xavier初始化_PyTorch 8.权值初始化与损失函数
权值初始化
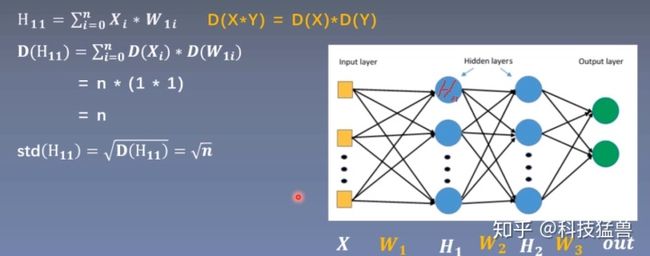
先做一个梯度爆炸与消失的实验吧:定义一个nn.Module的类。
import os
import torch
import random
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
from tools.common_tools import set_seed
set_seed(1) # 设置随机种子
class MLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, neural_num, layers):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
self.linears = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(neural_num, neural_num, bias=False) for i in range(layers)])
self.neural_num = neural_num
def forward(self, x):
for (i, linear) in enumerate(self.linears):
x = linear(x)
x = torch.relu(x)
print("layer:{}, std:{}".format(i, x.std()))
if torch.isnan(x.std()):
print("output is nan in {} layers".format(i))
break
return x
def initialize(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
# nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, std=np.sqrt(1/self.neural_num)) # normal: mean=0, std=1
# a = np.sqrt(6 / (self.neural_num + self.neural_num))
#
# tanh_gain = nn.init.calculate_gain('tanh')
# a *= tanh_gain
#
# nn.init.uniform_(m.weight.data, -a, a)
# nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight.data, gain=tanh_gain)
# nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, std=np.sqrt(2 / self.neural_num))
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight.data)flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
layer_nums = 100
neural_nums = 256
batch_size = 16
net = MLP(neural_nums, layer_nums)
net.initialize()
inputs = torch.randn((batch_size, neural_nums)) # normal: mean=0, std=1
output = net(inputs)
print(output)可能会出现梯度消失或爆炸的情况:
若随机变量
这个图是什么意思呢?
假设里面第1层的所有变量都互为独立,均值为0,方差为1,我们发现变量
看看上面的结果图,也印证了这一点。
所以,为了解决这个问题,权值的标准差必须为
这次结果就没啥问题:
但是如果加一个tanh的激活函数就不行了,会带来梯度消失的问题:
为了解决有激活函数时的问题:
def initialize(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
# nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data)
# nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, std=np.sqrt(1/self.neural_num)) # normal: mean=0, std=1
a = np.sqrt(6 / (self.neural_num + self.neural_num))
#
tanh_gain = nn.init.calculate_gain('tanh')
a *= tanh_gain
#
nn.init.uniform_(m.weight.data, -a, a)结果如下:
也可以直接使用PyTorch提供的:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight.data, gain=tanh_gain)但是使用了ReLU激活函数以后,传统的Xavier初始化方法又不适用了。
nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, std=np.sqrt(2 / self.neural_num))
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight.data)x = torch.randn(10000)
out = torch.tanh(x)
gain = x.std() / out.std()
print('gain:{}'.format(gain))
tanh_gain = nn.init.calculate_gain('tanh')
print('tanh_gain in PyTorch:', tanh_gain)
#Results = 1.60均值,1方差的输入经过tanh,标准差会减小1.6倍左右,所以我们在自己实现Xavier时,a要乘上这个值。
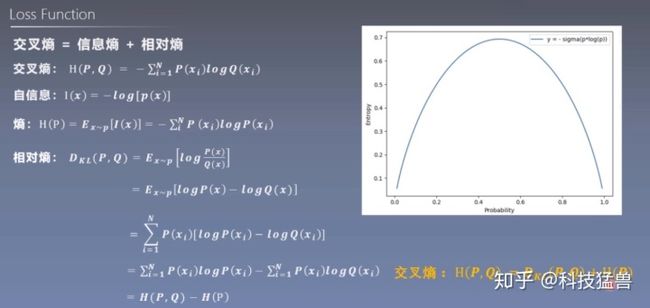
损失函数
# fake data
inputs = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [1, 3], [1, 3]], dtype=torch.float)
target = torch.tensor([0, 1, 1], dtype=torch.long)
# ----------------------------------- CrossEntropy loss: reduction -----------------------------------
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
# def loss function
loss_f_none = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, reduction='none')
loss_f_sum = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, reduction='sum')
loss_f_mean = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, reduction='mean')
# forward
loss_none = loss_f_none(inputs, target)
loss_sum = loss_f_sum(inputs, target)
loss_mean = loss_f_mean(inputs, target)
# view
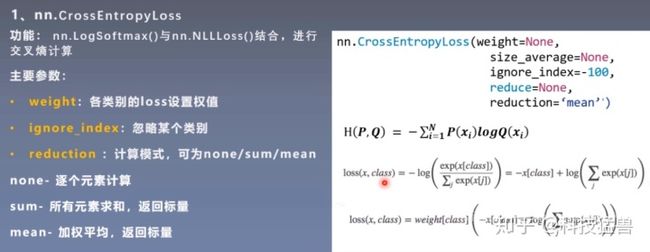
