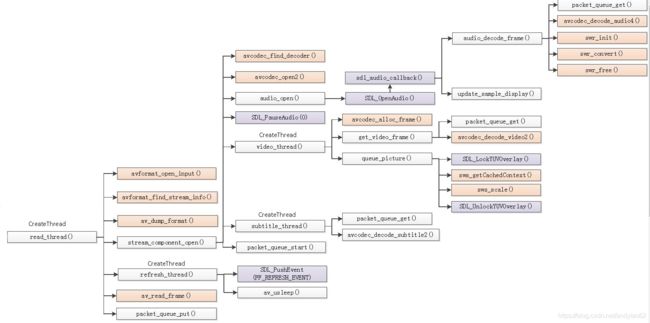
ijkplayer的read_thread线程分析(三)
目录
简介:
流程图:
代码分析:
1、avformat_open_input
2、avformat_find_stream_info
3、stream_component_open()
4、av_read_frame
5、主要循环
简介:
这个线程主要工作:
1)打开URL流媒体
2)解析视频流的相关信息
3)创建音视频解码器
4)创建SDL刷新线程
2)循环数据读取Packet,存入PacketQueue
与此同时,这个起播优化的相关修改也是在这个线程内
流程图:
代码分析:
1、avformat_open_input
avformat_open_input用于打开输入文件(对于网络流也是一样,在ffmpeg内部都抽象为URLProtocol,这里描述为文件是为了方便与后续提到的AVStream的流作区分),读取视频文件的基本信息。
int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps,
const char *filename,
AVInputFormat *fmt,
AVDictionary **options)
{
AVFormatContext *s = *ps;
int ret = 0;
AVFormatParameters ap = { { 0 } };
AVDictionary *tmp = NULL;
//创建上下文结构
if (!s && !(s = avformat_alloc_context()))
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
//如果用户指定了输入格式,直接使用它
if (fmt)
s->iformat = fmt;
//忽略
if (options)
av_dict_copy(&tmp, *options, 0);
if ((ret = av_opt_set_dict(s, &tmp)) < 0)
goto fail;
//打开输入媒体(如果需要的话),初始化所有与媒体读写有关的结构们,比如
//AVIOContext,AVInputFormat等等
if ((ret = init_input(s, filename)) < 0)
goto fail; 根据注释不难看懂代码。avformat_alloc_context主要malloc了一个AVFormatContext,并填充了默认值,主要分析init_input
static int init_input(AVFormatContext *s, const char *filename,
AVDictionary **options)
{
if ((ret = s->io_open(s, &s->pb, filename, AVIO_FLAG_READ | s->avio_flags, options)) < 0)
return ret;
return av_probe_input_buffer2(s->pb, &s->iformat, filename,
s, 0, s->format_probesize);
}如果从文件名中也猜不出媒体格式,则只能通过io_open打开这个文件进行探测了,先打开文件
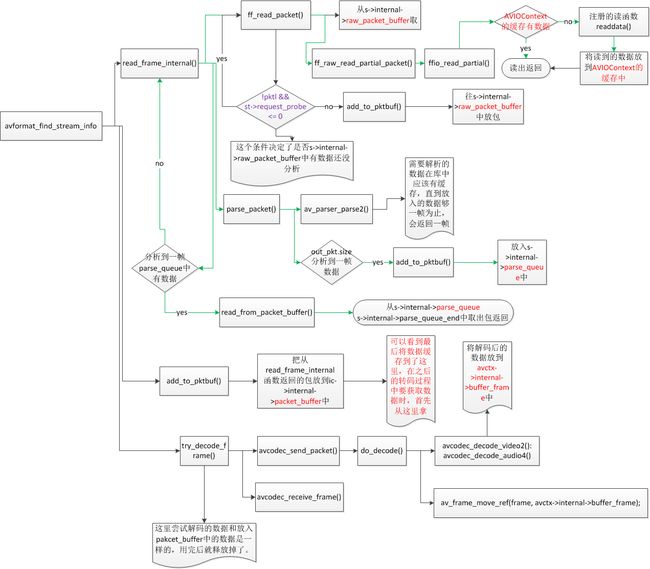
2、avformat_find_stream_info
这个过程比较复杂,起播优化也是主要针对这个函数进行优化。avformat_find_stream_info():获得媒体信息。这个函数有时候会影响首画的时间,看这个函数的源码发现:
这个函数会一直分析视频流的信息,当一直获取不到信息的时候就会一直在这个函数中,一直到它最大的限制,才会出来,会有好几秒的时间。如果网络卡的话,时间会
更长。但是我们可以自己给他添加限制,到达我们自己的限制条件的时候就会出来,不会一直在这个函数里面。
其中java部分设置的probsize和max_analyze_duration的控制行为,均是在这个函数里,
ic->probesize这个控制分析视频流的大小,当读的视频流大小达到这个size大小的时候,即使没有获取到信息 也会出来
ic->max_analyze_duration这个事控制视频流信息的大小,同理 当没有获取到信息,读取的视频流的时长达到这个duration的时候 也会出来。
if (read_size >= probesize) {
ret = count;
av_log(ic, AV_LOG_DEBUG,
"Probe buffer size limit of %"PRId64" bytes reached\n", probesize);
for (i = 0; i < ic->nb_streams; i++)
if (!ic->streams[i]->r_frame_rate.num &&
ic->streams[i]->info->duration_count <= 1 &&
ic->streams[i]->codecpar->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO &&
strcmp(ic->iformat->name, "image2"))
av_log(ic, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Stream #%d: not enough frames to estimate rate; "
"consider increasing probesize\n", i);
break;
} if (analyzed_all_streams) limit = max_analyze_duration;
else if (avctx->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE) limit = max_subtitle_analyze_duration;
else limit = max_stream_analyze_duration;
if (t >= limit) {
av_log(ic, AV_LOG_VERBOSE, "max_analyze_duration %"PRId64" reached at %"PRId64" microseconds st:%d\n",
limit,
t, pkt->stream_index);
if (ic->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_NOBUFFER)
av_packet_unref(pkt);
break;
}当达到上层设置的probsize和max_analyze_duration,就退出这个avformat_find_stream_info函数
