spring源码-依赖注入@Autowired
依赖注入的实现由后置处理器AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor实现
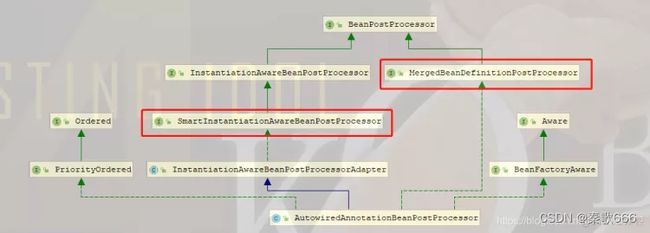
类图
实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ,MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口,如果对这两个接口不熟悉的可以阅读上篇文章后置处理器,实现这两个接口就可以介入到Bean的实例化前后和bean的元数据信息解析
依赖注入过程:
第一步、解析注解信息
入口方法:
postProcessMergedBeanDefinition该方法的作用其实比较简单,就是为了缓存下后续需要用到数据,findAutowiringMetadata 这个方法是有缓存的
处理的,所以重复调用的话是直接从缓存获取数据,加快注入的效率。这个方法其实就是去查找被 Autowired、Value 注解的所有属性和方法,当然包
括了目标类的所有父类都会去查找,所以查找的过程其实是个递归的过程。找到所有的成员后,会创建即实例化
InjectionMetadata 对象并缓存到injectionMetadataCache 。核心代码:
/**
*解析注解并缓存起来
**/
@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class beanType, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
//解析所有@Autowired @Value注解的方法和变量
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
//缓存起来
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List currElements = new ArrayList<>();
//解析带Autowired和@Value的字段
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
MergedAnnotation ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
//解析带Autowired和@Value的方法
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
} 第二步、注入
入口方法
postProcessProperties
该方法在bean实例化后被调用,属性值进行修改,如果postProcessAfterInstantiation方法返回false,该方法可能不会被调用。可以在该方法内对属性值进行修改核心代码
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
//findAutowiringMetadata方法已经在上一步被执行了一次了,并且将注解的元信息已经放到了缓存里,所以这里就直接从缓存中拿到了。
//拿到注解元数据后,就开始执行inject方法了。
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
//依赖注入的核心逻辑
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}拿到注解元数据后,就开始执行inject方法进行注入
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
//遍历所有元数据信息
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
//执行依赖注入逻辑
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
} 核心在DefaultListableBeanFactory#doResolveDependency
// 此处autowiredBeanNames是在inject的一个空的Set
// autowired表示最终可以注入进去的bean名称们(因为可能是会有多个符合条件的)
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
...
@Nullable
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Set autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
// 记录注入点,其实使用的ThreadLocal~
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
// 只有ShortcutDependencyDescriptor实现了resolveShortcut方法,其实就是根据
// 实现也就一句话:beanFactory.getBean(this.shortcut, this.requiredType)
// ShortcutDependencyDescriptor实在inject完成后创建的,就是有缓存的效果~~~
Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);
if (shortcut != null) {
return shortcut;
}
// interface com.fsx.dependency.AInterface
Class type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
// 拿到@Value注解的value值(是个字符串) 若没有标注@Value 显然就不用那啥了
// 从此处其实也可以看出,@Value注解的优先级对于找到bean来说还是蛮高的
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
// ============ 这部分主要是解析@Value注解
// 解析它的占位符,解析它的SpEL表达式
// 相关处理类曹靠BeanExpressionResolver和StandardBeanExpressionResolver StandardEvaluationContext等
// 因为关于@Value的文章里详细解过,此处一笔带过~~~
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof String) {
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ?
getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
try {
return converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getTypeDescriptor());
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) {
// A custom TypeConverter which does not support TypeDescriptor resolution...
return (descriptor.getField() != null ?
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));
}
}
// ============
// 此处处理的是多值注入的情况,比如注入Stream findAutowireCandidates源码分析
protected Map findAutowireCandidates(
@Nullable String beanName, Class requiredType, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
// 从BeanFactory中找出和requiredType所匹配的beanName,仅仅是beanName,这些bean不一定经过了实例化,只有到最终确定某个Bean了,如果这个Bean还没有实例化才会真正进行实例化
String[] candidateNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this, requiredType, true, descriptor.isEager());
Map result = CollectionUtils.newLinkedHashMap(candidateNames.length);
// 根据类型从resolvableDependencies中匹配Bean,resolvableDependencies中存放的是类型:Bean对象,比如BeanFactory.class:BeanFactory对象,在Spring启动时设置。
for (Map.Entry, Object> classObjectEntry : this.resolvableDependencies.entrySet()) {
// 得到当前Bean的类型
Class autowiringType = classObjectEntry.getKey();
if (autowiringType.isAssignableFrom(requiredType)) {
// 获取缓存中的值
Object autowiringValue = classObjectEntry.getValue();
// 这里会生成一个Bean的名字,放到缓存中的是没有Bean的名字的
autowiringValue = AutowireUtils.resolveAutowiringValue(autowiringValue, requiredType);
// 类型匹配,将当前值添加进去
if (requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) {
result.put(ObjectUtils.identityToString(autowiringValue), autowiringValue);
break;
}
}
}
// 这里理解就是注入同一个Bean的时候,先考虑同类型的其他Bean
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
// 如果不是自己,则判断该candidate到底能不能用来进行自动注入(@Bean(autowireCandidate = true))默认为true
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, descriptor)) {
// 不是自己,并且可以注入的时候,调用这个代码:添加候选者
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
// 为空要么是真的没有匹配的,要么是匹配的自己
if (result.isEmpty()) {
// 需要匹配的类型是不是Map、数组之类的
boolean multiple = indicatesMultipleBeans(requiredType);
// Consider fallback matches if the first pass failed to find anything...
// 如果第一遍找不到任何东西,请考虑回退匹配。
DependencyDescriptor fallbackDescriptor = descriptor.forFallbackMatch();
// 遍历每个候选者
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
// 不是自己并且可以被注入并且(不是Map、数组之类的或者@Qualifier指定了BeanName的)
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, fallbackDescriptor) &&
(!multiple || getAutowireCandidateResolver().hasQualifier(descriptor))) {
// 添加真正的候选者
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
// 匹配的是自己,把自己添加到result中。
if (result.isEmpty() && !multiple) {
// Consider self references as a final pass...
// but in the case of a dependency collection, not the very same bean itself.
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
if (isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) &&
(!(descriptor instanceof MultiElementDescriptor) || !beanName.equals(candidate)) &&
isAutowireCandidate(candidate, fallbackDescriptor)) {
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}