print("Cross Entropy Loss:n ", loss_none, loss_sum, loss_mean)输出信息:
Cross Entropy Loss:
tensor([1.3133, 0.1269, 0.1269]) tensor(1.5671) tensor(0.5224)BCELoss 是CrossEntropyLoss的一个特例,只用于二分类问题,而CrossEntropyLoss可以用于二分类,也可以用于多分类。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
# fake data
inputs = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [1, 3], [1, 3]], dtype=torch.float)
target = torch.tensor([0, 1, 1], dtype=torch.long)
# ----------------------------------- CrossEntropy loss: reduction -----------------------------------
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
# def loss function
loss_f_none = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, reduction='none')
loss_f_sum = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, reduction='sum')
loss_f_mean = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, reduction='mean')
# forward
loss_none = loss_f_none(inputs, target)
loss_sum = loss_f_sum(inputs, target)
loss_mean = loss_f_mean(inputs, target)
# view
print("Cross Entropy Loss:n ", loss_none, loss_sum, loss_mean)
# --------------------------------- compute by hand
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
idx = 0
input_1 = inputs.detach().numpy()[idx] # [1, 2]
target_1 = target.numpy()[idx] # [0]
# 第一项
x_class = input_1[target_1]
# 第二项
sigma_exp_x = np.sum(list(map(np.exp, input_1)))
log_sigma_exp_x = np.log(sigma_exp_x)
# 输出loss
loss_1 = -x_class + log_sigma_exp_x
print("第一个样本loss为: ", loss_1)
# ----------------------------------- weight -----------------------------------
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
# def loss function
weights = torch.tensor([1, 2], dtype=torch.float)
# weights = torch.tensor([0.7, 0.3], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f_none_w = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=weights, reduction='none')
loss_f_sum = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=weights, reduction='sum')
loss_f_mean = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=weights, reduction='mean')
# forward
loss_none_w = loss_f_none_w(inputs, target)
loss_sum = loss_f_sum(inputs, target)
loss_mean = loss_f_mean(inputs, target)
# view
print("nweights: ", weights)
print(loss_none_w, loss_sum, loss_mean)
# --------------------------------- compute by hand
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
weights = torch.tensor([1, 2], dtype=torch.float)
weights_all = np.sum(list(map(lambda x: weights.numpy()[x], target.numpy()))) # [0, 1, 1] # [1 2 2]
mean = 0
loss_sep = loss_none.detach().numpy()
for i in range(target.shape[0]):
x_class = target.numpy()[i]
tmp = loss_sep[i] * (weights.numpy()[x_class] / weights_all)
mean += tmp
print(mean)
# ----------------------------------- 2 NLLLoss -----------------------------------
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
weights = torch.tensor([1, 1], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f_none_w = nn.NLLLoss(weight=weights, reduction='none')
loss_f_sum = nn.NLLLoss(weight=weights, reduction='sum')
loss_f_mean = nn.NLLLoss(weight=weights, reduction='mean')
# forward
loss_none_w = loss_f_none_w(inputs, target)
loss_sum = loss_f_sum(inputs, target)
loss_mean = loss_f_mean(inputs, target)
# view
print("nweights: ", weights)
print("NLL Loss", loss_none_w, loss_sum, loss_mean)
# ----------------------------------- 3 BCE Loss -----------------------------------
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
inputs = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [2, 2], [3, 4], [4, 5]], dtype=torch.float)
