吴恩达深度学习第一周编码练习
1,使用numpy构建基本函数
import numpy as np
# 构建一个返回实数x的sigmoid的函数。将math.exp(x)用于指数函数。
import math
def basic_sigmoid(x):
# simoid s的值
s = 1 / (1 + math.exp(-x))
return s
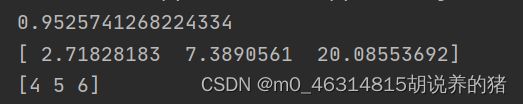
m = basic_sigmoid(3)
print(m)
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])
# np.array吧列表中的数据转换为矩阵或者向量,用于创建一个组
# x=basic_sigmoid(x)
# x是矢量,所以不能运行
print(np.exp(x))
# np.exp计算输入数组中的e^x每个值x,计算底数为e的指数函数
# 如果x是向量,则会将输出与x维度大小相同的向量
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(x + 3)
2,使用numpy实现sigmoid函数
def sigmoid(x):
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
return s
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])
m = sigmoid(x)
print(m)
3,创建函数sigmoid_grad()计算sigmoid函数相对于其输入x的梯度。
def sigmoid_derivative(x):
s = sigmoid(x)
ds = s * (1 - s)
return ds
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print("sigmoid_dervative(x)=" + str(sigmoid_derivative(x)))
def image2vector(image):
v = image.reshape(image.shape[0] * image.shape[1] * image.shape[2], 1)
return v
image = np.array([[[0.67826139, 0.29380381],
[0.90714982, 0.52835647],
[0.4215251, 0.45017551]],
[[0.92814219, 0.96677647],
[0.85304703, 0.52351845],
[0.19981397, 0.27417313]],
[[0.60659855, 0.00533165],
[0.10820313, 0.49978937],
[0.34144279, 0.94630077]]])
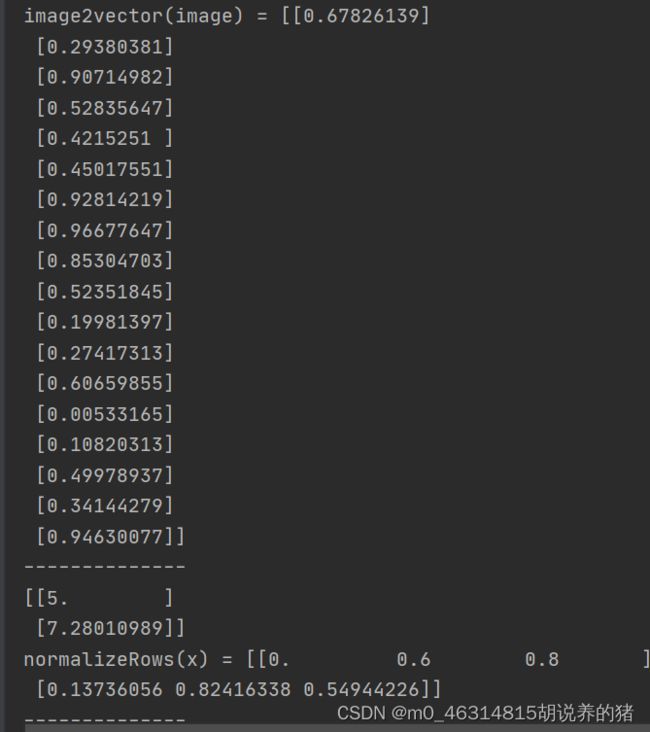
print("image2vector(image) = " + str(image2vector(image)))
print("--------------")
# 行标准化
def normalizeRows(x):
# 用于求范数,范数是把一个事物映射到非负实数,且满足非负性,齐次性,三角不等式,符合以上定义的都可以称之为范式
x_norm = np.linalg.norm(x, axis=1, keepdims=True)
# keepdims = True保持其二维亦或者三维的特性
print(x_norm)
x = x / x_norm
return x
x = np.array([
[0, 3, 4],
[1, 6, 4]])
print("normalizeRows(x) = " + str(normalizeRows(x)))
print("--------------")
5,广播
# softmax算法需要对两个或多个类进行分类时使用的标准化函数。
def softmax(x):
x_exp = np.exp(x)
# 计算以e为底的指数函数
x_sum = np.sum(x_exp, axis=1, keepdims=True)
s = x_exp / x_sum
return s
x = np.array([
[9, 2, 5, 0, 0],
[7, 5, 0, 0, 0]])
print("softmax(x) = " + str(softmax(x)))6,向量化
import time
x1 = [9, 2, 5, 0, 0, 7, 5, 0, 0, 0, 9, 2, 5, 0, 0]
x2 = [9, 2, 2, 9, 0, 9, 2, 5, 0, 0, 9, 2, 5, 0, 0]
tic = time.process_time()
# time.process_time()始终以秒为单位返回时间的浮点值
dot = 0
for i in range(len(x1)):
dot += x1[i] * x2[i]
toc = time.process_time()
print("dot = " + str(dot) + "\n ----- Computation time = " + str(1000 * (toc - tic)) + "ms")
tic = time.process_time()
outer = np.zeros((len(x1), len(x2))) # 返回来一个给定形状和类型的用0填充的数组;(len(x1)*len(x2))
for i in range(len(x1)):
for j in range(len(x2)): # 遍历这个数组
outer[i, j] = x1[i] * x2[j]
toc = time.process_time()
print("outer = " + str(outer) + "\n ----- Computation time = " + str(1000 * (toc - tic)) + "ms")
# 遍历输出15*15的数组,
tic = time.process_time()
mul = np.zeros(len(x1))
for i in range(len(x1)):
mul[i] = x1[i] * x2[i]
toc = time.process_time()
print("elementwise multiplication = " + str(mul) + "\n ----- Computation time = " + str(1000 * (toc - tic)) + "ms")
W = np.random.rand(3, len(x1)) # 随机产生一个3*len(x1)的数组
tic = time.process_time()
gdot = np.zeros(W.shape[0]) # shape[0]输出3,为矩阵的行数,同理shape[1]输出列数
for i in range(W.shape[0]):
for j in range(len(x1)): # 15*3
gdot[i] += W[i, j] * x1[j]
toc = time.process_time()
print("gdot = " + str(gdot) + "\n ----- Computation time = " + str(1000 * (toc - tic)) + "ms")
x1 = [9, 2, 5, 0, 0, 7, 5, 0, 0, 0, 9, 2, 5, 0, 0]
x2 = [9, 2, 2, 9, 0, 9, 2, 5, 0, 0, 9, 2, 5, 0, 0]
tic = time.process_time()
dot = np.dot(x1, x2)
toc = time.process_time()
print("dot = " + str(dot) + "\n ----- Computation time = " + str(1000 * (toc - tic)) + "ms")
tic = time.process_time()
outer = np.outer(x1, x2) # 表示的是两个向量相乘,拿第一个向量的元素分别与第二个向量所有元素相乘得到结果的一行。
toc = time.process_time()
print("outer = " + str(outer) + "\n ----- Computation time = " + str(1000 * (toc - tic)) + "ms")
tic = time.process_time()
mul = np.multiply(x1, x2) #计算a与b的内积
toc = time.process_time()
print("elementwise multiplication = " + str(mul) + "\n ----- Computation time = " + str(1000 * (toc - tic)) + "ms")
tic = time.process_time()
dot = np.dot(W, x1)
toc = time.process_time()
print("gdot = " + str(dot) + "\n ----- Computation time = " + str(1000 * (toc - tic)) + "ms")
7,实现L1和L2损失函数
def L1(yhat, y):
loss = np.sum(np.abs(y - yhat))
# np.abs()函数返回数字的绝对值
return loss
yhat = np.array([.9, 0.2, 0.1, .4, .9])
y = np.array([1, 0, 0, 1, 1])
print("L1 = " + str(L1(yhat, y)))
# 实现L2损失函数的Numpy向量化版本。
def L2(yhat, y):
loss = np.dot((y - yhat), (y - yhat).T)
# np.dot()获取两个元素的乘积
return loss
yhat = np.array([.9, 0.2, 0.1, .4, .9])
y = np.array([1, 0, 0, 1, 1])
print("L2 = " + str(L2(yhat, y)))