文章阅读 - Learned Multi-Patch Similarity (ICCV 2017)
问题:为什么不直接计算多目的相似性呢?
相关工作
深度图计算
双目中的benchmark:Middlebury Stereo [1]、KITTI [2]
多目中的benchmark:[3]、[4]
多目中深度图计算方法可分为两类:
- plane-sweeping
- 随机采样和扩散(如PatchMatch)
学习Patch的相似性
学习patch描述子:LIFT [5-6]:基于Siamese网络,loss function(匹配的patch对应小的欧氏距离,不匹配的patch对应大的欧氏距离),输出为一个128维的向量(对应于SIFT特征描述子)
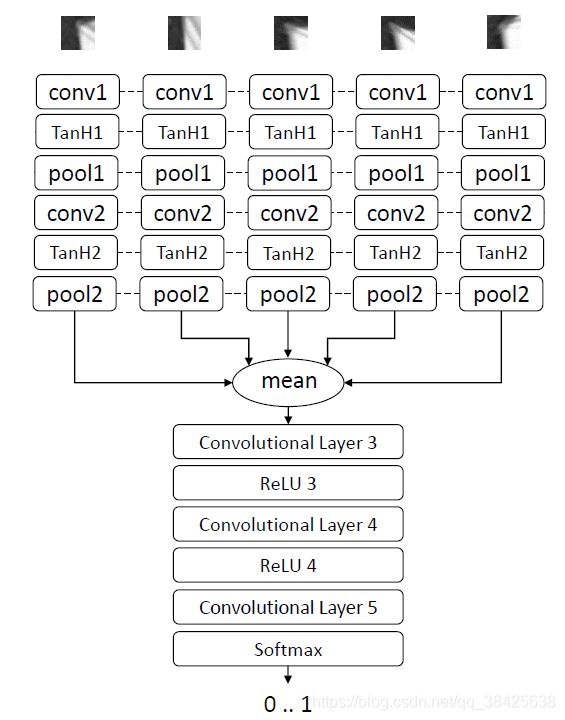
网络结构
注:所有的patch具有相同的权重
网络训练
- plane-sweeping
- 匹配的patch标注为1,不匹配的patch标注为0
- 正样本由ground truth的深度信息计算得到,负样本选取ground truth的前后15个深度平面(不选取极线外的不相关的负样本)
- 14700万正样本和14700万负样本;500000次迭代;batch size为1024;学习率开始为0.001,每迭代100000次减小10倍
实验结果
定性评价
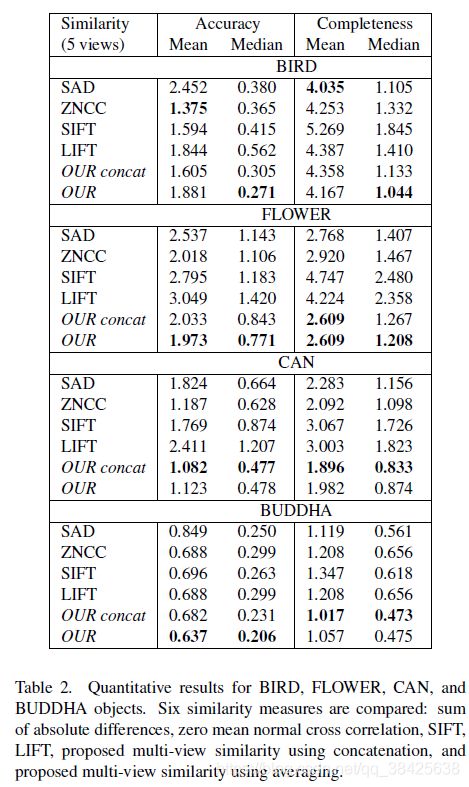
从左到右数据集依次为BIRD、FLOWER、CAN和BUDDHA。
BIRD:亮度变化较大。对于边缘区域,各个算法计算结果都不好。
FLOWER:thin结构和小叶子。对于花盆中的泥土,各个算法都难以解决。
CAN:存在均匀的纹理。文中提出的算法和ZNCC都可以较好地解决这个问题,但LIFT表现较差。
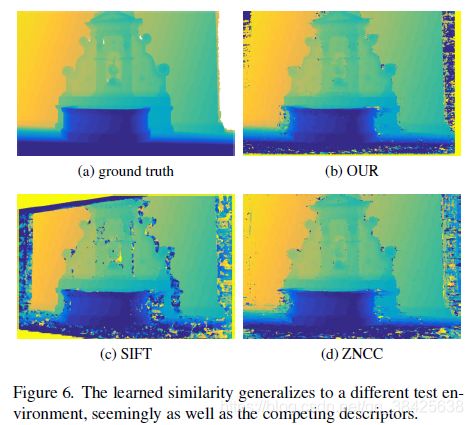
BUDDHA:镜面反射。文中提出的算法表现较好。
总结:ZNCC对物体边缘表现不好,LIFT对均匀纹理和镜面反射表现不好。
定量评价
参数
- Accuracy:重建出来的点到最近的ground truth的点(平均值)
- Completeness:ground truth的点到最近的重建出来的点(平均值)
1. 验证多目相似性计算的优越性
可以看出多目相似性计算得到的Completeness较好。
2. 在四个数据集上测试
OUR concat vs OUR:串联vs平均
OUR在BIRD数据集上效果不突出:部分区域亮度很低,导致深度学习提取到的特征误差较大?
改变输入patch的数量
在Fountain数据集上实验
参考文献
[1] D. Scharstein and R. Szeliski. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. International Journal of Computer Vision, 47(1-3):7–42, 2002.
[2] A. Geiger, P. Lenz, and R. Urtasun. Are we ready for autonomous driving? the KITTI vision benchmark suite. In CVPR 2012.
[3] S. M. Seitz, B. Curless, J. Diebel, D. Scharstein, and R. Szeliski. A comparison and evaluation of multi-view stereo reconstruction algorithms. In CVPR 2006.
[4] R. Jensen, A. Dahl, G. Vogiatzis, E. Tola, and H. Aans. Large scale multi-view stereopsis evaluation. In CVPR 2014.
[5] E. Simo-Serra, E. Trulls, L. Ferraz, I. Kokkinos, P. Fua, and F. Moreno-Noguer. Discriminative learning of deep convolutional feature point descriptors. In ICCV 2015.
[6] K. M. Yi, E. Trulls, V. Lepetit, and P. Fua. LIFT: learned invariant feature transform. CoRR, abs/1603.09114, 2016.
附:论文下载:https://www.ethz.ch/content/dam/ethz/special-interest/baug/igp/photogrammetry-remote-sensing-dam/documents/pdf/Papers/Learned-Multi-Patch-Similarity.pdf