使用Idea创建创建一个简单的SpringBoot+Mybatis框架的Web项目
文章目录
- SpringBoot简介:
- 1.使用IDEA选择需要的模块完成项目初始化
- 2.使用MyBatis逆向工程生成需要的model,接口和xml映射文件
- 3.配置SpringBoot核心配置文件完成数据源(datasource)和mybatis整合信息
- 4.整合Web模块,编写Controller控制器,Html视图完成测试
- 5.番外讲解
-
- 5.1 启动器
- 5.2 常用的核心文件配置信息表
SpringBoot简介:
Spring Boot 是由 Pivotal 团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新 Spring 应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。通过这种方式,Spring Boot 致力于在蓬勃发展的快速应用开发领域(rapidapplication development)成为领导者.
创建独立的 Spring 应用程序嵌入的 Tomcat,无需部署 WAR 文件简化 Maven 配置自动配置 Spring提供生产就绪型功能,如指标,健康检查和外部配置开箱即用,没有代码生成,也无需 XML 配置。
Spring Boot 并不是对 Spring 功能上的增强,而是提供了一种快速使用 Spring 的方式。类似于mybatis-plus和mybatis的区别。
1.使用IDEA选择需要的模块完成项目初始化
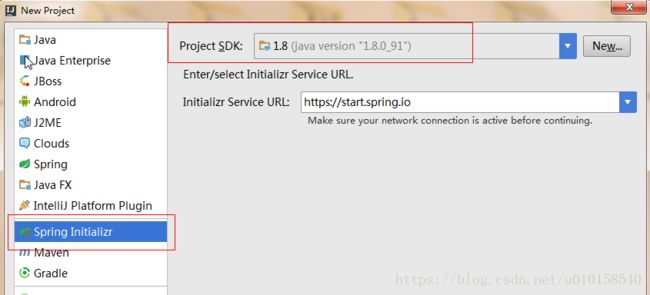
选择创建模式,设置jdk版本
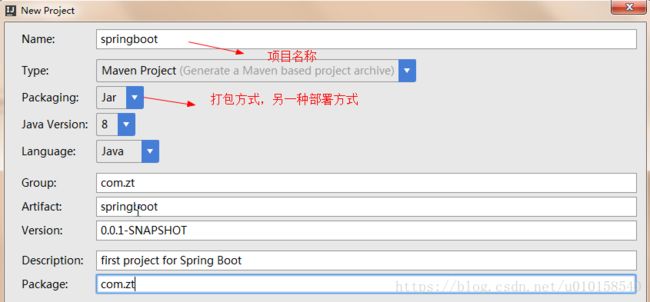
录入项目的名称和包结构以及项目构建类型
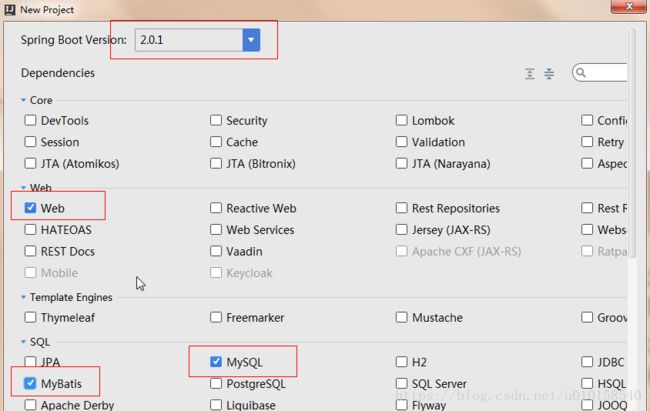
选择springboot的版本以及当前项目所需要的模块,当然也可以后面在.xml文件中手动添加
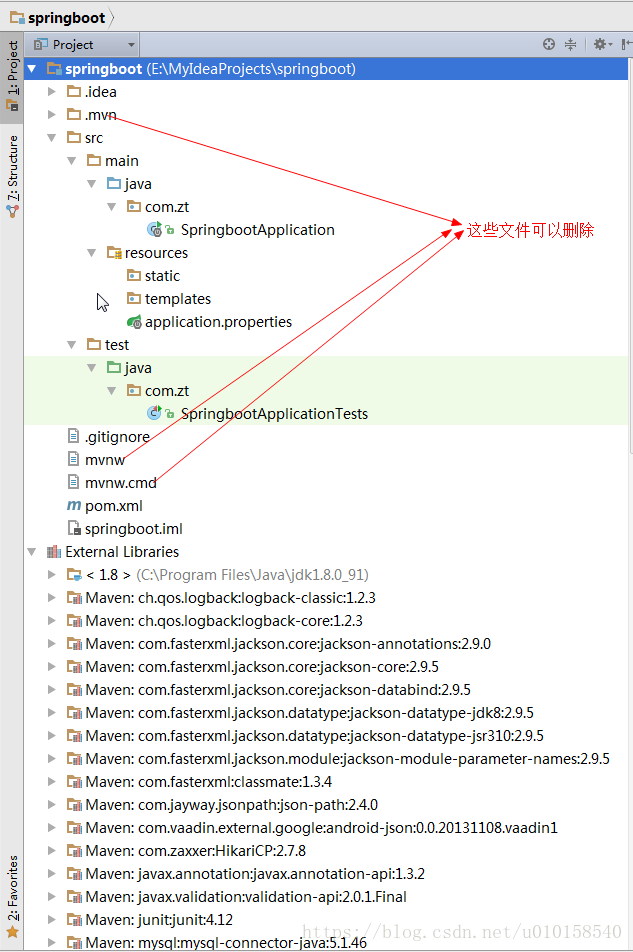
点击finlish,等待片刻,项目就初始化构建就完成了。项目架构如下:
项目架构说明:
- 初始化的项目中生成了一些无用的文件(.mvn、mvnw、mvnw.cmd)可以删除。
- 在main目录下的SpringbootApplication是项目的服务启动文件,后面我们的springboot项目启动可以通过这个文件来完成,而不再是传统的把项目打war包,在部署到tomcat中,这个步骤,springboot已经帮我们完成了。
- 在resources目录下的static目录,用于存放静态资源(images,js,css…)这是springboot默认存放的目录,当然也可以通过核心配置文件,自己指定
- 在resources目录下的templates目录,用于存放模板文件,springboot会进行渲染,当然也可以存储html,jsp等文件。
- test目录下的SpringbootApplicationTests是用于数据测试的。和传统的junit测试类似。
.xml文件如下:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org//4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org//4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.ztgroupId>
<artifactId>springbootartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<packaging>jarpackaging>
<name>springbootname>
<description>first project for Spring Bootdescription>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.3.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
这写都是我们选择好模块,idea工具自动生成的配置。
2.使用MyBatis逆向工程生成需要的model,接口和xml映射文件
在上述.xml配置文件中添加mybatis逆向工程的插件【mybatis-generator-maven-plugin】配置,用于后续的逆向生成。代码如下:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generatorgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-maven-pluginartifactId>
<version>1.3.5version>
<configuration>
<verbose>trueverbose>
<overwrite>trueoverwrite>
configuration>
plugin>
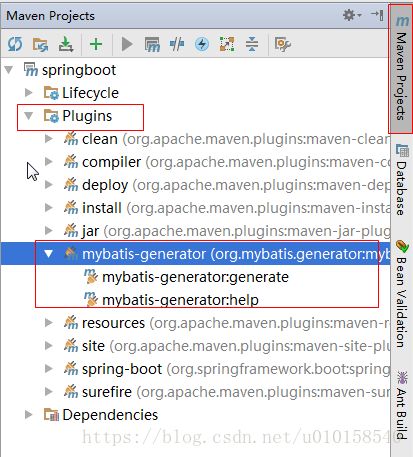
在idea右侧查看Maven Project–>Plugins下是否有一个mybatis-generator插件,如果有则表示插件配置没有问题,如图所示:
接下来,先在mysql数据库中创建一张dept表,用于测试,sql脚本如下:
create table tbl_dept(
dept_no int(6) primary key auto_increment,
dname varchar(25),
loc varchar(50)
);
接下来在src/main/resources目录下创建一个mybatis逆向工程的核心配置文件(generatorConfig.xml),用于指定生成文件所在目录,以及要涉及的数据库表指定。内容如下:
注意文件的名称需要保持一致,这样maven插件才能找到
<generatorConfiguration>
<classPathEntry location="F:\\SVN\\Document\\mysql-connector-java-5.1.44-bin.jar" />
<context id="infoGuardian" targetRuntime="MyBatis3">
<plugin type="org.mybatis.generator.plugins.SerializablePlugin">plugin>
<commentGenerator >
<property name="suppressAllComments" value="true"/>
commentGenerator>
<jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot"
userId="root"
password="root" />
<javaTypeResolver>
<property name="forceBigDecimals" value="false"/>
javaTypeResolver>
<javaModelGenerator targetPackage="com.zt.model"
targetProject="src/main/java" >
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false"/>
<property name="trimStrings" value="true"/>
javaModelGenerator>
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="mybatis/mappers"
targetProject="src/main/resources" >
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
sqlMapGenerator>
<javaClientGenerator targetPackage="com.zt.mapper" targetProject="src/main/java" type="XMLMAPPER" >
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
javaClientGenerator>
<table tableName="tbl_dept" domainObjectName="Dept" enableCountByExample="false" enableUpdateByExample="false" enableDeleteByExample="false" enableSelectByExample="false" selectByExampleQueryId="false">
<property name="useActualColumnNames" value="false" />
table>
context>
generatorConfiguration>
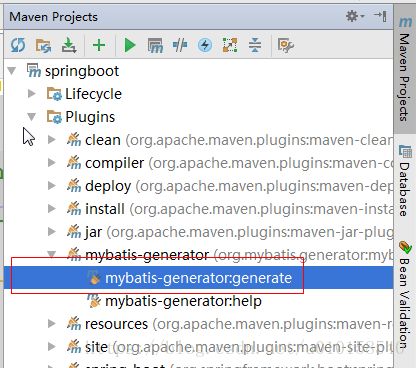
接下来,在maven插件处,找到mybatis-genterator插件,双击运行,完成逆向工程。
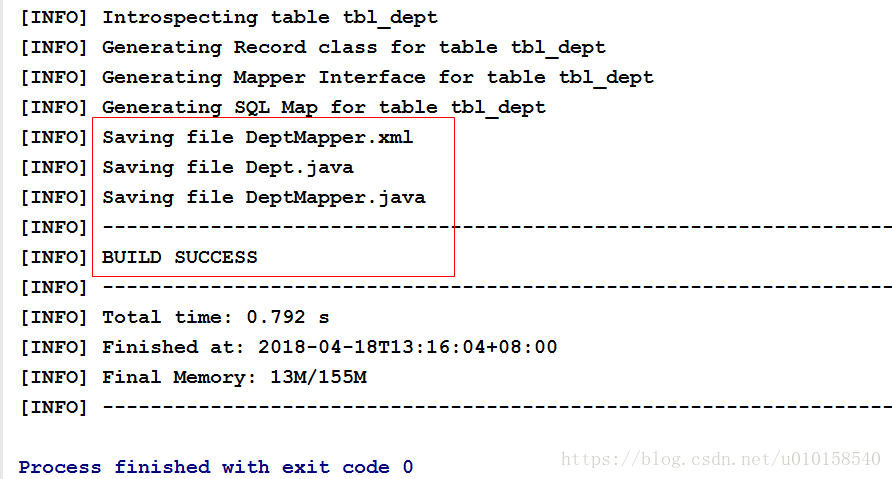
在控制台看到如下输出,证明生成成功:
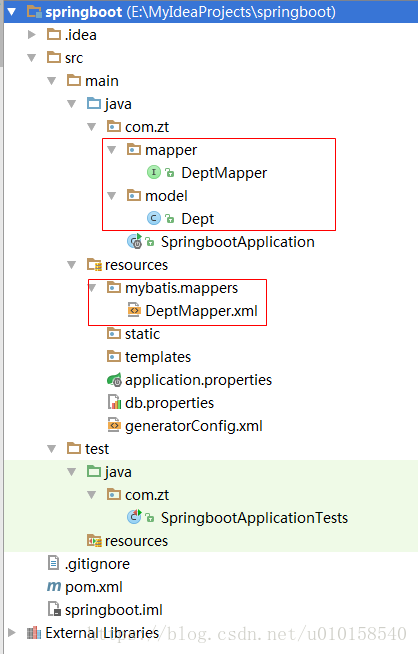
项目中生成文件如下:
src/java/com/zt/model/Dept.java
package com.zt.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Dept implements Serializable {
private Integer deptNo;
private String dname;
private String loc;
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public Integer getDeptNo() {
return deptNo;
}
public void setDeptNo(Integer deptNo) {
this.deptNo = deptNo;
}
public String getDname() {
return dname;
}
public void setDname(String dname) {
this.dname = dname == null ? null : dname.trim();
}
public String getLoc() {
return loc;
}
public void setLoc(String loc) {
this.loc = loc == null ? null : loc.trim();
}
}
src/java/com/zt/mapper/DeptMapper.java
package com.zt.mapper;
import com.zt.model.Dept;
public interface DeptMapper {
int deleteByPrimaryKey(Integer deptNo);
int insert(Dept record);
int insertSelective(Dept record);
Dept selectByPrimaryKey(Integer deptNo);
int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(Dept record);
int updateByPrimaryKey(Dept record);
}
src/main/resources/mybatis/mapper
<mapper namespace="com.zt.mapper.DeptMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.zt.model.Dept">
<id column="dept_no" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="deptNo" />
<result column="dname" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="dname" />
<result column="loc" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="loc" />
resultMap>
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
dept_no, dname, loc
sql>
<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from tbl_dept
where dept_no = #{deptNo,jdbcType=INTEGER}
select>
<delete id="deleteByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
delete from tbl_dept
where dept_no = #{deptNo,jdbcType=INTEGER}
delete>
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.zt.model.Dept">
insert into tbl_dept (dept_no, dname, loc
)
values (#{deptNo,jdbcType=INTEGER}, #{dname,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{loc,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
)
insert>
<insert id="insertSelective" parameterType="com.zt.model.Dept">
insert into tbl_dept
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="deptNo != null">
dept_no,
if>
<if test="dname != null">
dname,
if>
<if test="loc != null">
loc,
if>
trim>
<trim prefix="values (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="deptNo != null">
#{deptNo,jdbcType=INTEGER},
if>
<if test="dname != null">
#{dname,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
if>
<if test="loc != null">
#{loc,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
if>
trim>
insert>
<update id="updateByPrimaryKeySelective" parameterType="com.zt.model.Dept">
update tbl_dept
<set>
<if test="dname != null">
dname = #{dname,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
if>
<if test="loc != null">
loc = #{loc,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
if>
set>
where dept_no = #{deptNo,jdbcType=INTEGER}
update>
<update id="updateByPrimaryKey" parameterType="com.zt.model.Dept">
update tbl_dept
set dname = #{dname,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
loc = #{loc,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
where dept_no = #{deptNo,jdbcType=INTEGER}
update>
mapper>
到此逆向工程完成,接下来Mybatis框架、SpringBoot以及Mysql进行整合
3.配置SpringBoot核心配置文件完成数据源(datasource)和mybatis整合信息
先创建一个mybatis的核心配置文件,用于后面配置,保留这个文件,主要用于后续mybatis和spring的信息分离,文件信息如下:
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true" />
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="NULL" />
settings>
configuration>
在springboot核心配置文件(application.properties)中,配置服务器信息,数据源以及mybatis
#服务配置
#Tomcat端口号,默认8080
server.port = 80
#dispatcherServlet的映射路径,默认是/,方便用restful 风格操作
server.servlet.path = /
#数据源配置
spring.datasource.driver-class-name = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot
spring.datasource.username = root
spring.datasource.password = root
#mybatis框架配置
#核心配置文件路径
mybatis.config-location = classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
#Mapper映射文件路径
mybatis.mapper-locations = classpath:mybatis/mappers/*Mapper.xml
#别名配置
mybatis.type-aliases-package = com.zt.entity
配置完毕后,在src/main/java目录下找到项目的启动文件
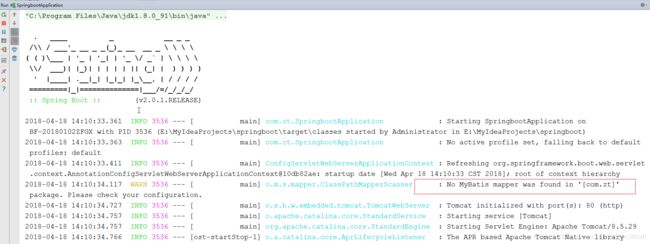
,运行该文件,查看控制台信息:
在这里显示我们没有Mybatis mapper的警告,这是因为在以前的ssm项目中,我们会在sqlsessionfactory中配置一个叫做basepack的包,让spring去扫描,而以上核心配置文件中,扫描文件这个操作已经被设置为自动扫描了,那么在这里只需要在
相应的Mapper接口上添加一个@Mapper的注解即可,或则在启动文件上添加一个@MapperScan(“com.zt.mapper”)注解,指定Mapper的扫描地址也行,本次项目中我就直接使用@Mapper来完成了。
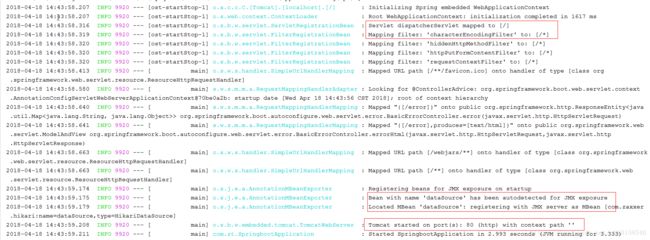
配置完毕后,再次启动查看,就没有Mybatis的警告了。
从控制台日志,可以看到核心配置文件中的配置信息已经生效,除此之外,还看到,对应的字符编码过滤器,数据源代理等,springboot都已经自己配置好了。不需要我们再去配置了。
4.整合Web模块,编写Controller控制器,Html视图完成测试
在src/main/java/com/zt目录下创建一个controller目录,并在该目录下创建一个DeptController控制器,完成添加和根据ID查询操作。
package com.zt.controller;
import com.zt.mapper.DeptMapper;
import com.zt.model.Dept;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2018/4/18.
