sql语句case when常用查询总结
一、case when 语句语法逻辑
case when 是mySQL里面的控制流语句,和if…then…的分支判断逻辑很相似。
case when语句有两种:
(1)简单case when
(2)case搜索函数法
简单case when只能处理等式问题,case搜索函数法可以处理等式问题也可以处理不等式问题。
case when的语法逻辑
#
case
when Condition1 then result1
when Condition2 then result2
......
else result
end
#或者end as name1
#end非常容易丢,一定要注意
二、case when语句在业务中常见的几种用法
2.1 数据映射处理
比如将分类变量中每一个取值分别映射成0、1、2…5;所有用户的性别映射成0、1;或者把数值映射成具体的实际含义。
如果是映射性别(0为女,1为男)
select *,
case
when is_male = 0 then '女'
else '男'
end as is_male_new
from table1
2.2. 连续数据离散化处理(分箱操作)
有时需要对数据进行分箱操作,也就是连续数据离散化处理。比如将所有用户按照收入分为高、中、低收入人群;按年龄可以将总体分为老年、中年、青年全体;按用户访问次数将群体分为高活跃状态用户、中等活跃状态用户、低活跃状态用户。分箱操作之后,就可以进行用户群分析等研究操作。
代码如下:
select *,
case
when year(Birthday) between 1960 and 1969 then '60后'
when year(Birthday) between 1970 and 1979 then '70后'
when year(Birthday) between 1980 and 1989 then '80后'
else '90后'
end as age_group
from table_user
这里的case when 语句是新建了一列,把每一个用户按照出生年份标记为60后、70后、80后、90后。
2.3 列方向上的聚合
首先什么是行方向上的聚合,什么是列方向的聚合?
下图是行方向上的聚合
 下图是列方向上的聚合
下图是列方向上的聚合
 行方向上的聚合一般用group by 结合聚合函数来计算;列方向上的聚合就要用case when 语句结合聚合函数来计算
行方向上的聚合一般用group by 结合聚合函数来计算;列方向上的聚合就要用case when 语句结合聚合函数来计算
首先,来看行方向上的聚合计算:
select product_type, sum(price) as sum_price
from table2
group by product_type
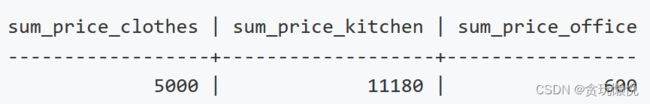
列方向上的聚合计算:
select
sum(case when product_type='衣服' then price else null end)as sum_price_clothes,
sum(case when product_type='厨房用品' then price else null end)as sum_price_kitchen,
sum(case when product_type='办公用品' then price else null end)as sum_price_office
from table3
实现行列转换的例子
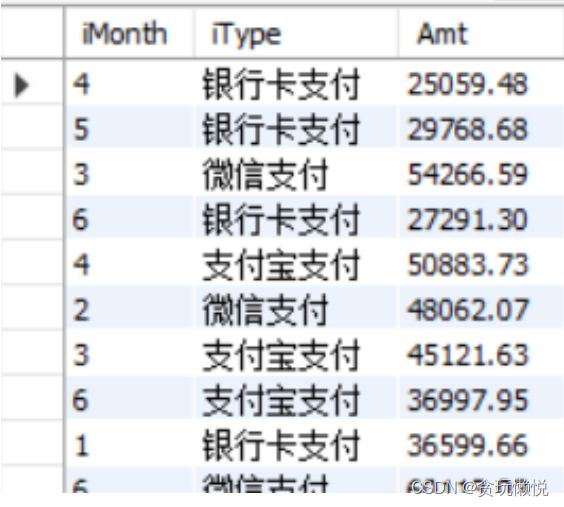 现在的数据是按照行方向聚合的结果,是按imonth(支付日期)和itype(支付方式)两个字段来聚合,出现以上结果的语句是这样的:
现在的数据是按照行方向聚合的结果,是按imonth(支付日期)和itype(支付方式)两个字段来聚合,出现以上结果的语句是这样的:
select month(Order_Date) as imonth,
case
when pay_type in (1,3,5,7,10) then '微信支付'
when pay_type in (6,9,2) then '银行卡支付'
else '支付宝支付'
end as iType,
sum(pay_amt) as amt
from paytable
group by iMonth,iType
select month(Order_date) as iMonth,
sum(case when pay_type in (1,3,5,7,10) then pay_amt else null end ) as wechat,
sum(case when pay_type in (6,9,12) then pay_amt else null end ) as bank_card,
sum(case when pay_type not in (1,3,5,7,10,6,9,12) then pay_amt else null end ) as ali_pay
from paytable
group by month(Order_date)

