VIM使用(三)
Vim自动补全神器:YouCompleteMe
Ubuntu下,先通过Bundle安装插件:
Bundle 'Valloric/YouCompleteMe'
Bundle 'scrooloose/syntastic'
Bundle 'Valloric/ListToggle'
Bundle 'SirVer/ultisnips'
YouCompleteMe的特别之处
基于语义补全
总所周知,Vim是一款文本编辑器。也就是说,其最基础的工作就是编辑文本,而不管该文本的内容是什么。在Vim被程序员所使用后,其慢慢的被肩负了与IDE一样的工作,文本自动补全(ie.acp,omnicppcompleter),代码检查(Syntastic)等等工作。
针对文本自动补全这个功能来说,主要有两种实现方式。
- 基于文本
我们常用的omnicppcompleter,acp,vim自带的c-x, c-n的实现方式就是基于文本。更通俗的说法,其实就是一个字:
猜
其通过文本进行一些正则表达式的匹配,再根据生成的tags(利用ctags生成)来实现自动补全的效果。
- 基于语义
顾名思义,其是通过分析源文件,经过语法分析以后进行补全。由于对源文件进行分析,基于语义的补全可以做到很精确。但是这显然是vim所不可能支持的。而且经过这么多年发展,由于语法分析有很高的难度,也一直没有合适的工具出现。直到,由apple支持的clang/llvm横空出世。YouCompleteMe也正是在clang/llvm的基础上进行构建的。
整合实现了多种插件
- clang_complete
- AutoComplPop
- Supertab
- neocomplcache
- Syntastic(类似功能,仅仅针对c/c++/obj-c代码)
支持语言
- c
- c++
- obj-c
- c#
- python
对于其他的语言,会调用vim设置的omnifunc来匹配,因此同样支持php,ruby等语言。
已知的有 * javascript —-tern_for_vim * ruby/java —-eclim
使用感受
- 和IDE一样,自动补全,
- 根据
include的文件进行补全 - 不用再蹩脚的生成tags
- 补全非常精准,而且速度很快,不会有延迟(以前在大项目上,acp用起来实在是很卡)
- 支持类似tags的跳转,跳到定义处以及使用处
- 出错提示很智能,并且用起来真的是如丝般柔滑,不用输入
:w进行强制检测
编译:
等待vundle将YouCompleteMe安装完成
而后进行编译安装:
sudo apt-get install python-dev
cd ~/.vim/bundle/YouCompleteMe ./install --clang-completer
如果不需要c-family的补全,可以去掉--clang-completer。如果需要c#的补全,请加上--omnisharp-completer。
正常来说,YCM会去下载clang的包,如果已经有,也可以用系统--system-libclang。
就这样,安装结束。打开vim,如果没有提示YCM未编译,则说明安装已经成功了。
配置
不同于很多vim插件,YCM首先需要编译,另外还需要有配置。在vim启动后,YCM会找寻当前路径以及上层路径的.ycm_extra_conf.py.在~/.vim/bundle/YouCompleteMe/cpp/ycm/.ycm_extra_conf.py中提供了默认的模板。也可以参考我的(就在模板上改改而已)。不过这个解决了标准库提示找不到的问题。
一般来说,我会在~目录下放一个默认的模板,而后再根据不同的项目在当前目录下再拷贝个.ycm_extra_conf.py。
# This file is NOT licensed under the GPLv3, which is the license for the rest # of YouCompleteMe. # # Here's the license text for this file: # # This is free and unencumbered software released into the public domain. # # Anyone is free to copy, modify, publish, use, compile, sell, or # distribute this software, either in source code form or as a compiled # binary, for any purpose, commercial or non-commercial, and by any # means. # # In jurisdictions that recognize copyright laws, the author or authors # of this software dedicate any and all copyright interest in the # software to the public domain. We make this dedication for the benefit # of the public at large and to the detriment of our heirs and # successors. We intend this dedication to be an overt act of # relinquishment in perpetuity of all present and future rights to this # software under copyright law. # # THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, # EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF # MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. # IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR # OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, # ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR # OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE. # # For more information, please refer to <http://unlicense.org/> import os