论文代码复现-深度补全算法
论文代码复现-深度补全算法
注:如果你有论文复现的需求可在文末留言
论文名称:A new method for inpainting of depth maps from time-of-flight sensors based on a modified closing by reconstruction algorithm
该文章采用传统的图像处理方法对深度图中缺失的区域进行补全
算法流程
首先是输入一张深度图,然后判断深度图中的缺失噪声点数据,如果存在噪声点将执行改进后的算法2,并根据指定的传播条件对缺失区域的进行填充。

可执行代码链接 https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_43627520/84278465
该算法流程图的运行代码
# 论文主函数
def MCrB_main(self):
lmd = 1
# 执行一次闭运算
self.g1 = cv2.morphologyEx(self.depth.copy(), cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, self.kernel,iterations=lmd)
# 判断噪声数
while len(self.g1[~(self.g1>0.)])>0:
print("size",len(self.g1[~(self.g1>0.1)]))
# 执行一次膨胀运算
self.depth_d = cv2.dilate(self.depth.copy(),self.kernel,iterations=lmd)
# 调用R_Close
self.g2 = self.R_Close2(self.depth.copy(),self.depth_d,iterations=lmd)
# 调用比较g_comparator
self.g1 = self.g_comparator(self.g1,self.g2)
lmd +=1
print(lmd)
self.depth[~self.n] = self.g1[~self.n]
# self.res = cv2.normalize(self.g1.copy(),None,0,255,cv2.NORM_MINMAX)
# self.depth = cv2.normalize(self.depth.copy(),None,0,255,cv2.NORM_MINMAX)
return self.g1,self.depth
关于该文中太多的原理就不做介绍,直接开始论文中核心算法的复现工作。
算法1:顺序对偶重构算法,该方法是引用了其他论文中的算法框架。

该算法主要使用8个领域点对P点进行处理
对算法1的改进后得到算法2
算法2函数的框架代码如下
1、在这个地方我写了三个函数,分别是 _Close()、R_Close、R_Close2;
2、_Close():用于对写的重构形态学闭合函数进行验证,判断算法过程是否正确;
3、R_Close、R_Close2作为方法中调用的子类函数,其中对R_Close进行了稍微的调整;论文中的原方法是R_Close2函数中的内容。
# 论文改进的重构形态学闭运算
# R*(f,g)
def _Close(self,f,J,iterations=1):
for i in range(iterations):
aux = J.copy()
flag = True
while flag:
J_ = np.pad(J.copy(), (1, 1), mode='edge')
for i in range(1, f.shape[0]+1):
for j in range(1, f.shape[1]+1):
Jp = [J_[i - 1, j - 1], J_[i - 1, j], J_[i - 1, j + 1], J_[i, j - 1], J_[i, j]]
# J[i,j] = max(depth[i,j],aux)
J[i - 1, j - 1] = max(min(Jp), f[i - 1, j - 1])
J_ = np.pad(J.copy(), (1, 1), mode='edge')
for i in range(1, f.shape[0] + 1):
for j in range(1, f.shape[1] + 1):
Jp = [J_[i, j], J_[i, j + 1], J_[i + 1, j - 1], J_[i + 1, j], J_[i + 1, j + 1]]
# J[i, j] = max(depth[i, j], aux)
J[i - 1, j - 1] = max(min(Jp), f[i - 1, j - 1])
diff = J - aux
if np.max(diff) == 0 or 255:
flag = False
return J
def R_Close(self,f,J,iterations=1):
for i in range(iterations):
aux = J.copy()
flag = True
while flag:
J_ = np.pad(J.copy(), (1, 1), mode='edge')
for i in range(1,f.shape[0]+1):
for j in range(1,f.shape[1]+1):
Jp = [J_[i - 1, j - 1], J_[i - 1, j], J_[i - 1, j + 1], J_[i, j - 1], J_[i, j]]
# aux = min(Jp)
J[i-1, j-1] = self.K(min(Jp),f[i-1,j-1])
J_ = np.pad(J.copy(), (1, 1), mode='edge')
for i in range(1,f.shape[0]+1):
for j in range(1,f.shape[1]+1):
Jp = [J_[i, j], J_[i, j + 1], J_[i + 1, j - 1], J_[i + 1, j], J_[i + 1, j + 1]]
J[i-1, j-1] = self.K(min(Jp), f[i-1, j-1])
diff = J-aux
if np.max(diff)==0 or 255:
flag = False
return J
def R_Close2(self,f,J,iterations=1):
for i in range(iterations):
aux = J.copy()
flag = True
while flag:
J_ = np.pad(J.copy(), (1, 1), mode='edge')
for i in range(f.shape[0]):
for j in range(f.shape[1]):
Jp = [J_[i, j], J_[i, j+1], J_[i, j+2], J_[i+1, j], J_[i+1, j+1]]
aux = min(Jp)
J[i, j] = self.K(min(Jp),f[i,j])
J_ = np.pad(J.copy(), (1, 1), mode='edge')
for i in range(f.shape[0]):
for j in range(f.shape[1]):
Jp = [J_[i+1, j+1], J_[i+1, j + 2], J_[i+2, j ], J_[i+2, j+1], J_[i + 2, j + 2]]
aux = min(Jp)
J[i, j] = self.K(min(Jp), f[i, j])
diff = J-aux
if np.max(diff)==0 or 255:
flag = False
return J
用例测试
文中中对该算法的验证给出了一个测试用例,我也用该用例对_Close()函数进行验证,验证程序如下,其中我们计算的结果与文中给出的用例结果一致,表明本文复现的重构形态学闭运算代码是正确的。

