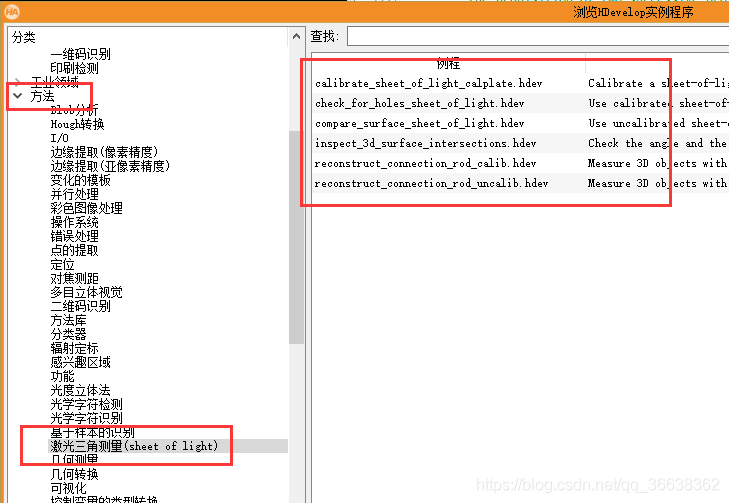
单目激光线扫3D三维坐标计算方法总结
- 此方法总结归纳来自于halcon的官方例程
- 官方图片位置 C:\Users\Public\Documents\MVTec\HALCON-18.05-Progress\examples\images\sheet_of_light
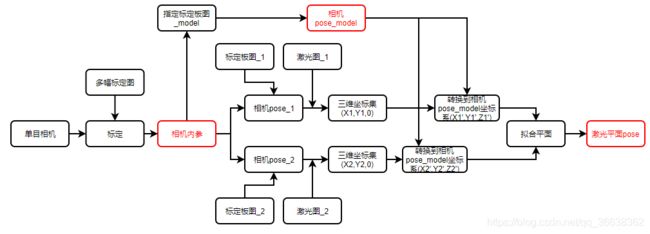
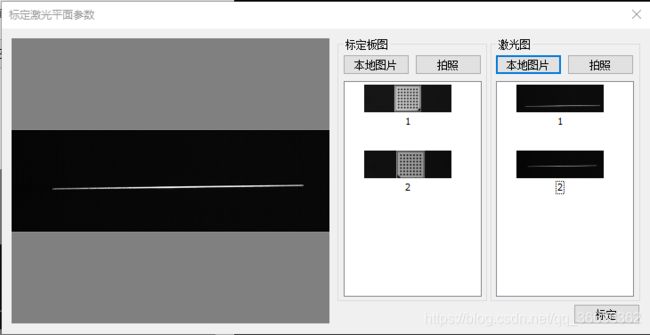
1、标定确定内参、确定激光平面
- 数据准备:多张标定板标定图、两组以上的标定板与激光线图。
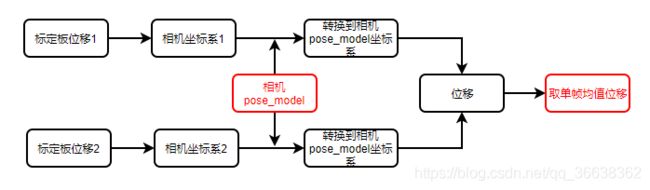
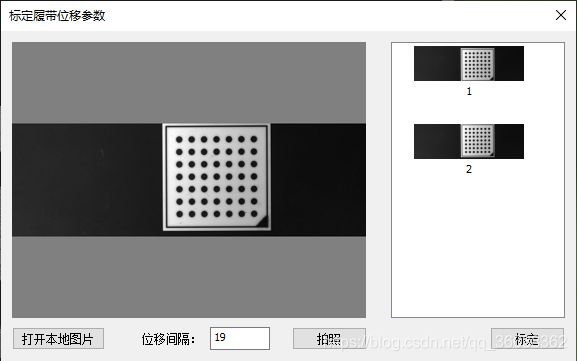
2、确定履带位移pose
- 数据准备:两个位置标定板图
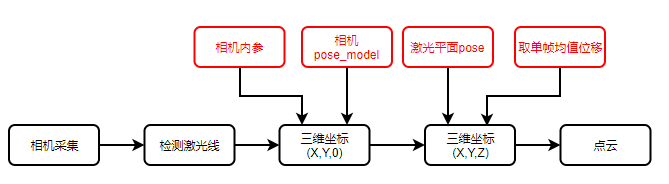
3、计算3D坐标
- 数据准备:采集N张线激光图像
基于opencv、pcl单目线激光三维重建完整代码下载:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_36638362/13082209
MFC应用程序下载(说明在文本下方):https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_36638362/13129186
配置教程:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_36638362/10809976
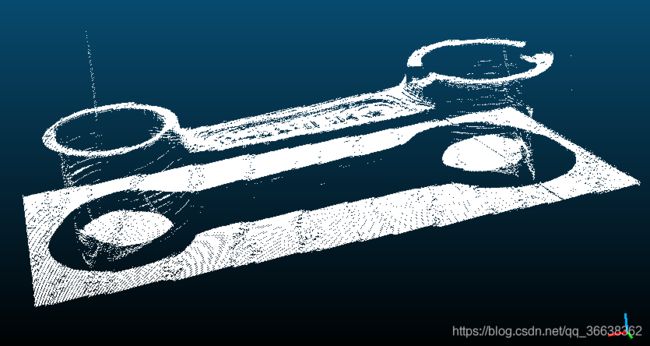
效果图:
opencv部分实现代码(含有部分PCL代码):
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void calRealPoint(std::vector>& obj, int boardwidth, int boardheight, int imgNumber, float squaresize)
{
// Mat imgpoint(boardheight, boardwidth, CV_32FC3,Scalar(0,0,0));
std::vector imgpoint;
for (int rowIndex = 0; rowIndex < boardheight; rowIndex++)
{
for (int colIndex = 0; colIndex < boardwidth; colIndex++)
{
// imgpoint.at(rowIndex, colIndex) = Vec3f(rowIndex * squaresize, colIndex*squaresize, 0);
imgpoint.push_back(cv::Point3f((float)colIndex * squaresize - (boardwidth / 2 * squaresize), (float)rowIndex * squaresize - (boardheight / 2 * squaresize), 0));
