Pandas库的Series类型
Series类型由一组数据及与之相关的数据 索引(自动索引,也可设置) 组成。
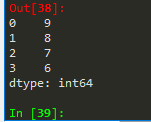
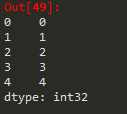
例1(列表创建Series类型):
import pandas as pd
a = pd.Series([9,8,7,6])
a
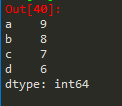
例2:
如果索引的位置是第二位,‘索引=’可省略
import pandas as pd
b = pd.Series([9,8,7,6],
index=['a','b','c','d'])
b
- Python列表
- 标量值
- Python字典
- ndarray
- 其他函数(range()函数)
1.标量值创建
不能省略 ‘index=’
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(25,index=['a','b','c'])
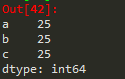
2.字典类型创建
import pandas as pd
d = pd.Series({'a':9,'b':8,'c':7})
import pandas as pd
c = pd.Series({'a':9,'b':8,'c':7},
index=('c','a','b','d'))
c
3.ndarray创建
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
n = pd.Series(np.arange(5))
n
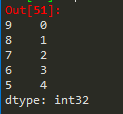
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
m=pd.Series(np.arange(5),
index=np.arange(9,4,-1))
m
Series类型的基本操作
与ndarray和python字典操作相似,可操作value和index。
import pandas as pd
b = pd.Series([9,8,7,6],
['a','b','c','d'])
print(b)
print('b.index:\n', b.index)
print('b.values:\n', b.values)
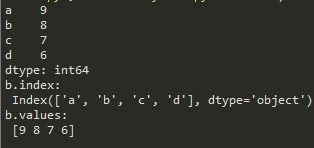
自动索引和自定义索引并存,虽然两套索引并存,但不能混用。
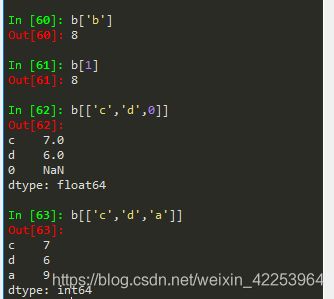
1.对Series类型操作后,仍是Series类型。但仅查询某一个值时,返回的就是一个值。
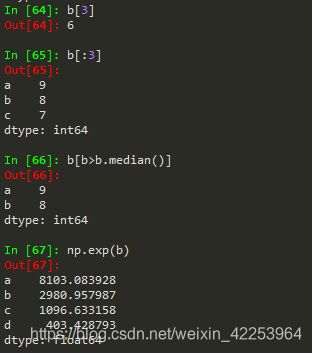
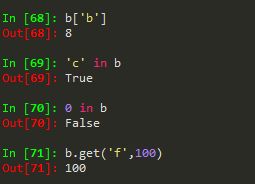
2.与字典操作相似,保留了in,和get方法。in是查询某个键在不在其中,并且in只能判断自动索引,不会判断自定义索引。在Series类型中就是判断某个索引在不在其中。get是提取某个索引对应的值。
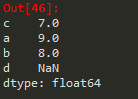
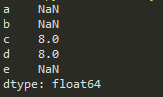
3.Series的对齐操作。
索引值相同的进行计算,最终得到的元素个数,是所有元素的并集。
import pandas as pd
a = pd.Series([1,2,3],['c','d','e'])
b = pd.Series([9,8,7,6],
['a','b','c','d'])
print(a+b)
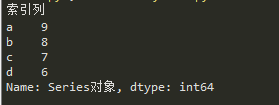
import pandas as pd
b = pd.Series([9,8,7,6],
['a','b','c','d'])
b.name = 'Series对象'
b.index.name = '索引列'
print(b)
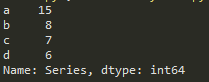
5.Series类型的修改
Series对象可以随时修改并即刻生效
import pandas as pd
b = pd.Series([9,8,7,6],
['a','b','c','d'])
b['a']=15
b.name = 'Series'
print(b)
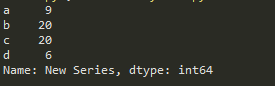
import pandas as pd
b = pd.Series([9,8,7,6],
['a','b','c','d'])
b['b','c'] = 20
b.name = 'New Series'
print(b)