Pyspark 案例实践 假新闻分类
前几天做大数据课设作业,要求用Hadoop构建单节点,然后用Spark训练个分类器。
具体代码可以看我的github
GitHub - qinxukun21/PysparkTest
数据集太大,github上传不上去(我是彩笔我不太懂怎么上传25M以上的文件,好像可以用一个gitbash的插件但我懒得下载),因此我放在云盘里了
百度网盘链接。 链接:百度网盘 请输入提取码 提取码:dqnz
现在简单讲讲我做的东西。
项目目的
本项目旨在构建一个分类器,帮助判断新闻是否为真。
数据介绍
整体数据介绍
首先先介绍一下我的数据集。
数据共包括各类别新闻44898条,其中正例21417条,负例23481条,正负例数量占比合适。
指标分析
首先分析各指标。在数据中,title指新闻标题,text指新闻内容,subject值新闻种类,date指新闻发布日期。首先,毋庸置疑的是title、text是判断新闻真假的根本依据,subject应该也能一定程度上的反应出新闻的某些特征。
关于date数据,我最开始初步认为,可以用格林威治时间戳转成标量放入模型中,但后来一想,模型做的目的就是为了预测以后发的新闻是真是假,新发新闻的时间一定不在训练范围内,因此使用date不仅不能能带来性能的提升,反而可能会造成有偏。因此不使用date作为输入。
环境配置
本项目在Linux虚拟机上进行虚拟机搭建在Oracle VM VirtualBox上,使用系统为ubuntu,使用jdk8(jdk1.8)、hadoop-3.3.1、spark3.2.0
通过Anaconda转载jupyter-notebook,用作IDE
此外,本实验需要工具包有 pandas numpy nltk pyspark (scipy sklearn)
数据处理
整体数据去重去脏
由于Pyspark中RDD数据常用map做处理,但对文本数据来说,对应于RDD的机器学习库Mllib中并不包括Tokenizer等一些既定的词袋统计器;而若读取数据为sql.DataFrame,又无法使用map做处理。因此我这边先用pandas对数据做处理,将清洗好的数据再放入Pyspark中使用。
首先先观察数据,发现其中有重复项和脏项。对相应数据做处理。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# 读入数据
true_news = pd.read_csv('./data/true.csv')
fake_news = pd.read_csv('./data/fake.csv')
# 打上标签
true_news["lable"] = [1] * 21417
fake_news["lable"] = [0] * 23481
# 合并数据并且分割x,y
df_all = pd.concat([true_news, fake_news]).reset_index()
df_no = df_all.copy()
# 观察数据,发现fake_news里边有脏,纯链接形式的,日期时间开头为"https://",因此筛一下;此外,还有一条title为"Homepage",应该是爬数据的时候首页错误,因此也筛去。提前用jupyter得到了下标
for i in [30775, 36924, 36925, 37256, 37257, 38849, 38850, 40350, 43286, 43287]:
df_all = df_all.drop(index=i)
df_all = df_all.drop('index',axis=1)
df_all = df_all.reset_index(drop=True)至此,数据清洗为符合要求的文本数据。
构建特征
文本特征构建
由于本数据中title与text均为文本,因此在构建特征时需要对这些特征做处理。
一、使用nltk中porter提取词干并去除停用词
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
# PorterStemmer词干提取与还原、去停用词
title = []
for i in df_all["title"]:
tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(i)
porter = nltk.PorterStemmer()
title.append(" ".join([porter.stem(t) for t in tokens]))
text = []
for i in df_all["text"]:
tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(i)
porter = nltk.PorterStemmer()
text.append(" ".join([porter.stem(t) for t in tokens]))
stop_words = stopwords.words('english')
for w in ['!',',','.','?','-s','-ly','','s',':',',','@']:
stop_words.append(w)
title_ok = []
for i in title:
tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(i)
title_ok.append(" ".join([x for x in tokens if x not in stop_words]))
text_ok = []
for i in text:
tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(i)
text_ok.append(" ".join([x for x in tokens if x not in stop_words]))
df_all["title"] = title_ok
df_all["text"] = text_ok
df_all = df_all.reset_index()