target = torch.tensor([[1, 0], [1, 0], [0, 1], [0, 1]], dtype=torch.float)
target_bce = target
# itarget
inputs = torch.sigmoid(inputs)
weights = torch.tensor([1, 1], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f_none_w = nn.BCELoss(weight=weights, reduction='none')
loss_f_sum = nn.BCELoss(weight=weights, reduction='sum')
loss_f_mean = nn.BCELoss(weight=weights, reduction='mean')
# forward
loss_none_w = loss_f_none_w(inputs, target_bce)
loss_sum = loss_f_sum(inputs, target_bce)
loss_mean = loss_f_mean(inputs, target_bce)
# view
print("nweights: ", weights)
print("BCE Loss", loss_none_w, loss_sum, loss_mean)
# --------------------------------- compute by hand
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
idx = 0
x_i = inputs.detach().numpy()[idx, idx]
y_i = target.numpy()[idx, idx] #
# loss
# l_i = -[ y_i * np.log(x_i) + (1-y_i) * np.log(1-y_i) ] # np.log(0) = nan
l_i = -y_i * np.log(x_i) if y_i else -(1-y_i) * np.log(1-x_i)
# 输出loss
print("BCE inputs: ", inputs)
print("the first loss is: ", l_i)
# ----------------------------------- 4 BCE with Logis Loss -----------------------------------
# flag = 1
flag = 1
if flag:
inputs = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [2, 2], [3, 4], [4, 5]], dtype=torch.float)
target = torch.tensor([[1, 0], [1, 0], [0, 1], [0, 1]], dtype=torch.float)
target_bce = target
# inputs = torch.sigmoid(inputs)
weights = torch.tensor([1, 2], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f_none_w = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=weights, reduction='none')
loss_f_sum = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=weights, reduction='sum')
loss_f_mean = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=weights, reduction='mean')
# forward
loss_none_w = loss_f_none_w(inputs, target_bce)
loss_sum = loss_f_sum(inputs, target_bce)
loss_mean = loss_f_mean(inputs, target_bce)
# view
print("nweights: ", weights)
print(loss_none_w, loss_sum, loss_mean)
# --------------------------------- pos weight
# flag = 0
flag = 0
if flag:
inputs = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [2, 2], [3, 4], [4, 5]], dtype=torch.float)
target = torch.tensor([[1, 0], [1, 0], [0, 1], [0, 1]], dtype=torch.float)
target_bce = target
# itarget
# inputs = torch.sigmoid(inputs)
weights = torch.tensor([1], dtype=torch.float)
pos_w = torch.tensor([3], dtype=torch.float) # 3
loss_f_none_w = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=weights, reduction='none', pos_weight=pos_w)
loss_f_sum = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=weights, reduction='sum', pos_weight=pos_w)
loss_f_mean = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=weights, reduction='mean', pos_weight=pos_w)
# forward
loss_none_w = loss_f_none_w(inputs, target_bce)
loss_sum = loss_f_sum(inputs, target_bce)
loss_mean = loss_f_mean(inputs, target_bce)
# view
print("npos_weights: ", pos_w)
print(loss_none_w, loss_sum, loss_mean)flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
inputs = torch.ones((2, 2))
target = torch.ones((2, 2)) * 3
loss_f = nn.L1Loss(reduction='none')
loss = loss_f(inputs, target)
print("input:{}ntarget:{}nL1 loss:{}".format(inputs, target, loss))
# ------------------------------------------------- 6 MSE loss ----------------------------------------------
loss_f_mse = nn.MSELoss(reduction='none')
loss_mse = loss_f_mse(inputs, target)
print("MSE loss:{}".format(loss_mse))输出为:
input:tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]])
target:tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]])
L1 loss:tensor([[2., 2.],
[2., 2.]])
