基于opencv的c++图像处理(霍夫直线检测与最小二乘法直线拟合)
前言
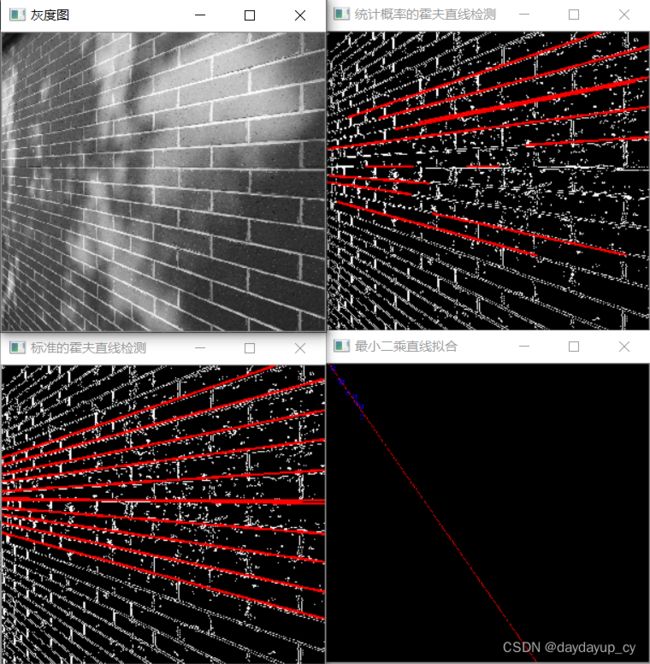
基于opencv的c++接口,实现标准的霍夫直线检测、基于统计概率的霍夫直线检测、以及最小二乘法直线拟合。
相关的opencv接口解析
CV_EXPORTS_W void HoughLines( InputArray image, OutputArray lines,
double rho, double theta, int threshold,
double srn = 0, double stn = 0,
double min_theta = 0, double max_theta = CV_PI );
该函数实现了用于线检测的标准或标准多尺度霍夫变换算法。请参阅 http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/HIPR2/hough.htm 以获得对 Hough 变换的良好解释。
@param image 8 位单通道二进制源图像。该功能可以修改图像。
@param lines 线的输出向量。每条线由 2 或 3 元素向量 (rho, theta)或 (rho, theta, votes) 表示。 rho是与坐标原点 (0,0)(图像左上角)的距离。theta是以弧度为单位的线旋转角度。 votes 是累加器的值。
@param rho 累加器的距离分辨率(以像素为单位)。
@param theta 累加器的角度分辨率(以弧度为单位)。
@param threshold 累加器阈值参数。仅返回那些获得足够票数的行。
@param srn 对于多尺度霍夫变换,它是距离分辨率 rho 的除数。粗略的累加器距离分辨率为 rho ,准确的累加器分辨率为 rho/srn 。如果 srn=0 和 stn=0 ,则使用经典的霍夫变换。否则,这两个参数都应该是正数。
@param stn 对于多尺度霍夫变换,它是距离分辨率 theta 的除数。
@param min_theta 对于标准和多尺度霍夫变换,检查线条的最小角度。必须介于 0 和 max_theta 之间。
@param max_theta 对于标准和多尺度霍夫变换,检查线条的最大角度。
必须介于 min_theta 和 CV_PI 之间。
CV_EXPORTS_W void HoughLinesP( InputArray image, OutputArray lines,
double rho, double theta, int threshold,
double minLineLength = 0, double maxLineGap = 0 );
该函数实现了用于线检测的概率霍夫变换算法。
@param image 8 位单通道二进制源图像。 该功能可以修改图像。
@param lines 线的输出向量。 每条线由一个 4 元素向量 (x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2) 表示,其中 (x_1,y_1) 和 (x_2, y_2) 是每个检测到的终点线段。
@param rho 累加器的距离分辨率(以像素为单位)。
@param theta 累加器的角度分辨率(以弧度为单位)。
@param threshold 累加器阈值参数。 仅返回那些获得足够票数的行( {threshold})。
@param minLineLength 最小行长度。 比这短的线段被拒绝。
@param maxLineGap 同一线上的点之间允许的最大间隙以链接它们。
CV_EXPORTS_W bool solve(InputArray src1, InputArray src2,
OutputArray dst, int flags = DECOMP_LU);
函数 cv::solve 解决线性系统或最小二乘问题(后者可以使用 SVD 或 QR 方法,或通过指定标志 #DECOMP_NORMAL )
@param src1 系统左侧的输入矩阵。
@param src2 系统右侧的输入矩阵。
@param dst 输出解决方案。
@param flags 解决方案(矩阵反转)方法(#DecompTypes)
//! matrix decomposition types
enum DecompTypes {
/** Gaussian elimination with the optimal pivot element chosen. */
DECOMP_LU = 0,
/** singular value decomposition (SVD) method; the system can be over-defined and/or the matrix
src1 can be singular */
DECOMP_SVD = 1,
/** eigenvalue decomposition; the matrix src1 must be symmetrical */
DECOMP_EIG = 2,
/** Cholesky \f$LL^T\f$ factorization; the matrix src1 must be symmetrical and positively
defined */
DECOMP_CHOLESKY = 3,
/** QR factorization; the system can be over-defined and/or the matrix src1 can be singular */
DECOMP_QR = 4,
/** while all the previous flags are mutually exclusive, this flag can be used together with
any of the previous; it means that the normal equations