*/
@RestController //该注解是一个组合注解(@Controller+@ResponseBody)
@RequestMapping("/dept")
public class DeptController {
/*注入deptMapper对象*/
@Autowired private DeptMapper deptMapper;
@GetMapping("/add/{dname}") //该注解是一个简写注解 @RequestMapping(value = "/add",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String add(@PathVariable("dname") String dname){
Dept dept = new Dept();
dept.setDname(dname);
dept.setLoc("重庆");
return deptMapper.insert(dept)>0?"添加成功!":"添加失败";
}
@GetMapping("/findById/{id}")
public Dept findById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return deptMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
}
}
启动项目,查看控制台日志,可以看到Controller的映射路径信息了,如下:
![]()
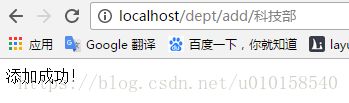
打开浏览器输入
localhost/dept/add/科技部,完成添加操作。执行完毕后,在浏览器上可以看到
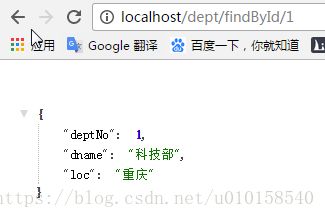
接着在调用查询方法输入地址:
localhost/dept/findById/1,完成查询操作, 执行完毕后,在浏览器上可以看到如下信息:
到此这个简单的入门案例就讲解完毕,如需源码,可以在这里下载码云下载
5.番外讲解
5.1 启动器
启动器是一组方便的依赖关系描述符,可以包含在应用程序中。 您可以获得所需的所有Spring和相关技术的一站式服务,无需通过示例代码搜索和复制粘贴依赖配置。 例如,如果要开始使用Spring和JPA进行数据库访问,那么只需在项目中包含spring-boot-starter-data-jpa依赖关系即可。
启动器包含许多依赖关系,包括您需要使项目快速启动并运行,并具有一致的受支持的依赖传递关系。
所有正式起动器都遵循类似的命名模式: spring-boot-starter- * ,其中 * 是特定类型的应用程序。 这个命名结构旨在帮助你快速找到一个启动器。
Spring Boot应用程序启动器:
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf | 使用Thymeleaf视图构建MVC Web应用程序的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-data-couchbase | 使用Couchbase面向文档的数据库和Spring Data Couchbase的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-artemis | 使用Apache Artemis的JMS启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-web-services | Spring Web Services 启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-mail | Java Mail和Spring Framework的电子邮件发送支持的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-data-redis | Redis key-value 数据存储与Spring Data Redis和Jedis客户端启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-web | 使用Spring MVC构建Web,包括RESTful应用程序。使用Tomcat作为默认的嵌入式容器的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-data-gemfire | 使用GemFire分布式数据存储和Spring Data GemFire的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-activemq | 使用Apache ActiveMQ的JMS启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch | 使用Elasticsearch搜索和分析引擎和Spring Data Elasticsearch的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-integration | Spring Integration 启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-test | 使用JUnit,Hamcrest和Mockito的库测试Spring Boot应用程序的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-jdbc | 使用JDBC与Tomcat JDBC连接池的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-mobile | 使用Spring Mobile构建Web应用程序的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-validation | 使用Java Bean Validation 与Hibernate Validator的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-hateoas | 使用Spring MVC和Spring HATEOAS构建基于超媒体的RESTful Web应用程序的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-jersey | 使用JAX-RS和Jersey构建RESTful Web应用程序的启动器。spring-boot-starter-web的替代方案 |
| spring-boot-starter-data-neo4j | 使用Neo4j图数据库和Spring Data Neo4j的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-data-ldap | 使用Spring Data LDAP的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-websocket | 使用Spring Framework的WebSocket支持构建WebSocket应用程序的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-aop | 使用Spring AOP和AspectJ进行面向切面编程的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-amqp | 使用Spring AMQP和Rabbit MQ的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra | 使用Cassandra分布式数据库和Spring Data Cassandra的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-social-facebook | 使用Spring Social Facebook 的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos | 使用Atomikos的JTA事务的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-security | 使用Spring Security的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-mustache | 使用Mustache视图构建MVC Web应用程序的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-data-jpa | 使用Spring数据JPA与Hibernate的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter | 核心启动器,包括自动配置支持,日志记录和YAML |
| spring-boot-starter-groovy-templates | 使用Groovy模板视图构建MVC Web应用程序的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-freemarker | 使用FreeMarker视图构建MVC Web应用程序的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-batch | 使用Spring Batch的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-social-linkedin | 使用Spring Social LinkedIn的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-cache | 使用Spring Framework缓存支持的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-data-solr | 使用Apache Solr搜索平台与Spring Data Solr的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb | 使用MongoDB面向文档的数据库和Spring Data MongoDB的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-jooq | 使用jOOQ访问SQL数据库的启动器。 spring-boot-starter-data-jpa或spring-boot-starter-jdbc的替代方案 |
| spring-boot-starter-jta-narayana | Spring Boot Narayana JTA 启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-cloud-connectors | 使用Spring Cloud连接器,简化了与Cloud Foundry和Heroku等云平台中的服务连接的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-jta-bitronix | 使用Bitronix进行JTA 事务的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-social-twitter | 使用Spring Social Twitter的启动器 |
| spring-boot-starter-data-rest | 通过使用Spring Data REST在REST上暴露Spring数据库的启动器 |
5.2 常用的核心文件配置信息表
banner.charset=UTF-8 # Banner file encoding.
banner.location=classpath:banner.txt # Banner file location.
banner.image.location=classpath:banner.gif # Banner image file location (jpg/png can also be used).
banner.image.width= # Width of the banner image in chars (default 76)
banner.image.height= # Height of the banner image in chars (default based on image height)
banner.image.margin= # Left hand image margin in chars (default 2)
banner.image.invert= # If images should be inverted for dark terminal themes (default false)
# LOGGING
logging.config= # Location of the logging configuration file. For instance `classpath:logback.xml` for Logback
logging.exception-conversion-word=%wEx # Conversion word used when logging exceptions.
logging.file= # Log file name. For instance `myapp.log`
logging.level.*= # Log levels severity mapping. For instance `logging.level.org.springframework=DEBUG`
logging.path= # Location of the log file. For instance `/var/log`
logging.pattern.console= # Appender pattern for output to the console. Only supported with the default logback setup.
logging.pattern.file= # Appender pattern for output to the file. Only supported with the default logback setup.
logging.pattern.level= # Appender pattern for log level (default %5p). Only supported with the default logback setup.
logging.register-shutdown-hook=false # Register a shutdown hook for the logging system when it is initialized.
# AOP
spring.aop.auto=true # Add @EnableAspectJAutoProxy.
spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false # Whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created (true) as opposed to standard Java interface-based proxies (false).
# IDENTITY (ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer)
spring.application.index= # Application index.
spring.application.name= # Application name.
# ADMIN (SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration)
spring.application.admin.enabled=false # Enable admin features for the application.
spring.application.admin.jmx-name=org.springframework.boot:type=Admin,name=SpringApplication # JMX name of the application admin MBean.
# AUTO-CONFIGURATION
spring.autoconfigure.exclude= # Auto-configuration classes to exclude.
# SPRING CORE
spring.beaninfo.ignore=true # Skip search of BeanInfo classes.
# SPRING CACHE (CacheProperties)
spring.cache.cache-names= # Comma-separated list of cache names to create if supported by the underlying cache manager.
spring.cache.caffeine.spec= # The spec to use to create caches. Check CaffeineSpec for more details on the spec format.
spring.cache.couchbase.expiration=0 # Entry expiration in milliseconds. By default the entries never expire.
spring.cache.ehcache.config= # The location of the configuration file to use to initialize EhCache.
spring.cache.guava.spec= # The spec to use to create caches. Check CacheBuilderSpec for more details on the spec format.
spring.cache.infinispan.config= # The location of the configuration file to use to initialize Infinispan.
spring.cache.jcache.config= # The location of the configuration file to use to initialize the cache manager.
spring.cache.jcache.provider= # Fully qualified name of the CachingProvider implementation to use to retrieve the JSR-107 compliant cache manager. Only needed if more than one JSR-107 implementation is available on the classpath.
spring.cache.type= # Cache type, auto-detected according to the environment by default.
# SPRING CONFIG - using environment property only (ConfigFileApplicationListener)
spring.config.location= # Config file locations.
spring.config.name=application # Config file name.
# HAZELCAST (HazelcastProperties)
spring.hazelcast.config= # The location of the configuration file to use to initialize Hazelcast.
# PROJECT INFORMATION (ProjectInfoProperties)
spring.info.build.location=classpath:META-INF/build-info.properties # Location of the generated build-info.properties file.
spring.info.git.location=classpath:git.properties # Location of the generated git.properties file.
# JMX
spring.jmx.default-domain= # JMX domain name.
spring.jmx.enabled=true # Expose management beans to the JMX domain.
spring.jmx.server=mbeanServer # MBeanServer bean name.
# Email (MailProperties)
spring.mail.default-encoding=UTF-8 # Default MimeMessage encoding.
spring.mail.host= # SMTP server host. For instance `smtp.example.com`
spring.mail.jndi-name= # Session JNDI name. When set, takes precedence to others mail settings.
spring.mail.password= # Login password of the SMTP server.
spring.mail.port= # SMTP server port.
spring.mail.properties.*= # Additional JavaMail session properties.
spring.mail.protocol=smtp # Protocol used by the SMTP server.
spring.mail.test-connection=false # Test that the mail server is available on startup.
spring.mail.username= # Login user of the SMTP server.
# APPLICATION SETTINGS (SpringApplication)
spring.main.banner-mode=console # Mode used to display the banner when the application runs.
spring.main.sources= # Sources (class name, package name or XML resource location) to include in the ApplicationContext.
spring.main.web-environment= # Run the application in a web environment (auto-detected by default).
# FILE ENCODING (FileEncodingApplicationListener)
spring.mandatory-file-encoding= # Expected character encoding the application must use.
# INTERNATIONALIZATION (MessageSourceAutoConfiguration)
spring.messages.always-use-message-format=false # Set whether to always apply the MessageFormat rules, parsing even messages without arguments.
spring.messages.basename=messages # Comma-separated list of basenames, each following the ResourceBundle convention.
spring.messages.cache-seconds=-1 # Loaded resource bundle files cache expiration, in seconds. When set to -1, bundles are cached forever.
spring.messages.encoding=UTF-8 # Message bundles encoding.
spring.messages.fallback-to-system-locale=true # Set whether to fall back to the system Locale if no files for a specific Locale have been found.
# PROFILES
spring.profiles.active= # Comma-separated list (or list if using YAML) of active profiles.
spring.profiles.include= # Unconditionally activate the specified comma separated profiles (or list of profiles if using YAML).
# ----------------------------------------
# WEB PROPERTIES
# ----------------------------------------
# EMBEDDED SERVER CONFIGURATION (ServerProperties)
server.address= # Network address to which the server should bind to.
server.compression.enabled=false # If response compression is enabled.
server.compression.excluded-user-agents= # List of user-agents to exclude from compression.
server.compression.mime-types= # Comma-separated list of MIME types that should be compressed. For instance `text/html,text/css,application/json`
server.compression.min-response-size= # Minimum response size that is required for compression to be performed. For instance 2048
server.connection-timeout= # Time in milliseconds that connectors will wait for another HTTP request before closing the connection. When not set, the connector's container-specific default will be used. Use a value of -1 to indicate no (i.e. infinite) timeout.
server.context-parameters.*= # Servlet context init parameters. For instance `server.context-parameters.a=alpha`
server.context-path= # Context path of the application.
server.display-name=application # Display name of the application.
server.max-http-header-size=0 # Maximum size in bytes of the HTTP message header.
server.error.include-stacktrace=never # When to include a "stacktrace" attribute.
server.error.path=/error # Path of the error controller.
server.error.whitelabel.enabled=true # Enable the default error page displayed in browsers in case of a server error.
server.jetty.acceptors= # Number of acceptor threads to use.
server.jetty.max-http-post-size=0 # Maximum size in bytes of the HTTP post or put content.
server.jetty.selectors= # Number of selector threads to use.
server.jsp-servlet.class-name=org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet # The class name of the JSP servlet.
server.jsp-servlet.init-parameters.*= # Init parameters used to configure the JSP servlet
server.jsp-servlet.registered=true # Whether or not the JSP servlet is registered
server.port=8080 # Server HTTP port.
server.server-header= # Value to use for the Server response header (no header is sent if empty)
server.servlet-path=/ # Path of the main dispatcher servlet.
server.use-forward-headers= # If X-Forwarded-* headers should be applied to the HttpRequest.
server.session.cookie.comment= # Comment for the session cookie.
server.session.cookie.domain= # Domain for the session cookie.
server.session.cookie.http-only= # "HttpOnly" flag for the session cookie.
server.session.cookie.max-age= # Maximum age of the session cookie in seconds.
server.session.cookie.name= # Session cookie name.
server.session.cookie.path= # Path of the session cookie.
server.session.cookie.secure= # "Secure" flag for the session cookie.
server.session.persistent=false # Persist session data between restarts.
server.session.store-dir= # Directory used to store session data.
server.session.timeout= # Session timeout in seconds.
server.session.tracking-modes= # Session tracking modes (one or more of the following: "cookie", "url", "ssl").
server.ssl.ciphers= # Supported SSL ciphers.
server.ssl.client-auth= # Whether client authentication is wanted ("want") or needed ("need"). Requires a trust store.
server.ssl.enabled= # Enable SSL support.
server.ssl.enabled-protocols= # Enabled SSL protocols.
server.ssl.key-alias= # Alias that identifies the key in the key store.
server.ssl.key-password= # Password used to access the key in the key store.
server.ssl.key-store= # Path to the key store that holds the SSL certificate (typically a jks file).
server.ssl.key-store-password= # Password used to access the key store.
server.ssl.key-store-provider= # Provider for the key store.
server.ssl.key-store-type= # Type of the key store.
server.ssl.protocol=TLS # SSL protocol to use.
server.ssl.trust-store= # Trust store that holds SSL certificates.
server.ssl.trust-store-password= # Password used to access the trust store.
server.ssl.trust-store-provider= # Provider for the trust store.
server.ssl.trust-store-type= # Type of the trust store.
server.tomcat.accept-count= # Maximum queue length for incoming connection requests when all possible request processing threads are in use.
server.tomcat.accesslog.buffered=true # Buffer output such that it is only flushed periodically.
server.tomcat.accesslog.directory=logs # Directory in which log files are created. Can be relative to the tomcat base dir or absolute.
server.tomcat.accesslog.enabled=false # Enable access log.
server.tomcat.accesslog.pattern=common # Format pattern for access logs.
server.tomcat.accesslog.prefix=access_log # Log file name prefix.
server.tomcat.accesslog.rename-on-rotate=false # Defer inclusion of the date stamp in the file name until rotate time.