df_all.to_csv('./data/train.csv', index=False)二、使用pyspark中tokenizer和word2vec构建词向量
将title和text均通过w2v打成20维的词向量。合并加总为40维的词向量。
title
title_tokenizer = Tokenizer(inputCol="title", outputCol="words")
title_w2v = Word2Vec(vectorSize=20, minCount=1, inputCol="words", outputCol="w2v")
x_train_title = train.select(["lable","title"])
x_test_title = test.select(["lable","title"])
# # 标题
#tokenizer
x_train_title_token = title_tokenizer.transform(x_train_title)
x_test_title_token = title_tokenizer.transform(x_test_title)
#tf
title_w2v_model = title_w2v.fit(x_train_title_token)
x_train_title_w2v = title_w2v_model.transform(x_train_title_token)
x_test_title_w2v = title_w2v_model.transform(x_test_title_token)
#训练集
x_train_title_w2v_1 = x_train_title_w2v.drop("title").drop("words")
pandasdf = x_train_title_w2v_1.toPandas()
# x_train_title_w2v.filter(x_train_title_w2v.lable==0 | x_train_title_w2v.lable==1)
neg = pandasdf[pandasdf["lable"]=="0"]
pos = pandasdf[pandasdf["lable"]=="1"]
train_new = pd.concat([neg,pos]).reset_index(drop=True)
train_new["lable"].astype(int)
values = train_new.values.tolist()
columns = train_new.columns.tolist()
train_new_sprak = spark.createDataFrame(values,columns)
train_new_sprak2 = train_new_sprak.withColumn("lable_int",train_new_sprak['lable'].cast('int')).drop('lable')
#测试集
x_test_title_w2v_1 = x_test_title_w2v.drop("title").drop("words")
pandasdf = x_test_title_w2v_1.toPandas()
# x_train_title_w2v.filter(x_train_title_w2v.lable==0 | x_train_title_w2v.lable==1)
neg = pandasdf[pandasdf["lable"]=="0"]
pos = pandasdf[pandasdf["lable"]=="1"]
test_new = pd.concat([neg,pos]).reset_index(drop=True)
test_new["lable"].astype(int)
values = test_new.values.tolist()
columns = test_new.columns.tolist()
test_new_sprak = spark.createDataFrame(values,columns)
test_new_sprak2 = test_new_sprak.withColumn("lable_int",test_new_sprak['lable'].cast('int')).drop('lable')text
最开始我也用的tokenizer+word2vec构建text的向量,但是在w2v.fit()时发生错误,Py4JJavaError原因是tokenizer在处理很长的词项时(例如网站等)无法转化,导致fit失败。因此我使用split()自己手切词项放入训练。
#训练集
x_train_text = train.select(["lable","text"])
df2 = x_train_text.toPandas()
text_list_train = list(map(lambda x: str(x).split(" "), list(df2["text"].astype(str))))
df2["words"] = text_list_train
values = df2.values.tolist()
columns = df2.columns.tolist()
x_train_text_token = spark.createDataFrame(values,columns)
#测试集
x_test_text = test.select(["lable","text"])
df2 = x_test_text.toPandas()
text_list_test = list(map(lambda x: str(x).split(" "), list(df2["text"].astype(str))))
df2["words"] = text_list_test
values = df2.values.tolist()
columns = df2.columns.tolist()
x_test_text_token = spark.createDataFrame(values,columns)
text_w2v = Word2Vec(vectorSize=20, minCount=1, inputCol="words", outputCol="w2v")
text_w2v_model = text_w2v.fit(x_train_text_token)
x_train_text_w2v = text_w2v_model.transform(x_train_text_token)
x_test_text_w2v = text_w2v_model.transform(x_test_text_token)
x_train_text_w2v_1=x_train_text_w2v.drop("text").drop("words")
x_test_text_w2v_1=x_test_text_w2v.drop("text").drop("words")
x_train_text_w2v_2 = x_train_text_w2v_1.withColumn("lable_int",x_train_text_w2v_1['lable'].cast('int')).drop('lable')
x_test_text_w2v_2 = x_test_text_w2v_1.withColumn("lable_int",x_test_text_w2v_1['lable'].cast('int')).drop('lable')concat合并
#train title+text
title_train_df = train_new_sprak2.toPandas()
text_train_df = x_train_text_w2v_2.toPandas()
concat_train = []
for i,j in zip(title_train_df["w2v"],text_train_df["w2v"]):
concat_train.append(DenseVector(list(i)+list(j)))
pddf_train = title_train_df.copy().drop("w2v",axis=1)
pddf_train["w2v"]=concat_train
values = pddf_train.values.tolist()
columns = pddf_train.columns.tolist()
spdf_train = spark.createDataFrame(values,columns)
#test title+text
title_test_df = test_new_sprak2.toPandas()
text_test_df = x_test_text_w2v_2.toPandas()
concat_test = []
for i,j in zip(title_test_df["w2v"],text_test_df["w2v"]):
concat_test.append(DenseVector(list(i)+list(j)))
pddf_test = title_test_df.copy().drop("w2v",axis=1)
pddf_test["w2v"]=concat_test
values = pddf_test.values.tolist()
columns = pddf_test.columns.tolist()
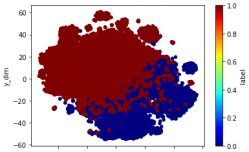
spdf_test = spark.createDataFrame(values,columns)使用TSNE查看效果
import ast
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
vec_train = []
vec_test = []
for i in pddf_train["w2v"]:
vec_train.append(ast.literal_eval(i))
for i in pddf_test["w2v"]:
vec_test.append(ast.literal_eval(i))
#训练集
ts = TSNE(n_components=2)
ts.fit_transform(vec_train)
vec_2 = pd.DataFrame(ts.embedding_)
df_vec_2 = pd.concat([pddf_train["lable_int"], vec_2], axis=1)
df_vec_2.columns = ['label','x_dim','y_dim']
df_vec_2.plot.scatter("x_dim", "y_dim", c="label", colormap='jet')
#测试集
ts = TSNE(n_components=2)
ts.fit_transform(vec_test)
vec_2 = pd.DataFrame(ts.embedding_)
df_vec_2 = pd.concat([pddf_test["lable_int"], vec_2], axis=1)
df_vec_2.columns = ['label','x_dim','y_dim']
df_vec_2.plot.scatter("x_dim", "y_dim", c="label", colormap='jet')类别特征构建
除了文本特征,本数据中还有类别特征subject表示新闻的种类。因此,我通过构建分类函数执行分类操作。(后续选择删除了类别指标,这点论文里会讲)
def category(li):
import pandas
if isinstance(li, pandas.core.series.Series):
li = list(li)
elif isinstance(li, list):
pass
else:
print("Error: Type of inputs is wrong! Please make sure \"list\" or \"pandas.core.series.Series\".")
return "Error Type!"
result = []
all_name = list(set(li))
all_len = len(all_name)
for i in range(all_len):
result.append([])
for e in li:
k = all_name.index(e)
for n in range(all_len):
if n != k:
result[n].append(0)
else:
result[n].append(1)
result = pandas.DataFrame(result).T
result.columns = all_name
return result
x_train_subject = category(x_train["subject"])
x_test_subject = category(x_test["subject"])该函数接收list或pandas中的Series类型数据,将数据中每一个类别离散为对应维度的矩阵表示。本数据中,新闻类别共8种,因此将每个sample中的subject项离散为了8*1的向量表示。
在观察数据时,发现数据集中真假新闻的类别是不相交的,即属于politicsNews和worldnews类的都是真新闻,属于其他六个类别的都是假新闻。这也解释了为什么我在sklean中使用类别数据做输入时效果极佳,达到了0.986以上。但是在真实场景中,这明显是不符合实际的,因此只使用文本数据来做统计。
模型训练与结果
模型选择
首先先选择模型。由于word2vec构建的词向量中存在负值,因此不能使用朴素贝叶斯进行分类。所以我用了LogisticRegression, DecisionTreeClassifier, RandomForestClassifier, LinearSVC, MultilayerPerceptronClassifier等分类器。
前四种分类器使用默认参数,多层感知机使用三个隐藏层,每层神经元数分别为40(词向量维度)、16、2。
训练结果
逻辑回归
lr = LogisticRegression(featuresCol="w2v",labelCol="lable_int")
lr_model = lr.fit(spdf_train)
result = lr_model.transform(spdf_test)决策树
dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(featuresCol="w2v",labelCol="lable_int")
dt_model = dt.fit(spdf_train)
result = dt_model.transform(spdf_test)随机森林
rf = RandomForestClassifier(featuresCol="w2v",labelCol="lable_int")
rf_model = rf.fit(spdf_train)
result = rf_model.transform(spdf_test)支持向量机
svc = LinearSVC(featuresCol="w2v",labelCol="lable_int")
svc_model = svc.fit(spdf_train)
result = svc_model.transform(spdf_test)多层感知机
mlp = MultilayerPerceptronClassifier(featuresCol="w2v",labelCol="lable_int",layers=[40,16,2])
mlp_model = mlp.fit(spdf_train)
result = mlp_model.transform(spdf_test)指标判断
p = MulticlassClassificationEvaluator(predictionCol='prediction', labelCol="lable_int", metricName='weightedPrecision').evaluate(result)
r = MulticlassClassificationEvaluator(predictionCol='prediction', labelCol="lable_int", metricName='weightedRecall').evaluate(result)
f1 = MulticlassClassificationEvaluator(predictionCol='prediction', labelCol="lable_int", metricName='f1').evaluate(result)
accuracy = MulticlassClassificationEvaluator(predictionCol='prediction', labelCol="lable_int", metricName='accuracy').evaluate(result)
roc_auc = BinaryClassificationEvaluator(rawPredictionCol='prediction', labelCol="lable_int", metricName='areaUnderROC').evaluate(result)
pr_auc = BinaryClassificationEvaluator(rawPredictionCol='prediction', labelCol="lable_int", metricName='areaUnderPR').evaluate(result)
print("MLP == accuracy-",accuracy,", precision-",p,", recall-",r,", f1 score-", f1,", roc-auc-",roc_auc,", pr-auc-",pr_auc)评价指标使用查准率precession、查全率recall、f1值f1_score、准确率accuracy、roc曲线下auc值、pr曲线下auc值作为评价指标。结果如下:
| precession | recall | f1 | accuracy | roc-auc | pr-auc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 逻辑回归 | 0.944667936 | 0.944310458 | 0.944291189 | 0.944310458 | 0.944169071 | 0.940780425 |
| 决策树 | 0.888426733 | 0.887524666 | 0.887429244 | 0.887524666 | 0.887281072 | 0.878294082 |
| 随机森林 | 0.916026865 | 0.916027187 | 0.91602663 | 0.916027187 | 0.916013521 | 0.897817471 |
| LinearSVC | 0.943058467 | 0.942775707 | 0.942759144 | 0.942775707 | 0.942648654 | 0.937842842 |
| MLP | 0.948849608 | 0.948476211 | 0.948457947 | 0.948476211 | 0.948333128 | 0.946091116 |
可以观察到,多层感知机在各指标中效果都更好,决策树、随机森林和支持向量机效果甚至不如逻辑回归。
代码运行
本项目代码共分为两个文件“步骤1词干还原与合并”和“步骤2处理与训练”,都是jupyter格式,顺序都已经弄好了,直接运行就行。