MSE loss:tensor([[4., 4.],
[4., 4.]])
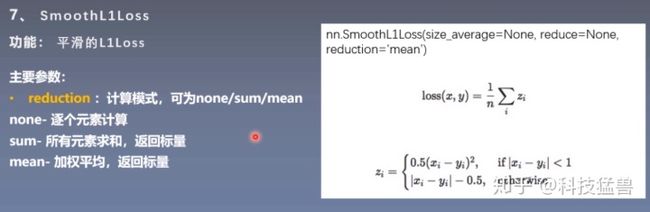
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
inputs = torch.linspace(-3, 3, steps=500)
target = torch.zeros_like(inputs)
loss_f = nn.SmoothL1Loss(reduction='none')
loss_smooth = loss_f(inputs, target)
loss_l1 = np.abs(inputs.numpy())
plt.plot(inputs.numpy(), loss_smooth.numpy(), label='Smooth L1 Loss')
plt.plot(inputs.numpy(), loss_l1, label='L1 loss')
plt.xlabel('x_i - y_i')
plt.ylabel('loss value')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
inputs = torch.randn((2, 2))
target = torch.randn((2, 2))
loss_f = nn.PoissonNLLLoss(log_input=True, full=False, reduction='none')
loss = loss_f(inputs, target)
print("input:{}ntarget:{}nPoisson NLL loss:{}".format(inputs, target, loss))
# --------------------------------- compute by hand
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
idx = 0
loss_1 = torch.exp(inputs[idx, idx]) - target[idx, idx]*inputs[idx, idx]
print("the first loss:", loss_1)就是因为nn.KLDivLoss函数的缺陷,你在使用之前要先把输入通过nn.logsoftmax来计算一个log值,因为nn.KLDivLoss函数本身不会计算这个。
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
inputs = torch.tensor([[0.5, 0.3, 0.2], [0.2, 0.3, 0.5]])
inputs_log = torch.log(inputs)
target = torch.tensor([[0.9, 0.05, 0.05], [0.1, 0.7, 0.2]], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f_none = nn.KLDivLoss(reduction='none')
loss_f_mean = nn.KLDivLoss(reduction='mean')
loss_f_bs_mean = nn.KLDivLoss(reduction='batchmean')
loss_none = loss_f_none(inputs, target)
loss_mean = loss_f_mean(inputs, target)
loss_bs_mean = loss_f_bs_mean(inputs, target)
print("loss_none:n{}nloss_mean:n{}nloss_bs_mean:n{}".format(loss_none, loss_mean, loss_bs_mean))
# --------------------------------- compute by hand
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
idx = 0
loss_1 = target[idx, idx] * (torch.log(target[idx, idx]) - inputs[idx, idx])
print("第一个元素loss:", loss_1)flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
x1 = torch.tensor([[1], [2], [3]], dtype=torch.float)
x2 = torch.tensor([[2], [2], [2]], dtype=torch.float)
target = torch.tensor([1, 1, -1], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f_none = nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=0, reduction='none')
loss = loss_f_none(x1, x2, target)
print(loss)flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
x = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8]])
y = torch.tensor([[0, 3, -1, -1]], dtype=torch.long)
loss_f = nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss(reduction='none')
loss = loss_f(x, y)
print(loss)
# --------------------------------- compute by hand
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
x = x[0]
item_1 = (1-(x[0] - x[1])) + (1 - (x[0] - x[2])) # [0]
item_2 = (1-(x[3] - x[1])) + (1 - (x[3] - x[2])) # [3]
loss_h = (item_1 + item_2) / x.shape[0]
print(loss_h)让第0类和第3类比其他2类的预测值至少大1以上。
注意:y = torch.tensor([[0, 3, -1, -1]], dtype=torch.long)表示第0和第3类为1,其他-1为占位符。
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
inputs = torch.tensor([[0.3, 0.7], [0.5, 0.5]])
target = torch.tensor([[-1, 1], [1, -1]], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f = nn.SoftMarginLoss(reduction='none')
loss = loss_f(inputs, target)
print("SoftMargin: ", loss)
# --------------------------------- compute by hand
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
idx = 0
inputs_i = inputs[idx, idx]