server.tomcat.accesslog.request-attributes-enabled=false # Set request attributes for IP address, Hostname, protocol and port used for the request.
server.tomcat.accesslog.rotate=true # Enable access log rotation.
server.tomcat.accesslog.suffix=.log # Log file name suffix.
server.tomcat.additional-tld-skip-patterns= # Comma-separated list of additional patterns that match jars to ignore for TLD scanning.
server.tomcat.background-processor-delay=30 # Delay in seconds between the invocation of backgroundProcess methods.
server.tomcat.basedir= # Tomcat base directory. If not specified a temporary directory will be used.
server.tomcat.internal-proxies=10\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|\\
192\\.168\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|\\
169\\.254\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|\\
127\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|\\
172\\.1[6-9]{1}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|\\
172\\.2[0-9]{1}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3}|\\
172\\.3[0-1]{1}\\.\\d{1,3}\\.\\d{1,3} # regular expression matching trusted IP addresses.
server.tomcat.max-connections= # Maximum number of connections that the server will accept and process at any given time.
server.tomcat.max-http-post-size=0 # Maximum size in bytes of the HTTP post content.
server.tomcat.max-threads=0 # Maximum amount of worker threads.
server.tomcat.min-spare-threads=0 # Minimum amount of worker threads.
server.tomcat.port-header=X-Forwarded-Port # Name of the HTTP header used to override the original port value.
server.tomcat.protocol-header= # Header that holds the incoming protocol, usually named "X-Forwarded-Proto".
server.tomcat.protocol-header-https-value=https # Value of the protocol header that indicates that the incoming request uses SSL.
server.tomcat.redirect-context-root= # Whether requests to the context root should be redirected by appending a / to the path.
server.tomcat.remote-ip-header= # Name of the http header from which the remote ip is extracted. For instance `X-FORWARDED-FOR`
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=UTF-8 # Character encoding to use to decode the URI.
server.undertow.accesslog.dir= # Undertow access log directory.
server.undertow.accesslog.enabled=false # Enable access log.
server.undertow.accesslog.pattern=common # Format pattern for access logs.
server.undertow.accesslog.prefix=access_log. # Log file name prefix.
server.undertow.accesslog.rotate=true # Enable access log rotation.
server.undertow.accesslog.suffix=log # Log file name suffix.
server.undertow.buffer-size= # Size of each buffer in bytes.
server.undertow.buffers-per-region= # Number of buffer per region.
server.undertow.direct-buffers= # Allocate buffers outside the Java heap.
server.undertow.io-threads= # Number of I/O threads to create for the worker.
server.undertow.max-http-post-size=0 # Maximum size in bytes of the HTTP post content.
server.undertow.worker-threads= # Number of worker threads.
# FREEMARKER (FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration)
spring.freemarker.allow-request-override=false # Set whether HttpServletRequest attributes are allowed to override (hide) controller generated model attributes of the same name.
spring.freemarker.allow-session-override=false # Set whether HttpSession attributes are allowed to override (hide) controller generated model attributes of the same name.
spring.freemarker.cache=false # Enable template caching.
spring.freemarker.charset=UTF-8 # Template encoding.
spring.freemarker.check-template-location=true # Check that the templates location exists.
spring.freemarker.content-type=text/html # Content-Type value.
spring.freemarker.enabled=true # Enable MVC view resolution for this technology.
spring.freemarker.expose-request-attributes=false # Set whether all request attributes should be added to the model prior to merging with the template.
spring.freemarker.expose-session-attributes=false # Set whether all HttpSession attributes should be added to the model prior to merging with the template.
spring.freemarker.expose-spring-macro-helpers=true # Set whether to expose a RequestContext for use by Spring's macro library, under the name "springMacroRequestContext".
spring.freemarker.prefer-file-system-access=true # Prefer file system access for template loading. File system access enables hot detection of template changes.
spring.freemarker.prefix= # Prefix that gets prepended to view names when building a URL.
spring.freemarker.request-context-attribute= # Name of the RequestContext attribute for all views.
spring.freemarker.settings.*= # Well-known FreeMarker keys which will be passed to FreeMarker's Configuration.
spring.freemarker.suffix= # Suffix that gets appended to view names when building a URL.
spring.freemarker.template-loader-path=classpath:/templates/ # Comma-separated list of template paths.
spring.freemarker.view-names= # White list of view names that can be resolved.
# GROOVY TEMPLATES (GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration)
spring.groovy.template.allow-request-override=false # Set whether HttpServletRequest attributes are allowed to override (hide) controller generated model attributes of the same name.
spring.groovy.template.allow-session-override=false # Set whether HttpSession attributes are allowed to override (hide) controller generated model attributes of the same name.
spring.groovy.template.cache= # Enable template caching.
spring.groovy.template.charset=UTF-8 # Template encoding.
spring.groovy.template.check-template-location=true # Check that the templates location exists.
spring.groovy.template.configuration.*= # See GroovyMarkupConfigurer
spring.groovy.template.content-type=test/html # Content-Type value.
spring.groovy.template.enabled=true # Enable MVC view resolution for this technology.
spring.groovy.template.expose-request-attributes=false # Set whether all request attributes should be added to the model prior to merging with the template.
spring.groovy.template.expose-session-attributes=false # Set whether all HttpSession attributes should be added to the model prior to merging with the template.
spring.groovy.template.expose-spring-macro-helpers=true # Set whether to expose a RequestContext for use by Spring's macro library, under the name "springMacroRequestContext".
spring.groovy.template.prefix= # Prefix that gets prepended to view names when building a URL.
spring.groovy.template.request-context-attribute= # Name of the RequestContext attribute for all views.
spring.groovy.template.resource-loader-path=classpath:/templates/ # Template path.
spring.groovy.template.suffix=.tpl # Suffix that gets appended to view names when building a URL.
spring.groovy.template.view-names= # White list of view names that can be resolved.
# SPRING HATEOAS (HateoasProperties)
spring.hateoas.use-hal-as-default-json-media-type=true # Specify if application/hal+json responses should be sent to requests that accept application/json.
# HTTP message conversion
spring.http.converters.preferred-json-mapper=jackson # Preferred JSON mapper to use for HTTP message conversion. Set to "gson" to force the use of Gson when both it and Jackson are on the classpath.
# HTTP encoding (HttpEncodingProperties)
spring.http.encoding.charset=UTF-8 # Charset of HTTP requests and responses. Added to the "Content-Type" header if not set explicitly.
spring.http.encoding.enabled=true # Enable http encoding support.
spring.http.encoding.force= # Force the encoding to the configured charset on HTTP requests and responses.
spring.http.encoding.force-request= # Force the encoding to the configured charset on HTTP requests. Defaults to true when "force" has not been specified.
spring.http.encoding.force-response= # Force the encoding to the configured charset on HTTP responses.
spring.http.encoding.mapping= # Locale to Encoding mapping.
# MULTIPART (MultipartProperties)
spring.http.multipart.enabled=true # Enable support of multi-part uploads.
spring.http.multipart.file-size-threshold=0 # Threshold after which files will be written to disk. Values can use the suffixed "MB" or "KB" to indicate a Megabyte or Kilobyte size.
spring.http.multipart.location= # Intermediate location of uploaded files.
spring.http.multipart.max-file-size=1MB # Max file size. Values can use the suffixed "MB" or "KB" to indicate a Megabyte or Kilobyte size.
spring.http.multipart.max-request-size=10MB # Max request size. Values can use the suffixed "MB" or "KB" to indicate a Megabyte or Kilobyte size.
spring.http.multipart.resolve-lazily=false # Whether to resolve the multipart request lazily at the time of file or parameter access.
# JACKSON (JacksonProperties)
spring.jackson.date-format= # Date format string or a fully-qualified date format class name. For instance `yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss`.
spring.jackson.default-property-inclusion= # Controls the inclusion of properties during serialization.
spring.jackson.deserialization.*= # Jackson on/off features that affect the way Java objects are deserialized.
spring.jackson.generator.*= # Jackson on/off features for generators.
spring.jackson.joda-date-time-format= # Joda date time format string. If not configured, "date-format" will be used as a fallback if it is configured with a format string.
spring.jackson.locale= # Locale used for formatting.
spring.jackson.mapper.*= # Jackson general purpose on/off features.
spring.jackson.parser.*= # Jackson on/off features for parsers.
spring.jackson.property-naming-strategy= # One of the constants on Jackson's PropertyNamingStrategy. Can also be a fully-qualified class name of a PropertyNamingStrategy subclass.
spring.jackson.serialization.*= # Jackson on/off features that affect the way Java objects are serialized.
spring.jackson.time-zone= # Time zone used when formatting dates. For instance `America/Los_Angeles`
# JERSEY (JerseyProperties)
spring.jersey.application-path= # Path that serves as the base URI for the application. Overrides the value of "@ApplicationPath" if specified.
spring.jersey.filter.order=0 # Jersey filter chain order.
spring.jersey.init.*= # Init parameters to pass to Jersey via the servlet or filter.
spring.jersey.servlet.load-on-startup=-1 # Load on startup priority of the Jersey servlet.
spring.jersey.type=servlet # Jersey integration type.
# SPRING LDAP (LdapProperties)
spring.ldap.urls= # LDAP URLs of the server.
spring.ldap.base= # Base suffix from which all operations should originate.
spring.ldap.username= # Login user of the server.
spring.ldap.password= # Login password of the server.
spring.ldap.base-environment.*= # LDAP specification settings.
# EMBEDDED LDAP (EmbeddedLdapProperties)
spring.ldap.embedded.base-dn= # The base DN
spring.ldap.embedded.credential.username= # Embedded LDAP username.
spring.ldap.embedded.credential.password= # Embedded LDAP password.
spring.ldap.embedded.ldif=classpath:schema.ldif # Schema (LDIF) script resource reference.
spring.ldap.embedded.port= # Embedded LDAP port.
spring.ldap.embedded.validation.enabled=true # Enable LDAP schema validation.
spring.ldap.embedded.validation.schema= # Path to the custom schema.
# SPRING MOBILE DEVICE VIEWS (DeviceDelegatingViewResolverAutoConfiguration)
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.enable-fallback=false # Enable support for fallback resolution.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.enabled=false # Enable device view resolver.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.mobile-prefix=mobile/ # Prefix that gets prepended to view names for mobile devices.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.mobile-suffix= # Suffix that gets appended to view names for mobile devices.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.normal-prefix= # Prefix that gets prepended to view names for normal devices.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.normal-suffix= # Suffix that gets appended to view names for normal devices.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.tablet-prefix=tablet/ # Prefix that gets prepended to view names for tablet devices.
spring.mobile.devicedelegatingviewresolver.tablet-suffix= # Suffix that gets appended to view names for tablet devices.
# SPRING MOBILE SITE PREFERENCE (SitePreferenceAutoConfiguration)
spring.mobile.sitepreference.enabled=true # Enable SitePreferenceHandler.
# MUSTACHE TEMPLATES (MustacheAutoConfiguration)
spring.mustache.allow-request-override= # Set whether HttpServletRequest attributes are allowed to override (hide) controller generated model attributes of the same name.
spring.mustache.allow-session-override= # Set whether HttpSession attributes are allowed to override (hide) controller generated model attributes of the same name.
spring.mustache.cache= # Enable template caching.
spring.mustache.charset= # Template encoding.
spring.mustache.check-template-location= # Check that the templates location exists.
spring.mustache.content-type= # Content-Type value.
spring.mustache.enabled= # Enable MVC view resolution for this technology.
spring.mustache.expose-request-attributes= # Set whether all request attributes should be added to the model prior to merging with the template.
spring.mustache.expose-session-attributes= # Set whether all HttpSession attributes should be added to the model prior to merging with the template.
spring.mustache.expose-spring-macro-helpers= # Set whether to expose a RequestContext for use by Spring's macro library, under the name "springMacroRequestContext".
spring.mustache.prefix=classpath:/templates/ # Prefix to apply to template names.
spring.mustache.request-context-attribute= # Name of the RequestContext attribute for all views.
spring.mustache.suffix=.html # Suffix to apply to template names.
spring.mustache.view-names= # White list of view names that can be resolved.
# SPRING MVC (WebMvcProperties)
spring.mvc.async.request-timeout= # Amount of time (in milliseconds) before asynchronous request handling times out.
spring.mvc.date-format= # Date format to use. For instance `dd/MM/yyyy`.
spring.mvc.dispatch-trace-request=false # Dispatch TRACE requests to the FrameworkServlet doService method.
spring.mvc.dispatch-options-request=true # Dispatch OPTIONS requests to the FrameworkServlet doService method.
spring.mvc.favicon.enabled=true # Enable resolution of favicon.ico.
spring.mvc.formcontent.putfilter.enabled=true # Enable Spring's HttpPutFormContentFilter.
spring.mvc.ignore-default-model-on-redirect=true # If the content of the "default" model should be ignored during redirect scenarios.
spring.mvc.locale= # Locale to use. By default, this locale is overridden by the "Accept-Language" header.
spring.mvc.locale-resolver=accept-header # Define how the locale should be resolved.
spring.mvc.log-resolved-exception=false # Enable warn logging of exceptions resolved by a "HandlerExceptionResolver".
spring.mvc.media-types.*= # Maps file extensions to media types for content negotiation.
spring.mvc.message-codes-resolver-format= # Formatting strategy for message codes. For instance `PREFIX_ERROR_CODE`.
spring.mvc.servlet.load-on-startup=-1 # Load on startup priority of the Spring Web Services servlet.
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/** # Path pattern used for static resources.
spring.mvc.throw-exception-if-no-handler-found=false # If a "NoHandlerFoundException" should be thrown if no Handler was found to process a request.
spring.mvc.view.prefix= # Spring MVC view prefix.
spring.mvc.view.suffix= # Spring MVC view suffix.
# SPRING RESOURCES HANDLING (ResourceProperties)
spring.resources.add-mappings=true # Enable default resource handling.
spring.resources.cache-period= # Cache period for the resources served by the resource handler, in seconds.
spring.resources.chain.cache=true # Enable caching in the Resource chain.
spring.resources.chain.enabled= # Enable the Spring Resource Handling chain. Disabled by default unless at least one strategy has been enabled.
spring.resources.chain.gzipped=false # Enable resolution of already gzipped resources.
spring.resources.chain.html-application-cache=false # Enable HTML5 application cache manifest rewriting.
spring.resources.chain.strategy.content.enabled=false # Enable the content Version Strategy.
spring.resources.chain.strategy.content.paths=/** # Comma-separated list of patterns to apply to the Version Strategy.
spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.enabled=false # Enable the fixed Version Strategy.
spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.paths=/** # Comma-separated list of patterns to apply to the Version Strategy.
spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.version= # Version string to use for the Version Strategy.
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/META-INF/resources/,classpath:/resources/,classpath:/static/,classpath:/public/ # Locations of static resources.
# SPRING SESSION (SessionProperties)
spring.session.hazelcast.flush-mode=on-save # Sessions flush mode.
spring.session.hazelcast.map-name=spring:session:sessions # Name of the map used to store sessions.
spring.session.jdbc.initializer.enabled= # Create the required session tables on startup if necessary. Enabled automatically if the default table name is set or a custom schema is configured.
spring.session.jdbc.schema=classpath:org/springframework/session/jdbc/schema-@@platform@@.sql # Path to the SQL file to use to initialize the database schema.
spring.session.jdbc.table-name=SPRING_SESSION # Name of database table used to store sessions.
spring.session.mongo.collection-name=sessions # Collection name used to store sessions.
spring.session.redis.flush-mode=on-save # Sessions flush mode.
spring.session.redis.namespace= # Namespace for keys used to store sessions.
spring.session.store-type= # Session store type.
# SPRING SOCIAL (SocialWebAutoConfiguration)
spring.social.auto-connection-views=false # Enable the connection status view for supported providers.
# SPRING SOCIAL FACEBOOK (FacebookAutoConfiguration)
spring.social.facebook.app-id= # your application's Facebook App ID
spring.social.facebook.app-secret= # your application's Facebook App Secret
# SPRING SOCIAL LINKEDIN (LinkedInAutoConfiguration)
spring.social.linkedin.app-id= # your application's LinkedIn App ID
spring.social.linkedin.app-secret= # your application's LinkedIn App Secret
# SPRING SOCIAL TWITTER (TwitterAutoConfiguration)
spring.social.twitter.app-id= # your application's Twitter App ID
spring.social.twitter.app-secret= # your application's Twitter App Secret
# THYMELEAF (ThymeleafAutoConfiguration)
spring.thymeleaf.cache=true # Enable template caching.
spring.thymeleaf.check-template=true # Check that the template exists before rendering it.
spring.thymeleaf.check-template-location=true # Check that the templates location exists.
spring.thymeleaf.content-type=text/html # Content-Type value.
spring.thymeleaf.enabled=true # Enable MVC Thymeleaf view resolution.
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8 # Template encoding.
spring.thymeleaf.excluded-view-names= # Comma-separated list of view names that should be excluded from resolution.
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5 # Template mode to be applied to templates. See also StandardTemplateModeHandlers.
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/ # Prefix that gets prepended to view names when building a URL.
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html # Suffix that gets appended to view names when building a URL.
spring.thymeleaf.template-resolver-order= # Order of the template resolver in the chain.
spring.thymeleaf.view-names= # Comma-separated list of view names that can be resolved.
# SPRING WEB SERVICES (WebServicesProperties)
spring.webservices.path=/services # Path that serves as the base URI for the services.
spring.webservices.servlet.init= # Servlet init parameters to pass to Spring Web Services.
spring.webservices.servlet.load-on-startup=-1 # Load on startup priority of the Spring Web Services servlet.
# ----------------------------------------
# SECURITY PROPERTIES
# ----------------------------------------
# SECURITY (SecurityProperties)
security.basic.authorize-mode=role # Security authorize mode to apply.
security.basic.enabled=true # Enable basic authentication.
security.basic.path=/** # Comma-separated list of paths to secure.
security.basic.realm=Spring # HTTP basic realm name.
security.enable-csrf=false # Enable Cross Site Request Forgery support.
security.filter-order=0 # Security filter chain order.
security.filter-dispatcher-types=ASYNC, FORWARD, INCLUDE, REQUEST # Security filter chain dispatcher types.
security.headers.cache=true # Enable cache control HTTP headers.
security.headers.content-security-policy= # Value for content security policy header.
security.headers.content-security-policy-mode=default # Content security policy mode.
security.headers.content-type=true # Enable "X-Content-Type-Options" header.
security.headers.frame=true # Enable "X-Frame-Options" header.
security.headers.hsts=all # HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) mode (none, domain, all).
security.headers.xss=true # Enable cross site scripting (XSS) protection.
security.ignored= # Comma-separated list of paths to exclude from the default secured paths.
security.require-ssl=false # Enable secure channel for all requests.
security.sessions=stateless # Session creation policy (always, never, if_required, stateless).
security.user.name=user # Default user name.
security.user.password= # Password for the default user name. A random password is logged on startup by default.
security.user.role=USER # Granted roles for the default user name.
# SECURITY OAUTH2 CLIENT (OAuth2ClientProperties)
security.oauth2.client.client-id= # OAuth2 client id.
security.oauth2.client.client-secret= # OAuth2 client secret. A random secret is generated by default
# SECURITY OAUTH2 RESOURCES (ResourceServerProperties)
security.oauth2.resource.filter-order= # The order of the filter chain used to authenticate tokens.
security.oauth2.resource.id= # Identifier of the resource.
security.oauth2.resource.jwt.key-uri= # The URI of the JWT token. Can be set if the value is not available and the key is public.
security.oauth2.resource.jwt.key-value= # The verification key of the JWT token. Can either be a symmetric secret or PEM-encoded RSA public key.
security.oauth2.resource.prefer-token-info=true # Use the token info, can be set to false to use the user info.
security.oauth2.resource.service-id=resource #
security.oauth2.resource.token-info-uri= # URI of the token decoding endpoint.
security.oauth2.resource.token-type= # The token type to send when using the userInfoUri.
security.oauth2.resource.user-info-uri= # URI of the user endpoint.
# SECURITY OAUTH2 SSO (OAuth2SsoProperties)
security.oauth2.sso.filter-order= # Filter order to apply if not providing an explicit WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
security.oauth2.sso.login-path=/login # Path to the login page, i.e. the one that triggers the redirect to the OAuth2 Authorization Server
# MONGODB (MongoProperties)
spring.data.mongodb.authentication-database= # Authentication database name.
spring.data.mongodb.database=test # Database name.
spring.data.mongodb.field-naming-strategy= # Fully qualified name of the FieldNamingStrategy to use.
spring.data.mongodb.grid-fs-database= # GridFS database name.
spring.data.mongodb.host=localhost # Mongo server host. Cannot be set with uri.
spring.data.mongodb.password= # Login password of the mongo server. Cannot be set with uri.
spring.data.mongodb.port=27017 # Mongo server port. Cannot be set with uri.
spring.data.mongodb.repositories.enabled=true # Enable Mongo repositories.
spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://localhost/test # Mongo database URI. Cannot be set with host, port and credentials.
spring.data.mongodb.username= # Login user of the mongo server. Cannot be set with uri.
# DATA REDIS
spring.data.redis.repositories.enabled=true # Enable Redis repositories.
# SOLR (SolrProperties)
spring.data.solr.host=http://127.0.0.1:8983/solr # Solr host. Ignored if "zk-host" is set.
spring.data.solr.repositories.enabled=true # Enable Solr repositories.
spring.data.solr.zk-host= # ZooKeeper host address in the form HOST:PORT.
# DATASOURCE (DataSourceAutoConfiguration & DataSourceProperties)
spring.datasource.continue-on-error=false # Do not stop if an error occurs while initializing the database.
spring.datasource.data= # Data (DML) script resource references.
spring.datasource.data-username= # User of the database to execute DML scripts (if different).
spring.datasource.data-password= # Password of the database to execute DML scripts (if different).
spring.datasource.dbcp2.*= # Commons DBCP2 specific settings
spring.datasource.driver-class-name= # Fully qualified name of the JDBC driver. Auto-detected based on the URL by default.
spring.datasource.generate-unique-name=false # Generate a random datasource name.
spring.datasource.hikari.*= # Hikari specific settings
spring.datasource.initialize=true # Populate the database using 'data.sql'.
spring.datasource.jmx-enabled=false # Enable JMX support (if provided by the underlying pool).
spring.datasource.jndi-name= # JNDI location of the datasource. Class, url, username & password are ignored when set.
spring.datasource.name=testdb # Name of the datasource.
spring.datasource.password= # Login password of the database.
spring.datasource.platform=all # Platform to use in the schema resource (schema-${platform}.sql).
spring.datasource.schema= # Schema (DDL) script resource references.
spring.datasource.schema-username= # User of the database to execute DDL scripts (if different).
spring.datasource.schema-password= # Password of the database to execute DDL scripts (if different).
spring.datasource.separator=; # Statement separator in SQL initialization scripts.
spring.datasource.sql-script-encoding= # SQL scripts encoding.
spring.datasource.tomcat.*= # Tomcat datasource specific settings
spring.datasource.type= # Fully qualified name of the connection pool implementation to use. By default, it is auto-detected from the classpath.
spring.datasource.url= # JDBC url of the database.
spring.datasource.username=
# JPA (JpaBaseConfiguration, HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration)
spring.data.jpa.repositories.enabled=true # Enable JPA repositories.
spring.jpa.database= # Target database to operate on, auto-detected by default. Can be alternatively set using the "databasePlatform" property.
spring.jpa.database-platform= # Name of the target database to operate on, auto-detected by default. Can be alternatively set using the "Database" enum.
spring.jpa.generate-ddl=false # Initialize the schema on startup.
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto= # DDL mode. This is actually a shortcut for the "hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" property. Default to "create-drop" when using an embedded database, "none" otherwise.
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.implicit-strategy= # Hibernate 5 implicit naming strategy fully qualified name.
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.physical-strategy= # Hibernate 5 physical naming strategy fully qualified name.
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.strategy= # Hibernate 4 naming strategy fully qualified name. Not supported with Hibernate 5.
spring.jpa.hibernate.use-new-id-generator-mappings= # Use Hibernate's newer IdentifierGenerator for AUTO, TABLE and SEQUENCE.
spring.jpa.open-in-view=true # Register OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor. Binds a JPA EntityManager to the thread for the entire processing of the request.
spring.jpa.properties.*= # Additional native properties to set on the JPA provider.
spring.jpa.show-sql=false # Enable logging of SQL statements.
# EMBEDDED MONGODB (EmbeddedMongoProperties)
spring.mongodb.embedded.features=SYNC_DELAY # Comma-separated list of features to enable.
spring.mongodb.embedded.storage.database-dir= # Directory used for data storage.
spring.mongodb.embedded.storage.oplog-size= # Maximum size of the oplog in megabytes.
spring.mongodb.embedded.storage.repl-set-name= # Name of the replica set.
spring.mongodb.embedded.version=2.6.10 # Version of Mongo to use.
