经验模态分解(EMD)方法的python实现
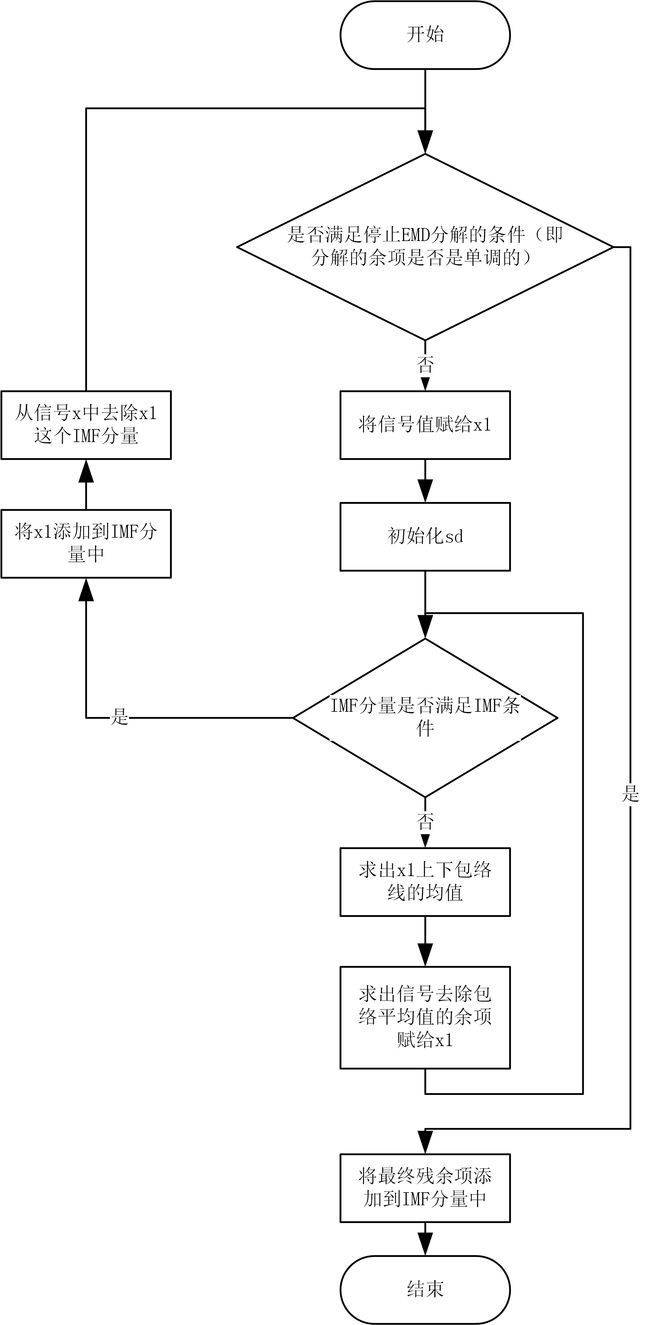
EMD算法的程序流程图
EMD算法的初步python实现
import math
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.signal as signal
from scipy import fftpack
import scipy.signal as signal
from scipy import interpolate
#判定当前的时间序列是否是单调序列
def ismonotonic(x):
max_peaks=signal.argrelextrema(x,np.greater)[0]
min_peaks=signal.argrelextrema(x,np.less)[0]
all_num=len(max_peaks)+len(min_peaks)
if all_num>0:
return False
else:
return True
#寻找当前时间序列的极值点
def findpeaks(x):
return signal.argrelextrema(x,np.greater)[0]
#判断当前的序列是否为 IMF 序列
def isImf(x):
N=np.size(x)
pass_zero=np.sum(x[0:N-2]*x[1:N-1]<0)#过零点的个数
peaks_num=np.size(findpeaks(x))+np.size(findpeaks(-x))#极值点的个数
if abs(pass_zero-peaks_num)>1:
return False
else:
return True
#获取当前样条曲线
def getspline(x):
N=np.size(x)
peaks=findpeaks(x)
print '当前极值点个数:',len(peaks)
if(len(peaks)<=3):
if(len(peaks)<2):
peaks=np.concatenate(([0],peaks))
peaks=np.concatenate((peaks,[N-1]))#这里是为了防止样条次数不够,无法插值的情况
t=interpolate.splrep(peaks,y=x[peaks], w=None, xb=None, xe=None,k=len(peaks)-1)
return interpolate.splev(np.arange(N),t)
t=interpolate.splrep(peaks,y=x[peaks])
return interpolate.splev(np.arange(N),t)