import ycm_core # These are the compilation flags that will be used in case there's no # compilation database set (by default, one is not set). # CHANGE THIS LIST OF FLAGS. YES, THIS IS THE DROID YOU HAVE BEEN LOOKING FOR. flags = [ '-Wall', '-Wextra', #'-Werror', #'-Wc++98-compat', '-Wno-long-long', '-Wno-variadic-macros', '-fexceptions', '-stdlib=libc++', # THIS IS IMPORTANT! Without a "-std=<something>" flag, clang won't know which # language to use when compiling headers. So it will guess. Badly. So C++ # headers will be compiled as C headers. You don't want that so ALWAYS specify # a "-std=<something>". # For a C project, you would set this to something like 'c99' instead of # 'c++11'. '-std=c++11', # ...and the same thing goes for the magic -x option which specifies the # language that the files to be compiled are written in. This is mostly # relevant for c++ headers. # For a C project, you would set this to 'c' instead of 'c++'. '-x', 'c++', '-I', '.', '-isystem', '/usr/include', '-isystem', '/usr/local/include', '-isystem', '/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/usr/include', '-isystem', '/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/usr/bin/../lib/c++/v1', ] # Set this to the absolute path to the folder (NOT the file!) containing the # compile_commands.json file to use that instead of 'flags'. See here for # more details: http://clang.llvm.org/docs/JSONCompilationDatabase.html # # Most projects will NOT need to set this to anything; you can just change the # 'flags' list of compilation flags. Notice that YCM itself uses that approach. compilation_database_folder = '' if os.path.exists( compilation_database_folder ): database = ycm_core.CompilationDatabase( compilation_database_folder ) else: database = None SOURCE_EXTENSIONS = [ '.cpp', '.cxx', '.cc', '.c', '.m', '.mm' ] def DirectoryOfThisScript(): return os.path.dirname( os.path.abspath( __file__ ) ) def MakeRelativePathsInFlagsAbsolute( flags, working_directory ): if not working_directory: return list( flags ) new_flags = [] make_next_absolute = False path_flags = [ '-isystem', '-I', '-iquote', '--sysroot=' ] for flag in flags: new_flag = flag if make_next_absolute: make_next_absolute = False if not flag.startswith( '/' ): new_flag = os.path.join( working_directory, flag ) for path_flag in path_flags: if flag == path_flag: make_next_absolute = True break if flag.startswith( path_flag ): path = flag[ len( path_flag ): ] new_flag = path_flag + os.path.join( working_directory, path ) break if new_flag: new_flags.append( new_flag ) return new_flags def IsHeaderFile( filename ): extension = os.path.splitext( filename )[ 1 ] return extension in [ '.h', '.hxx', '.hpp', '.hh' ] def GetCompilationInfoForFile( filename ): # The compilation_commands.json file generated by CMake does not have entries # for header files. So we do our best by asking the db for flags for a # corresponding source file, if any. If one exists, the flags for that file # should be good enough. if IsHeaderFile( filename ): basename = os.path.splitext( filename )[ 0 ] for extension in SOURCE_EXTENSIONS: replacement_file = basename + extension if os.path.exists( replacement_file ): compilation_info = database.GetCompilationInfoForFile( replacement_file ) if compilation_info.compiler_flags_: return compilation_info return None return database.GetCompilationInfoForFile( filename ) def FlagsForFile( filename, **kwargs ): if database: # Bear in mind that compilation_info.compiler_flags_ does NOT return a # python list, but a "list-like" StringVec object compilation_info = GetCompilationInfoForFile( filename ) if not compilation_info: return None final_flags = MakeRelativePathsInFlagsAbsolute( compilation_info.compiler_flags_, compilation_info.compiler_working_dir_ ) # NOTE: This is just for YouCompleteMe; it's highly likely that your project # does NOT need to remove the stdlib flag. DO NOT USE THIS IN YOUR # ycm_extra_conf IF YOU'RE NOT 100% SURE YOU NEED IT. #try: # final_flags.remove( '-stdlib=libc++' ) #except ValueError: # pass else: relative_to = DirectoryOfThisScript() final_flags = MakeRelativePathsInFlagsAbsolute( flags, relative_to ) return { 'flags': final_flags, 'do_cache': True }
YouCompleteMe提供的其他功能
YCM除了提供了基本的补全功能,自动提示错误的功能外,还提供了类似tags的功能:
- 跳转到定义
GoToDefinition - 跳转到声明
GoToDeclaration - 以及两者的合体
GoToDefinitionElseDeclaration
可以在.vimrc中配置相应的快捷键。
|
1
2
3
|
nnoremap <leader>gl :YcmCompleter GoToDeclaration<CR>
nnoremap <leader>gf :YcmCompleter GoToDefinition<CR>
nnoremap <leader>gg :YcmCompleter GoToDefinitionElseDeclaration<CR>
|
另外,YCM也提供了丰富的配置选项,同样在.vimrc中配置。具体请参考
|
1
2
|
let
g:ycm_error_symbol =
'>>'
let
g:ycm_warning_symbol =
'>*'
|
同时,YCM可以打开location-list来显示警告和错误的信息:YcmDiags。个人关于ycm的配置如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
"
for
ycm
let
g:ycm_error_symbol =
'>>'
let
g:ycm_warning_symbol =
'>*'
nnoremap <leader>gl :YcmCompleter GoToDeclaration<CR>
nnoremap <leader>gf :YcmCompleter GoToDefinition<CR>
nnoremap <leader>gg :YcmCompleter GoToDefinitionElseDeclaration<CR>
nmap <F4> :YcmDiags<CR>
|
YCM提供的跳跃功能采用了vim的jumplist,往前跳和往后跳的快捷键为Ctrl+O以及Ctrl+I。
UltiSnips简介:
详细参考:http://mednoter.com/UltiSnips.html
UltiSnips 只是个引擎,需要搭配预设的代码块才能运转起来,以下是我创建的几个常用代码块。
代码块集合 honza/vim-snippets 通过Bundle安装:
Bundle 'honza/vim-snippets'
如果想自己创建代码块,也参考:http://mednoter.com/UltiSnips.html的内容.
这个插件很简单,给你看我的设置好了:
NeoBundle 'SirVer/ultisnips' let g:UltiSnipsSnippetDirectories=['UltiSnips'] let g:UltiSnipsSnippetsDir = '~/.vim/UltiSnips' let g:UltiSnipsExpandTrigger = '<Tab>' let g:UltiSnipsListSnippets = '<C-Tab>' let g:UltiSnipsJumpForwardTrigger = '<Tab>' let g:UltiSnipsJumpBackwardTrigger = '<S-Tab>'
哦,对了,我想起来一件事情。g:UltiSnipsSnippetDirectories 选项的值必须是文件夹名称(可以是多个),并且这个(些)文件夹必须存在于 runtimepath 中的某一项之下。比如说 ~/.vim 就是 runtimepath 中的一项。默认的文件夹 UltiSnips 会自动创建,如果你换了,那你必须保证这个文件夹是存在的。我看你换成了 snippets,如果你事先安装过 SnipMate,那么 snippets 才会存在,否则你得自行创建。g:UltiSnipsSnippetDirectories 选项的作用是指定 UltiSnips 的搜索路径,你找不到 snippets 的原因大概就是这样。
