Coursera课程Big Data Analysis with Scala and Spark Week 1笔记
Coursera上的spark课程笔记。
spark为什么快
把尽可能多的不可变数据存到内存里,记录对数据的一系列操作。如果某个节点出现问题,重新执行一遍操作即可还原结果,无需太多的磁盘操作。
这就是它的容错思路。
RDD
大数据的hello world程序:word count
val rdd = spark.textFile("hdfs://...")
val count = rdd.flatMap(line => line.split(" "))
.map(word => (word, 1))
.reduceByKey(_ + _)
创建RDD的方式
- 从已有的RDD转换;
- 从SparkContext或SparkSession对象创建;
SparkContext或SparkSession是程序与spark集群交互的入口,最常用的创建RDD的方式是:
- parallelize: 从一个普通的Scala Collections创建RDD;往往在真正项目中不会用到,因为这需要已有一个很大的集合对象;
- textFile: 从HDFS或本地文件系统读取文本文件,得到一个String类型的RDD;项目中最常用的方式。
RDD的Transformation 和 Action 操作
对比Scala中序列和并行collection中的transformers和accessors。
transformers: 返回一个新的collection;
accessors: 整合所有结果返回单独的值,如reduce, fold, aggregate等操作。
- Transformation:返回新的RDD,lazy,并不立即计算;
- Action:基于RDD计算出结果,要么直接返回,要么存起来,eager,立即计算。
Laziness / eagerness ,是Spark处理延时的策略。
val lastYearsLogs: RDD[String] = ...
val firstLogsWithErrors = lastYearsLogs.filter(_.contains("ERROR")).take(10)
当取够10个元素时,就停止filter操作了。真聪明!
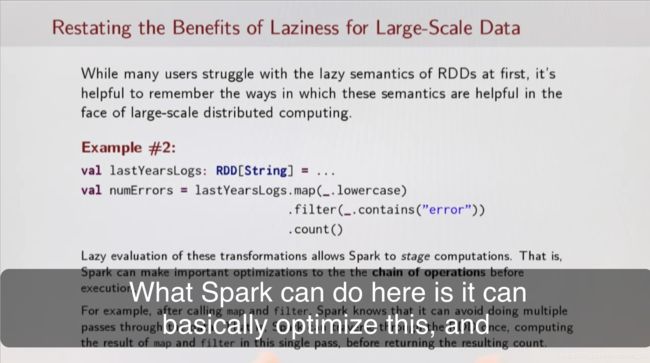
还有更牛的,如上图中,有一个map操作和一个count操作,spark在执行map的时候就顺便count了!只需一次遍历!
例子:
//这三行下来其实啥都没做,得到的只是对一个并不存在的RDD的引用
val largeList : List[String] = ...
val wordsRdd = sc.parallelize(largeList)
val lengthsRdd = wordsRdd.map(_.length)
//必须加上action操作才真正开始执行
val totalChars = lengthsRdd.reduce(_+_)
常用Transformation
map: 一一映射;
flatmap: 先 map, 然后再将 map 出来的这些列表首尾相接 (flatten);
filter:过滤;
dictinct:去重
常用Actions
collect: 返回RDD中所有元素;
count: 返回RDD元素个数;
take(num: Int): Array[T]:返回RDD中前num个元素;
reduce:
foreach:
看返回类型,就能区分Transformation和Actions。
Spark性能评估
每次reduce操作都会触发之前stage的所有transformations操作,重复计算严重。

这时候就需要缓存结果了:

persist()
cache()
例如下面连着执行了两次action,就可以将logsWithErrors rdd缓存起来。否则filter会执行两遍:
val lastYearsLogs: RDD[String] = ...
val logsWithErrors = lastYearsLogs.filter(_.contains("ERROR")).persist()
val firstLogsWithErrors = logsWithErrors.take(10)
val numErrors = logsWithErrors.count() //faster
Spark job执行原理
week1 作业
package wikipedia
import org.apache.spark.SparkConf
import org.apache.spark.SparkContext
import org.apache.spark.SparkContext._
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
case class WikipediaArticle(title: String, text: String) {
/**
* @return Whether the text of this article mentions `lang` or not
* @param lang Language to look for (e.g. "Scala")
*/
def mentionsLanguage(lang: String): Boolean = text.split(' ').contains(lang)
}
object WikipediaRanking extends WikipediaRankingInterface {
val langs = List(
"JavaScript", "Java", "PHP", "Python", "C#", "C++", "Ruby", "CSS",
"Objective-C", "Perl", "Scala", "Haskell", "MATLAB", "Clojure", "Groovy")
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf()
.setMaster("local[*]")
.setAppName("Wikipedia")
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf)
// Hint: use a combination of `sc.parallelize`, `WikipediaData.lines` and `WikipediaData.parse`
val wikiRdd: RDD[WikipediaArticle] = sc.parallelize(WikipediaData.lines.map(WikipediaData.parse))
/** Returns the number of articles on which the language `lang` occurs.
* Hint1: consider using method `aggregate` on RDD[T].
* Hint2: consider using method `mentionsLanguage` on `WikipediaArticle`
*/
def occurrencesOfLang(lang: String, rdd: RDD[WikipediaArticle]): Int = {
rdd.filter(_.mentionsLanguage(lang)).count.toInt
}
/* (1) Use `occurrencesOfLang` to compute the ranking of the languages
* (`val langs`) by determining the number of Wikipedia articles that
* mention each language at least once. Don't forget to sort the
* languages by their occurrence, in decreasing order!
*
* Note: this operation is long-running. It can potentially run for
* several seconds.
*/
def rankLangs(langs: List[String], rdd: RDD[WikipediaArticle]): List[(String, Int)] = {
rdd.cache()
langs.map(lang => (lang, occurrencesOfLang(lang, rdd))).sortBy(-_._2)
}
/* Compute an inverted index of the set of articles, mapping each language
* to the Wikipedia pages in which it occurs.
*/
def makeIndex(langs: List[String], rdd: RDD[WikipediaArticle]): RDD[(String, Iterable[WikipediaArticle])] = {
rdd.flatMap(article => {
langs.filter(article.mentionsLanguage)
.map(lang => (lang, article))
}).groupByKey()
}
/* (2) Compute the language ranking again, but now using the inverted index. Can you notice
* a performance improvement?
*
* Note: this operation is long-running. It can potentially run for
* several seconds.
*/
def rankLangsUsingIndex(index: RDD[(String, Iterable[WikipediaArticle])]): List[(String, Int)] = {
index.mapValues(_.size).sortBy(-_._2).collect().toList
}
/* (3) Use `reduceByKey` so that the computation of the index and the ranking are combined.
* Can you notice an improvement in performance compared to measuring *both* the computation of the index
* and the computation of the ranking? If so, can you think of a reason?
*
* Note: this operation is long-running. It can potentially run for
* several seconds.
*/
def rankLangsReduceByKey(langs: List[String], rdd: RDD[WikipediaArticle]): List[(String, Int)] = {
rdd.flatMap(article => {
langs.filter(article.mentionsLanguage)
.map((_,1))
}).reduceByKey(_+_).sortBy(-_._2).collect.toList
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
/* Languages ranked according to (1) */
val langsRanked: List[(String, Int)] = timed("Part 1: naive ranking", rankLangs(langs, wikiRdd))
/* An inverted index mapping languages to wikipedia pages on which they appear */
def index: RDD[(String, Iterable[WikipediaArticle])] = makeIndex(langs, wikiRdd)
/* Languages ranked according to (2), using the inverted index */
val langsRanked2: List[(String, Int)] = timed("Part 2: ranking using inverted index", rankLangsUsingIndex(index))
/* Languages ranked according to (3) */
val langsRanked3: List[(String, Int)] = timed("Part 3: ranking using reduceByKey", rankLangsReduceByKey(langs, wikiRdd))
/* Output the speed of each ranking */
println(timing)
sc.stop()
}
val timing = new StringBuffer
def timed[T](label: String, code: => T): T = {
val start = System.currentTimeMillis()
val result = code
val stop = System.currentTimeMillis()
timing.append(s"Processing $label took ${stop - start} ms.\n")
result
}
}
打印结果:
Processing Part 1: naive ranking took 29278 ms.
Processing Part 2: ranking using inverted index took 11789 ms.
Processing Part 3: ranking using reduceByKey took 7427 ms.