# f=interp1d(np.concatenate(([0,1],peaks,[N+1])),np.concatenate(([0,1],x[peaks],[0])),kind='cubic')
# f=interp1d(peaks,x[peaks],kind='cubic')
# return f(np.linspace(1,N,N))
#经验模态分解方法
def emd(x):
imf=[]
while not ismonotonic(x):
x1=x
sd=np.inf
while sd>0.1 or (not isImf(x1)):
print isImf(x1)
s1=getspline(x1)
s2=-getspline(-1*x1)
x2=x1-(s1+s2)/2
sd=np.sum((x1-x2)**2)/np.sum(x1**2)
x1=x2
imf.append(x1)
x=x-x1
imf.append(x)
return imf
def wgn(x, snr):
snr = 10**(snr/10.0)
xpower = np.sum(x**2)/len(x)
npower = xpower / snr
return np.random.randn(len(x)) * np.sqrt(npower)
sampling_rate=30000
f0=92
fg=4000
fft_size = 512
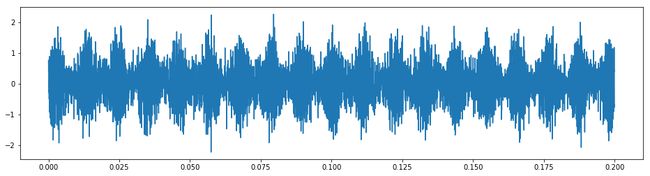
t=np.arange(0, 0.2, 1.0/sampling_rate)
x1=0.6*(1+np.sin(2*np.pi*f0*t))*np.sin(2*np.pi*fg*t)
x1+=wgn(x1, 3)
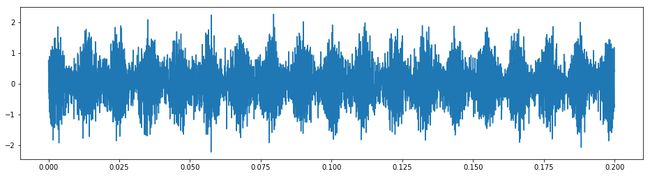
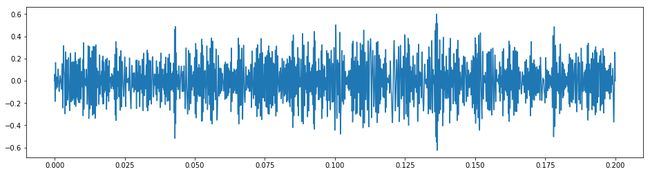
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,x1)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
imf1=emd(x1)
False
当前极值点个数: 1550
当前极值点个数: 1551
...
True
当前极值点个数: 0
当前极值点个数: 0
len(imf1)
22
imf1
[array([-0.38012969, -0.21587489, 0.32847722, ..., -0.35597983,
-4.250271 , -8.53108409]),
...
array([ 0.02505203, 0.02504342, 0.02503481, ..., -0.0079153 ,
-0.00791768, -0.00792006])]
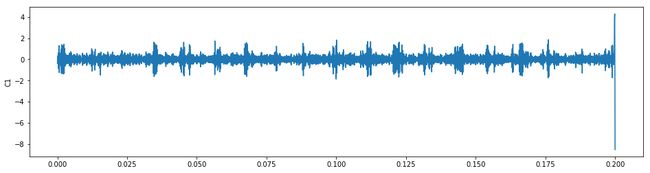
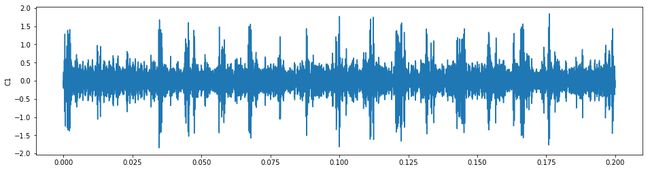
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,imf1[0])
# plt.plot(t,imf1[0],'*')
plt.ylabel("C1")
# plt.xlim(0,0.005)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
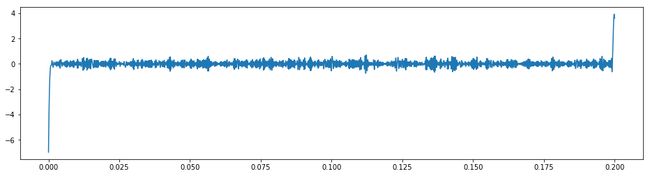
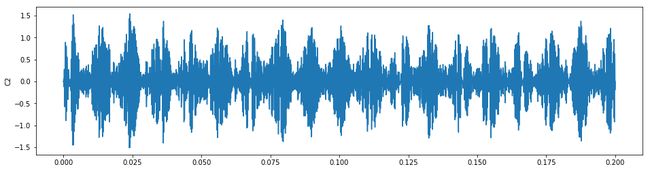
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,imf1[1])
plt.ylabel("C2")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
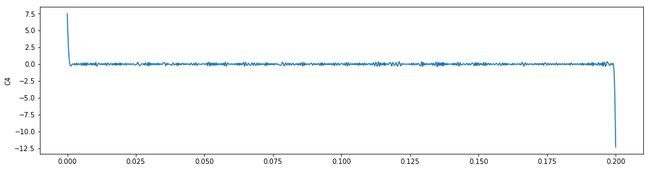
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,imf1[2])
# plt.plot(t,imf1[2],'o')
# plt.ylabel("C3")
# plt.xlim(0,0.01)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
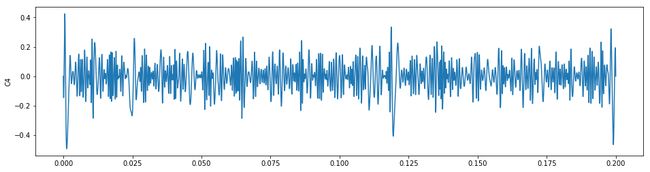
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,imf1[3])
plt.ylabel("C4")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
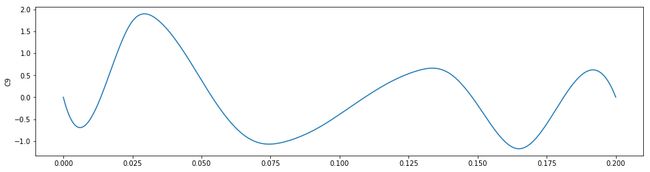
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,imf1[8])
plt.ylabel("C9")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
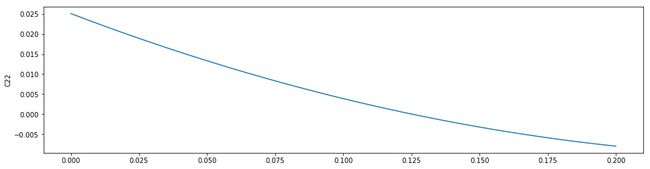
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,imf1[21])
plt.ylabel("C22")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
可见,由于对于极值点的样条插值,使得IMF分量边界处的导数很大。因此,将曲线的两端点加入到样条中是一种方法。如下所示:
改进算法
下面是对于同样数据的EMD算法分析
import math
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.signal as signal
from scipy import fftpack
import scipy.signal as signal
from scipy import interpolate
#判定当前的时间序列是否是单调序列
def ismonotonic(x):
max_peaks=signal.argrelextrema(x,np.greater)[0]
min_peaks=signal.argrelextrema(x,np.less)[0]
all_num=len(max_peaks)+len(min_peaks)
if all_num>0:
return False
else:
return True
#寻找当前时间序列的极值点
def findpeaks(x):
# df_index=np.nonzero(np.diff((np.diff(x)>=0)+0)<0)
# u_data=np.nonzero((x[df_index[0]+1]>x[df_index[0]]))
# df_index[0][u_data[0]]+=1
# return df_index[0]
return signal.argrelextrema(x,np.greater)[0]
#判断当前的序列是否为 IMF 序列
def isImf(x):
N=np.size(x)
pass_zero=np.sum(x[0:N-2]*x[1:N-1]<0)#过零点的个数
peaks_num=np.size(findpeaks(x))+np.size(findpeaks(-x))#极值点的个数
if abs(pass_zero-peaks_num)>1:
return False
else:
return True
#获取当前样条曲线
def getspline(x):
N=np.size(x)
peaks=findpeaks(x)
# print '当前极值点个数:',len(peaks)
peaks=np.concatenate(([0],peaks))
peaks=np.concatenate((peaks,[N-1]))
if(len(peaks)<=3):
# if(len(peaks)<2):
# peaks=np.concatenate(([0],peaks))
# peaks=np.concatenate((peaks,[N-1]))
# t=interpolate.splrep(peaks,y=x[peaks], w=None, xb=None, xe=None,k=len(peaks)-1)
# return interpolate.splev(np.arange(N),t)
t=interpolate.splrep(peaks,y=x[peaks], w=None, xb=None, xe=None,k=len(peaks)-1)
return interpolate.splev(np.arange(N),t)
t=interpolate.splrep(peaks,y=x[peaks])
return interpolate.splev(np.arange(N),t)
# f=interp1d(np.concatenate(([0,1],peaks,[N+1])),np.concatenate(([0,1],x[peaks],[0])),kind='cubic')
# f=interp1d(peaks,x[peaks],kind='cubic')
# return f(np.linspace(1,N,N))
#经验模态分解方法
def emd(x):
imf=[]
while not ismonotonic(x):
x1=x
sd=np.inf
while sd>0.1 or (not isImf(x1)):
# print isImf(x1)
s1=getspline(x1)
s2=-getspline(-1*x1)
x2=x1-(s1+s2)/2
sd=np.sum((x1-x2)**2)/np.sum(x1**2)
x1=x2
imf.append(x1)
x=x-x1
imf.append(x)
return imf
def wgn(x, snr):
snr = 10**(snr/10.0)
xpower = np.sum(x**2)/len(x)
npower = xpower / snr
return np.random.randn(len(x)) * np.sqrt(npower)
sampling_rate=30000
f0=92
fg=4000
fft_size = 512
t=np.arange(0, 0.2, 1.0/sampling_rate)
x1=0.6*(1+np.sin(2*np.pi*f0*t))*np.sin(2*np.pi*fg*t)
x1+=wgn(x1, 3)
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,x1)
# plt.ylabel("Volt")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
imf1=emd(x1)
len(imf1)
12
imf1
[array([ 3.35782798e-18, -1.86352711e-01, 2.38661655e-01, ...,
7.34715585e-02, -1.94968312e-01, 0.00000000e+00]),
array([ 5.10303853e-19, 1.24980995e-03, 1.27222343e-02, ...,
1.26203500e-02, -1.93462908e-01, 0.00000000e+00]),
...
array([ 0.76565882, 0.76540996, 0.76516111, ..., -0.68788932,
-0.68812522, -0.68836112])]
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,imf1[0])
# plt.plot(t,imf1[0],'*')
plt.ylabel("C1")
# plt.xlim(0,0.005)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,imf1[1])
plt.ylabel("C2")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,imf1[2])
# plt.plot(t,imf1[2],'o')
# plt.ylabel("C3")
# plt.xlim(0,0.01)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,imf1[3])
plt.ylabel("C4")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,imf1[8])
plt.ylabel("C9")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
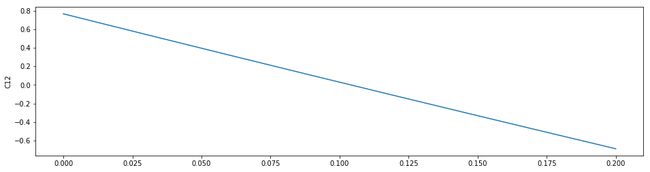
plt.figure(figsize=(16,4))
plt.plot(t,imf1[11])
plt.ylabel("C12")
plt.legend()
plt.show()