Pytorch搭建常见分类网络模型------VGG、Googlenet、ResNet50 、MobileNetV2(4)
接上一节内容:Pytorch搭建常见分类网络模型------VGG、Googlenet、ResNet50 、MobileNetV2(3)_一只小小的土拨鼠的博客-CSDN博客
mobilenet系列:mobilenetV1、mobilenetV2、mobilenetV3是三个特征提取网络。MobileNet模型是Google针对手机等嵌入式设备提出的一种轻量级的深层神经网络,其使用的核心思想便是 depthwise separable convolution(深度可分离卷积) 。 从模型结构上主要对以下几点做了研究:
- V1:深度可分离卷积
- V2:倒置残差块 和 线性瓶颈层
- V3:网络架构搜索
1、什么是深度可分离卷积(Mobilenetv1提出)?
MobileNetV1是基于深度可分离卷积而构建的模型。 深度可分离卷积是将标准卷积分解成 深度卷积 和1x1 点向卷积 的卷积结构。 深度卷积对每个输入通道都使用一个单一的卷积核,点向卷积就将深度卷积的输出组合起来。 一个标准的卷积在一步内做了上面2件事情,而深度可分离卷积将它们分成两步。 这种分解显着的减小了模型的计算量和大小。其示意图如下所示。
(1)假设一卷积层,其卷积核大小为3×3,输入通道为3,输出通道为4; 常规卷积操作是将4个3×3×3的卷积核作用于3通道输入图像,根据卷积层参数量计算公式, 卷积计算+卷积参数量+卷积计量量 。得到所需参数为4*(3*3*3+1)= 112个。
(2)若先用3个、大小为3×3的卷积核(3*3*1)作用于3个通道的输入图像,得到了3个特征图,在做融合操作之前,接着用4个大小为1×1的卷积核(1*1*3)遍历上述得到的3个特征图,根据卷积层参数计算公式,所需参数为(3*3*1*3+3) + (1*1*3*4+4) = 46个。
上述即为深度可分离卷积的过程,普通卷积层的特征提取与特征组合一次完成并输出,而深度可分离卷积先用input_channels个厚度为1的3*3的卷积核( depthwise分层卷积 ),再用output_channels个厚度为input_channels的1*1的卷积核( pointwise 卷积 )调整通道数,将特征提取与特征组合分开进行。
2、深度可分离卷积具体结构如下图(可大大减少模型的参数):
在MobileNet中,每个层后面都接上了BN,除了最后一个全连接层接的Softmax之外,其他都接了ReLU。整个网络共有28层。
- 在进行 deepthwise(DW) 卷积时只使用了
一种维度为in_channels的卷积核进行 特征提取 (没有进行特征组合); - 在进行 pointwise(PW) 卷积时只使用了
output_channels 种维度为in_channels1*1 的卷积核进行 特征组合。
MobileNet V1网络结构(深度可分离卷积的堆叠。):
4、改进后的网络MobileNet V2
V2使用了跟V1类似的深度可分离结构,不同之处也正对应着V1中逐深度卷积的缺点改进:
- 结构问题:V1结构过于简单,没有复用图像特征,即没有concat/eltwise+ 等操作进行特征融合,而后续的一系列的ResNet, DenseNet等结构已经证明复用图像特征的有效性。
- 逐深度卷积问题:在处理低维数据(比如逐深度的卷积)时,relu函数会造成信息的丢失。DW 卷积由于本身的计算特性决定它自己没有改变通道数的能力,上一层给它多少通道,就只能输出多少通道。所以如果上一层给的通道数本身很少的话,DW 也只能在低维空间提特征,因此效果不够好。即对低维度做ReLU运算,很容易造成信息的丢失。而在高维度进行ReLU运算的话,信息的丢失则会很少。
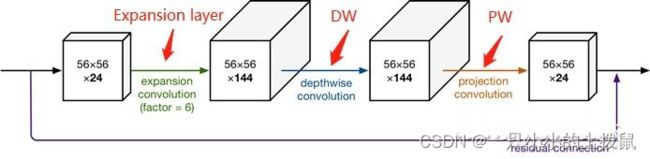
Mobilenetv2提出Inverted Residuals结构:即:1、在可分离卷积的前面增加一个大小为1*1的卷积进行升维(Expansion layer);2、将输入和输出的部分进行连接(residual connection), 如下图所示。
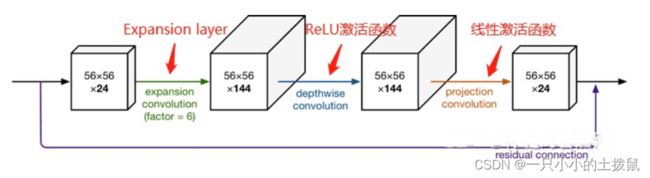
Mobilenetv2提出Linear Bottlenck结构:由于DW、PW都是以Relu作为激活函数,且 PW会做降维 , 再对低维特征做ReLU时会丢失很多信息, 所以从高维向低维转换,使用ReLU激活函数可能会造成信息丢失或破坏(所以不使用非线性激活数函数),即在PW这一部分,不再使用ReLU激活函数而是使用线性激活函数,如下图。
- V2 在 DW 卷积之前新加了一个 PW 卷积。(Inverted Residuals结构)
给每个 DW 之前都配备了一个 PW,专门用来升维,定义升维系数 ,这样不管输入通道数 是多是少,经过第一个 PW 升维之后,DW 都是在相对的更高维 ( ) 进行更好的特征提取。 - V2 去掉了第二个 PW 的激活函数改为线性激活。
- 论文作者称其为 Linear Bottleneck。原因如上所述是因为作者认为激活函数在高维空间能够有效的增加非线性,而在低维空间时则会破坏特征,不如线性的效果好。
MobileNet V2网络结构:
上图中,Mobilenet v2中有两种深度可分离模块,步长为1时输入输出size相等,此时使用shortcut结构。步长为2时,由于input与outputsize不符,不添加shortcut结构。
