PyTorch深度学习实践 Lecture05 线性回归
Author :Horizon Max
✨ 编程技巧篇:各种操作小结
机器视觉篇:会变魔术 OpenCV
深度学习篇:简单入门 PyTorch
神经网络篇:经典网络模型
算法篇:再忙也别忘了 LeetCode
视频链接:Lecture 05 Linear_Regression_with_PyTorch
文档资料:
//Here is the link:
课件链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1vZ27gKp8Pl-qICn_p2PaSw
提取码:cxe4
文章目录
- Linear_Regression_with_PyTorch(使用PyTorch实现线性回归)
-
- 概述
-
- PyTorch Fashion
- Code
- 运行结果
- Exercise
-
- Code
- 八种优化器比较(optimizer)
-
- torch.optim.Adagrad()
- torch.optim.Adam()
- torch.optim.Adamax()
- torch.optim.ASGD()
- torch.optim.LBFGS()
- torch.optim.RMSprop()
- torch.optim.Rprop()
- torch.optim.SGD()
- 附录:相关文档资料
Linear_Regression_with_PyTorch(使用PyTorch实现线性回归)
概述
PyTorch Fashion

利用PyTorch建模的 基本流程 :
1、Prepare dataset
2、Design model using Class
3、Construct loss and optimizer
4、Training cycle
下面结合代码概述以上 基本流程 :
Code
# Here is the code :
import torch
# 1、Prepare dataset
x_data = torch.tensor([[1.0], [2.0], [3.0]])
y_data = torch.tensor([[2.0], [4.0], [6.0]])
# 2、Design model using Class
class LinearModel(torch.nn.Module): # Our model class should be inherit from nn.Module
# which is Base class for all neural network modules
def __init__(self):
super(LinearModel, self).__init__()
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1) # nn.Linear(1, 1)输入输出维度均为1
def forward(self, x): # 前向传播
y_pred = self.linear(x)
return y_pred
model = LinearModel()
# 3、Construct loss and optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction = 'sum') # 即返回loss.sum(),默认 reduction='mean' 返回 loss.mean()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr = 0.01) # model.parameters()参数初始化
# 4、Training cycle
for epoch in range(100):
y_pred = model(x_data) # forward(得到预测值 y_hat)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_data) # 计算loss值
print(epoch, loss.item())
optimizer.zero_grad() # grad 参数置零
loss.backward() # backward(会自动计算梯度)
optimizer.step() # update(更新参数 w 和 b)
print('w = ', model.linear.weight.item())
print('b = ', model.linear.bias.item())
x_test = torch.tensor([[4.0]]) # 预测 x=4 时 y 的值
y_test = model(x_test)
print('y_pred = ', y_test.data)
运行结果
0 50.871299743652344
1 23.290237426757812
2 11.00268268585205
3 5.523491859436035
4 3.0753233432769775
5 1.9766101837158203
... ...
96 0.29678839445114136
97 0.29252320528030396
98 0.2883186936378479
99 0.2841755151748657
w = 1.6451170444488525
b = 0.8067324757575989
y_pred = tensor([[7.3872]])
Exercise
Code
# Here is the code :
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1、Prepare dataset
x_data = torch.tensor([[1.0], [2.0], [3.0]])
y_data = torch.tensor([[2.0], [4.0], [6.0]])
# 2、Design model using Class
class LinearModel(torch.nn.Module): # Our model class should be inherit from nn.Module
# which is Base class for all neural network modules
def __init__(self):
super(LinearModel, self).__init__()
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1) # nn.Linear(1, 1)输入输出维度均为1
def forward(self, x): # 前向传播
y_pred = self.linear(x)
return y_pred
model = LinearModel()
# 3、Construct loss and optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum')
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01) # model.parameters()参数初始化
# 4、Training cycle
epoch_list = [] # 构建数组存放迭代过程中的 epoch 和 cost 值
cost_list = []
for epoch in range(100):
y_pred = model(x_data) # forward(得到预测值 y_hat)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_data) # 计算loss值
epoch_list.append(epoch)
cost_list.append(loss.item()/len(x_data))
optimizer.zero_grad() # grad 参数置零
loss.backward() # backward(会自动计算梯度)
optimizer.step() # update(更新参数 w 和 b)
print('w = ', model.linear.weight.item())
print('b = ', model.linear.bias.item())
x_test = torch.tensor([[4.0]]) # 预测 x=4 时 y 的值
y_test = model(x_test)
print('y_pred = ', y_test.data)
plt.plot(epoch_list, cost_list) # 绘图
plt.title('SGD')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.show()
神经网络优劣的指标—— 代价函数(Cost Function)
我们需要通过 优化器(Optimizer) 不断改进神经网络来使 代价函数 最小
八种优化器比较(optimizer)
各优化器介绍参考 Pytorch中文文档
torch.optim.Adagrad()
def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-2, lr_decay=0, weight_decay=0, initial_accumulator_value=0, eps=1e-10):

