Java编程练习题:Demo96 - Demo105(多维数组)
目录
Demo96. (代数方面:两个矩阵相乘)编写两个矩阵相乘的方法。
Demo97. (距离最近的两个点)程序清单8-3给出找到二维空间中距离最近的两个点的程序。 修改该程序,让程序能够找出在三维空间上距离最近的两个点。
Demo98. (最大的行和列)编写一个程序,在一个4×4的矩阵中随机填人0和1, 打印该矩阵,找到第一个具有最多1的行和列。
Demo99. (游戏:九个正面和背面) 编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个在0到511之间的数字,然后显示用字符H和T表示的对应的矩阵。
Demo100. (模式识别:连续的四个相等的数)编写下面的方法,测试一个二维数组是否有四个连续的数字具有相同的值, 这四个数可以是水平方向的、垂直方向的或者对角线方向的。
Demo101. (游戏:四子连)四子连是一个两个人玩的棋盘游戏,在游戏中, 玩家轮流将有颜色的棋子放在一个六行七列的垂直悬挂的网格中,如下所示。 这个游戏的目的是在对手实现一行、一列或者一条对角线上有四个相同颜色的棋子之前, 你能先做到。
Demo102. (马尔科夫矩阵)一个n×n的矩阵被称为一个正马尔科夫矩阵,当且仅当每个元素都是正数, 并且每列的元素的和为1。编写下面的方法来检测一个矩阵是否是一个马尔科夫矩阵。
Demo103. (几何:三角形面积)编写一个方法,使用下面的方法头,返回一个三角形的面积
Demo104. (几何:多边形的子面积)一个具有四个顶点的凸多边形被分为四个三角形,编写一个程序,提示用户输入四个顶点的坐标,然后以升序显示四个三角形的面积。
Demo105. (拉丁正方形)拉丁正方形是一个n×n的数组,由n个不同的拉丁字母填充,每个拉丁字母恰好只在每行和每列中出现一次。编写一个程序,提示用户输人数字n以及字符数组,如示例输出所示,检测该输出数组是否是一个拉丁正方形。字符是从A开始的前面n个字符。
Demo96. (代数方面:两个矩阵相乘)编写两个矩阵相乘的方法。
方法头如下: public static double[][] multiplyMatrix(double[][] a,double[][] b) 为了使矩阵a能够和矩阵b相乘,矩阵a的列数必须与矩阵b的行数相同,并且两个矩阵的元素要具有相同或兼容的数据类型。 假设矩阵c是相乘的结果,而a的列数是n,那么每个元素cij就是ai1 x b1j + ai2 x b2j +…+ ain x bnj。 例如,对于两个3×3的矩阵a和 b,c就有: cij = ai1 x b1j + ai2 x b2j + ai3 x b3j。 编写一个测试程序,提示用户输人两个3×3的矩阵,然后显示它们的乘积。下面是一个运行示例:
package Exer2;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo96 {
/*
(代数方面:两个矩阵相乘)编写两个矩阵相乘的方法。方法头如下:
public static double[][] multiplyMatrix(double[][] a,double[][] b)
为了使矩阵a能够和矩阵b相乘,矩阵a的列数必须与矩阵b的行数相同,并且两个矩阵的元素要具有相同或兼容的数据类型。
假设矩阵c是相乘的结果,而a的列数是n,那么每个元素cij就是ai1 x b1j + ai2 x b2j +…+ aim x bnj。
例如,对于两个3×3的矩阵a和 b,c就有: cij = ai1 x b1j + ai2 x b2j + ai3 x b3j。
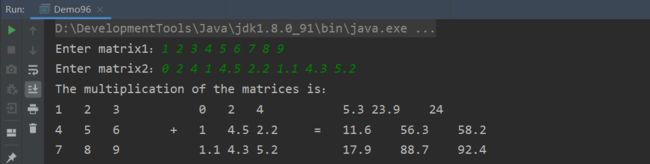
编写一个测试程序,提示用户输人两个3×3的矩阵,然后显示它们的乘积。下面是一个运行示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0 2 4 1 4.5 2.2 1.1 4.3 5.2
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter matrix1:");
double[][] a = new double[3][3];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) {
a[i][j] = scan.nextDouble();
}
}
double[][] b = new double[3][3];
System.out.print("Enter matrix2:");
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < b[i].length; j++) {
b[i][j] = scan.nextDouble();
}
}
System.out.println("The multiplication of the matrices is:");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a[0].length; j++) {
System.out.print(new DecimalFormat("#.##").format(a[i][j]) + "\t");
}
System.out.print(i == 1 ? "\t+\t" : "\t\t");
for (int j = 0; j < a[0].length; j++) {
System.out.print(new DecimalFormat("#.##").format(b[i][j]) + "\t");
}
System.out.print(i == 1 ? "\t=\t" : "\t\t");
for (int j = 0; j < a[0].length; j++) {
// new DecimalFormat("#.##").format(double d) 让小数点后为0的显示为整数,不为零的显示为double
System.out.print(new DecimalFormat("#.##").format(multiplyMatrix(a, b)[i][j]) + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
scan.close();
}
public static double[][] multiplyMatrix(double[][] a, double[][] b){