- MobileNet V2 借鉴 ResNet。使用 Shortcut 将输出与输入相加 。但是ResNet 先降维 (0.25倍)、卷积、再升维,而 MobileNet V2 则是 先升维 (6倍)、之后在用深度可分离卷积来提取特征、再降维,让网络从新变小。直观的形象上来看,ResNet 的微结构是 沙漏形 ,而 MobileNet V2 则是 纺锤形 。因此论文作者将 MobileNet V2 的结构称为 Inverted Residual Block。
5、ResNet50网络模型搭建
from torch import nn
from torch.hub import load_state_dict_from_url
__all__ = ['MobileNetV2', 'mobilenet_v2']
model_urls = {
'mobilenet_v2': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/mobilenet_v2-b0353104.pth',}
#input_channel * width_mult, round_nearest -----》(32*1,8)------》(1280,8)
def _make_divisible(v, divisor, min_value=None):
if min_value is None:
min_value = divisor # min_value=8
new_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)#max(8,0) max(8,20)
if new_v < 0.9 * v:# if 8 < 28.8
new_v += divisor # new_v = 16 new_v = 28
return new_v
class ConvBNReLU(nn.Sequential):#卷积、正则,激活
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, groups=1):
padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
super(ConvBNReLU, self).__init__(
nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride, padding, groups=groups, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes),
nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
)
#倒残差结构:在可分离卷积的前面增加一个大小为1*1的卷积进行升维(Expansion layer);
#将输入和输出的部分进行连接(residual connection)
#Mobilenet v2中有两种深度可分离模块,步长为1时输入输出size相等,此时使用shortcut结构。
#步长为2时,由于input与outputsize不符,不添加shortcut结构。
class InvertedResidual(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, stride, expand_ratio):#
super(InvertedResidual, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
assert stride in [1, 2] # 用于判断关键字是否在字典中,存在则返回true,不存在则返回false。
hidden_dim = int(round(inp * expand_ratio)) # 输入维度*扩展,四舍五入参数
self.use_res_connect = self.stride == 1 and inp == oup#输入输出的通道相同且步距为1,use_res_connect 为真
layers = []
if expand_ratio != 1:#当扩展维度不为1时
layers.append(ConvBNReLU(inp, hidden_dim, kernel_size=1))#卷积核为1*1的升维层,输入维度inp,输出维度inp*expand_ratio
layers.extend([
ConvBNReLU(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, stride=stride, groups=hidden_dim),#特征提取层,卷积核大小为3*3,输入和输出维度相同
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),#卷积核为1*1的降维层,输入维度hidden_dim,输出维度oup
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),#正则化
])
self.conv = nn.Sequential(*layers)#将上述结构添加到self.conv结构中
def forward(self, x):
if self.use_res_connect:#如果输入输出的通道size相同,且步距为1,此时使用shortcut结构。
return x + self.conv(x)#将卷积层的输出与输入相加
else:
return self.conv(x)#步长为2时,由于input与outputsize不符,不添加shortcut结构。
