图像分类——猫狗大战问题
目录
一.数据处理
二.构造网络
三.训练和测试
四.展示结果
一.数据处理
Dogs vs. Cats(猫狗大战),其中训练集有20000张,猫狗各占一半,验证集20000,测试集2000张,没有标定是猫还是狗。要求设计一种算法对测试集中的猫狗图片进行判别,是一个传统的二分类问题。
拿到数据,先查看数据集,可以看到图片的大小均不一致且没有y值。所以我们需要自己在先将数据处理好。
以下是代码。
class Datachushihua(Dataset):
def __init__(self,mode,dir) :
self.mode=mode
self.img_list=[]# 存放路径
self.label_list=[] #转化输出
self.data_size=0
self.transform=afterdata
if self.mode == 'train'or self.mode =='val':
dir = dir + self.mode+'/'
for file in tqdm(os.listdir(dir)):
img = Image.open(dir+file) # 打开图片
self.img_list.append(self.transform(img))
self.data_size += 1
file_try=file
name=file_try.split(sep='_') #切割字符串返回
if name[0]=='cat':
self.label_list.append(0)
else:
self.label_list.append(1)
self.label_list = torch.LongTensor(self.label_list)
elif self.mode == 'test': # 测试集模式下,只需要提取图片路径就行
dir = dir + '/test/' # 测试集路径为"dir"/test/
for file in os.listdir(dir):
self.img_list.append(dir + file) # 添加图片路径至image list
self.data_size += 1
else:
print('Undefined Dataset!')
def __getitem__(self,item):#返回下标
if self.mode == 'train'or self.mode =='val': # 训练集模式下需要读取数据集的image和label
return self.img_list[item], self.label_list[item]
elif self.mode == 'test': # 测试集只需读取image
img = Image.open(self.img_list[item])
return self.transform(img) # 只返回image
else:
print('None')
def __len__(self):
return self.data_size
二.构造网络
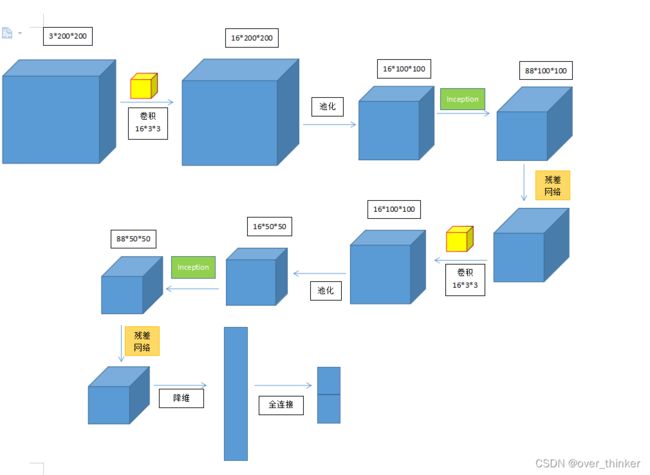
构造model并且加入inception和残差网络,具体的网络结构如图所示。
#网络结构
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self) :
super(Model,self).__init__()
self.Conv1=torch.nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 3, padding=1)
#3*200*200-->16*200*200
self.Conv2=torch.nn.Conv2d(88, 16, 3, padding=1)
self.incept1 = InceptionA(in_channels=16)
self.rblock1=ResidualBlock(88)
self.pooling=torch.nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.linear1=torch.nn.Linear(220000,2)
# self.linear4=torch.nn.Linear(40000,128)
#
# #self.linear3=torch.nn.Linear(64,2)
def forward(self,x):
x=F.relu(self.Conv1(x))
x=self.pooling(x)
#16*200*200-->16*100*100
x = self.incept1(x)
#16*100*100-->88*100*100
x=self.rblock1(x)
x=F.relu(self.Conv2(x))
#88*100*100-->16*100*100
x=self.pooling(x)
#16*100*100-->16*50*50
x = self.incept1(x)
#16*50*50-->88*50*50
x=self.rblock1(x)
x=x.view(x.size()[0], -1)
#x=F.relu(self.linear1(x))
#x=F.relu(self.linear4(x))
#x=F.relu(self.linear2(x))
x=self.linear1(x)
return x
# 构造自己的Net
class ResidualBlock(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self,channels):
super(ResidualBlock,self).__init__()
self.channels=channels
self.conv1=torch.nn.Conv2d(channels,channels,kernel_size=3,padding=1)#为了使大小不变
self.conv2=torch.nn.Conv2d(channels,channels,kernel_size=3,padding=1)
def forward(self,x):
y=F.relu(self.conv1(x))
y=self.conv2(y)
return F.relu(x+y)
# 构造Inception block
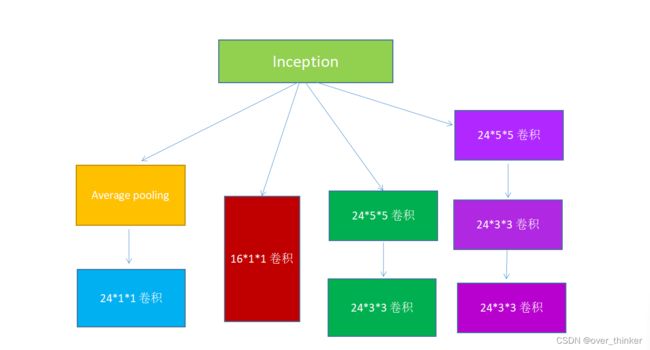
class InceptionA(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels):
super(InceptionA, self).__init__()
self.averag_pool = torch.nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv1_1_24 = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels,24,kernel_size=1)
self.conv1_1_16 = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels,16,kernel_size=1)
self.conv5_5_24 = torch.nn.Conv2d(16,24,kernel_size=5,padding=2)
self.conv3_3_24_1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(16,24,kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.conv3_3_24_2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(24,24,kernel_size=3,padding=1)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.averag_pool(x)
#不改变大小
x1 = self.conv1_1_24(x1)
#16*100*100-->24*100*100(1)
x2 = self.conv1_1_16(x)
#16*100*100-->16*100*100(1)
x3 = self.conv1_1_16(x)
#16*100*100-->16*100*100(1)
x3 = self.conv5_5_24(x3)
#16*100*100-->24*100*100(1)
x4 = self.conv1_1_16(x)
#16*100*100-->16*100*100(1)
x4 = self.conv3_3_24_1(x4)
#16*100*100-->24*100*100(1)
x4 = self.conv3_3_24_2(x4)
#24*100*100-->24*100*100
outputs = [x1,x2,x3,x4]
return torch.cat(outputs, dim=1)
#88*100*100
三.训练和测试
这里的test修改了以下,可以随机从测试集中选取图片。
model=Model()
model.cuda()
batch_size=16
lr=0.001
sunshi=torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
youhua=optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=lr,momentum=0.5)
#训练,验证,与测试
def train(epoch):
print("epoch:",epoch+1)
running_loss = 0
for batch_index,data in enumerate(tqdm(train_loader)):
input,target=data
input = input.cuda()
target = target.cuda()
output=model(input)
loss=sunshi(output,target)
running_loss += loss
youhua.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
youhua.step()
print("train loss:", (running_loss).item()/batch_index)
torch.save(model.state_dict(), './model.pth') # 训练所有数据后,保存网络的参数
def val(val_loader, model):
total = 0
correct = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for batch_index, data in enumerate(val_loader,0):
inputs, labels = data
inputs = inputs.cuda()
labels = labels.cuda()
outputs = model(inputs)
# 取维度最大
_, predicts = torch.max(outputs,dim=1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicts==labels).sum().item()
print("正确率:", correct/total)
return correct/total
def test():
font={ 'color': 'red',
'size': 20,
'family': 'Times New Roman',
'style':'italic'}
model=Model()
model = model.cuda()
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("model.pth"))
index = np.random.randint(0, test_dataset.data_size, 1)[0] # 获取一个随机数,即随机从数据集中获取一个测试图片
img = test_dataset.__getitem__(index) # 获取一个图像
img = img.unsqueeze(0) # 因为网络的输入是一个4维Tensor,3维数据,1维样本大小,所以直接获取的图像数据需要增加1个维度
img = img.cuda() # 将数据放置在PyTorch的Variable节点中,并送入GPU中作为网络计算起点
out = model(img) # 网路前向计算,输出图片属于猫或狗的概率,第一列维猫的概率,第二列为狗的概率
out = F.softmax(out, dim=1) # 采用SoftMax方法将输出的2个输出值调整至[0.0, 1.0],两者和为1
img = Image.open(test_dataset.img_list[index]) # 打开测试的图片
plt.figure('image')
plt.imshow(img)
if out[0, 0] > out[0, 1]: # 猫的概率大于狗
plt.text(0, -6.0, "prediction: cat", fontdict=font)
else: # 猫的概率小于狗
plt.text(0, -6.0, "prediction: dog", fontdict=font)
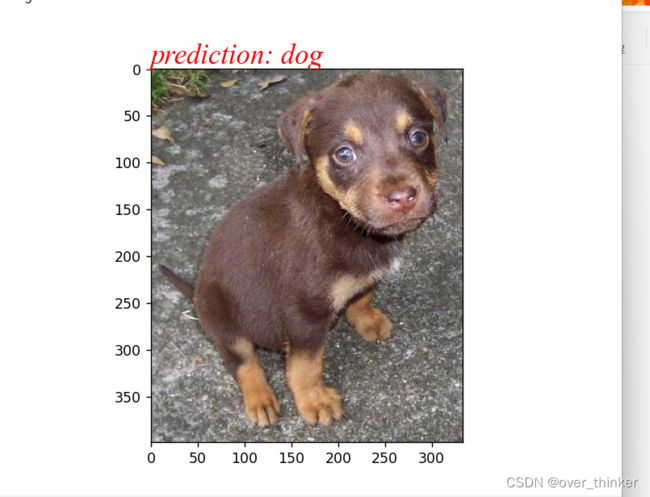
plt.show()四.展示结果
dataset_dir='./cat_dog/'
train_dataset = Datachushihua('train', dataset_dir)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
print('Dataset loaded! length of train set is {0}'.format(len(train_loader)))
val_dataset=Datachushihua('val', dataset_dir)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=64)
test_dataset=Datachushihua('test', dataset_dir)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=64)
if __name__=='__main__':
for epoch in range(20):
train(epoch)
val(val_loader, model)
test()可以看到正确率稳定在了 78%左右。
主要·时间还是浪费在了数据处理那一块,好在网络改进后正确率提高了。