target_i = target[idx, idx]
loss_h = np.log(1 + np.exp(-target_i * inputs_i))
print(loss_h)flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
inputs = torch.tensor([[0.3, 0.7, 0.8]])
target = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 1]], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f = nn.MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss(reduction='none')
loss = loss_f(inputs, target)
print("MultiLabel SoftMargin: ", loss)
# --------------------------------- compute by hand
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
i_0 = torch.log(torch.exp(-inputs[0, 0]) / (1 + torch.exp(-inputs[0, 0])))
i_1 = torch.log(1 / (1 + torch.exp(-inputs[0, 1])))
i_2 = torch.log(1 / (1 + torch.exp(-inputs[0, 2])))
loss_h = (i_0 + i_1 + i_2) / -3
print(loss_h)下面举个例子:
假设有2个样本,标签分别是1和2,预测的概率分别是[0.1, 0.2, 0.7], [0.2, 0.5, 0.3]。
x[y]=x[1]=0.2
margin - (x[1] - x[0])=0.9
margin - (x[1] - x[2])=1.5
希望x[1]尽量大。
loss=(0.9+1.5)/3=0.8
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
x = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.2, 0.7], [0.2, 0.5, 0.3]])
y = torch.tensor([1, 2], dtype=torch.long)
loss_f = nn.MultiMarginLoss(reduction='none')
loss = loss_f(x, y)
print("Multi Margin Loss: ", loss)
# --------------------------------- compute by hand
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
x = x[0]
margin = 1
i_0 = margin - (x[1] - x[0])
# i_1 = margin - (x[1] - x[1])
i_2 = margin - (x[1] - x[2])
loss_h = (i_0 + i_2) / x.shape[0]
print(loss_h)这个意思是:想让Anchor与Positive之间的距离
只有Anchor与Positive之间的距离比Anchor与Negative之间的距离小margin以上时,才不会产生损失。
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
anchor = torch.tensor([[1.]])
pos = torch.tensor([[2.]])
neg = torch.tensor([[0.5]])
loss_f = nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.0, p=1)
loss = loss_f(anchor, pos, neg)
print("Triplet Margin Loss", loss)
# --------------------------------- compute by hand
flag = 1
# flag = 1
if flag:
margin = 1
a, p, n = anchor[0], pos[0], neg[0]
d_ap = torch.abs(a-p)
d_an = torch.abs(a-n)
loss = d_ap - d_an + margin
print(loss)flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
inputs = torch.tensor([[1., 0.8, 0.5]])
target = torch.tensor([[1, 1, -1]])
loss_f = nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(margin=1, reduction='none')
loss = loss_f(inputs, target)
print("Hinge Embedding Loss", loss)
# --------------------------------- compute by hand
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
margin = 1.
loss = max(0, margin - inputs.numpy()[0, 2])
print(loss)flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
x1 = torch.tensor([[0.3, 0.5, 0.7], [0.3, 0.5, 0.7]])
x2 = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.3, 0.5], [0.1, 0.3, 0.5]])
target = torch.tensor([[1, -1]], dtype=torch.float)
loss_f = nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss(margin=0., reduction='none')
loss = loss_f(x1, x2, target)
print("Cosine Embedding Loss", loss)
# --------------------------------- compute by hand
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag:
margin = 0.
def cosine(a, b):
numerator = torch.dot(a, b)
denominator = torch.norm(a, 2) * torch.norm(b, 2)
return float(numerator/denominator)
l_1 = 1 - (cosine(x1[0], x2[0]))
l_2 = max(0, cosine(x1[0], x2[0]))
print(l_1, l_2)输出为:
Cosine Embedding Loss tensor([[0.0167, 0.9833]])
0.016662120819091797 0.9833378791809082