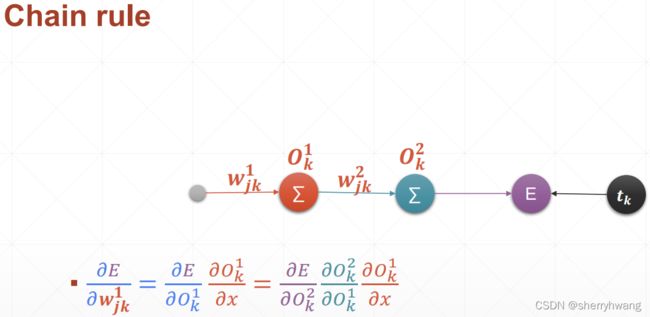pytorch基础(三)- 随机梯度下降
目录
- 梯度介绍
- 激活函数及其梯度
-
- Sigmoid/Logistic
- Tanh
- ReLU
- Loss函数及其梯度
-
- 均方差 MSE
- autograd.grad()求梯度
- loss.backward()求梯度
- Softmax
- 链式法则
-
- 单层感知机的求导
- 多输出感知机的求导
- 链式法则
- MLP反向传播
- 2D函数优化实例
梯度介绍
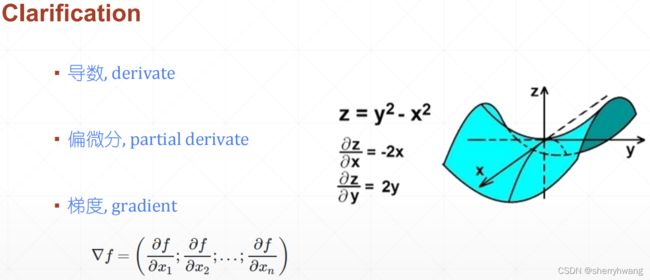
导数: 与梯度相近,针对一维函数,导数表示函数在x处的变换率;导数是一个标量,反应给定方向的函数值变换率,标量的长度反映了变换率的大小。
偏微分: 函数对它自变量的变化率的描述程度,跟导数区别,导数方向可以随意指定,而偏微分只能是自变量的方向;函数有多少自变量就有多少偏微分;
梯度: 函数所有偏微分的向量。
利用梯度进行优化:

常见函数的梯度:
一维函数的梯度和导数基本上一样,不过导数没有方向,梯度有方向。
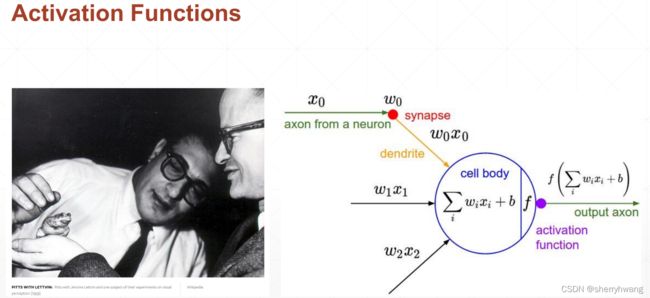
激活函数及其梯度
Sigmoid/Logistic
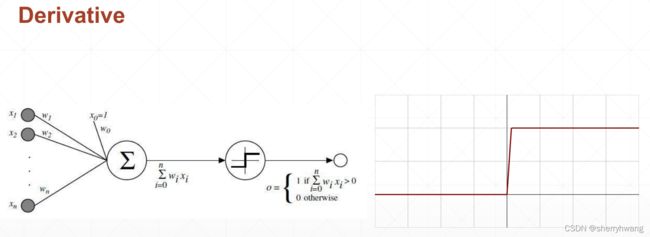
解决单层感知机激活函数不可导的情况,提出了一个连续的光滑的sigmoid函数。
将输出压缩到0-1之间的范围。对于输出概率类问题或者图像RGB值,需要使用sigmoid将输出值压缩到0-1。
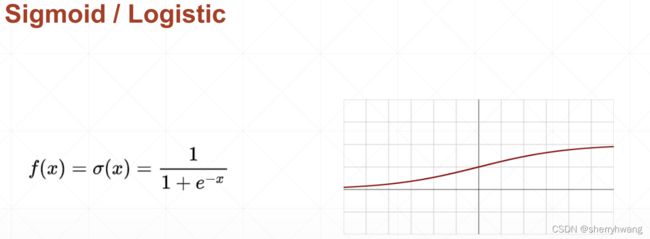

Sigmoid缺点:当输输出值处于非常大的时候,sigmoid梯度为0,会导致参数长时间得不到更新(参数更新慢),这就叫梯度弥散现象。
代码:
import torch
a = torch.linspace(-100,100,100,requires_grad=True)
b = torch.sigmoid(a)
print(b)
输出:
tensor([0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00,
6.8349e-39, 5.1533e-38, 3.8855e-37, 2.9296e-36, 2.2089e-35, 1.6655e-34,
1.2557e-33, 9.4681e-33, 7.1388e-32, 5.3825e-31, 4.0584e-30, 3.0599e-29,
2.3072e-28, 1.7396e-27, 1.3116e-26, 9.8893e-26, 7.4564e-25, 5.6220e-24,
4.2389e-23, 3.1961e-22, 2.4098e-21, 1.8169e-20, 1.3699e-19, 1.0329e-18,
7.7881e-18, 5.8721e-17, 4.4274e-16, 3.3382e-15, 2.5170e-14, 1.8978e-13,
1.4309e-12, 1.0789e-11, 8.1345e-11, 6.1333e-10, 4.6244e-09, 3.4867e-08,
2.6289e-07, 1.9822e-06, 1.4945e-05, 1.1267e-04, 8.4891e-04, 6.3653e-03,
4.6075e-02, 2.6696e-01, 7.3304e-01, 9.5392e-01, 9.9363e-01, 9.9915e-01,
9.9989e-01, 9.9999e-01, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00,
1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00,
1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00,
1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00,