# REDIS (RedisProperties)
spring.redis.cluster.max-redirects= # Maximum number of redirects to follow when executing commands across the cluster.
spring.redis.cluster.nodes= # Comma-separated list of "host:port" pairs to bootstrap from.
spring.redis.database=0 # Database index used by the connection factory.
spring.redis.url= # Connection URL, will override host, port and password (user will be ignored), e.g. redis://user:[email protected]:6379
spring.redis.host=localhost # Redis server host.
spring.redis.password= # Login password of the redis server.
spring.redis.ssl=false # Enable SSL support.
spring.redis.pool.max-active=8 # Max number of connections that can be allocated by the pool at a given time. Use a negative value for no limit.
spring.redis.pool.max-idle=8 # Max number of "idle" connections in the pool. Use a negative value to indicate an unlimited number of idle connections.
spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1 # Maximum amount of time (in milliseconds) a connection allocation should block before throwing an exception when the pool is exhausted. Use a negative value to block indefinitely.
spring.redis.pool.min-idle=0 # Target for the minimum number of idle connections to maintain in the pool. This setting only has an effect if it is positive.
spring.redis.port=6379 # Redis server port.
spring.redis.sentinel.master= # Name of Redis server.
spring.redis.sentinel.nodes= # Comma-separated list of host:port pairs.
spring.redis.timeout=0 # Connection timeout in milliseconds.
# TRANSACTION (TransactionProperties)
spring.transaction.default-timeout= # Default transaction timeout in seconds.
spring.transaction.rollback-on-commit-failure= # Perform the rollback on commit failures.
# APACHE KAFKA (KafkaProperties)
spring.kafka.bootstrap-servers= # Comma-delimited list of host:port pairs to use for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster.
spring.kafka.client-id= # Id to pass to the server when making requests; used for server-side logging.
spring.kafka.consumer.auto-commit-interval= # Frequency in milliseconds that the consumer offsets are auto-committed to Kafka if 'enable.auto.commit' true.
spring.kafka.consumer.auto-offset-reset= # What to do when there is no initial offset in Kafka or if the current offset does not exist any more on the server.
spring.kafka.consumer.bootstrap-servers= # Comma-delimited list of host:port pairs to use for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster.
spring.kafka.consumer.client-id= # Id to pass to the server when making requests; used for server-side logging.
spring.kafka.consumer.enable-auto-commit= # If true the consumer's offset will be periodically committed in the background.
spring.kafka.consumer.fetch-max-wait= # Maximum amount of time in milliseconds the server will block before answering the fetch request if there isn't sufficient data to immediately satisfy the requirement given by "fetch.min.bytes".
spring.kafka.consumer.fetch-min-size= # Minimum amount of data the server should return for a fetch request in bytes.
spring.kafka.consumer.group-id= # Unique string that identifies the consumer group this consumer belongs to.
spring.kafka.consumer.heartbeat-interval= # Expected time in milliseconds between heartbeats to the consumer coordinator.
spring.kafka.consumer.key-deserializer= # Deserializer class for keys.
spring.kafka.consumer.max-poll-records= # Maximum number of records returned in a single call to poll().
spring.kafka.consumer.value-deserializer= # Deserializer class for values.
spring.kafka.listener.ack-count= # Number of records between offset commits when ackMode is "COUNT" or "COUNT_TIME".
spring.kafka.listener.ack-mode= # Listener AckMode; see the spring-kafka documentation.
spring.kafka.listener.ack-time= # Time in milliseconds between offset commits when ackMode is "TIME" or "COUNT_TIME".
spring.kafka.listener.concurrency= # Number of threads to run in the listener containers.
spring.kafka.listener.poll-timeout= # Timeout in milliseconds to use when polling the consumer.
spring.kafka.producer.acks= # Number of acknowledgments the producer requires the leader to have received before considering a request complete.
spring.kafka.producer.batch-size= # Number of records to batch before sending.
spring.kafka.producer.bootstrap-servers= # Comma-delimited list of host:port pairs to use for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster.
spring.kafka.producer.buffer-memory= # Total bytes of memory the producer can use to buffer records waiting to be sent to the server.
spring.kafka.producer.client-id= # Id to pass to the server when making requests; used for server-side logging.
spring.kafka.producer.compression-type= # Compression type for all data generated by the producer.
spring.kafka.producer.key-serializer= # Serializer class for keys.
spring.kafka.producer.retries= # When greater than zero, enables retrying of failed sends.
spring.kafka.producer.value-serializer= # Serializer class for values.
spring.kafka.properties.*= # Additional properties used to configure the client.
spring.kafka.ssl.key-password= # Password of the private key in the key store file.
spring.kafka.ssl.keystore-location= # Location of the key store file.
spring.kafka.ssl.keystore-password= # Store password for the key store file.
spring.kafka.ssl.truststore-location= # Location of the trust store file.
spring.kafka.ssl.truststore-password= # Store password for the trust store file.
spring.kafka.template.default-topic= # Default topic to which messages will be sent.
# RABBIT (RabbitProperties)
spring.rabbitmq.addresses= # Comma-separated list of addresses to which the client should connect.
spring.rabbitmq.cache.channel.checkout-timeout= # Number of milliseconds to wait to obtain a channel if the cache size has been reached.
spring.rabbitmq.cache.channel.size= # Number of channels to retain in the cache.
spring.rabbitmq.cache.connection.mode=channel # Connection factory cache mode.
spring.rabbitmq.cache.connection.size= # Number of connections to cache.
spring.rabbitmq.connection-timeout= # Connection timeout, in milliseconds; zero for infinite.
spring.rabbitmq.dynamic=true # Create an AmqpAdmin bean.
spring.rabbitmq.host=localhost # RabbitMQ host.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.acknowledge-mode= # Acknowledge mode of container.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.auto-startup=true # Start the container automatically on startup.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.concurrency= # Minimum number of consumers.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.default-requeue-rejected= # Whether or not to requeue delivery failures; default `true`.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.idle-event-interval= # How often idle container events should be published in milliseconds.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.max-concurrency= # Maximum number of consumers.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.prefetch= # Number of messages to be handled in a single request. It should be greater than or equal to the transaction size (if used).
spring.rabbitmq.listener.retry.enabled=false # Whether or not publishing retries are enabled.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.retry.initial-interval=1000 # Interval between the first and second attempt to deliver a message.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.retry.max-attempts=3 # Maximum number of attempts to deliver a message.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.retry.max-interval=10000 # Maximum interval between attempts.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.retry.multiplier=1.0 # A multiplier to apply to the previous delivery retry interval.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.retry.stateless=true # Whether or not retry is stateless or stateful.
spring.rabbitmq.listener.transaction-size= # Number of messages to be processed in a transaction. For best results it should be less than or equal to the prefetch count.
spring.rabbitmq.password= # Login to authenticate against the broker.
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672 # RabbitMQ port.
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirms=false # Enable publisher confirms.
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-returns=false # Enable publisher returns.
spring.rabbitmq.requested-heartbeat= # Requested heartbeat timeout, in seconds; zero for none.
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.enabled=false # Enable SSL support.
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.key-store= # Path to the key store that holds the SSL certificate.
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.key-store-password= # Password used to access the key store.
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.trust-store= # Trust store that holds SSL certificates.
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.trust-store-password= # Password used to access the trust store.
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.algorithm= # SSL algorithm to use. By default configure by the rabbit client library.
spring.rabbitmq.template.mandatory=false # Enable mandatory messages.
spring.rabbitmq.template.receive-timeout=0 # Timeout for `receive()` methods.
spring.rabbitmq.template.reply-timeout=5000 # Timeout for `sendAndReceive()` methods.
spring.rabbitmq.template.retry.enabled=false # Set to true to enable retries in the `RabbitTemplate`.
spring.rabbitmq.template.retry.initial-interval=1000 # Interval between the first and second attempt to publish a message.
spring.rabbitmq.template.retry.max-attempts=3 # Maximum number of attempts to publish a message.
spring.rabbitmq.template.retry.max-interval=10000 # Maximum number of attempts to publish a message.
spring.rabbitmq.template.retry.multiplier=1.0 # A multiplier to apply to the previous publishing retry interval.
spring.rabbitmq.username= # Login user to authenticate to the broker.
spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host= # Virtual host to use when connecting to the broker.