解释为什么错了真的很累,换个角度告诉你,如果你做对了是什么样子的:
-
let g:UltiSnipsSnippetsDir = '~/.vim/UltiSnips'这个设置会确保 snippets 都在指定的文件夹内(你自己编辑的也会保存在这里,如果你用了第三方的并且还要进一步编辑,你得确保都复制到了这里)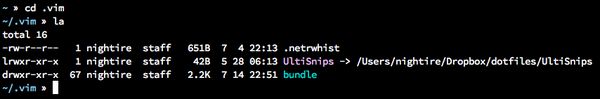
-
let g:UltiSnipsSnippetDirectories = ['UltiSnips']这个设置会告诉 UltiSnips 去哪儿找 snippets,可以是多个地方,所以如果你用第三方的 snippets,和上一个设置不在一起的话,你得把它们的路径放这里。要注意的是,这个数组里的每一项都必须在runtimepath其中的一项之下,所以不确定的话,先看看runtimepath的值。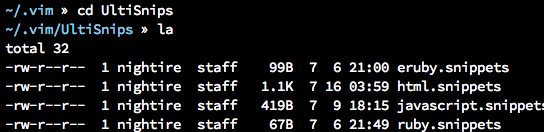
-
若上述两点都做对了,那么在任意类型文件打开的前提下输入
:UltiSnipsEdit都会打开对应类型的 snippets,能不能用,哪些能用,一看便知。
注:代码片段的扩展引用
-
比如在 cpp.snippets 文件的第一行增加一句 extends c ,在打开一个cpp 文件时,会首先查找搜索路径内的所有 c.snippets 文件,所以可以很容易复用已有的代码片段文件。
相关的配置内容:
"""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""' " " YouCompleteMe 设置 " """"""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""" let g:ycm_global_ycm_extra_conf = '~/.vim/.ycm_extra_conf.py' let g:ycm_confirm_extra_conf = 0 let g:ycm_collect_identifiers_from_tags_files = 1 "settags+=./.tags nnoremap <leader>gl :YcmCompleter GoToDeclaration<CR> nnoremap <leader>gf :YcmCompleter GoToDefinition<CR> nnoremap <leader>gg :YcmCompleter GoToDefinitionElseDeclaration<CR> let g:ycm_key_list_select_completion = [ ' <c-n> ', ' <Down> '] let g:ycm_key_list_previous_completion = ['<c-p>', '<Up>'] "设置error和warning的提示符,如果没有设置,ycm会以syntastic的 " g:syntastic_warning_symbol 和 g:syntastic_error_symbol 这两个为准 let g:ycm_error_symbol='>>' let g:ycm_warning_symbol='>*' let g:ycm_complete_in_comments = 1 "在注释输入中也能补全 let g:ycm_complete_in_strings = 1 "在字符串输入中也能补全 "每次重新生成匹配项,禁止缓存匹配项 let g:ycm_cache_omnifunc=0 "不查询ultisnips提供的代码模板补全,如果需要,设置成1即可 let g:ycm_use_ultisnips_completer=1 let g:ycm_seed_identifiers_with_syntax=1 "语言关键字补全, 不过python关键字都很短,所以,需要的自己打开 " 直接触发自动补全 " 修改对C函数的补全快捷键,默认是CTRL + space,修改为ALT + ; let g:ycm_key_invoke_completion = '<M-c>' nnoremap <F5> :YcmForceCompileAndDiagnostics<CR> set completeopt=menuone,longest set pumheight=15 " 黑名单,不启用 let g:ycm_filetype_blacklist = { \ 'tagbar' : 1, \ 'gitcommit' : 1, \} """""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""' " " UltiSnips 设置 " ultisnips内置了很多代码片段,并且支持自定义。 " """"""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""" " Snippets are separated from the engine. Add this if you want them: "Plugin 'honza/vim-snippets' " Trigger configuration. Do not use <tab> if you use https://github.com/Valloric/YouCompleteMe. let g:UltiSnipsExpandTrigger="<tab>" let g:UltiSnipsJumpForwardTrigger="<c-b>" let g:UltiSnipsJumpBackwardTrigger="<c-z>" " If you want :UltiSnipsEdit to split your window. "let g:UltiSnipsEditSplit="vertical" """""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""' " " syntastic 设置 用于语法检查 " syntastic 与 YouComleteMe 结合对语法 进行检查,并将警告和错误信息显示在行号那一栏的左侧。添加下面的命令安装 syntastic: " """"""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""" let g:syntastic_error_symbol='✗' let g:syntastic_warning_symbol='⚠' let g:syntastic_enable_highlighting = 1 let g:syntastic_stl_format = '[%E{Err: %fe #%e}%B{, }%W{Warn: %fw #%w}]'