一种对抗性攻击的方法AdvDrop
AdvDrop: Adversarial Attack to DNNs by Dropping Information论文解读
代码参考:https://github.com/RjDuan/AdvDrop
提出了一种新的对抗性的攻击,名为AdvDrop,它通过丢弃现有的图像信息来制作对抗性的例子。
步骤:

数学表达:
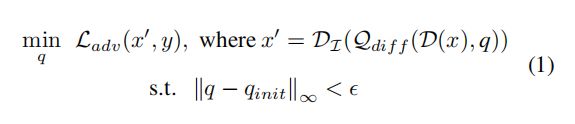
D()为DCT函数,Qdiff()为量化函数,Di()为DCT的逆函数。
步骤一
构建block,将图片分为NxN的形式,减少计算成本:
def block_splitting(image, block_size = 8):
k = block_size
height, width = image.shape[1:3]
desired_height = int(np.ceil(height/k) * k)
batch_size = image.shape[0]
desired_img = torch.zeros(batch_size, desired_height, desired_height)
desired_img[:,:height, :width] = image
image_reshaped = desired_img.view(batch_size, desired_height // k, k, -1, k)
image_transposed = image_reshaped.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4)
return image_transposed.contiguous().view(batch_size, -1, k, k)
步骤二:
DCT,将图片由空间域转换为频域,以便量化过程drop information:
def dct_8x8_ref(image):
image = image - 128
result = np.zeros((8, 8), dtype=np.float32)
for u, v in itertools.product(range(8), range(8)):
value = 0
for x, y in itertools.product(range(8), range(8)):
value += image[x, y] * np.cos((2 * x + 1) * u *
np.pi / 16) * np.cos((2 * y + 1) * v * np.pi / 16)
result[u, v] = value
alpha = np.array([1. / np.sqrt(2)] + [1] * 7)
scale = np.outer(alpha, alpha) * 0.25
return result * scale
步骤三
Quantization,对图片信息进行drop information,使用一个可训练的量化表q来对输入图像在转换为频域后的x进行量化:
def phi_diff(x, alpha):
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
x = x.to(device)
alpha = torch.where(alpha >= 2.0, torch.tensor([2.0]).cuda(), alpha)
s = 1/(1-alpha).to(device)
k = torch.log(2/alpha -1).to(device)
phi_x = torch.tanh((x - (torch.floor(x) + 0.5)) * k) * s
x_ = (phi_x + 1)/2 + torch.floor(x)
return x_
self.q_tables[k] = self.q_tables[k].detach() - torch.sign(self.q_tables[k].grad)
步骤四
IDCT ,将图片转换为空间域:
DCT的逆运算
def idct_8x8(image):
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
alpha = np.array([1. / np.sqrt(2)] + [1] * 7)
# alpha = np.outer(alpha, alpha)
alpha = nn.Parameter(torch.from_numpy(np.outer(alpha, alpha)).float()).to(device)
image = image.to(device)
image = image * alpha
tensor = np.zeros((8, 8, 8, 8), dtype=np.float32)
for x, y, u, v in itertools.product(range(8), repeat=4):
tensor[x, y, u, v] = np.cos((2 * u + 1) * x * np.pi / 16) * np.cos(
(2 * v + 1) * y * np.pi / 16)
tensor = nn.Parameter(torch.from_numpy(tensor).float()).to(device)
result = 0.25 * torch.tensordot(image, tensor, dims=2) + 128
result.view(image.shape)
return result
损失函数:




