ML_Decision Tree
机器学习100天系列学习笔记 机器学习100天(中文翻译版)机器学习100天(英文原版)
代码阅读:
第一步:导包
#Step 1: Importing the Libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
第二步:导入数据
#Step 2: Importing the dataset
dataset = pd.read_csv('D:/daily/机器学习100天/100-Days-Of-ML-Code-中文版本/100-Days-Of-ML-Code-master/datasets/Social_Network_Ads.csv')
X = dataset.iloc[:, [2, 3]].values
y = dataset.iloc[:, 4].values
第三步:划分训练集、测试集
#Step 3: Splitting the dataset into the Training set and Test set
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 0)
第四步:特征缩放
#Step 4: Feature Scaling
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
经过特征缩放后的X_train:
[[ 0.58164944 -0.88670699]
[-0.60673761 1.46173768]
[-0.01254409 -0.5677824 ]
[-0.60673761 1.89663484]
[ 1.37390747 -1.40858358]
[ 1.47293972 0.99784738]
[ 0.08648817 -0.79972756]
[-0.01254409 -0.24885782]
[-0.21060859 -0.5677824 ]...]
对于进行特征缩放这一步,个人认为是非常重要的,它可以加快收敛速度,在深度学习中间尤为重要(梯度爆炸问题)。
第五步:DecisionTreeClassifier
#Step 5: Fitting DecisionTreeClassifier to the Training set
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
classifier = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = 'entropy', random_state = 0)
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
第六步:预测
#Step 6: Predicting the Test set results
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
第七步:混淆矩阵
#Step 7: Making the Confusion Matrix
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print(cm) # print confusion_matrix
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred)) # print classification report
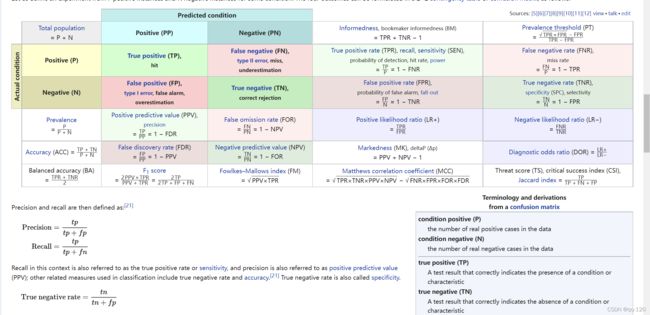
混淆:简单理解为一个class被预测成另一个class。
给一个参考链接 混淆矩阵
然后谈谈classification_report函数;科学上网,正常上网
输出:
[[63 5]
[ 4 28]]
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.94 0.93 0.93 68
1 0.85 0.88 0.86 32
accuracy 0.91 100
macro avg 0.89 0.90 0.90 100
weighted avg 0.91 0.91 0.91 100
precision:精确度;
recall:召回率;
f1-score:precision、recall的调和函数,越接近1越好;
support:每个标签的出现次数;
avg / total行为各列的均值(support列为总和);
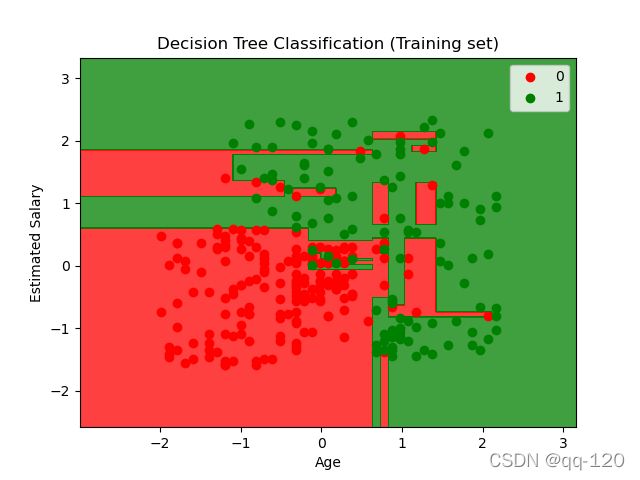
第八步:可视化
#Step 8: Visualization
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
X_set,y_set = X_train,y_train
X1,X2 = np. meshgrid(np. arange(start=X_set[:,0].min()-1, stop=X_set[:,0].max()+1, step=0.01),
np. arange(start=X_set[:,1].min()-1, stop=X_set[:,1].max()+1, step=0.01))
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(),X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
plt.xlim(X1.min(),X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(),X2.max())
for i,j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set==j,0],X_set[y_set==j,1],
c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label=j)
plt. title(' Decision Tree Classification (Training set)')
plt. xlabel(' Age')
plt. ylabel(' Estimated Salary')
plt. legend()
plt. show()
X_set,y_set=X_test,y_test
X1,X2=np. meshgrid(np. arange(start=X_set[:,0].min()-1, stop=X_set[:, 0].max()+1, step=0.01),
np. arange(start=X_set[:,1].min()-1, stop=X_set[:,1].max()+1, step=0.01))
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(),X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
plt.xlim(X1.min(),X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(),X2.max())
for i,j in enumerate(np. unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set==j,0],X_set[y_set==j,1],
c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label=j)
plt. title(' Decision Tree Classification (Test set)')
plt. xlabel(' Age')
plt. ylabel(' Estimated Salary')
plt. legend()
plt. show()
全部代码:
#Day7: Decision Tree (DT) 2022/04/10
#Step 1: Importing the libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
#Step 2: Importing the dataset
dataset = pd.read_csv('D:/daily/机器学习100天/100-Days-Of-ML-Code-中文版本/100-Days-Of-ML-Code-master/datasets/Social_Network_Ads.csv')
X = dataset.iloc[:, [2, 3]].values
y = dataset.iloc[:, 4].values
#Step 3: Splitting the dataset into the Training set and Test set
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 0)
#Step 4: Feature Scaling
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
#Step 5: Fitting Decision Tree Classification to the Training set
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
classifier = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = 'entropy', random_state = 0)
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
#Step 6: Predicting the Test set results
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
#Step 7: Making the Confusion Matrix
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print(cm)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
#Step 8: Visualising the Training set results
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = X_train, y_train
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01),
np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01))
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(), X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max())
for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1],
c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
plt.title('Decision Tree Classification (Training set)')
plt.xlabel('Age')
plt.ylabel('Estimated Salary')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Visualising the Test set results
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = X_test, y_test
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01),
np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01))
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(), X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max())
for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1],
c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
plt.title('Decision Tree Classification (Test set)')
plt.xlabel('Age')
plt.ylabel('Estimated Salary')
plt.legend()
plt.show()