ret = read_frame_internal(ic, &pkt1);read_frame_internal 在ffmpeg中实现了将format格式的packet,最终转换成一帧帧的es流packet,并解析填充了packet的pts,dts等信息,为最终解码提供了重要的数据,read_frame_internal,调用ff_read_packet,每次只读取一个包,然后直到parser完这个包的所有数据,才开始读取下一个包,parser完的数据被保存在parser结构的数据缓冲中,这样即使ff_read_packet读取的下一包和前一包的流不一样,由于parser也不一样,所以实现了read_frame_internal这个函数调用,可以解析出不同流的es流,而read_frame_internal函数除非出错否则必须解析出一帧数据才能返回.
ret = add_to_pktbuf(&ic->internal->packet_buffer, pkt,
&ic->internal->packet_buffer_end, 0);add_to_pktbuf这个是把读到的paket加入到buffer里
try_decode_frame(ic, st, pkt,(options && i < orig_nb_streams) ? &options[i] : NULL);顾名思义,尝试解码一帧数据,整个avformat_find_stream_info耗时的地方就在这个函数里
static int try_decode_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVStream *st, AVPacket *avpkt,
AVDictionary **options)
{
// 1. 判断是否已经打开 avcodec(条件为: AVCodecInternal 是否存在,found_decoder,codec_id)
if (!avcodec_is_open(avctx) &&
st->info->found_decoder <= 0 &&
(st->codecpar->codec_id != -st->info->found_decoder || !st->codecpar->codec_id)) {
// 如果未初始化decoder,则从codec_list[]查找与 codec_id 匹配的 AVCodec 结构体对象
codec = find_probe_decoder(s, st, st->codecpar->codec_id);
/* Force thread count to 1 since the H.264 decoder will not extract
* SPS and PPS to extradata during multi-threaded decoding. */
av_dict_set(options ? options : &thread_opt, "threads", "1", 0);
if (s->codec_whitelist)
av_dict_set(options ? options : &thread_opt, "codec_whitelist", s->codec_whitelist, 0);
// 调用 avcodec_open2() 打开及初始化 codec
ret = avcodec_open2(avctx, codec, options ? options : &thread_opt);
if (!options)
av_dict_free(&thread_opt);
if (ret < 0) {
st->info->found_decoder = -avctx->codec_id;
goto fail;
}
st->info->found_decoder = 1;
} else if (!st->info->found_decoder)
st->info->found_decoder = 1;
// 2. 判断是否需要跳过 1 帧
if (avpriv_codec_get_cap_skip_frame_fill_param(avctx->codec)) {
do_skip_frame = 1;
skip_frame = avctx->skip_frame;
avctx->skip_frame = AVDISCARD_ALL;
}
// 3. 开始解码
while ((pkt.size > 0 || (!pkt.data && got_picture)) &&
ret >= 0 &&
(!has_codec_parameters(st, NULL) || !has_decode_delay_been_guessed(st) ||
(!st->codec_info_nb_frames &&
(avctx->codec->capabilities & AV_CODEC_CAP_CHANNEL_CONF)))) {
got_picture = 0;
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "Tango try_decode_frame 4444 -1\n");
if (avctx->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO ||
avctx->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO) {
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "Tango try_decode_frame 4444 -1-1,pkt.size=%d\n",pkt.size);
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Tango try_decode_frame height 1111 = %d\n", avctx->height);
// 如果是video 或 audio ,发 packet 进入解码队列进行解码
ret = avcodec_send_packet(avctx, &pkt);
if (ret < 0 && ret != AVERROR(EAGAIN) && ret != AVERROR_EOF)
break;
if (ret >= 0)
pkt.size = 0;
ret = avcodec_receive_frame(avctx, frame);
}
}
}总共三个步骤: avcodec_is_open,avpriv_codec_get_cap_skip_frame_fill_param,decode_frame
decode_frame借助ffmpeg的两个方法来完成解码:
int avcodec_send_packet(AVCodecContex* *avctx, const AVPacket *avpkt);往解码器里面发送pkt数据。
