; --y) {
pband->RasterIO(GF_Read, 0, y, sizex, 1, pdata, sizex, 1, GDT_Float32, 0, 0, 0);
for (int x = 0; x < sizex; ++x) {
if (hasNodata && pdata[x] == nodata)
continue;
maxv = max(maxv, static_cast<DT_64F>(pdata[x]));
minv = min(minv, static_cast<DT_64F>(pdata[x]));
}
fwrite(pdata, sizeof(DT_32F), sizex, fout);
}
delete[] pdata;
header.zmin = static_cast<DT_64F>(minv);
header.zmax = static_cast<DT_64F>(maxv);
fseek(fout, 40, SEEK_SET);
fwrite(&header.zmin, sizeof(DT_64F), 1, fout);
fwrite(&header.zmax, sizeof(DT_64F), 1, fout);
PrintDSBBInfo(header);
fclose(fout);
return true;
}
测试
测试结果
输入 grd 图像:
可以看到 grd 文件的坐标原点在左下角(西南点)
原点(1,1)的地理坐标为 (113.312567, 33.917719)原图可在此处下载(里面还有一个等值线文件):
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1MPuikSRIbUdi0S_pQXT0-A
提取码:fta4
输出结果:
--- 使用gdal读取grd ---
Size: 1485 x 1317
band: 1
scale: 0.000270 x -0.000270
Tie points(WN): (113.312432, 34.272779)
Tie points(ES): (113.712937, 33.917584)
Center Points(WN): (113.312567, 34.272644)
Center Points(ES): (113.712802, 33.917719)
Nodata: 99999.000
Data Type: GDT_Float32
Data range: 70.954514 ~ 3075.133301
--- Header Info ---
ID: DSBB
Size: 1485 x 1317
scale: 0.000270 x -0.000270
Center Points(WN): (113.312567, 34.272644)
Center Points(ES): (113.712802, 33.917719)
Tie points(WN): (113.312432, 34.272779)
Tie points(ES): (113.712937, 33.917584)
Data range: 70.954512 ~ 3075.133384
--- 手动读取grd ---
Size: 1485 x 1317
band: 1
scale: 0.000270 x -0.000270
Tie points(WN): (113.312567, 34.272779)
Tie points(ES): (113.713071, 33.917584)
Center Points(WN): (113.312702, 34.272644)
Center Points(ES): (113.712937, 33.917719)
Nodata: 99999.000
Data Type: GDT_Float32
Data range: 70.954514 ~ 3075.133301
--- 将gdal保存为grd ---
ID: DSBB
Size: 1485 x 1317
scale: 0.000270 x -0.000270
Center Points(WN): (113.312567, 34.272644)
Center Points(ES): (113.712802, 33.917719)
Tie points(WN): (113.312432, 34.272779)
Tie points(ES): (113.712937, 33.917584)
Data range: 70.954514 ~ 3075.133301
保存成功: C:/Users/q2799/Project/saved_res.grd
手动读取grd和gdal读取,得到的
tie point及 分辨率都是一致的,Data range由于float的精度,有少许的不同(毕竟float有效数字大概就7位)。
测试代码
main.cpp
#include rwgrd.h
#ifndef _RWGRD_H_
#define _RWGRD_H_
#include rwgrd.cpp
#include