1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00,
1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00,
1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00,
1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00, 1.0000e+00],
grad_fn=<SigmoidBackward>)
Tanh
在RNN中用的比较多,可以由sigmoid函数变换而来;输出值为[-1,1]区间。

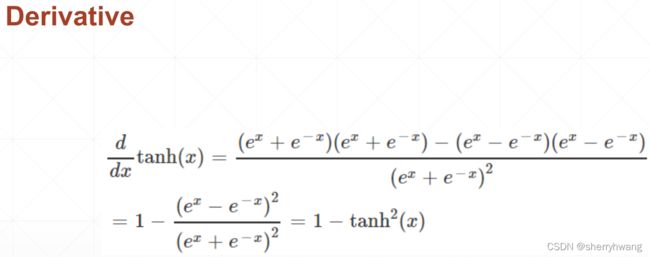
代码:
import torch
a = torch.linspace(-1,1,10,requires_grad=True)
b = torch.tanh(a)
print(b)
输出:
tensor([-0.7616, -0.6514, -0.5047, -0.3215, -0.1107, 0.1107, 0.3215, 0.5047,
0.6514, 0.7616], grad_fn=<TanhBackward>)
ReLU
深度学习奠基石的激活函数。ReLU函数非常适合做Deep learning。导数计算非常简单,当值大于0时不会放大或缩小梯度。
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
a = torch.linspace(-1,1,10,requires_grad=True)
b = torch.relu(a)
c = F.relu(a)
print(b)
print(c)
输出:
tensor([0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.1111, 0.3333, 0.5556, 0.7778,
1.0000], grad_fn=<ReluBackward0>)
tensor([0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.1111, 0.3333, 0.5556, 0.7778,
1.0000], grad_fn=<ReluBackward0>)
Loss函数及其梯度
均方差 MSE
autograd.grad()求梯度
autograd.grad(y_loss,tensorlist)
代码:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
x = torch.ones(1)
w = torch.full([1],2., requires_grad=True) #长度为1,值为2
mse = F.mse_loss(torch.ones(1), x*w) #第一个参数为predict值 第二个为label值
print(mse)
print(torch.autograd.grad(mse, [w]))
输出:
tensor(1., grad_fn=<MseLossBackward>)
(tensor([2.]),)
loss.backward()求梯度
给tensor的grad属性赋值,可以通过tensor的grad属性得到其梯度。
(梯度值直接赋在tensor的grad成员上面,没有额外的返回)
代码:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
x = torch.ones(1)
w = torch.full([1],2., requires_grad=True) #长度为1,值为2
mse = F.mse_loss(torch.ones(1), x*w) #第一个参数为predict值 第二个为label值
print(mse)
mse.backward()
print(w.grad)
输出:
tensor(1., grad_fn=<MseLossBackward>)
tensor([2.])