测试代码:
T = np.array([
[9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9],
[9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 9],
[9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 7, 0, 0, 0, 7, 9],
[9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 7, 0, 5, 0, 7, 9],
[9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 7, 0, 0, 0, 7, 9],
[9, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 9],
[9, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9],
[9, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9],
[9, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9],
[9, 7, 0, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 7, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9],
[9, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9],
[9, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9],
[9, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9],
[9, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9],
[9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9],
],dtype=np.float32)
def test_paper(Mcbr):
KERNEL_3 = np.ones((3, 3))
# 原始变化
Mcbr = Mcbr(T.copy())
b = cv2.dilate(T.copy(),KERNEL_3,iterations=1)
print("b\n",b)
c = Mcbr._Close(T.copy(),b)
print("c\n",c)
d = cv2.dilate(T.copy(),KERNEL_3,iterations=2)
print("d\n",d)
e = Mcbr._Close(T.copy(),d,iterations=2)
print("e\n",e)
# 论文方法
f = cv2.dilate(T.copy(),KERNEL_3,iterations=1)
print("f\n",f)
g = Mcbr.R_Close(T.copy(),f)
print("g\n",g)
h = cv2.dilate(g.copy(),KERNEL_3,iterations=2)
print("h\n",h)
i = Mcbr.R_Close(T.copy(),h,iterations=2)
print("i\n",i)
g[~(g>0)] = i[~(g>0)]
print("j\n",g)
print(Mcbr.MCrB_main())
算法3 定义的传播条件
# 定义传播条件 conditional propagation k
def K(self,aux,Ip):
list = [Ip,aux]
propagated = 0
for x in list:
if x>propagated and propagated<255:
propagated = x
return propagated
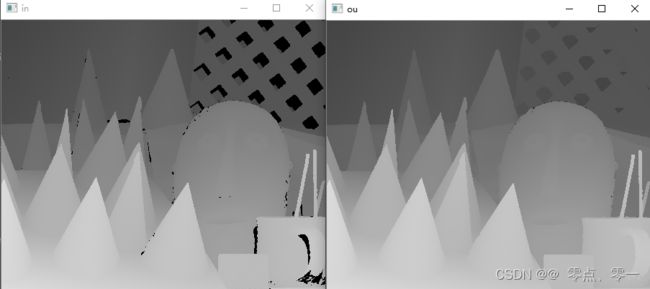
算法4 对比功能
def g_comparator(self,g1,g2):
non_1 = (self.g1 > 0)
self.g1[~non_1] = g1[~non_1]
non_2 = (self.g1 > 0)
self.g1[~non_2] = g2[~non_2]
return self.g1
测试结果
对于其他测试图像,我们修复的结果与文中的结果一致。
错误1:测试了原文中所使用的图像后,却得不到与原文中相同的结果,只对缺陷中前半部分数据进行了修复。
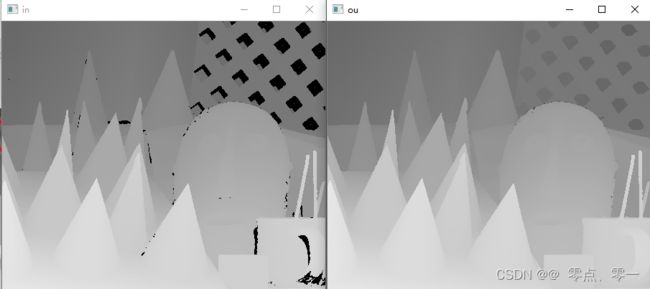
随后我们对输入图像进行调整;此时可以得到与论文中相同相近似的结果。
如果您找到出现该现象的原因,非常欢迎您来指正,在此感谢!
结论:该方法可以对深度图中缺失的区域进行有效的补全,但缺陷就是速度太慢。
可执行代码链接 https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_43627520/84278465
参考文献
【1】Garduño-Ramón M A, Terol-Villalobos I R, Osornio-Rios R A, et al. A new method for inpainting of depth maps from time-of-flight sensors based on a modified closing by reconstruction algorithm[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2017, 47: 36-47.