HDU 4947 GCD Array 容斥原理+树状数组
GCD Array
Time Limit: 11000/5500 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 843 Accepted Submission(s): 205
Problem Description
Teacher Mai finds that many problems about arithmetic function can be reduced to the following problem:
Maintain an array a with index from 1 to l. There are two kinds of operations:
1. Add v to a x for every x that gcd(x,n)=d.
2. Query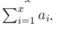
Maintain an array a with index from 1 to l. There are two kinds of operations:
1. Add v to a x for every x that gcd(x,n)=d.
2. Query
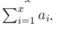
Input
There are multiple test cases, terminated by a line "0 0".
For each test case, the first line contains two integers l,Q(1<=l,Q<=5*10^4), indicating the length of the array and the number of the operations.
In following Q lines, each line indicates an operation, and the format is "1 n d v" or "2 x" (1<=n,d,v<=2*10^5,1<=x<=l).
For each test case, the first line contains two integers l,Q(1<=l,Q<=5*10^4), indicating the length of the array and the number of the operations.
In following Q lines, each line indicates an operation, and the format is "1 n d v" or "2 x" (1<=n,d,v<=2*10^5,1<=x<=l).
Output
For each case, output "Case #k:" first, where k is the case number counting from 1.
Then output the answer to each query.
Then output the answer to each query.
Sample Input
6 4
1 4 1 2
2 5
1 3 3 3
2 3
0 0
Sample Output
Case #1:
6
7
Author
xudyh
Source
题意:2个操作
在长度长度为len的数组操作
1 n v d 给数组x下标满足 gcd(x,n)=d的对应位置+v.
2 x 询问数组sum(a1,,,ax)的和
思路:如果一个一个更新是会超时的。
方法大致是这样,首先和GCD()问题类似,从反面着手,首先全部数字+v,然后在gcd(x,n)!=d的位置-v。
gcd(x,n) = d 可以转化为gcd(x/d,n/d)=1; 转化为求互质。这个应该容易理解些。
现在我设立一个数组a[ ] ,a[i] 代表的意思是 gcd(x,n)为i的倍数的时候的方案数。
那么原来的问题,N = n/d ,现在就分解N的素因子,并进行容斥。比如6 : 2 , 3 , -6.
首先在所有的数字上加v,然后用容斥的结果在数组上进行对不互质的地方进行-v。
举一个例子。
比如len = 10 , gcd(x,6) = 2; ==> gcd(x/2,3)=1;
那么我们只能在[1-10/2]进行更新。
求得的容斥结果为 2 , 3, -6.那么首先我们在所有的数字上+v,就是a[d]=v,(a[2]=v);
然后在2*d上减去v,3*d上减去v,6*d上加上v。就是这样。
至于为什么要*d,这个思考一下就会知道的。
这就是第一个操作了。
第二个操作就是询问数组【1-x】的和,转化为求数组在a[i]有多少个 x/i 个。
就是sum(a[i]*x/i) ;由于 x/i 我们能用sqrt()的算法来做。这里也就牵涉到求和,用树状数组。
代码比较挫,几乎是压线过。
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<cstdlib> 5 using namespace std; 6 typedef __int64 LL; 7 8 const int maxn = 50000+3; 9 const int INF = 2e5+3; 10 LL p[maxn]; 11 bool s[INF]; 12 int prime[17985],len; 13 14 void Init() 15 { 16 len = 0; 17 memset(s,false,sizeof(s)); 18 for(int i=2;i<INF;i++) 19 { 20 if(s[i]==true)continue; 21 prime[++len] = i; 22 for(int j=i+i;j<INF;j=j+i) 23 s[j]=true; 24 } 25 } 26 void add(int x,int n,int num1) 27 { 28 for(int i=x;i<=n;i=i+(i&(-i))) 29 p[i] = p[i] + num1; 30 } 31 LL query(int x) 32 { 33 if(x==0)return 0; 34 LL sum1 = 0; 35 while(x) 36 { 37 sum1=sum1+p[x]; 38 x=x-(x&(-x)); 39 } 40 return sum1; 41 } 42 int Q[5003],yz[1000],ylen,qlen; 43 void init(int n) 44 { 45 ylen = qlen = 0; 46 for(int i=1;prime[i]*prime[i]<=n;i++) 47 { 48 if(n%prime[i]==0) 49 { 50 while(n%prime[i]==0) n=n/prime[i]; 51 yz[++ylen] = prime[i]; 52 } 53 } 54 if(n!=1) yz[++ylen] = n; 55 Q[0]=-1; 56 for(int i=1;i<=ylen;i++) 57 { 58 int k = qlen; 59 for(int j=0;j<=k;j++) 60 Q[++qlen] = -1*Q[j]*yz[i]; 61 } 62 } 63 int main() 64 { 65 int n,m,hxl,d,v,size1,x,T=0; 66 Init(); 67 while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)>0) 68 { 69 if(n==0&&m==0)break; 70 memset(p,0,sizeof(p)); 71 printf("Case #%d:\n",++T); 72 while(m--) 73 { 74 scanf("%d",&size1); 75 if(size1==1) 76 { 77 scanf("%d%d%d",&hxl,&d,&v); 78 if(hxl%d!=0)continue; 79 hxl = hxl /d; 80 int tom = n/d; 81 add(d,n,v); 82 init(hxl); 83 for(int i=1;i<=qlen;i++) 84 if(Q[i]<0) { 85 Q[i] = -Q[i]; 86 if(Q[i]>tom)continue; 87 add(Q[i]*d,n,v); 88 } 89 else { 90 if(Q[i]>tom)continue; 91 add(Q[i]*d,n,-v); 92 } 93 } 94 else{ 95 scanf("%d",&x); 96 LL sum1 = 0; 97 for(int i=1,la=0;i<=x;i=la+1){ 98 la = x/(x/i); 99 sum1 = sum1 + (query(la)-query(i-1))*(x/i); 100 } 101 printf("%I64d\n",sum1); 102 } 103 } 104 } 105 return 0; 106 }