int avcodec_receive_frame(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *frame);从解码器里面读取出frame帧数据。
decode_frame这个步骤是比较耗时的,起播优化就是要跳过这个步骤
3、stream_component_open()
stream_component_open():打开相应解码器,并创建相应的解码线程。
static int stream_component_open(FFPlayer *ffp, int stream_index)
{
AVCodecContext *avctx;//解码器上下文
AVCodec *codec = NULL;//解码器
//找到解码器
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(avctx->codec_id);
switch (avctx->codec_type) {
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO:
ret = audio_open(ffp, channel_layout, nb_channels, sample_rate, &is->audio_tgt);
//decoder初始化
decoder_init(&is->auddec, avctx, &is->audioq, is->continue_read_thread);
//decoder启动,启动audio_thread线程
if ((ret = decoder_start(&is->auddec, audio_thread, ffp, "ff_audio_dec")) < 0)
goto out;
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO:
//decoder初始化
decoder_init(&is->viddec, avctx, &is->videoq, is->continue_read_thread);
ffp->node_vdec = ffpipeline_open_video_decoder(ffp->pipeline, ffp);
if (!ffp->node_vdec)
goto fail;
//解码器开始
if ((ret = decoder_start(&is->viddec, video_thread, ffp, "ff_video_dec")) < 0)
goto out;
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE:
//decoder初始化
decoder_init(&is->subdec, avctx, &is->subtitleq, is->continue_read_thread);
//解码器开始
if ((ret = decoder_start(&is->subdec, subtitle_thread, ffp, "ff_subtitle_dec")) < 0)
goto out;
break;
}4、av_read_frame
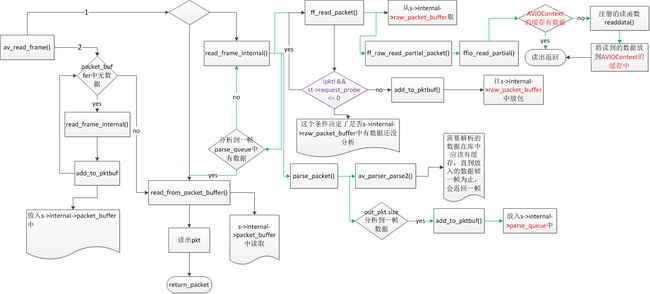
ffmpeg中的av_read_frame()的作用是读取码流中的音频若干帧或者视频一帧。例如,解码视频的时候,每解码一个视频帧,需要先调用 av_read_frame()获得一帧视频的压缩数据,
然后才能对该数据进行解码(例如H.264中一帧压缩数据通常对应一个NAL)
如果packet_buffer存在数据,根据pts返回AVPacket
如果packet_buffer不存在数据调用函数read_frame_internal
read_frame_internal()代码比较长,这里只简单看一下它前面的部分。它前面部分有2步是十分关键的:
(1)调用了ff_read_packet()从相应的AVInputFormat读取数据。
(2)如果媒体频流需要使用AVCodecParser,则调用parse_packet()解析相应的AVPacket。
5、主要循环
这部分是read_thread的主循环,主要工作:
1)处理seek请求
2)控制缓冲状态
3)读取packet帧数据
4)把读到的packet放入Packetqueue
for (;;) {
if (is->abort_request)
break;//处理退出请求
if (is->paused != is->last_paused) {
//处理暂停/恢复
}
if (is->seek_req) {
//处理seek请求
ret = avformat_seek_file(is->ic, -1, seek_min, seek_target, seek_max, is->seek_flags);
}
//控制缓冲区大小
if (infinite_buffer<1 &&
(is->audioq.size + is->videoq.size + is->subtitleq.size > MAX_QUEUE_SIZE
|| (stream_has_enough_packets(is->audio_st, is->audio_stream, &is->audioq) &&
stream_has_enough_packets(is->video_st, is->video_stream, &is->videoq) &&
stream_has_enough_packets(is->subtitle_st, is->subtitle_stream, &is->subtitleq)))) {
/* wait 10 ms */
continue;
}
//播放完成,循环播放
if (!is->paused &&
(!is->audio_st || (is->auddec.finished == is->audioq.serial && frame_queue_nb_remaining(&is->sampq) == 0)) &&
(!is->video_st || (is->viddec.finished == is->videoq.serial && frame_queue_nb_remaining(&is->pictq) == 0))) {
if (loop != 1 && (!loop || --loop)) {
stream_seek(is, start_time != AV_NOPTS_VALUE ? start_time : 0, 0, 0);
} else if (autoexit) {
ret = AVERROR_EOF;
goto fail;
}
}
//读取一个Packet(解封装后的数据)
ret = av_read_frame(ic, pkt);
//放入PacketQueue
packet_queue_put();
}