要求:使用10-fold交叉验证方法实现SVM的对人脸库识别,列出不同核函数参数对识别结果的影响,要求画对比曲线。
使用Python完成,主要参考文献【4】,其中遇到不懂的功能函数一个一个的查官方文档和相关资料。其中包含了使用Python画图,遍历文件,读取图片,PCA降维,SVM,交叉验证等知识。
0.数据说明预处理
下载AT&T人脸数据(http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/research/dtg/attarchive/facedatabase.html),解压缩后为40个文件夹,每个文件夹是一个人的10张人脸照片。使用Python的glob库和PIL的Image读取照片,并转化为一维向量。这里需要注意,glob并非按照顺序读取,所以需要按照文件夹一个人一个人的读取数据,并标记对应分类。
1 PICTURE_PATH = u"F:\\att_faces" 2 3 all_data_set = [] #原始总数据集,二维矩阵n*m,n个样例,m个属性 4 all_data_label = [] #总数据对应的类标签 5 def get_picture(): 6 label = 1 7 #读取所有图片并一维化 8 while (label <= 20): 9 for name in glob.glob(PICTURE_PATH + "\\s" + str(label) + "\\*.pgm"): 10 img = Image.open(name) 11 #img.getdata() 12 #np.array(img).reshape(1, 92*112) 13 all_data_set.append( list(img.getdata()) ) 14 all_data_label.append(label) 15 label += 1 16 17 get_picture()
1.PCA降维
获得原始数据后,对数据使用PCA降维处理,其中设定降维后的特征数目时遇到了问题,参考资料中n_components设定为150,但是该数据集采用大的该值后识别率会非常低,即虽然可以百分百识别出训练集人脸,但无法预测识别出新的脸,发生了过拟合(?)。经过把参数n_components设置为16后,产生了非常好的结果。PCA降维后数据的维数取多少比较好?有什么标准判断?注意,若维数较高,SVM训练会非常慢并且占用很高内存,维数小反而取得了很好的结果和效率。
另外,例子中是分别对测试集与训练集使用PCA降维,即PCA fit时只用了训练集。将数据转换为numpy的array类型是为了后面编程方便。
1 n_components = 16#这个降维后的特征值个数如果太大,比如100,结果将极其不准确,为何?? 2 pca = PCA(n_components = n_components, svd_solver='auto', 3 whiten=True).fit(all_data_set) 4 #PCA降维后的总数据集 5 all_data_pca = pca.transform(all_data_set) 6 #X为降维后的数据,y是对应类标签 7 X = np.array(all_data_pca) 8 y = np.array(all_data_label)
2. SVM训练与识别
对降维后的数据进行训练与识别。
1 #输入核函数名称和参数gamma值,返回SVM训练十折交叉验证的准确率 2 def SVM(kernel_name, param): 3 #十折交叉验证计算出平均准确率 4 #n_splits交叉验证,随机取 5 kf = KFold(n_splits=10, shuffle = True) 6 precision_average = 0.0 7 param_grid = {'C': [1e3, 5e3, 1e4, 5e4, 1e5]}#自动穷举出最优的C参数 8 clf = GridSearchCV(SVC(kernel=kernel_name, class_weight='balanced', gamma = param), 9 param_grid) 10 for train, test in kf.split(X): 11 clf = clf.fit(X[train], y[train]) 12 #print(clf.best_estimator_) 13 test_pred = clf.predict(X[test]) 14 #print classification_report(y[test], test_pred) 15 #计算平均准确率 16 precision = 0 17 for i in range(0, len(y[test])): 18 if (y[test][i] == test_pred[i]): 19 precision = precision + 1 20 precision_average = precision_average + float(precision)/len(y[test]) 21 precision_average = precision_average / 10 22 #print (u"准确率为" + str(precision_average)) 23 return precision_average
3.主程序,设置不同参数对比分析
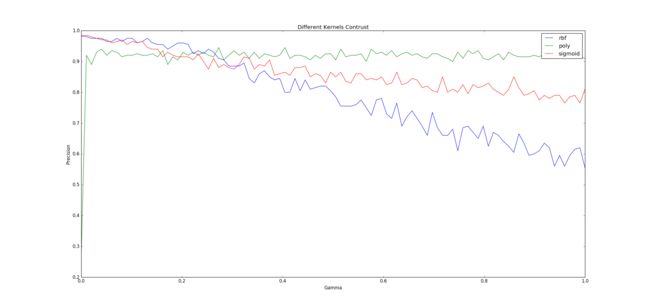
根据例子中的gamma值选择,发现其可以从非常小开始,即0.0001,经过人工实验,到1时rbf kernel出现了较差的结果,所以画图对比时在0.0001至1之间取100个点,因为点多后程序运行会非常慢。程序中的x_label即枚举的gamma参数值。为了节省时间,数据只选择了前20个人,最终执行时间为366.672秒。
1 t0 = time() 2 kernel_to_test = ['rbf', 'poly', 'sigmoid'] 3 #rint SVM(kernel_to_test[0], 0.1) 4 plt.figure(1) 5 6 for kernel_name in kernel_to_test: 7 x_label = np.linspace(0.0001, 1, 100) 8 y_label = [] 9 for i in x_label: 10 y_label.append(SVM(kernel_name, i)) 11 plt.plot(x_label, y_label, label=kernel_name) 12 13 14 print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0)) 15 plt.xlabel("Gamma") 16 plt.ylabel("Precision") 17 plt.title('Different Kernels Contrust') 18 plt.legend() 19 plt.show() 20 21
Figure 1 不同核函数不同参数识别率对比图
参考:
[1] Philipp Wagner.Face Recognition with Python. July 18, 2012
[2] Chih-Wei Hsu, Chih-Chung Chang, and Chih-Jen Lin. A Practical Guide to Support Vector Classication. National Taiwan University, Taipei 106, Taiwan.
[3] http://www.cnblogs.com/cvlabs/archive/2010/04/13/1711470.html
[4]http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/applications/face_recognition.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-applications-face-recognition-py
[5] http://blog.csdn.net/ikerpeng/article/details/20370041
附录完整代码:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 """ 3 Created on Fri Dec 02 15:51:14 2016 4 5 @author: JiaY 6 """ 7 from time import time 8 from PIL import Image 9 import glob 10 import numpy as np 11 import sys 12 from sklearn.model_selection import KFold 13 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 14 from sklearn.decomposition import PCA 15 from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV 16 from sklearn.svm import SVC 17 from sklearn.metrics import classification_report 18 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 19 20 #设置解释器为utf8编码,不知为何文件开头的注释没用。 21 #尽管这样设置,在IPython下仍然会出错,只能用原装Python解释器执行本程序 22 reload(sys) 23 sys.setdefaultencoding("utf8") 24 print sys.getdefaultencoding() 25 26 PICTURE_PATH = u"F:\\课程相关资料\\研究生——数据挖掘\\16年作业\\att_faces" 27 28 all_data_set = [] #原始总数据集,二维矩阵n*m,n个样例,m个属性 29 all_data_label = [] #总数据对应的类标签 30 def get_picture(): 31 label = 1 32 #读取所有图片并一维化 33 while (label <= 20): 34 for name in glob.glob(PICTURE_PATH + "\\s" + str(label) + "\\*.pgm"): 35 img = Image.open(name) 36 #img.getdata() 37 #np.array(img).reshape(1, 92*112) 38 all_data_set.append( list(img.getdata()) ) 39 all_data_label.append(label) 40 label += 1 41 42 get_picture() 43 44 n_components = 16#这个降维后的特征值个数如果太大,比如100,结果将极其不准确,为何?? 45 pca = PCA(n_components = n_components, svd_solver='auto', 46 whiten=True).fit(all_data_set) 47 #PCA降维后的总数据集 48 all_data_pca = pca.transform(all_data_set) 49 #X为降维后的数据,y是对应类标签 50 X = np.array(all_data_pca) 51 y = np.array(all_data_label) 52 53 54 #输入核函数名称和参数gamma值,返回SVM训练十折交叉验证的准确率 55 def SVM(kernel_name, param): 56 #十折交叉验证计算出平均准确率 57 #n_splits交叉验证,随机取 58 kf = KFold(n_splits=10, shuffle = True) 59 precision_average = 0.0 60 param_grid = {'C': [1e3, 5e3, 1e4, 5e4, 1e5]}#自动穷举出最优的C参数 61 clf = GridSearchCV(SVC(kernel=kernel_name, class_weight='balanced', gamma = param), 62 param_grid) 63 for train, test in kf.split(X): 64 clf = clf.fit(X[train], y[train]) 65 #print(clf.best_estimator_) 66 test_pred = clf.predict(X[test]) 67 #print classification_report(y[test], test_pred) 68 #计算平均准确率 69 precision = 0 70 for i in range(0, len(y[test])): 71 if (y[test][i] == test_pred[i]): 72 precision = precision + 1 73 precision_average = precision_average + float(precision)/len(y[test]) 74 precision_average = precision_average / 10 75 #print (u"准确率为" + str(precision_average)) 76 return precision_average 77 78 t0 = time() 79 kernel_to_test = ['rbf', 'poly', 'sigmoid'] 80 #rint SVM(kernel_to_test[0], 0.1) 81 plt.figure(1) 82 83 for kernel_name in kernel_to_test: 84 x_label = np.linspace(0.0001, 1, 100) 85 y_label = [] 86 for i in x_label: 87 y_label.append(SVM(kernel_name, i)) 88 plt.plot(x_label, y_label, label=kernel_name) 89 90 91 print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0)) 92 plt.xlabel("Gamma") 93 plt.ylabel("Precision") 94 plt.title('Different Kernels Contrust') 95 plt.legend() 96 plt.show() 97 98 99 100 """ 101 clf = GridSearchCV(SVC(kernel='rbf', class_weight='balanced'), param_grid) 102 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( 103 X, y, test_size=0.1, random_state=42) 104 clf = clf.fit(X_train, y_train) 105 test_pred = clf.predict(X_test) 106 print classification_report(y_test, test_pred) 107 108 #十折交叉验证计算出平均准确率 109 precision_average = 0.0 110 for train, test in kf.split(X): 111 clf = clf.fit(X[train], y[train]) 112 #print(clf.best_estimator_) 113 test_pred = clf.predict(X[test]) 114 #print classification_report(y[test], test_pred) 115 #计算平均准确率 116 precision = 0 117 for i in range(0, len(y[test])): 118 if (y[test][i] == test_pred[i]): 119 precision = precision + 1 120 precision_average = precision_average + float(precision)/len(y[test]) 121 precision_average = precision_average / 10 122 print ("准确率为" + str(precision_average)) 123 print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0)) 124 """ 125 """ 126 print("Fitting the classifier to the training set") 127 t0 = time() 128 param_grid = {'C': [1e3, 5e3, 1e4, 5e4, 1e5], 129 'gamma': [0.0001, 0.0005, 0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.1], } 130 clf = GridSearchCV(SVC(kernel='rbf', class_weight='balanced'), param_grid) 131 clf = clf.fit(all_data_pca, all_data_label) 132 print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0)) 133 print("Best estimator found by grid search:") 134 print(clf.best_estimator_) 135 all_data_set_pred = clf.predict(all_data_pca) 136 #target_names = range(1, 11) 137 print(classification_report(all_data_set_pred, all_data_label)) 138 """