w = -0.0708811953663826
b = -0.07163553684949875
y_pred = tensor([[-0.3552]])
torch.optim.Adam()
def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-8,
weight_decay=0, amsgrad=False):

w = 0.051138054579496384
b = 0.2211645096540451
y_pred = tensor([[0.4257]])
torch.optim.Adamax()
def __init__(self, params, lr=2e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-8,
weight_decay=0):

w = -0.0033778981305658817
b = 0.9950549006462097
y_pred = tensor([[0.9815]])
torch.optim.ASGD()
def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-2, lambd=1e-4, alpha=0.75, t0=1e6, weight_decay=0):

w = 2.03299617767334
b = -0.07502224296331406
y_pred = tensor([[8.0570]])
torch.optim.LBFGS()
def __init__(self,
params,
lr=1, # 学习率 默认1
max_iter=20, # (int) 最大迭代次数 默认20
max_eval=None, # (int) 最大函数评价次数 默认max_iter * 1.25
tolerance_grad=1e-7, # (float) 一阶最优的终止容忍度 默认1e-5
tolerance_change=1e-9, # (float) 函数值/参数变化量的终止容忍度 默认1e-9
history_size=100, # (int) 更新历史的大小 默认100
line_search_fn=None):
一些优化算法 例如 Conjugate Gradient 和 LBFGS 需要重复多次计算函数
因此需要传入一个闭包去允许它们重新计算你的模型,这个闭包会清空梯度, 计算损失,然后返回。
代码如下:
for epoch in range(100):
def closure():
y_pred = model(x_data) # forward(得到预测值 y_hat)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_data) # 计算loss值
epoch_list.append(epoch)
cost_list.append(loss.item()/len(x_data))
optimizer.zero_grad() # grad 参数置零
loss.backward() # backward(会自动计算梯度)
return loss
optimizer.step(closure) # update(更新参数 w 和 b)

w = 1.999942421913147
b = 4.552656173473224e-05
y_pred = tensor([[7.9998]])
torch.optim.RMSprop()
def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-2, alpha=0.99, eps=1e-8, weight_decay=0, momentum=0, centered=False):
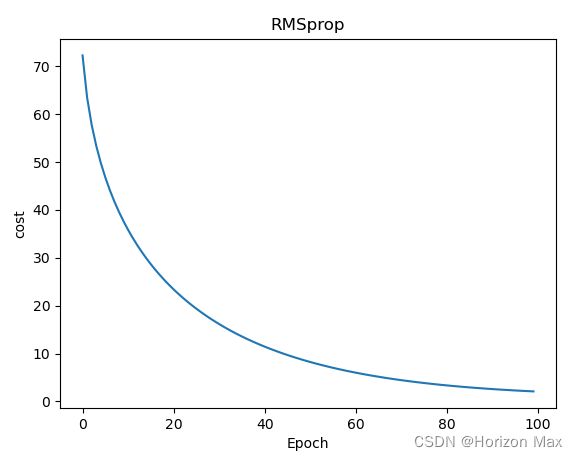
w = 1.115038275718689
b = 1.3704285621643066
y_pred = tensor([[5.8306]])
torch.optim.Rprop()
def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-2, etas=(0.5, 1.2), step_sizes=(1e-6, 50)):

w = 1.9998326301574707
b = 0.00040745444130152464
y_pred = tensor([[7.9997]])
torch.optim.SGD()
def __init__(self, params, lr=required, momentum=0, dampening=0,
weight_decay=0, nesterov=False):

w = 1.662644386291504
b = 0.7668885588645935
y_pred = tensor([[7.4175]])
参考:https://ruder.io/optimizing-gradient-descent/index.html
附录:相关文档资料
PyTorch 官方文档: PyTorch Documentation
PyTorch 中文手册: PyTorch Handbook
《PyTorch深度学习实践》系列链接:
Lecture01 Overview
Lecture02 Linear_Model
Lecture03 Gradient_Descent
Lecture04 Back_Propagation
Lecture05 Linear_Regression_with_PyTorch
Lecture06 Logistic_Regression
Lecture07 Multiple_Dimension_Input
Lecture08 Dataset_and_Dataloader
Lecture09 Softmax_Classifier
Lecture10 Basic_CNN
Lecture11 Advanced_CNN
Lecture12 Basic_RNN
Lecture13 RNN_Classifier