double[][] c = new double[3][3];
for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < c[i].length; j++) {
c[i][j] = BigDecimal.valueOf(a[i][0]).multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(b[0][j]))
.add(BigDecimal.valueOf(a[i][1]).multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(b[1][j]))
.add(BigDecimal.valueOf(a[i][2]).multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(b[2][j]))))
.doubleValue();
}
}
return c;
}
}
结果:
Demo97. (距离最近的两个点)程序清单8-3给出找到二维空间中距离最近的两个点的程序。 修改该程序,让程序能够找出在三维空间上距离最近的两个点。
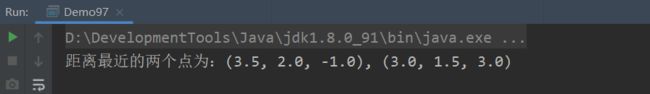
使用一个二维数组表示这些点。使用下面的点来测试这个程序: double[][] points = {{-1,0,3},{-1,-1,-1},{4,1,1},{2,0.5,9},{3.5,2,-1},{3,1.5,3},{-1.5,4,2},{5.5,4,-0.5}}; 计算两个点(x1,y1,z1)和(x2,y2,z2)之间距离的公式是√((x2-x1)²+(y2-y1)²+(z2-z1)²)。
package Exer2;
public class Demo97 {
/*
(距离最近的两个点)程序清单8-3给出找到二维空间中距离最近的两个点的程序。
修改该程序,让程序能够找出在三维空间上距离最近的两个点。使用一个二维数组表示这些点。使用下面的点来测试这个程序:
double[][] points = {{-1,0,3},{-1,-1,-1},{4,1,1},{2,0.5,9},{3.5,2,-1},{3,1.5,3},{-1.5,4,2},{5.5,4,-0.5}};
计算两个点(x1,y1,z1)和(x2,y2,z2)之间距离的公式是√((x2-x1)²+(y2-y1)²+(z2-z1)²)。
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[][] points = {{-1, 0, 3}, {-1, -1, -1}, {4, 1, 1}, {2, 0.5, 9},
{3.5, 2, -1}, {3, 1.5, 3}, {-1.5, 4, 2}, {5.5, 4, -0.5}};
// System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(minDistance(points)));
System.out.printf("距离最近的两个点为:(%s, %s, %s), (%s, %s, %s)%n",
minDistance(points)[0][0], minDistance(points)[0][1], minDistance(points)[0][2],
minDistance(points)[1][0], minDistance(points)[1][1], minDistance(points)[1][2]);
}
private static double[][] minDistance(double[][] points) {
double[][] twoPoints = new double[2][3];
double minD = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < points.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < points.length; j++) {
double d = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(points[j][0] - points[i][0], 2)
+ Math.pow(points[j][1] - points[i][1], 2) + Math.pow(points[j][1] - points[i][1], 2));
if (d < minD) {
minD = d;
twoPoints[0] = points[i];
twoPoints[1] = points[j];
}
}
}
return twoPoints;
}
}
结果:
Demo98. (最大的行和列)编写一个程序,在一个4×4的矩阵中随机填人0和1, 打印该矩阵,找到第一个具有最多1的行和列。
下面是一个程序的运行示例:
package Exer2;
import java.util.Random;
public class Demo98 {
/*
(最大的行和列)编写一个程序,在一个4×4的矩阵中随机填人0和1,
打印该矩阵,找到第一个具有最多1的行和列。下面是一个程序的运行示例:
0011
0011
1101
1010
The largest row index:2
The largest column index:2
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] nums = new int[4][4];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums[i].length; j++) {
nums[i][j] = new Random().nextInt(2);
}
}
for (int[] arr : nums) {
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
int rowIndex = 0, columnIndex = 0;
int largestRow = 0;
int largestColumn = 0;
// int[][] largest = new int[2][2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int rowSum = 0, ColumnSum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < nums[i].length; j++) {