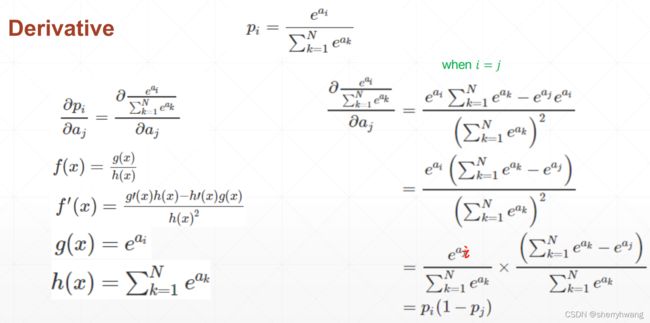
Softmax
适多分类的情况;同时将多个数值差异很大的映射到一个比较密集的空间。

当i=j时,softmax的求导:
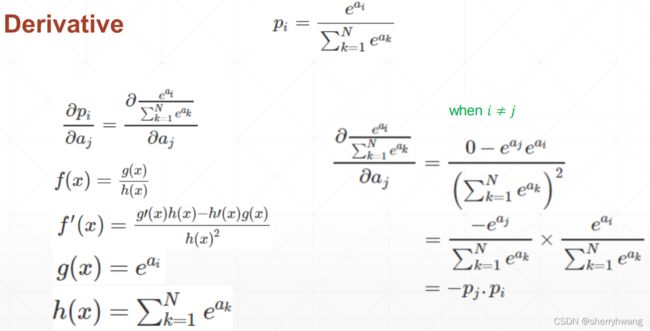
当i!=j时,softmax的求导:
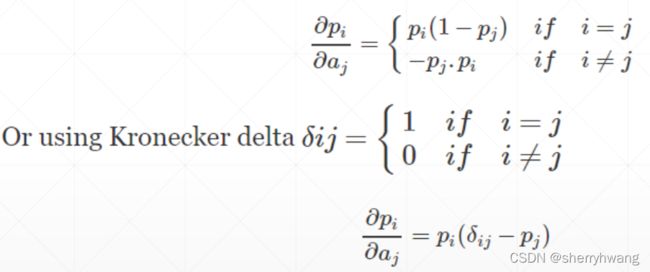
代码:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
a = torch.rand(3)
a.requires_grad_()
print(a)
p = F.softmax(a, dim = 0)
print(p)
print(torch.autograd.grad(p[0], [a], retain_graph=True)) #动态图不会被清除,可以连续多次求梯度,或者多次backward
print(torch.autograd.grad(p[1], [a], retain_graph=True))
print(torch.autograd.grad(p[2], [a], retain_graph=True))
输出:
tensor([0.8659, 0.0540, 0.4153], requires_grad=True)
tensor([0.4805, 0.2133, 0.3062], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward>)
(tensor([ 0.2496, -0.1025, -0.1471]),)
(tensor([-0.1025, 0.1678, -0.0653]),)
(tensor([-0.1471, -0.0653, 0.2124]),)
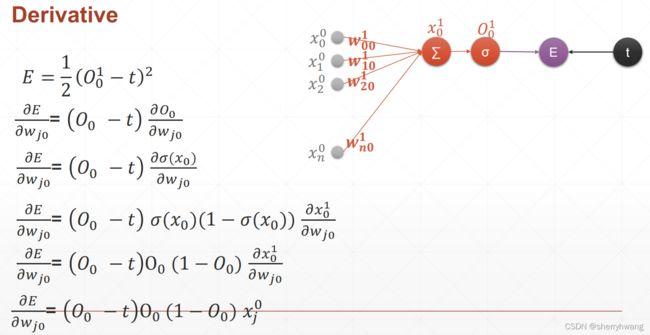
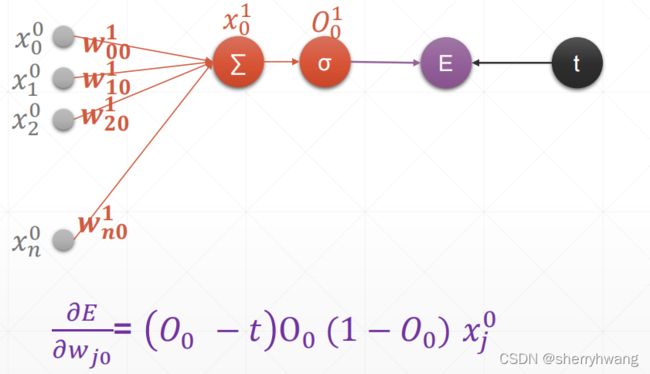
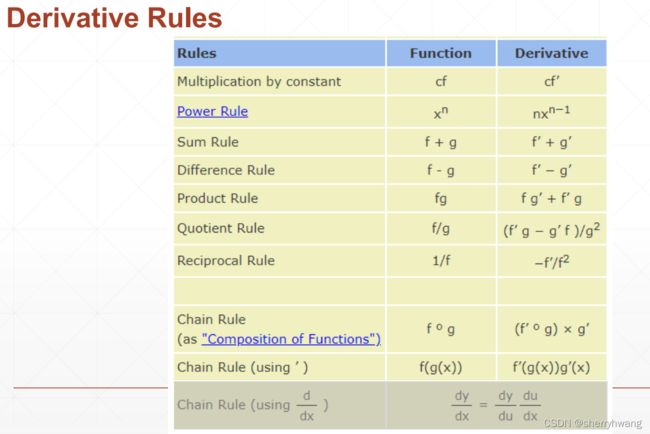
链式法则
单层感知机的求导
代码:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
x = torch.randn(1,10)
w = torch.randn(1,10, requires_grad=True)
y = x@w.t()
o = torch.sigmoid(y)
loss = F.mse_loss(torch.ones(1,1), o)
print(loss)
loss.backward()
print(w.grad)
输出:
tensor(0.9582, grad_fn=<MseLossBackward>)
tensor([[-0.0427, 0.0890, -0.0167, 0.0014, -0.0213, -0.0562, -0.0084, 0.0488,
0.0099, 0.0158]])
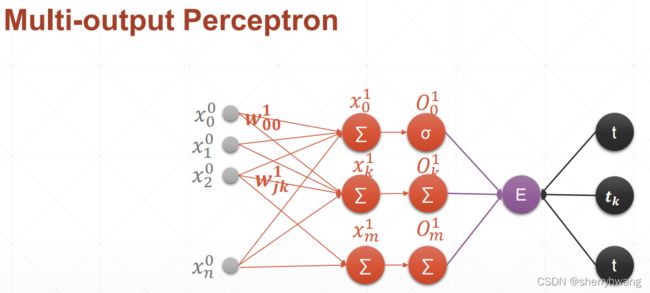
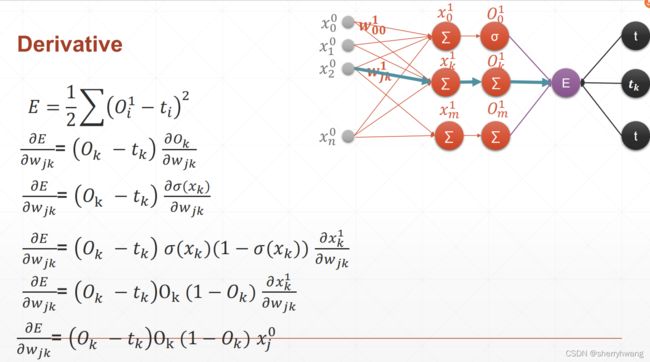