}
}
for (int imgIndex = 0; imgIndex < imgNumber; imgIndex++)
{
obj.push_back(imgpoint);
}
}
//像素位置、内参、R、T==》》世界坐标
Point3f getWorldPoints(Point2f &inPoints, Mat &rvec, Mat &tvec, Mat &cameraMatrix)
{
//initialize parameter
Mat rotationMatrix;//3*3
Rodrigues(rvec, rotationMatrix);
double zConst = 0;//实际坐标系的距离,若工作平面与相机距离固定可设置为0
double s;
//获取图像坐标
cv::Mat imagePoint = (Mat_(3, 1) << double(inPoints.x), double(inPoints.y), 1);
// cv::Mat::ones(3, 1, cv::DataType::type); //u,v,1
// imagePoint.at(0, 0) = inPoints.x;
// imagePoint.at(1, 0) = inPoints.y;
//计算比例参数S
cv::Mat tempMat, tempMat2;
tempMat = rotationMatrix.inv() * cameraMatrix.inv() * imagePoint;
tempMat2 = rotationMatrix.inv() * tvec;
s = zConst + tempMat2.at(2, 0);
s /= tempMat.at(2, 0);
//计算世界坐标
Mat wcPoint = rotationMatrix.inv() * (s * cameraMatrix.inv() * imagePoint - tvec);
Point3f worldPoint(wcPoint.at(0, 0), wcPoint.at(1, 0), wcPoint.at(2, 0));
return worldPoint;
}
//Ax+by+cz=D
void cvFitPlane(const CvMat* points, float* plane) {
// Estimate geometric centroid.
int nrows = points->rows;
int ncols = points->cols;
int type = points->type;
CvMat* centroid = cvCreateMat(1, ncols, type);
cvSet(centroid, cvScalar(0));
for (int c = 0; c < ncols; c++) {
for (int r = 0; r < nrows; r++)
{
centroid->data.fl[c] += points->data.fl[ncols*r + c];
}
centroid->data.fl[c] /= nrows;
}
// Subtract geometric centroid from each point.
CvMat* points2 = cvCreateMat(nrows, ncols, type);
for (int r = 0; r < nrows; r++)
for (int c = 0; c < ncols; c++)
points2->data.fl[ncols*r + c] = points->data.fl[ncols*r + c] - centroid->data.fl[c];
// Evaluate SVD of covariance matrix.
CvMat* A = cvCreateMat(ncols, ncols, type);
CvMat* W = cvCreateMat(ncols, ncols, type);
CvMat* V = cvCreateMat(ncols, ncols, type);
cvGEMM(points2, points, 1, NULL, 0, A, CV_GEMM_A_T);
cvSVD(A, W, NULL, V, CV_SVD_V_T);
// Assign plane coefficients by singular vector corresponding to smallest singular value.
plane[ncols] = 0;
for (int c = 0; c < ncols; c++) {
plane[c] = V->data.fl[ncols*(ncols - 1) + c];
plane[ncols] += plane[c] * centroid->data.fl[c];
}
// Release allocated resources.
cvReleaseMat(¢roid);
cvReleaseMat(&points2);
cvReleaseMat(&A);
cvReleaseMat(&W);
cvReleaseMat(&V);
}
//主函数
int main()
{
//检测圆形标定板
cv::Mat rgbImage, grayImage;
std::vector corner;
std::vector> imagePoint;
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++)
{
string path = "img/connection_rod_calib_" + to_string(i / 10) + to_string(i % 10) + ".png";
rgbImage = cv::imread(path, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
cv::cvtColor(rgbImage, grayImage, CV_BGR2GRAY);
bool isFind;
isFind = findCirclesGrid(grayImage, cv::Size(7, 7), corner);
if (isFind)
{
//cornerSubPix(grayImage, corner, cv::Size(7, 7), cv::Size(-1, -1), cv::TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS | CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 30, 0.1));
drawChessboardCorners(rgbImage, cv::Size(7, 7), corner, isFind);
imagePoint.push_back(corner);
}
}
//标准图用于投影变换
std::vector> objRealPoint;
calRealPoint(objRealPoint, 7, 7, 20, 3);
//标定
cv::Mat cameraMatrix, distCoeff;
vector rvecsMat;
vector tvecsMat;
float rms = calibrateCamera(objRealPoint, imagePoint, cv::Size(rgbImage.cols, rgbImage.rows), cameraMatrix, distCoeff, rvecsMat, tvecsMat, CV_CALIB_FIX_K3);
std::vector Points3d_19;
//第19张标定图激光图==》》三维坐标(Z坐标为0)
//cameraMatrix, distCoeff, rvecsMat[18], tvecsMat[18]
Mat rod_lightline_19 = imread("img/connection_rod_lightline_019.png", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
threshold(rod_lightline_19, rod_lightline_19, 80, 255, THRESH_BINARY);
for (size_t i = 0; i < rod_lightline_19.cols; i++)
{
int sum = 0; int num = 0;
for (size_t j = 0; j < rod_lightline_19.rows; j++)
{
if (rod_lightline_19.at(j, i) == 255)
{
sum += j;
num++;
}
}
if (num == 0)
continue;
Points3d_19.push_back(getWorldPoints(Point2f(i, 1.0*sum / num), rvecsMat[18], tvecsMat[18], cameraMatrix));
}
std::vector Points3d_20;
//第20张标定图激光图==》》三维坐标(Z坐标为0)需要转到19张图坐标系下
//cameraMatrix, distCoeff, rvecsMat[19], tvecsMat[19]
Mat rod_lightline_20 = imread("img/connection_rod_lightline_020.png", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
threshold(rod_lightline_20, rod_lightline_20, 80, 255, THRESH_BINARY);
for (size_t i = 0; i < rod_lightline_20.cols; i++)
{
int sum = 0; int num = 0;
for (size_t j = 0; j < rod_lightline_20.rows; j++)
{
if (rod_lightline_20.at(j, i) == 255)
{
sum += j;
num++;
}
}
if (num == 0)
continue;
Points3d_20.push_back(getWorldPoints(Point2f(i, 1.0*sum / num), rvecsMat[19], tvecsMat[19], cameraMatrix));
}
std::vector Points3d_20to19;
for (size_t i = 0; i < Points3d_20.size(); i++)
{
Mat Point3d_mat = (Mat_(3, 1) << double(Points3d_20[i].x), double(Points3d_20[i].y), double(Points3d_20[i].z));
Mat rotationMatrix1;//3*3
Rodrigues(rvecsMat[19], rotationMatrix1);
Mat rotationMatrix2;//3*3
Rodrigues(rvecsMat[18], rotationMatrix2);
Mat Point3d_to19_mat = rotationMatrix2*rotationMatrix1.inv()*(Point3d_mat - tvecsMat[19]) + tvecsMat[18];
Points3d_20to19.push_back(Point3f(Point3d_to19_mat.at(0, 0), Point3d_to19_mat.at(1, 0), Point3d_to19_mat.at(2, 0)));
}
//拟合激光平面
CvMat*points_mat = cvCreateMat(Points3d_19.size() + Points3d_20to19.size(), 3, CV_32FC1);//定义用来存储需要拟合点的矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < Points3d_19.size(); ++i)
{
points_mat->data.fl[i * 3 + 0] = Points3d_19[i].x;//矩阵的值进行初始化 X的坐标值
points_mat->data.fl[i * 3 + 1] = Points3d_19[i].y;// Y的坐标值
points_mat->data.fl[i * 3 + 2] = Points3d_19[i].z;// Z的坐标值
}
for (int i = 0; i < Points3d_20to19.size(); ++i)
{
points_mat->data.fl[Points3d_19.size() * 3 + i * 3 + 0] = Points3d_20to19[i].x;//矩阵的值进行初始化 X的坐标值
points_mat->data.fl[Points3d_19.size() * 3 + i * 3 + 1] = Points3d_20to19[i].y;// Y的坐标值
points_mat->data.fl[Points3d_19.size() * 3 + i * 3 + 2] = Points3d_20to19[i].z;// Z的坐标值
}
float line_plane[4] = { 0 };//定义用来储存平面参数的数组
cvFitPlane(points_mat, line_plane);//调用方程 line_plane[2]=-0.23太小
//line_plane[2] = -0.5;
//确定履带位移:根据内参+像素点 => 计算RT
std::vector corner_1, corner_20;
Mat caltab_at_position_1 = imread("img/caltab_at_position_1.png", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
bool isFind_1 = findCirclesGrid(caltab_at_position_1, cv::Size(7, 7), corner_1);
drawChessboardCorners(caltab_at_position_1, cv::Size(7, 7), corner_1, isFind_1);
Mat caltab_at_position_20 = imread("img/caltab_at_position_2.png", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
bool isFind_20 = findCirclesGrid(caltab_at_position_20, cv::Size(7, 7), corner_20);
drawChessboardCorners(caltab_at_position_20, cv::Size(7, 7), corner_20, isFind_20);
std::vector> objRealPoint2;
calRealPoint(objRealPoint2, 7, 7, 2, 3);
std::vector> imagePoint2;
imagePoint2.push_back(corner_1);
imagePoint2.push_back(corner_20);
vector rvecsMat2;
rvecsMat2.resize(2);
vector tvecsMat2;
tvecsMat2.resize(2);
solvePnP(objRealPoint2[0], imagePoint2[0], cameraMatrix, distCoeff, rvecsMat2[0], tvecsMat2[0], false, SOLVEPNP_DLS);
solvePnP(objRealPoint2[1], imagePoint2[1], cameraMatrix, distCoeff, rvecsMat2[1], tvecsMat2[1], false, SOLVEPNP_DLS);
Mat Point3d_mat = (Mat_(3, 1) << 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
Mat rotationMatrix1;//3*3
Rodrigues(rvecsMat2[0], rotationMatrix1);
Mat rotationMatrix20;//3*3
Rodrigues(rvecsMat2[1], rotationMatrix20);
Mat rotationMatrix19;//3*3
Rodrigues(rvecsMat[18], rotationMatrix19);//标杆
Mat Point3d_1to19_mat = rotationMatrix19*rotationMatrix1.inv()*(Point3d_mat - tvecsMat2[0]) + tvecsMat[18];
Mat Point3d_20to19_mat = rotationMatrix19*rotationMatrix20.inv()*(Point3d_mat - tvecsMat2[1]) + tvecsMat[18];
Mat move_steps = Point3d_20to19_mat - Point3d_1to19_mat;//1-20移动距离
Mat move_step = move_steps / 19;//单步移动距离
//计算
std::vector Points3d_all;
for (size_t k = 1; k <= 290; k++)
{
string path = "img/connection_rod_" + to_string(k / 100) + to_string(k / 10 % 10) + to_string(k % 10) + ".png";
Mat image = cv::imread(path, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
threshold(image, image, 80, 255, THRESH_BINARY);
for (size_t i = 0; i < image.cols; i++)
{
int sum = 0; int num = 0;
for (size_t j = 0; j < image.rows; j++)
{
if (image.at(j, i) == 255)
{
sum += j;
num++;
}
}
if (num == 0)
continue;
cv::Point3f Points3d = getWorldPoints(Point2f(i, 1.0*sum / num), rvecsMat[18], tvecsMat[18], cameraMatrix);
Points3d.z = (line_plane[3] - line_plane[0] * Points3d.x - line_plane[1] * Points3d.y) / line_plane[2];
Points3d += Point3f((k - 1)*move_step.at(0, 0), (k - 1)* move_step.at(1, 0), (k - 1)*move_step.at(2, 0));
Points3d_all.push_back(Points3d);
}
//imshow("image", image);
//waitKey(10);
}
//显示
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud); // 创建点云(指针)
(*cloud).points.resize(Points3d_all.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < Points3d_all.size(); i++)
{
(*cloud).points[i].x = Points3d_all[i].x;
(*cloud).points[i].y = Points3d_all[i].y;
(*cloud).points[i].z = Points3d_all[i].z;
}
pcl::io::savePLYFileASCII("point3d.ply", *cloud);
pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer("ply viewer");
viewer.showCloud(cloud);
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
}
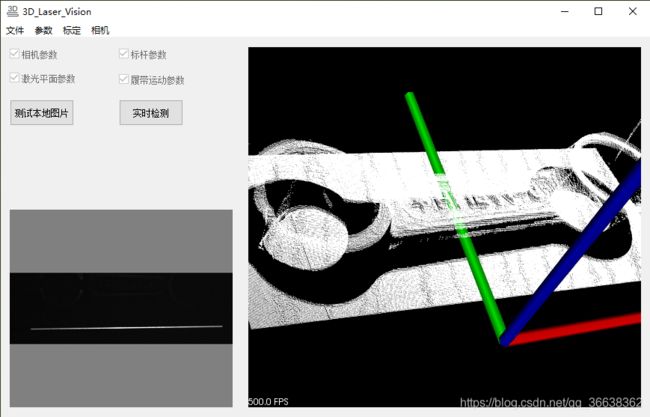
} MFC软件 https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_36638362/13129186
下面的测试本地图片作为例子介绍。支持usb相机标定和实时检测。
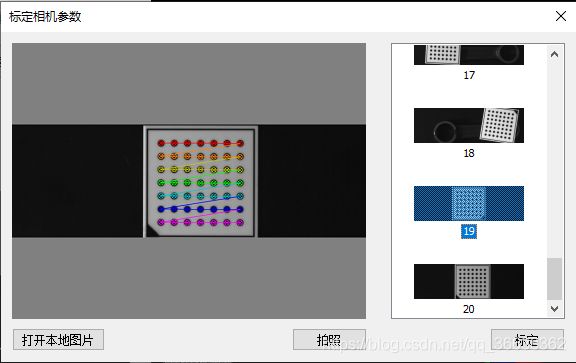
1.标定相机:标定,并将19幅图右击作为标杆
2.标定激光平面
3.标定履带位移参数