二叉树的常见遍历方式
遍历
前序遍历
void preorder(TreeNode * treeNode){
if(!treeNode) return;
printf("%d ",treeNode->val);
preorder(treeNode->left);
preorder(treeNode->right);
}
中序遍历
void midorder(TreeNode * treeNode){
if(!treeNode) return;
midorder(treeNode->left);
printf("%d ",treeNode->val);
midorder(treeNode->right);
}
不用递归,可利用栈实现中序遍历
void in_order(struct TreeNode* root){
struct TreeNode* stack[1005]={0};
int top=0;
int in_order;
while(root||top){
while(root){
stack[top++]=root;
root=root->left;
}
root=stack[--top];
in_order=root->val;
printf("%d ",in_order);
root=root->right;
}
}
后序遍历
void postorder(TreeNode * treeNode){
if(!treeNode) return;
postorder(treeNode->left);
postorder(treeNode->right);
printf("%d ",treeNode->val);
}
层序遍历
不用递归,而是利用队列思想
void leveOrder(TreeNode * treeNode){
TreeNode * q[20];
int head=0,tail=0;
q[tail++]=treeNode;
int depth=1;
while(head!=tail){
int len=tail-head;//计算当前队列中的个数,每层加的个数,深度+1;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){//执行完for循环,队列中存放下一层结点
TreeNode * node=q[head++];
printf("%d ",node->val);
if(node->left) q[tail++]=node->left;
if(node->right) q[tail++]=node->right;
}
printf("\n");
depth++;
}
}
练习
99. 恢复二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/recover-binary-search-tree/
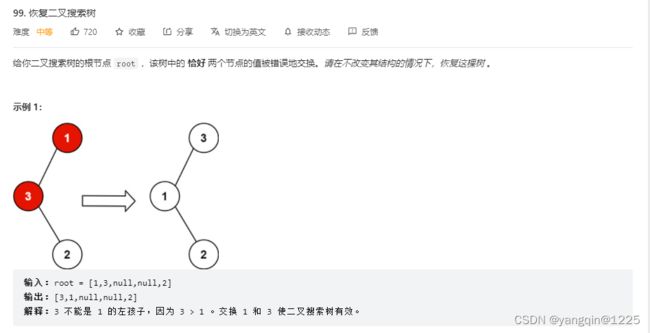
方案一:
利用中序遍历,再排升序(大部分有序选择插入排序),最后将升序数组再按照中序遍历复制给树
#define swap(a,b){__typeof(a) __tmp=a;a=b;b=__tmp;}
//中序遍历,order首位存个数
void in_order(struct TreeNode* root,int * order){
if(!root) return;
in_order(root->left,order);
order[++order[0]]=root->val;
in_order(root->right,order);
}
//插入排序
void insert_order(int *nums){
int len=nums[0];
for(int i=1;i<=len;i++){
for(int j=i;j>1;j--){
if(nums[j]>nums[j-1]) break;
swap(nums[j],nums[j-1]);
}
}
}
//将排好升序数组覆盖到二叉树
void convert(struct TreeNode* root,int * order){
if(!root) return;
convert(root->left,order);
root->val=order[++order[0]];
convert(root->right,order);
}
void recoverTree(struct TreeNode* root){
int * order=(int *) malloc(sizeof(int)*1005);
order[0]=0;
in_order(root,order);
insert_order(order);
order[0]=0;//覆盖时需要重置索引;
convert(root,order);
free(order);
}
方案二:
利用中序遍历(非递归),记录顺序错误的两个值,最后交换
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
#define swap(a,b){__typeof(a) __tmp=a;a=b;b=__tmp;}
//不用递归的中序遍历
void in_order(struct TreeNode* root){
struct TreeNode* sk[1005]={0};
int top=0;
struct TreeNode *pre=NULL,*node1=NULL,*node2=NULL;
while(root||top){
while(root){
sk[top++]=root;
root=root->left;
}
root=sk[--top];
if(pre&&root->val<=pre->val){
if(!node1) node1=pre; //找到第一个大于等于右侧的值,如1,5,3,4,2,6中的5
node2=root; //找到第一个小于等于左侧的值,如1,5,3,4,2,6中的2
}
pre=root;
root=root->right;
}
swap(node1->val,node2->val);
}
void recoverTree(struct TreeNode* root){
in_order(root);
}
方案三:
和方案二思想一样,只是利用递归进行中序遍历
#define swap(a,b){__typeof(a) __tmp=a;a=b;b=__tmp;}
//用递归的中序遍历
void in_order(struct TreeNode* root,struct TreeNode** arg){
if(!root) return;
in_order(root->left,arg);
if(arg[0]&&arg[0]->val>=root->val){
if(!arg[1]) arg[1]=arg[0];
arg[2]=root;
}
arg[0]=root;
in_order(root->right,arg);
}
void recoverTree(struct TreeNode* root){
//三个元素,第一个存pre,第二个存node1(第一个大于等于右侧的值),第三个存node2(第一个小于等于左侧的值)
struct TreeNode** arg=(struct TreeNode**)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode*)*3);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
arg[i]=NULL;
}
in_order(root,arg);
//printf("%d %d",p->val,q->val);
swap(arg[1]->val,arg[2]->val);
}