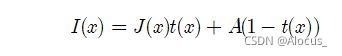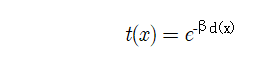完善后的根据深度图加雾代码Python
前言:
以下代码根据实验需要进一步了修改,尚有不完善之处,多多指教!
由于本人需要,代码中有加噪步骤,可以自行去除。加噪方式参考论文:bringing old photos back to life
其中包含数据集reside中加雾算法的个人实现,可能存在错误或不足,如有请劳烦联系告诉我,可以留言或者加本人联系方式(代码中有)==!
原理:
不赘述,如下。
大气模型:
其中
I为雾化图像,J为原图,t为转移矩阵,A为大气光,d为深度矩阵
代码:
#coding:utf-8
# import cv2
# import os
# import glob
# import cv2, math
# import numpy as np
# Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
# Licensed under the MIT License.
# import os.path
# import io
# import zipfile
#
# import torchvision.transforms as transforms
#author WeChat:Alocus
#author QQ:1913434222
#source:https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/121520268
from io import BytesIO
import os
import glob
import cv2, math
import random
import numpy as np
# import h5py
import os
from PIL import Image
import scipy.io
def pil_to_np(img_PIL):
'''Converts image in PIL format to np.array.
From W x H x C [0...255] to C x W x H [0..1]
'''
ar = np.array(img_PIL)
if len(ar.shape) == 3:
ar = ar.transpose(2, 0, 1)
else:
ar = ar[None, ...]
return ar.astype(np.float32) / 255.
def np_to_pil(img_np):
'''Converts image in np.array format to PIL image.
From C x W x H [0..1] to W x H x C [0...255]
'''
ar = np.clip(img_np * 255, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
if img_np.shape[0] == 1:
ar = ar[0]
else:
ar = ar.transpose(1, 2, 0)
return Image.fromarray(ar)
def synthesize_salt_pepper(image,amount,salt_vs_pepper):
## Give PIL, return the noisy PIL
img_pil=pil_to_np(image)
out = img_pil.copy()
p = amount
q = salt_vs_pepper
flipped = np.random.choice([True, False], size=img_pil.shape,
p=[p, 1 - p])
salted = np.random.choice([True, False], size=img_pil.shape,
p=[q, 1 - q])
peppered = ~salted
out[flipped & salted] = 1
out[flipped & peppered] = 0.
noisy = np.clip(out, 0, 1).astype(np.float32)
return np_to_pil(noisy)
def synthesize_gaussian(image,std_l,std_r):
## Give PIL, return the noisy PIL
img_pil=pil_to_np(image)
mean=0
std=random.uniform(std_l/255.,std_r/255.)
gauss=np.random.normal(loc=mean,scale=std,size=img_pil.shape)
noisy=img_pil+gauss
noisy=np.clip(noisy,0,1).astype(np.float32)
return np_to_pil(noisy)
def synthesize_speckle(image,std_l,std_r):
## Give PIL, return the noisy PIL
img_pil=pil_to_np(image)
mean=0
std=random.uniform(std_l/255.,std_r/255.)
gauss=np.random.normal(loc=mean,scale=std,size=img_pil.shape)
noisy=img_pil+gauss*img_pil
noisy=np.clip(noisy,0,1).astype(np.float32)
return np_to_pil(noisy)
def synthesize_low_resolution(img):
w,h=img.size
new_w=random.randint(int(w/2),w)
new_h=random.randint(int(h/2),h)
img=img.resize((new_w,new_h),Image.BICUBIC)
if random.uniform(0,1)<0.5:
img=img.resize((w,h),Image.NEAREST)
else:
img = img.resize((w, h), Image.BILINEAR)
return img
def convertToJpeg(im,quality):
with BytesIO() as f:
im.save(f, format='JPEG',quality=quality)
f.seek(0)
return Image.open(f).convert('RGB')
def blur_image_v2(img):
x=np.array(img)
kernel_size_candidate=[(3,3),(5,5),(7,7)]
kernel_size=random.sample(kernel_size_candidate,1)[0]
std=random.uniform(1.,5.)
#print("The gaussian kernel size: (%d,%d) std: %.2f"%(kernel_size[0],kernel_size[1],std))
blur=cv2.GaussianBlur(x,kernel_size,std)
return Image.fromarray(blur.astype(np.uint8))
def srgb2lrgb(I0):
gamma = ((I0 + 0.055) / 1.055)**2.4
scale = I0 / 12.92
return np.where (I0 > 0.04045, gamma, scale)
def lrgb2srgb(I1):
gamma = 1.055*I1**(1/2.4)-0.055
scale = I1 * 12.92
return np.where (I1 > 0.0031308, gamma, scale)
def hazy_simu(img_name,depth_or_trans_name,airlight=0.76,is_imdepth=1): ##for outdoor
"""
This is the function for haze simulation with the parameters given by
the paper:
HAZERD: an outdoor scene dataset and benchmark for single image dehazing
IEEE Internation Conference on Image Processing, Sep 2017
The paper and additional information on the project are available at:
https://labsites.rochester.edu/gsharma/research/computer-vision/hazerd/
If you use this code, please cite our paper.
IMPORTANT NOTE: The code uses the convention that pixel locations with a
depth value of 0 correspond to objects that are very far and for the
simulation of haze these are placed a distance of 2 times the visual
range.
Authors:
Yanfu Zhang: [email protected]
Li Ding: [email protected]
Gaurav Sharma: [email protected]
Last update: May 2017
python version update : Aug 2021
Authors :
Haoying Sun : [email protected]
parse inputs and set default values
Set default parameter values. Some of these are used only if they are not
passed in
:param img_name: the directory and name of a haze-free RGB image, the name
should be in the format of ..._RGB.jpg
:param depth_name: the corresponding directory and name of the depth map, in
.mat file, the name should be in the format of ..._depth.mat
:param save_dir: the directory to save the simulated images
:param pert_perlin: 1 for adding perlin noise, default 0
:param airlight: 3*1 matrix in the range [0,1]
:param visual_range: a vector of any size
:return: image name of hazy image
"""
# if random.uniform(0, 1) < 0.5:
visual_range = [0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1] # visual range in km #可自行调整,或者使用range函数设置区间,此时需要修改beta_param,尚未研究
beta_param = 3.912 #Default beta parameter corresponding to visual range of 1000m
A = airlight
#print('Simulating hazy image for:{}'.format(img_name))
VR = random.choice(visual_range)
#print('Viusal value: {} km'.format(VR) )
#im1 = cv2.imread(img_name)
img_pil = pil_to_np(img_name)
#convert sRGB to linear RGB
I = srgb2lrgb(img_pil)
if is_imdepth:
depths = depth_or_trans_name
d = depths/1000 # convert meter to kilometer
if depths.max()==0:
d = np.where(d == 0,0.01, d) ####
else:
d = np.where(d==0,2*VR,d)
#Set regions where depth value is set to 0 to indicate no valid depth to
#a distance of two times the visual range. These regions typically
#correspond to sky areas
#convert depth map to transmission
beta = beta_param / VR
beta_return = beta
beta = np.ones(d.shape) * beta
transmission = np.exp((-beta*d))
transmission_3 = np.array([transmission,transmission,transmission])
#Obtain simulated linear RGB hazy image.Eq. 3 in the HazeRD paper
Ic = transmission_3 * I + (1 - transmission_3) * A
else:
Ic = pil_to_np(depth_or_trans_name) * I + (1 - pil_to_np(depth_or_trans_name)) * A
# convert linear RGB to sRGB
I2 = lrgb2srgb(Ic)
haze_img = np_to_pil(I2)
# haze_img = np.asarray(haze_img)
# haze_img = cv2.cvtColor(haze_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# haze_img = Image.fromarray(haze_img)
return haze_img,airlight,beta_return
def hazy_reside_training(img_name,depth_or_trans_name,is_imdepth=1):
"""
RESIDE的 training中:A :(0.7, 1.0) , beta:(0.6, 1.8)
:param img_name:
:param depth_or_trans_name:
:param pert_perlin:
:param is_imdepth:
:return:
"""
beta = random.uniform(0.6, 1.8)
beta_return = beta
airlight = random.uniform(0.7, 1.0)
A = airlight
#print('Viusal value: {} km'.format(VR) )
#im1 = cv2.imread(img_name)
img_pil = pil_to_np(img_name)
#convert sRGB to linear RGB
I = srgb2lrgb(img_pil)
if is_imdepth:
depths = depth_or_trans_name
#convert depth map to transmission
if depths.max()==0:
d = np.where(depths == 0,1, depths)
else:
d = depths / depths.max()
d = np.where(d == 0, 1, d)
beta = np.ones(d.shape) * beta
transmission = np.exp((-beta*d))
transmission_3 = np.array([transmission,transmission,transmission])
#Obtain simulated linear RGB hazy image.Eq. 3 in the HazeRD paper
Ic = transmission_3 * I + (1 - transmission_3) * A
else:
Ic = pil_to_np(depth_or_trans_name) * I + (1 - pil_to_np(depth_or_trans_name)) * A
# convert linear RGB to sRGB
I2 = lrgb2srgb(Ic)
#I2 = cv2.cvtColor(I2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
haze_img = np_to_pil(I2)
# haze_img = np.asarray(haze_img)
# haze_img = cv2.cvtColor(haze_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# haze_img = Image.fromarray(haze_img)
return haze_img,airlight,beta_return
def hazy_reside_OTS(img_name,depth_or_trans_name,is_imdepth=1):
"""
RESIDE的 OTS中:A [0.8, 0.85, 0.9, 0.95, 1] , beta:[0.04, 0.06, 0.08, 0.1, 0.12, 0.16, 0.2]
:param img_name:
:param depth_or_trans_name:
:param pert_perlin:
:param is_imdepth:
:return:
"""
beta = random.choice([0.04, 0.06, 0.08, 0.1, 0.12, 0.16, 0.2])
beta_return = beta
airlight = random.choice([0.8, 0.85, 0.9, 0.95, 1])
#print(beta)
#print(airlight)
A = airlight
#print('Viusal value: {} km'.format(VR) )
#im1 = cv2.imread(img_name)
#img = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img_name), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
img_pil = pil_to_np(img_name)
#convert sRGB to linear RGB
I = srgb2lrgb(img_pil)
if is_imdepth:
depths = depth_or_trans_name
#convert depth map to transmission
if depths.max()==0:
d = np.where(depths == 0, 1, depths)
else:
d = depths/(depths.max())
d = np.where(d == 0, 1, d)
# #深度图可视化
# dd = (depth_or_trans_name-depth_or_trans_name.min())/(depth_or_trans_name.max()-depth_or_trans_name.min())
# Image.fromarray(dd * 255).show()
beta = np.ones(d.shape) * beta
transmission = np.exp((-beta*d))
# #透射图可视化
# transmission1 = (transmission-transmission.min())/(transmission.max()-transmission.min())#np.std
# Image.fromarray(transmission1*255).show()
transmission_3 = np.array([transmission,transmission,transmission])
#Obtain simulated linear RGB hazy image.Eq. 3 in the HazeRD paper
Ic = transmission_3 * I + (1 - transmission_3) * A
else:
Ic = pil_to_np(depth_or_trans_name) * I + (1 - pil_to_np(depth_or_trans_name)) * A
# convert linear RGB to sRGB
I2 = lrgb2srgb(Ic)
haze_img = np_to_pil(I2)
#haze_img = np.asarray(haze_img)
#haze_img = cv2.cvtColor(haze_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
#haze_img = Image.fromarray(haze_img)
return haze_img,airlight,beta_return
def online_add_degradation_v2(img,depth_or_trans):
noise = 0
task_id=np.random.permutation(4)
if random.uniform(0,1)<0.3:
noise = 1
#print('noise')
for x in task_id:
#为增加更多变化,随机进行30%的丢弃,即<0.7
if x==0 and random.uniform(0,1)<0.7:
img = blur_image_v2(img)
if x==1 and random.uniform(0,1)<0.7:
flag = random.choice([1, 2, 3])
if flag == 1:
img = synthesize_gaussian(img, 5, 50) # Gaussian white noise with σ ∈ [5,50]
if flag == 2:
img = synthesize_speckle(img, 5, 50)
if flag == 3:
img = synthesize_salt_pepper(img, random.uniform(0, 0.01), random.uniform(0.3, 0.8))
if x==2 and random.uniform(0,1)<0.7:
img=synthesize_low_resolution(img)
if x==3 and random.uniform(0,1)<0.7:
img=convertToJpeg(img,random.randint(40,100))
#JPEG compression whose level is in the range of [40,100]
#img.show('noise')
add_haze = random.choice([1,2,3])
if add_haze == 1:
img, airlight, beta = hazy_reside_OTS(img, depth_or_trans)
elif add_haze == 2:
img, airlight, beta = hazy_simu(img, depth_or_trans)
else:
img, airlight, beta = hazy_reside_training(img, depth_or_trans)
# else:
# if add_haze < 0.1:
# img = hazy_reside_OTS(img, depth_or_trans)
# elif add_haze > 0.1 and add_haze < 0.2:
# img = hazy_simu(img, depth_or_trans)
# else:
# img = hazy_reside_training(img, depth_or_trans)
return img,noise,airlight,beta
path1 = r'J:\dataset\GT\1449.png'
path2 = r'J:\dataset\npy\1449.npy'
path3 = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop'
# for i in range(1400,1450):
# path11 = os.path.join(path1,str(i) + '.png')
# path22 = os.path.join(path2, str(i) + '.npy')
# npy = np.load(path22)
#
# img = Image.open(path11)
# for j in range(1,11):
# #hazy_simu hazy_reside_training hazy_reside_OTS
# img_haze,noise,airlight,beta_return = online_add_degradation_v2(img,npy)
# airlight = round(airlight, 2)
# beta_return = round(beta_return, 2)
#
# #Image.Image.show(img)
# path_save =os.path.join(path3,str(i) + '_' + str(j) + '_'+ str(noise) + '_'+ str(airlight) + '_' + str(beta_return)+ '.png')
# img_haze.save(path_save)
npy = np.load(path2)
img = Image.open(path1)
for j in range(1,11):
#hazy_simu hazy_reside_training hazy_reside_OTS
img_haze,airlight,noise,beta_return = hazy_reside_OTS(img,npy)
airlight = round(airlight, 2)
beta_return = round(beta_return, 2)
#Image.Image.show(img)
path_save =os.path.join(path3,str(j) + '_' + str(j) + '_'+str(noise)+ '_'+ str(airlight) + '_' + str(beta_return)+ '.png')
img_haze.save(path_save)
结果:
原图:
无噪声
有噪声
深度图:(需要设置显示色彩)
透射图:
注意,其中npy文件为利用numpy库将深度信息转为npy类型文件,其实质就是矩阵。另外,我在代码中加入了一些可视化,如深度图,透射图等,如果需要的话可以取消注释。
另外,我所用的数据集为NYUv2,深度矩阵npy文件为从中提取,网上应该有或者从官方网站中自行提取。如有需要,可联系本人,联系方式在代码中。
更新,数据集下载地址:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ZaQMPfXlD6CCgSWXxutSsA?pwd=jqu0
提取码:jqu0
只可用作学习交流,请勿转载,完善后的根据深度图加雾代码Python_Alocus的博客-CSDN博客