rowSum += nums[i][j];
ColumnSum += nums[j][i];
if (ColumnSum > largestColumn) {
columnIndex = j;
largestColumn = ColumnSum;
}
}
if (rowSum > largestRow) {
rowIndex = i;
largestRow = rowSum;
}
}
System.out.println("The largest row index:" + rowIndex);
System.out.println("The largest column index:" + columnIndex);
}
}
结果:
Demo99. (游戏:九个正面和背面) 编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个在0到511之间的数字,然后显示用字符H和T表示的对应的矩阵。
一个3×3的矩阵中放置了9个硬币,这些硬币有些面向上,有些面向下。 可以使用3×3的矩阵中的0(正面)或1(反面)表示硬币的状态。下面是一些例子: 
每个状态都可以使用一个二进制数表示。例如,前面的矩阵对应到数字: 000010000 101001100 110100001 101110100 100111110 总共会有512种可能性。所以,可以使用十进制数0,1,2,3,...,511来表示这个矩阵的所有状态。下面是一个运行示例:
package Exer2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo99 {
/*
(游戏:九个正面和背面)一个3×3的矩阵中放置了9个硬币,这些硬币有些面向上,有些面向下。
可以使用3×3的矩阵中的0(正面)或1(反面)表示硬币的状态。下面是一些例子:
0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
每个状态都可以使用一个二进制数表示。例如,前面的矩阵对应到数字:
000010000 101001100 110100001 101110100 100111110
总共会有512种可能性。所以,可以使用十进制数0,1,2,3,...,511来表示这个矩阵的所有状态。
编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个在0到511之间的数字,然后显示用字符H和T表示的对应的矩阵。下面是一个运行示例:
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number between 0 and 511:");
int number = scan.nextInt();
int[][] binaryArr = toBinaryArr(number);
// System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(binaryArr));
for (int[] nums : binaryArr) {
for (int n : nums) {
if (n == 0) {
System.out.print("H ");
} else {
System.out.print("T ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
scan.close();
}
private static int[][] toBinaryArr(int number) {
int[][] arr = new int[3][3];
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = arr[i].length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (number > 0) {
arr[i][j] = number % 2;
number /= 2;
}
}
}
return arr;
}
}
结果:
Demo100. (模式识别:连续的四个相等的数)编写下面的方法,测试一个二维数组是否有四个连续的数字具有相同的值, 这四个数可以是水平方向的、垂直方向的或者对角线方向的。
public static boolean isConsecutiveFour(int[][]values) 编写一个测试程序,提示用户输人一个二维数组的行数、列数以及数组中的值。 如果这个数组有四个连续的数字具有相同的值,就显示true;否则,显示false。下面是结果为true的一些例子:
这里我只做出来水平方向:
package Exer2;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo100 {
/*
(模式识别:连续的四个相等的数)编写下面的方法,测试一个二维数组是否有四个连续的数字具有相同的值,
这四个数可以是水平方向的、垂直方向的或者对角线方向的。
public static boolean isConsecutiveFour(int[][]values)
编写一个测试程序,提示用户输人一个二维数组的行数、列数以及数组中的值。
如果这个数组有四个连续的数字具有相同的值,就显示true;否则,显示false。下面是结果为true的一些例子:
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个二维数组的行数、列数以及数组中的值(前两个数分别表示行、列):");
int row = scan.nextInt();
int column = scan.nextInt();
int[][] values = new int[row][column];
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < values[i].length; j++) {
values[i][j] = scan.nextInt();
}
}
// 6 7 0 1 0 3 1 6 1 0 1 6 8 6 0 1 5 6 2 1 8 2 9 6 5 6 1 1 9 1 1 3 6 1 4 0 7 3 3 3 3 4 0 7
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(values));
System.out.println(isConsecutiveFour(values));
}
public static boolean isConsecutiveFour(int[][] values) {
if (values.length < 4 || values[0].length < 4) {
return false;
}
int rowCount = 1, columnCount = 1, count = 1, antiCount = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < values[i].length; j++) {
// 判断行
if (values[i - 1][j - 1] == values[i - 1][j] || values[i][j - 1] == values[i][j]){
rowCount++;
} else {
rowCount = 1;
}
// 判断列
if (values[i - 1][j - 1] == values[i][j - 1] || values[i - 1][j] == values[i][j]){
columnCount++;
} else {
columnCount = 0;
}
// 副对角线
if (i >= 3) {
// TODO
}
// 主对角线
if (j <= 3) {
// TODO
}
if (rowCount >= 4 || columnCount >= 4) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
Demo101. (游戏:四子连)四子连是一个两个人玩的棋盘游戏,在游戏中, 玩家轮流将有颜色的棋子放在一个六行七列的垂直悬挂的网格中,如下所示。 这个游戏的目的是在对手实现一行、一列或者一条对角线上有四个相同颜色的棋子之前, 你能先做到。
程序提示两个玩家交替地下红子Red或黄子Yellow。 当放下一子时,程序在控制台重新显示这个棋盘,然后确定游戏的状态(赢、平局还是继续)。
下面是一个运行示例:
package Exer2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo101 {
/*
(游戏:四子连)四子连是一个两个人玩的棋盘游戏,在游戏中,
玩家轮流将有颜色的棋子放在一个六行七列的垂直悬挂的网格中,如下所示。
这个游戏的目的是在对手实现一行、一列或者一条对角线上有四个相同颜色的棋子之前,
你能先做到。程序提示两个玩家交替地下红子Red或黄子Yellow。
当放下一子时,程序在控制台重新显示这个棋盘,然后确定游戏的状态(赢、平局还是继续)。下面是一个运行示例:
*/
static Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[][] chess = new char[6][15];
for (int i = 0; i < chess.length; i++) //初始化棋盘
{
for (int j = 0; j < chess[i].length; j++) {
if (j % 2 == 0)
chess[i][j] = '|';
else
chess[i][j] = ' ';
}
}
beginGame(chess);
in.close();
}
//开始比赛
public static void beginGame(char[][] chess) {
char disk;
for (int i = 0; i < 42; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0)
disk = 'R';
else
disk = 'Y';
printChessBoard(chess);
System.out.println("——————————————");
if (dropDisk(chess, disk) == 0) {
i--;
continue;
}
if (judge(chess) == 0) {
System.out.println("The red player won");
return;
} else if (judge(chess) == 1) {
System.out.println("The yellow player won");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("No winner");
}
//落子
public static int dropDisk(char[][] chess, char disk) {
if (disk == 'R')
System.out.print("Drop a red disk at column(0-6):");
else
System.out.print("Drop a yellow disk at column(0-6):");
int key = in.nextInt();
if (key < 0 || key > 6) {
System.out.println("Enter error!");
return 0;
}
key = key * 2 + 1;
for (int row = chess.length - 1; row >= 0; row--) {
if (chess[row][key] == ' ') {
chess[row][key] = disk;
return 1;
}
}
System.out.println("This colum is no more position!");
return 0;
}
//打印棋盘
public static void printChessBoard(char[][] chess) {
for (int i = 0; i < chess.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chess[i].length; j++)
System.out.print(chess[i][j]);
System.out.println();
}
}
//判断输赢,返回0'R'赢,返回1'Y'赢,返回2未分出胜负
public static int judge(char[][] chess) {
if (judgeRow(chess) != 2)
return judgeRow(chess);
if (judgeCol(chess) != 2)