\f$\texttt{src1}^T\cdot\texttt{src1}\cdot\texttt{dst}=\texttt{src1}^T\texttt{src2}\f$ are
solved instead of the original system
\f$\texttt{src1}\cdot\texttt{dst}=\texttt{src2}\f$ */
DECOMP_NORMAL = 16
};
示例代码
lines.h
#pragma once
#include lines.cpp
#include"lines.h"
int ImgLocate::FindLines::StandardHoughLineDetect(cv::Mat srcImage, cv::Mat &dstImage, double rhoStep, double thetaStep, int threshold)
{
//判断图像是否加载成功
if (srcImage.empty())
{
cout << "图像加载失败!" << endl;
return 1;
}
dstImage = srcImage.clone();
cv::cvtColor(dstImage, dstImage, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
//Mat houghMat = srcImage.clone();
// 标准的霍夫变换
vector<Vec2f> lines;
HoughLines(srcImage, lines, rhoStep, thetaStep, threshold, 0, 0);
std::cout << "直线数量:" << lines.size() << std::endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++)
{
// 根据直线参数表达式绘制相应检测结果
float rho = lines[i][0], theta = lines[i][1];
Point pt1, pt2;
double a = cos(theta), b = sin(theta);
double x0 = a*rho, y0 = b*rho;
pt1.x = cvRound(x0 + 1000 * (-b));
pt1.y = cvRound(y0 + 1000 * (a));
pt2.x = cvRound(x0 - 1000 * (-b));
pt2.y = cvRound(y0 - 1000 * (a));
line(dstImage, pt1, pt2, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 3, 8);
}
//cv::namedWindow("houghMat", 0);
//cv::imshow("houghMat", dstImage);
return 0;
}
int ImgLocate::FindLines::StatisticalProbabilityHoughLineDetect(cv::Mat srcImage, cv::Mat &dstImage, double rhoStep, double thetaStep, int threshold, double minLineLength, double maxLineGap)
{
//判断图像是否加载成功
if (srcImage.empty())
{
cout << "图像加载失败!" << endl;
return 1;
}
dstImage = srcImage.clone();
cv::cvtColor(dstImage, dstImage, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
// 统计概率的霍夫变换
vector<Vec4i> lines;
HoughLinesP(srcImage, lines, rhoStep, thetaStep, threshold, minLineLength, maxLineGap);
std::cout << "直线数量:" << lines.size() << std::endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++)
{
Vec4i l = lines[i];
// 绘制线检测结果
line(dstImage, Point(l[0], l[1]), Point(l[2], l[3]), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 3, 8);
}
return 0;
}
int ImgLocate::FindLines::LeastSquaresLineFit(cv::Mat srcImage, cv::Mat &dstImage, vector<Point> points, Mat &result)
{
dstImage = srcImage.clone();
//cv::cvtColor(dstImage, dstImage, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
//在原图上画出点
circle(dstImage, points[i], 3, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1, 8);
}
//构建A矩阵
int N = 2;
Mat A = Mat::zeros(N, N, CV_64FC1);
for (int row = 0; row < A.rows; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < A.cols; col++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < points.size(); k++)
{
A.at<double>(row, col) = A.at<double>(row, col) + pow(points[k].x, row + col);
}
}
}
//构建B矩阵
Mat B = Mat::zeros(N, 1, CV_64FC1);
for (int row = 0; row < B.rows; row++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < points.size(); k++)
{
B.at<double>(row, 0) = B.at<double>(row, 0) + pow(points[k].x, row)*points[k].y;
}
}
//A*X=B
Mat X;
//cout << A << endl << B << endl;
solve(A, B, X, DECOMP_LU);
cout << "[k;b]=" << X << endl;
result = X;
vector<Point>lines;
for (int x = 0; x < srcImage.size().width; x++)
{ // y = b + ax;
double y = X.at<double>(0, 0) + X.at<double>(1, 0)*x;
printf("(%d,%lf)\n", x, y);
lines.push_back(Point(x, y));
}
polylines(dstImage, lines, false, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, 8);
//namedWindow("srcImageLine",0);
//imshow("srcImageLine", dstImage);
return 0;
}
test.cpp
#include"lines.h"
ImgLocate::FindLines ImgFindLine;
int main()
{
// 读取源图像及判断
cv::Mat srcImage = cv::imread("building.jpg", 0);
if (!srcImage.data)
{
return 1;
}
cv::namedWindow("原始图", 0);
cv::imshow("原始图", srcImage);
// 转化为灰度图像
cv::Mat srcGray;
if (srcImage.channels() == 3)
{
cv::cvtColor(srcImage, srcGray, COLOR_RGB2GRAY);
}
else
{
srcGray = srcImage.clone();
}
cv::namedWindow("灰度图", 0);
cv::imshow("灰度图", srcGray);
cv::Mat edgeMat;
// Canny边缘检测 二值图像
Canny(srcGray, edgeMat, 50, 200, 3);
cv::namedWindow("edgeMat", 0);
cv::imshow("edgeMat", edgeMat);
标准的霍夫直线检测
Mat standardLineImage;
ImgFindLine.StandardHoughLineDetect(edgeMat, standardLineImage, 3, CV_PI / 180, 600);
cv::namedWindow("标准的霍夫直线检测", 0);
cv::imshow("标准的霍夫直线检测", standardLineImage);
//统计概率的霍夫直线检测
Mat statisticalImage;
ImgFindLine.StatisticalProbabilityHoughLineDetect(edgeMat, statisticalImage, 3, CV_PI / 180, 600,50,10);
cv::namedWindow("统计概率的霍夫直线检测", 0);
cv::imshow("统计概率的霍夫直线检测", statisticalImage);
//最小二乘法直线拟合:y=kx+b
vector<Point>points;
//(27 39) (8 5) (8 9) (16 22) (44 71) (35 44) (43 57) (19 24) (27 39) (37 52)
points.push_back(Point(27, 39));
points.push_back(Point(8, 5));
points.push_back(Point(8, 9));
points.push_back(Point(16, 22));
points.push_back(Point(44, 71));
points.push_back(Point(35, 44));
points.push_back(Point(43, 57));
points.push_back(Point(19, 24));
points.push_back(Point(27, 39));
points.push_back(Point(37, 52));
Mat src = Mat::zeros(400, 400, CV_8UC3);
Mat dstImage,result;
ImgFindLine.LeastSquaresLineFit(src, dstImage, points, result);
cv::namedWindow("最小二乘直线拟合", 0);
cv::imshow("最小二乘直线拟合", dstImage);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}