多输出感知机的求导
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
x = torch.randn(1,10)
w = torch.randn(3,10, requires_grad=True)
y = x@w.t()
o = torch.sigmoid(y) # shape (1,3)
loss = F.mse_loss(torch.ones(1,3), o)
print(loss)
loss.backward()
print(w.grad)
输出:
tensor(0.3267, grad_fn=<MseLossBackward>)
tensor([[ 0.0159, 0.0368, -0.0310, 0.0295, 0.0147, 0.0086, 0.0291, -0.0319,
-0.0170, -0.0093],
[ 0.0002, 0.0004, -0.0004, 0.0004, 0.0002, 0.0001, 0.0004, -0.0004,
-0.0002, -0.0001],
[ 0.0135, 0.0314, -0.0264, 0.0252, 0.0125, 0.0074, 0.0248, -0.0272,
-0.0145, -0.0079]])
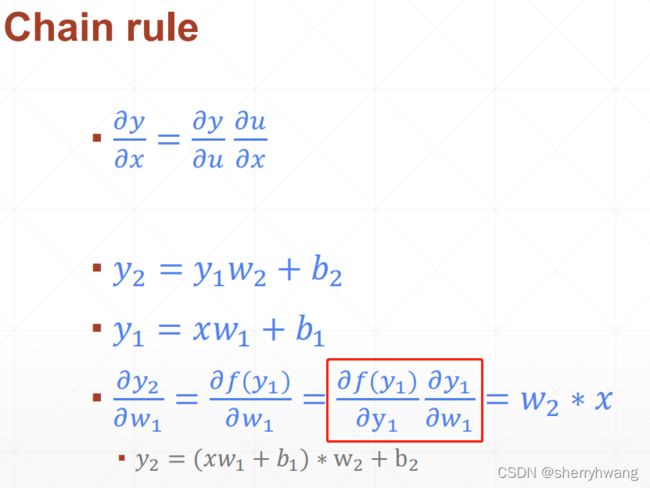
链式法则
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
x = torch.tensor(1.)
w1 = torch.tensor(2., requires_grad=True)
b1 = torch.tensor(1., requires_grad=True)
w2 = torch.tensor(2., requires_grad=True)
b2 = torch.tensor(1., requires_grad=True)
y1 = w1*x + b1
y2 = w2*y1 + b2
dy2_dy1 = torch.autograd.grad(y2, [y1], retain_graph=True)
dy1_dw1 = torch.autograd.grad(y1, [w1], retain_graph=True)
dy2_dw1 = torch.autograd.grad(y2, [w1], retain_graph=True)
print(dy2_dy1)
print(dy1_dw1)
print(dy2_dw1)
输出:
(tensor(2.),)
(tensor(1.),)
(tensor(2.),)
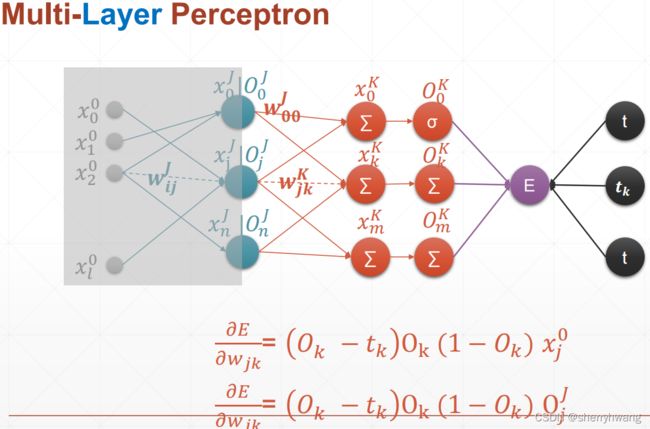
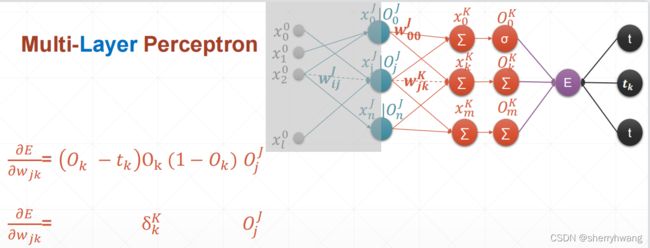
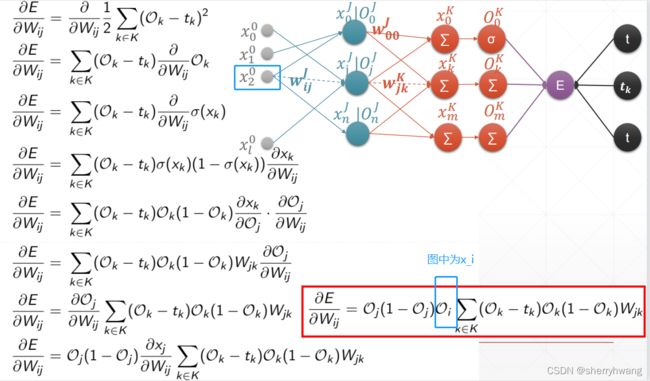
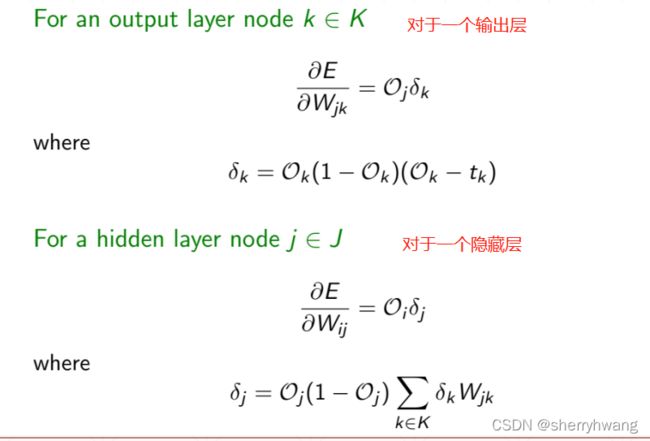
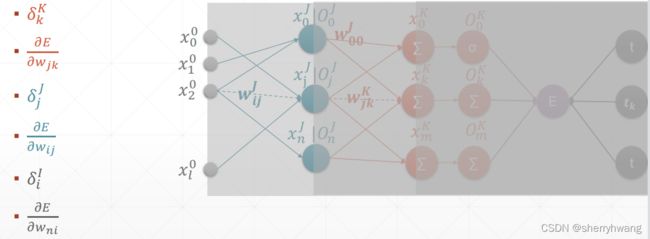
MLP反向传播
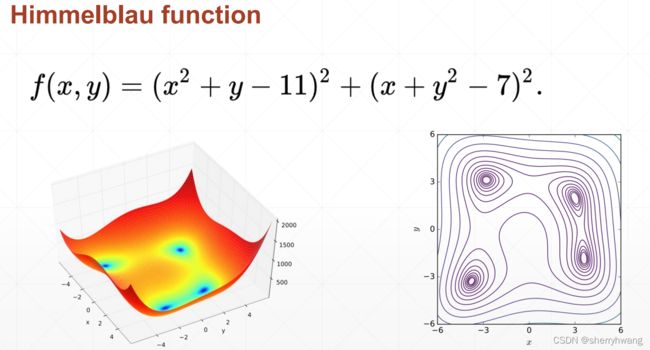
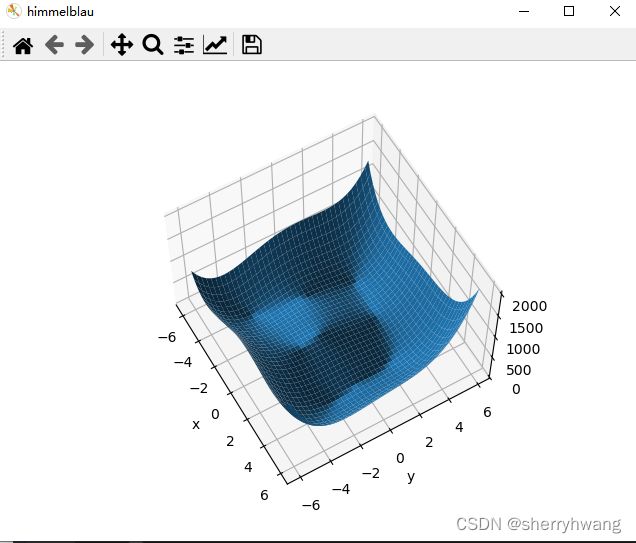
2D函数优化实例
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def himmelblau(x):
return (x[0] ** 2 + x[1] - 11) ** 2 + (x[0] + x[1] ** 2 - 7) ** 2
def plot():
x = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
y = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
print('x,y range:', x.shape, y.shape)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
print('X,Y maps:', X.shape, Y.shape)
Z = himmelblau([X, Y])
fig = plt.figure('himmelblau')
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
ax.view_init(60, -30)
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
plot()
x = torch.tensor([0.,0.], requires_grad=True)
adam = torch.optim.Adam([x], 1e-2)
for step in range(20000):
pred = himmelblau(x)
adam.zero_grad()
pred.backward()
adam.step()
if step % 2000 == 0:
print('step {0}: x = {1}, f(x) = {2}'.format(step, x.tolist(), pred.item()))
结果:
x,y range: (120,) (120,)
X,Y maps: (120, 120) (120, 120)
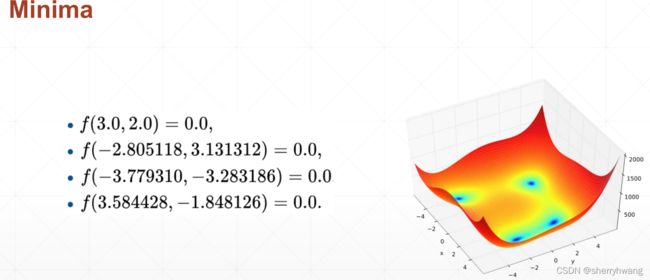
step 0: x = [0.009999999776482582, 0.009999999776482582], f(x) = 170.0
step 2000: x = [2.999997854232788, 2.0000030994415283], f(x) = 2.0099832909181714e-10
step 4000: x = [2.9999992847442627, 2.0000009536743164], f(x) = 1.6370904631912708e-11
step 6000: x = [2.999999761581421, 2.000000238418579], f(x) = 1.8189894035458565e-12
step 8000: x = [3.0, 2.0], f(x) = 0.0
step 10000: x = [3.0, 2.0], f(x) = 0.0
step 12000: x = [3.0, 2.0], f(x) = 0.0
step 14000: x = [3.0, 2.0], f(x) = 0.0
step 16000: x = [3.0, 2.0], f(x) = 0.0
step 18000: x = [3.0, 2.0], f(x) = 0.0