class MobileNetV2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, width_mult=1.0, inverted_residual_setting=None, round_nearest=8):
super(MobileNetV2, self).__init__()
block = InvertedResidual#倒残差结构
input_channel = 32
last_channel = 1280
#倘若为空,就添加一些值
if inverted_residual_setting is None:
inverted_residual_setting = [
# t, c, n, s
[1, 16, 1, 1],
[6, 24, 2, 2],
[6, 32, 3, 2],
[6, 64, 4, 2],
[6, 96, 3, 1],
[6, 160, 3, 2],
[6, 320, 1, 1],
]
#如果不符合标准要求,则报错
if len(inverted_residual_setting) == 0 or len(inverted_residual_setting[0]) != 4:
raise ValueError("inverted_residual_setting should be non-empty "
"or a 4-element list, got {}".format(inverted_residual_setting))
input_channel = _make_divisible(input_channel * width_mult, round_nearest)
self.last_channel = _make_divisible(last_channel * max(1.0, width_mult), round_nearest)
features = [ConvBNReLU(3, input_channel, stride=2)]#特征提取层,输入维度3,输出维度32,卷积核大小3*3,步距为2
#有深度可分离卷积的倒残差结构层
# t扩展因子即升维倍数,c输出特征矩阵深度,n重复次数,s步距
for t, c, n, s in inverted_residual_setting:
output_channel = _make_divisible(c * width_mult, round_nearest)#输出深度的计算
for i in range(n):
stride = s if i == 0 else 1 #仅针对第一层,步距为stride = s,如果是其它层。步距为1
features.append(block(input_channel, output_channel, stride, expand_ratio=t))
input_channel = output_channel
#在加上没有残差结构的卷积层,input_channel=320,last_channel=1280,步距为1
features.append(ConvBNReLU(input_channel, self.last_channel, kernel_size=1))
self.features = nn.Sequential(*features)
#添加分类结构,通过一个线性分类器,输出维度为num_classes
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(0.2),
nn.Linear(self.last_channel, num_classes),
)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.ones_(m.weight)
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = x.mean([2, 3])
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def mobilenet_v2(pretrained=False, progress=True, num_classes=10):
model = MobileNetV2(num_classes=num_classes) #num_classes=num_classes
if pretrained:
state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url(model_urls['mobilenet_v2'], model_dir='./model_data',
progress=progress)
model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
model.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(0.2),
nn.Linear(model.last_channel, num_classes),
)
return model
net = mobilenet_v2()
net.to(device)
print(net.to(device)) # 输出模型结构
test1 = torch.ones(64, 3, 120, 120) # 测试一下输出的形状大小 输入一个64,3,120,120的向量
test1 = net(test1.to(device)) # 将向量打入神经网络进行测试
print(test1.shape) # 查看输出的结果