SpringMvc参数传递
SpringMvc两种映射规则
1.spring mvc 默认参数映射规则:名字一致 自动映射
2.spring mvc自定义映射规则:可以通过注解来实现=> @RequestParam
传递基本数据类型
@RequestParam,POST和GET均支持
注解定义
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER}) // 只能作用于参数上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestParam {
// 定义参数名称,默认和名字一致
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
// 定义参数名称,默认和名字一致
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
// 默认必填,一旦加上该注解,前台必须传递此参数
boolean required() default true;
// 定义默认值
String defaultValue() default "\n\t\t\n\t\t\n\ue000\ue001\ue002\n\t\t\t\t\n";
}关于@AliasFor注解说明:标识2个属性作用一致
在Spring的众多注解中,经常会发现很多注解的不同属性起着相同的作用,比如@RequestParam 的value属性和name属性,这就需要做一些基本的限制,比如value和path的值不能冲突,比如任意设置value或者设置path属性的值,都能够通过另一个属性来获取值等等。为了统一处理这些情况,Spring创建了@AliasFor标签。
@RequestMapping注解中也有应用。
注解使用示例
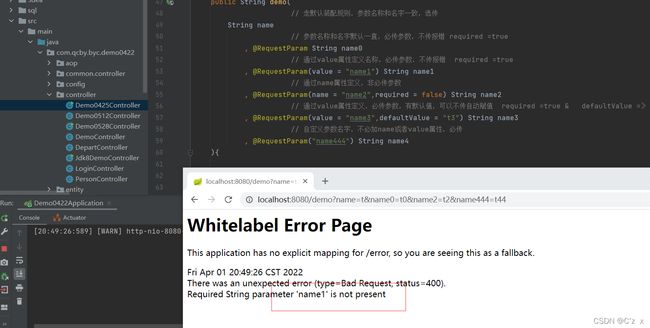
@RequestMapping("demo")
public String demo(Model model
// 走默认装配规则,参数名称和名字一致,选传
,String name
// 参数名称和名字默认一直,必传参数,不传报错
,@RequestParam String name0
// 通过value属性定义名称,必传参数,不传报错
,@RequestParam(value = "name1") String name1
// 通过name属性定义,非必传参数
,@RequestParam(name = "name2",required = false) String name2
// 通过value属性定义,必传参数,有默认值,可以不传自动赋值
,@RequestParam(value = "name3",defaultValue = "t3") String name3
// 自定义参数名字,不必加name或者value属性,必传
,@RequestParam("name444") String name4
){
System.out.println("name:"+name);
System.out.println("name0:"+name0);
System.out.println("name1:"+name1);
System.out.println("name2:"+name2);
System.out.println("name3:"+name3);
System.out.println("name4:"+name4);
return "hello";
}请求连接:
/demo?name=t&name0=t0&name1=t1&name2=t2&name444=t44
结果展示
必传参数name1,不传会报400错误,如下:
@PathVariable,POST和GET均支持
注:和@RequestParam注解使用相同的地方简述
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface PathVariable {
// 定义参数名称,默认和名字一致
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
// 定义参数名称,默认和名字一致
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
// 默认必填,一旦加上该注解,前台必须传递此参数
boolean required() default true;
}注解使用示例
@RequestMapping(value={
"demo1/{name1}/{name2}/{name3}"
// 配合name3选传,此种场景应用较少,一般使用此注解均为必传参数
,"demo1/{name1}/{name2}"
})
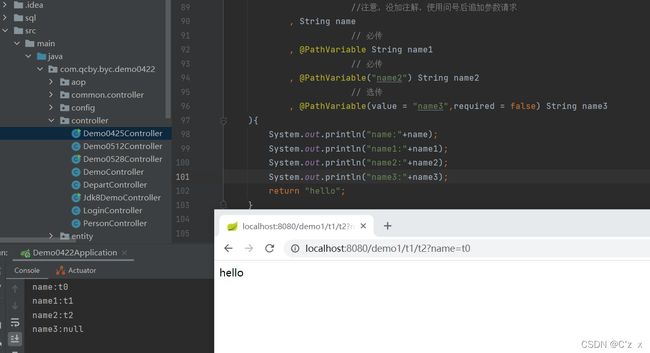
public String demo1(Model model
//注意,没加注解,使用问号后追加参数请求
,String name
// 必传
,@PathVariable String name1
// 必传
,@PathVariable("name2") String name2
// 选传
,@PathVariable(value = "name3",required = false) String name3
){
System.out.println("name:"+name);
System.out.println("name1:"+name1);
System.out.println("name2:"+name2);
System.out.println("name3:"+name3);
return "hello";
}请求连接:
/demo1/t1/t2?name=t0
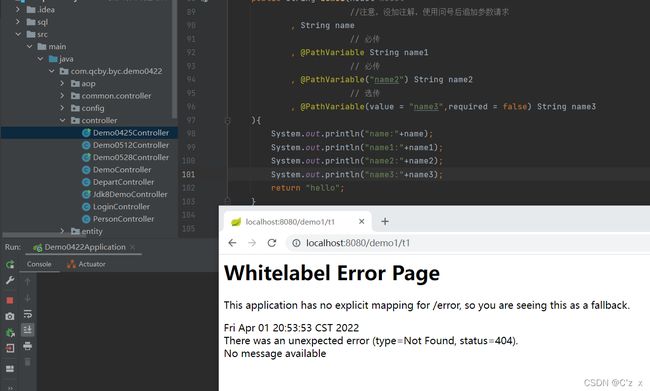
/demo1/t1/t2/t3
/demo1/t1 ===> 404地址找不到
结果展示
如果是使用注解@PathVariable必传的参数类型,不加参数会报404。
总结:参数传递时,可以使用@RequestParam和@PathVariable传递参数,也可以走Spring Mvc默认的装配规则,根据实际使用场景来选择即可。
传递普通对象
对象参数名称不影响参数传递
非JSON请求
前台
localhost:8080/demo2?name=1&number=2
后台
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo2")
public Demo demo2(Demo demo){
System.out.println("demo:"+demo);
return demo;
}结果展示
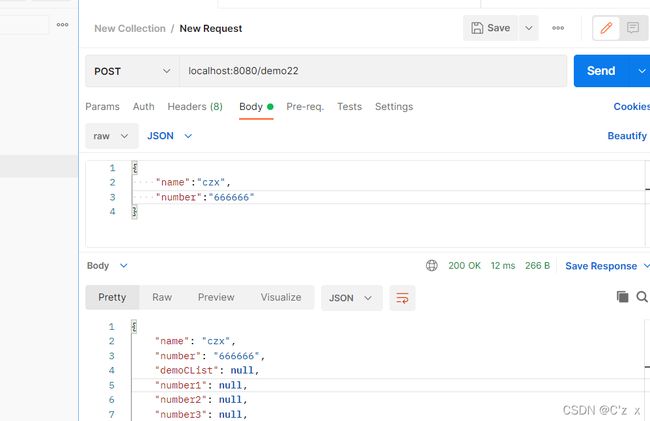
JSON请求
这里使用了postman
后台
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("demo22")
public Demo demo22(@RequestBody Demo demo){
System.out.println("demo:"+demo);
return demo;
}传递数组
非JSON请求
前台
localhost:8080/demo3?ids=1&ids=2&ids=3
或
localhost:8080/demo3?ids=1,2,3
后台
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo3")
public Long[] demo3(Long[] ids){
System.out.println("ids:"+ids.length);
return ids;
}JSON请求
前台
后台
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo33")
public Long[] demo33(@RequestBody Long[] ids){
System.out.println("ids:"+ids.length);
return ids;
}传递集合List
非JSON请求
前台
localhost:8080/demo4?idList=1&idList=2
或
http://localhost:8080/demo4?idList=1,2,3
后台(@RequestParam注解不可缺少)
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo4")
public List demo4(@RequestParam List idList){
System.out.println("ids:"+idList);
return idList;
} JSON请求
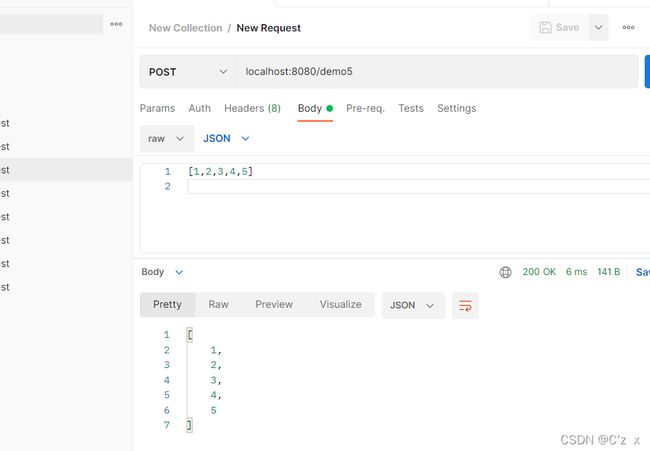
前台
后台
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo5")
public List demo5(@RequestBody List idList){
System.out.println("ids:"+idList);
return idList;
} 对象+List同时接收
场景
- rbac更新某个角色的权限信息=> 角色id + List idList
- 考试答题:个人信息 + 每道题的唯一标识 和 所选答案
非JSON请求=>不是content-type:application/json
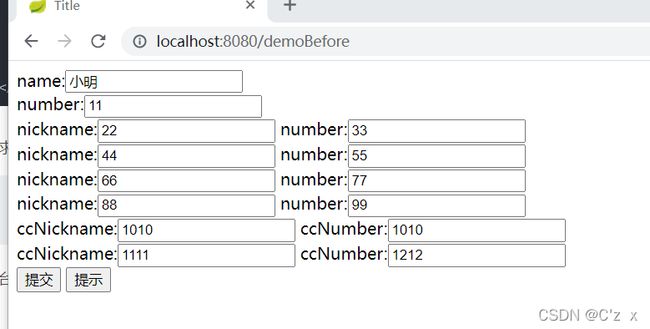
前台 html
请求地址
http://localhost:8080/demoBefore
前台
后台
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo6")
public Demo demo6(Demo demo){
System.out.println("demo:"+demo);
return demo;
}
==============================================
public class Demo {
private String name;
private String number;
private List demoCList;
....省略get set方法....
} JSON请求=>content-type:application/json
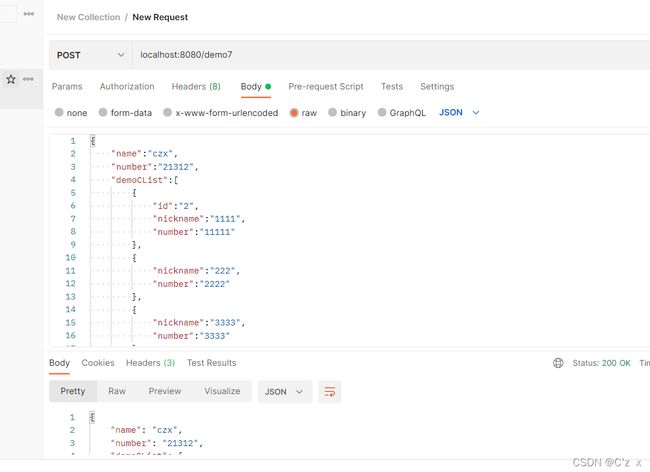
前台
后台
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo7")
public Demo demo7(@RequestBody Demo demo){
System.out.println("demo:"+demo);
return demo;
}源码
@Controller
@RequestMapping // 默认 /
public class DemoController {
protected Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Autowired
private HttpSession httpSession;
/**
*
* 1.spring mvc 默认参数映射规则:名字一致 自动映射
* 2.自定义映射规则:可以通过注解来实现=> @RequestParam
* 所有的注解的效果 都由解析的地方来决定用
*
*
* @param model
* @param name
* @param name0
* @param name1
* @param name2
* @param name3
* @param name4
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(path= "demo") // demo : ip+端口 +项目根路径 + / + demo
@ResponseBody // 返回类型是一个对象:可以是字符串、对象、List等等;不是一个页面
public String demo(
// 走默认装配规则,参数名称和名字一致,选传
String name
// 参数名称和名字默认一直,必传参数,不传报错 required =true
, @RequestParam String name0
// 通过value属性定义名称,必传参数,不传报错 required =true
, @RequestParam(value = "name1") String name1
// 通过name属性定义,非必传参数
, @RequestParam(name = "name2",required = false) String name2
// 通过value属性定义,必传参数,有默认值,可以不传自动赋值 required =true & defaultValue =》 required =false
, @RequestParam(value = "name3",defaultValue = "t3") String name3
// 自定义参数名字,不必加name或者value属性,必传
, @RequestParam("name444") String name4
){
// 0不能作为被除数
// int c= 1 / 0;
// for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
// System.out.println("name:"+name);
// System.out.println("name:"+name);
// System.out.println("i:"+i);
// if(i == 56){
// int c = i/0;
// }
// }
System.out.println("name:"+name);
System.out.println("name0:"+name0);
System.out.println("name1:"+name1);
System.out.println("name2:"+name2);
System.out.println("name3:"+name3);
System.out.println("name4:"+name4);
return "hello";
}
@RequestMapping(value={
"demo1/{name1}/{name2}/{name3}"
// 配合name3选传,此种场景应用较少,一般使用此注解均为必传参数
,"demo1/{name1}/{name2}"
})
@ResponseBody
public String demo1(Model model
//注意,没加注解,使用问号后追加参数请求
, String name
// 必传
, @PathVariable String name1
// 必传
, @PathVariable("name2") String name2
// 选传
, @PathVariable(value = "name3",required = false) String name3
){
System.out.println("name:"+name);
System.out.println("name1:"+name1);
System.out.println("name2:"+name2);
System.out.println("name3:"+name3);
return "hello";
}
private String test(){
return "";
}
// @RequestMapping("demoBefore")
// @GetMapping("demoBefore")
@RequestMapping(
method = {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST}
,value = "demoBefore"
)
public String demoBefore(){
// if(httpSession.getAttribute("user") == null){
// return "login";
// }
return "demo";
}
// form表单传参
/**
* 添加、修改 都是以对象作为参数;
* 查询时以对象为参数,查询条件变动时,同理
* @param demo
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody //返回是一个对象 不是渲染页面
@RequestMapping("demo2")
// @RequestMapping(value = "demo2",
// method = {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST})
// @GetMapping("demo2")
// @PostMapping("demo2")
public Demo demo2(Demo demo){
System.out.println("demo:"+demo);
return demo;
}
/**
* @RequestBody 要求前台通过json格式传递参数 header: content-type : application/josn
* @param demo
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("demo22") // 只允许使用post方式
// @GetMapping
// @RequestMapping(
// method = {RequestMethod.POST},value = "demo22"
// )
public Demo demo22(@RequestBody Demo demo){
System.out.println("demo:"+demo);
return demo;
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo3")
public Long[] demo3(Long[] ids){
System.out.println("ids:"+ids.length);
return ids;
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo33")
public Long[] demo33(@RequestBody Long[] ids){
System.out.println("ids:"+ids.length);
return ids;
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo4")
public List demo4(@RequestParam List idList){
// 0不能作为被除数
// int c= 1/ 0;
System.out.println("ids:"+idList);
return idList;
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo5")
public List demo5(@RequestBody List idList){
System.out.println("ids:"+idList);
return idList;
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo6")
public Demo demo6(Demo demo){
System.out.println("demo:"+demo);
return demo;
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("demo7")
public Demo demo7(@RequestBody Demo demo){
System.out.println("demo:"+demo);
return demo;
}
}