return judgeCol(chess);
if (judgeMainDiagonal(chess) != 2)
return judgeMainDiagonal(chess);
if (judgeSubDiagonal(chess) != 2)
return judgeSubDiagonal(chess);
return 2;
}
//判断行是否有四个相等的
public static int judgeRow(char[][] chess) {
for (int i = 0; i < chess.length; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < chess[i].length - 6; j += 2) {
if (chess[i][j] == chess[i][j + 2] && chess[i][j] == chess[i][j + 4] && chess[i][j] == chess[i][j + 6] && chess[i][j] != ' ')
if (chess[i][j] == 'R')
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
return 2;
}
//判断列是否有四个相等的
public static int judgeCol(char[][] chess) {
for (int i = 0; i < chess.length - 3; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < chess[i].length; j += 2) {
if (chess[i][j] == chess[i + 1][j] && chess[i][j] == chess[i + 2][j] && chess[i][j] == chess[i + 3][j] && chess[i][j] != ' ')
if (chess[i][j] == 'R')
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
return 2;
}
//判断主对角线是否有四个相等的
public static int judgeMainDiagonal(char[][] chess) {
for (int i = 0; i < chess.length - 3; i++)//主对角线
for (int j = 1; j < chess[i].length - 6; j += 2) {
if (chess[i][j] == chess[i + 1][j + 2] && chess[i][j] == chess[i + 2][j + 4] && chess[i][j] == chess[i + 3][j + 6] && chess[i][j] != ' ')
if (chess[i][j] == 'R')
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
return 2;
}
//判断副对角线是否有四个相等的
public static int judgeSubDiagonal(char[][] chess) {
for (int i = 3; i < chess.length; i++)//副对角线
for (int j = 1; j < chess[i].length - 6; j += 2) {
if (chess[i][j] == chess[i - 1][j + 2] && chess[i][j] == chess[i - 2][j + 4] && chess[i][j] == chess[i - 3][j + 6] && chess[i][j] != ' ')
if (chess[i][j] == 'R')
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
return 2;
}
}
结果:
Demo102. (马尔科夫矩阵)一个n×n的矩阵被称为一个正马尔科夫矩阵,当且仅当每个元素都是正数, 并且每列的元素的和为1。编写下面的方法来检测一个矩阵是否是一个马尔科夫矩阵。
public static boolean isMarkovMatrix(double[][] m) 编写一个测试程序,提示用户输人一个3×3的double值的矩阵,测试它是否是一个马尔科夫矩阵。下面是一个运行示例:
package Exer2;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo102 {
/*
(马尔科夫矩阵)一个n×n的矩阵被称为一个正马尔科夫矩阵,当且仅当每个元素都是正数,
并且每列的元素的和为1。编写下面的方法来检测一个矩阵是否是一个马尔科夫矩阵。
public static boolean isMarkovMatrix(double[][] m)
编写一个测试程序,提示用户输人一个3×3的double值的矩阵,测试它是否是一个马尔科夫矩阵。下面是一个运行示例:
*/
/*
0.15 0.875 0.375
0.55 0.005 0.225
0.30 0.12 0.4
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
double[][] m = new double[3][3];
System.out.println("Enter a 3-by-3 matrix row by row:");
for (int i = 0; i < m.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m[i].length; j++) {
m[i][j] = scan.nextDouble();
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(m));
if (isMarkovMatrix(m)) {
System.out.println("It is a Markov matrix");
} else {
System.out.println("It is not a Markov matrix");
}
}
public static boolean isMarkovMatrix(double[][] m) {
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m[i].length; j++) {
sum += m[j][i];
if (m[i][j] <= 0) {
return false;
}
}
if (sum != 1) {
return false;
} else {
sum = 0;
}
}
return true;
}
}
结果:
Demo103. (几何:三角形面积)编写一个方法,使用下面的方法头,返回一个三角形的面积
public static double getTriangleArea(double[][] points)
点保存在一个3×2的二维矩阵points中,其中 ( points[0][0],points[0][1])代表(x1, y1)。三角形面积的计算可以使用编程练习题2.19中的公式。如果三个点在一条直线上,方法返回0。编写一个程序,提示用户输入三角形的三个点,然后显示三角形的面积。下面是一个运行示例。
package Exer2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo103 {
/*
(几何:三角形面积)编写一个方法,使用下面的方法头,返回一个三角形的面积
public static double getTriangleArea(double[][] points)
点保存在一个3×2的二维矩阵points中,其中 ( points[0][0],points[0][1])代表(x1, y1)。
三角形面积的计算可以使用编程练习题2.19中的公式。如果三个点在一条直线上,方法返回0。
编写一个程序,提示用户输入三角形的三个点,然后显示三角形的面积。下面是一个运行示例。
计算三角形面积的公式是:
s = (边1 + 边2 + 边3 ) / 2
面积 = √(s(s - 边1)(s - 边2)(s - 边3))
2.5 2 5 -1.0 4.0 2.0
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3:");
double[][] points = new double[3][2];
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < points[i].length; j++) {
points[i][j] = scan.nextDouble();
}
}
scan.close();
if (getTriangleArea(points) == 0) {
System.out.println("The three points are on the same Line");
} else {
System.out.printf("The ares of the triangle is %.2f", getTriangleArea(points));
}
}
public static double getTriangleArea(double[][] points) {
double area = 0;
double d1 = Math.pow(Math.pow(points[1][0] - points[0][0], 2) + Math.pow(points[1][1] - points[0][1], 2), 0.5);
double d2 = Math.pow(Math.pow(points[2][0] - points[1][0], 2) + Math.pow(points[2][1] - points[1][1], 2), 0.5);
double d3 = Math.pow(Math.pow(points[2][0] - points[0][0], 2) + Math.pow(points[2][1] - points[0][1], 2), 0.5);
// double d1 = Math.pow(((x2 - x1) * (x2 - x1) + (y2 - y1) * (y2 - y1)), 0.5);
// double d2 = Math.pow(((x2 - x3) * (x2 - x3) + (y2 - y3) * (y2 - y3)), 0.5);
// double d3 = Math.pow(((x1 - x3) * (x1 - x3) + (y1 - y3) * (y1 - y3)), 0.5);
if (d1 <= d2 + d3 || d1 >= Math.abs(d2 - d3)) {
double s = (d1 + d2 + d3) / 2;
area = Math.pow(s * (s - d1) * (s - d2) * (s - d3), 0.5);
} else {
return 0;
}
return area;
}
}
结果:注意精度问题,double运算时,失之毫厘,缪之千里
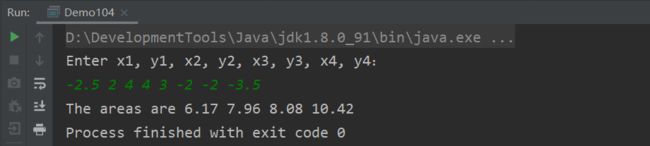
Demo104. (几何:多边形的子面积)一个具有四个顶点的凸多边形被分为四个三角形,编写一个程序,提示用户输入四个顶点的坐标,然后以升序显示四个三角形的面积。
下面是一个运行示例。
package Exer2;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo104 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
Enter x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4:
-2.5 2 4 4 3 -2 -2 -3.5
The areas are 6.17 7.96 8.08 10.42
*/
//1. 获取四个点的坐标,使用数组读入
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4:");
double[][] points = new double[4][2];
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < points[i].length; j++) {
points[i][j] = scan.nextDouble();
}
}
scan.close();
//2. 求v1v3和v2v4线的交点坐标
double[] crossPoint = intersection(points);
//3. 自定义方法求三角形面积(传入数组、下标、交点坐标数组),使用数组接收
double[] areas = new double[4];
for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){
areas[i] = getTriangleArea(points, i, crossPoint);
}
Arrays.sort(areas);
System.out.print("The areas are ");
for (double area : areas) {
System.out.printf("%.2f ", area);
}
}
// 求v1v3和v2v4线的交点坐标
public static double[] intersection(double[][] arr) {
double[] feedback = new double[2];
double k02 = (arr[2][1] - arr[0][1]) / (arr[2][0] - arr[0][0]);
double k13 = (arr[3][1] - arr[1][1]) / (arr[3][0] - arr[1][0]);
double b02 = arr[0][1] - k02 * arr[0][0];
double b13 = arr[1][1] - k13 * arr[1][0];
double x = (b02 - b13) / (k13 - k02);
double y = (b02 * k13 - b13 * k02) / (k13 - k02);
feedback[0] = x;
feedback[1] = y;
return feedback;
}
// 求三角形面积
public static double getTriangleArea(double[][] points, int index, double[] crossPoint) {
double area = 0;
int index1 = (index + 1) % 4;
double d1 = Math.pow(Math.pow(points[index1][0] - points[index][0], 2) + Math.pow(points[index1][1] - points[index][1], 2), 0.5);
double d2 = Math.pow(Math.pow(points[index1][0] - crossPoint[0], 2) + Math.pow(points[index1][1] - crossPoint[1], 2), 0.5);
double d3 = Math.pow(Math.pow(points[index][0] - crossPoint[0], 2) + Math.pow(points[index][1] - crossPoint[1], 2), 0.5);
double s = (d1 + d2 + d3) / 2;
area = Math.pow(s * (s - d1) * (s - d2) * (s - d3), 0.5);
return area;
}
}
结果:
Demo105. (拉丁正方形)拉丁正方形是一个n×n的数组,由n个不同的拉丁字母填充,每个拉丁字母恰好只在每行和每列中出现一次。编写一个程序,提示用户输人数字n以及字符数组,如示例输出所示,检测该输出数组是否是一个拉丁正方形。字符是从A开始的前面n个字符。
package Exer2;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo105 {
/*
(拉丁正方形)拉丁正方形是一个n×n的数组,由n个不同的拉丁字母填充,每个拉丁字母恰好只在每行和每列中出现一次。
编写一个程序,提示用户输人数字n以及字符数组,如示例输出所示,检测该输出数组是否是一个拉丁正方形。字符是从A开始的前面n个字符。
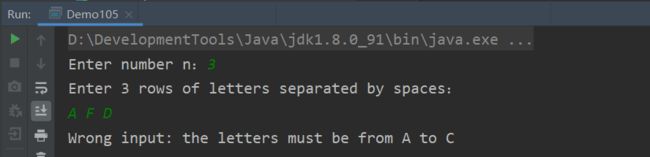
Enter number n:4
Enter 4 rows of letters separated by spaces:
A B C D
B A D C
C D B A
D C A B
The input array is a Latin square
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter number n:");
int number = scan.nextInt();
System.out.printf("Enter %s rows of letters separated by spaces:%n", number);
char[][] latin = new char[number][number];
for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < number; j++) {
latin[i][j] = scan.next().charAt(0);
if (latin[i][j] > ('A' - 1 + number)) {
System.out.println("Wrong input: the letters must be from A to " + (char) ('A' - 1 + number));
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
if (isLatin(latin)) {
System.out.println("The input array is a Latin square");
} else {
System.out.println("The input array is not a Latin square");
}
}
private static boolean isLatin(char[][] latin) {
HashSet set1 = new HashSet<>();
HashSet set2 = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < latin.length; i++) {
set1.clear();
set2.clear();
for (int j = 0; j < latin[i].length; j++) {
if (!set1.add(latin[i][j]) || !set2.add(latin[j][i])) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
结果: