scrapy框架初识1
目录
scrapy框架介绍:
scrapy框架的基本使用:
scrapy数据解析操作:
scrapy持久化存储:
将爬取到的数据一份存储到本地一份存储到数据库,如何实现?
scrapy框架介绍:
框架就是一个集成了很多功能并且具有很强通用性的一个项目模板。
scrapy框架:是爬虫中封装好的一个明星框架。
功能:高性能的持久化存储,异步的数据下载,高性能的数据解析,分布式。
scrapy框架的基本使用:
—环境的安装:pip install scrapy
—创建一个工程:scrapy startproject xxxPro(项目名称)
-cd xxx ->scrapy genspider spiderName www.xxx.com(在spiders子目录中创建一个爬 虫文件)
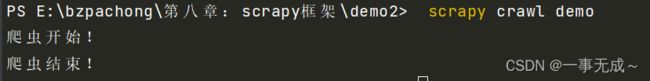
—执行工程: - scrapy crawl spiderName
例如 :
scrapy数据解析操作:
对最新段子_搞笑段子_幽默段子 - 糗事大百科进行一个爬取,获取段子名称+内容
爬虫文件代码
import scrapy
class DemoSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'demo'
#allowed_domains = ['www.xxx.com']
start_urls = ['http://www.qiushidabaike.com/']
def parse(self, response):
dl_list = response.xpath('//div[@class="main-left fl"]/dl')
for dl in dl_list:
# xpath返回的是列表,但是列表元素一定是Selector类型的对象
# extract()可以将Selector对象中data参数存储的字符串提取出来
# author=dl.xpath('./dt/span/a/text()')[0].extract()
author = dl.xpath('./dt/span/a/text()').extract_first() # 列表中只有一个元素可以使用extract_first()
text = dl.xpath('./dd[1]//text() | ./dd[1]/p//text()').extract()
text = ''.join(text)
print(author,text) scrapy持久化存储:
scrapy持久化存储:
-基于终端指令:
-要求:只可以将parse方法的返回值存储到本地的文本文件中
-注意:持久化存储对应的文本文件的类型只可以为:'json', 'jsonlines', 'jl', 'csv', 'xml', 'marshal', 'pickle
- 指令:scrapy crawl xxx -o filePath
- 好处:简介高效便捷
- 缺点:局限性比较强(数据只可以存储到指定后缀的文本文件中)
import scrapy
class DemoSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'demo'
#allowed_domains = ['www.xxx.com']
start_urls = ['http://www.qiushidabaike.com/']
def parse(self, response):
dl_list = response.xpath('//div[@class="main-left fl"]/dl')
all_data = []
for dl in dl_list:
# xpath返回的是列表,但是列表元素一定是Selector类型的对象
# extract()可以将Selector对象中data参数存储的字符串提取出来
# author=dl.xpath('./dt/span/a/text()')[0].extract()
author = dl.xpath('./dt/span/a/text()').extract_first() # 列表中只有一个元素可以使用extract_first()
text = dl.xpath('./dd[1]//text() | ./dd[1]/p//text()').extract()
text = ''.join(text)
dic = {
'author': author,
'text': text
}
all_data.append(dic)
return all_data- 基于管道:
- 编码流程:
- 数据解析
- 在item类中定义相关的属性
- 将解析的数据封装存储到item类型的对象
- 将item类型的对象提交给管道进行持久化存储的操作
- 在管道类的process_item中要将其接受到的item对象中存储的数据进行持久化存 储操作
- 在配置文件中开启管道
- 好处:通用性强。
demo.py
import scrapy
from demo2.items import Demo2Item
class DemoSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'demo'
#allowed_domains = ['www.xxx.com']
start_urls = ['http://www.qiushidabaike.com/']
def parse(self, response):
# 解析作者的名称+段子内容
dl_list = response.xpath('//div[@class="main-left fl"]/dl')
for dl in dl_list:
# xpath返回的是列表,但是列表元素一定是Selector类型的对象
# extract()可以将Selector对象中data参数存储的字符串提取出来
# author=dl.xpath('./dt/span/a/text()')[0].extract()
author = dl.xpath('./dt/span/a/text()').extract_first() # 列表中只有一个元素可以使用extract_first()
text = dl.xpath('./dd[1]//text() | ./dd[1]/p//text()').extract()
text = ''.join(text)
item = Demo2Item()
item['author'] = author
item['text'] = text
yield item # 将item提交给了管道
items.py
# Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
import scrapy
class Demo2Item(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
author = scrapy.Field()
text = scrapy.Field()
pass
pipelines.py
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
# useful for handling different item types with a single interface
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
class Demo2Pipeline:
fp=None
#重写父类的一个方法:该方法只会在开始爬虫的时候被调用一次
def open_spider(self,spider):
print('爬虫开始!')
self.fp = open('./qiushi.txt','w',encoding='utf-8')
#该方法用来接受爬虫文件提交过来的item对象
def process_item(self, item, spider):
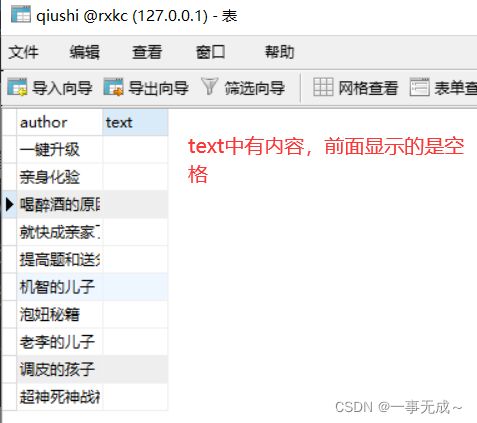
author=item['author']
text=item['text']
self.fp.write(author+':'+text+'\n')
return item #传递给下一个即将被执行的管道类
def close_spider(self,spider):
print('爬虫结束!')
self.fp.close()
将爬取到的数据一份存储到本地一份存储到数据库,如何实现?
- 管道文件中一个管道类对应的是将数据存储到一种平台
- 爬虫文件提交的item只会给管道文件中第一个被执行的管道类接受
- process_item中的return item表示将item传递给下一个即将被执行的管道类
pipelines.py
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
import pymysql
class Demo2Pipeline:
fp=None
#重写父类的一个方法:该方法只会在开始爬虫的时候被调用一次
def open_spider(self,spider):
print('爬虫开始!')
self.fp = open('./demo.txt','w',encoding='utf-8')
#该方法用来接受爬虫文件提交过来的item对象
def process_item(self, item, spider):
author=item['author']
text=item['text']
self.fp.write(author+':'+text+'\n')
return item #传递给下一个即将被执行的管道类
def close_spider(self,spider):
print('爬虫结束!')
self.fp.close()
class mysqlPileLine:
conn=None
cursor = None
def open_spider(self,spider):
self.coon = pymysql.Connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',password='123456',db='rxkc',charset='utf8')
def process_item(self, item, spider):
self.cursor=self.coon.cursor()
try:
self.cursor.execute('insert into qiushi values("%s","%s")'%(item["author"],item["text"]))
self.coon.commit()
except Exception as e:
print(e)
self.coon.rollback()
return item
def close_spider(self,spider):
self.cursor.close()
self.coon.close()结果: