Python——爬虫+词云+数据库
爬取指定新闻网站,将爬取到的数据做词频统计生成词云图,做相应的词频分析饼状图,柱状图,散点图。最后将词频数据存至MySQL数据库。
编译环境:PyCharm
数据库下载:AppServ8.5
需用到的模块有:
import time
from PySide2.QtCore import QFile
from PySide2.QtGui import QPixmap
from PySide2.QtWidgets import QApplication, QGraphicsScene, QGraphicsPixmapItem
from PySide2.QtUiTools import QUiLoader
from urllib import request
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import wordcloud # 词云图
import collections
import jieba
import re
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import threading # 多线程
from string import punctuation as Englishpunctuation # 获取英文标点集合
from zhon.hanzi import punctuation as zhonpunctuation # 获取中文标点集合
from selenium import webdriver
import csv
import xlwt
import pymysql
import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie,Bar,EffectScatter
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType主程序:
import time
from PySide2.QtCore import QFile # .ui文件获取
from PySide2.QtGui import QPixmap # 加载图片
from PySide2.QtWidgets import QApplication, QGraphicsScene, QGraphicsPixmapItem # 加载图片
from PySide2.QtUiTools import QUiLoader
from urllib import request # 爬取URL
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # 筛取爬完的html文件
import wordcloud # 词云图
import collections # 词频计数
import jieba # 分词
import re
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image # 加载图片
import threading # 多线程
from string import punctuation as Englishpunctuation # 获取英文标点集合
from zhon.hanzi import punctuation as zhonpunctuation # 获取中文标点集合
import showpie # 自己定义
from selenium import webdriver # 用浏览器打开html
import 数据库 # 自己定义
import CSV # 自己定义
# 三个ui文件“UI.ui”,"denlu.ui","zhuce.ui"
# 词云图片保存为“wc.png”
# 词云数据保存为“word_counts_topALL.text”
# xls文件保存为“myexcel.xls”
# 数据库 URL:"http://localhost:8080/phpMyAdmin/" 登录名:root 密码:12345678 数据库名:db.db
url = []
url_sina = ['https://news.sina.com.cn/c/xl/2022-01-01/doc-ikyakumx7683060.shtml','https://news.sina.com.cn/o/2022-01-01/doc-ikyamrmz2472300.shtml','https://news.sina.com.cn/o/2022-01-01/doc-ikyamrmz2467548.shtml',
'https://news.sina.com.cn/c/2022-01-01/doc-ikyamrmz2515302.shtml','https://news.sina.com.cn/c/2021-12-31/doc-ikyamrmz2441156.shtml','https://finance.sina.com.cn/roll/2022-01-01/doc-ikyakumx7644198.shtml',
'https://news.sina.com.cn/c/2021-12-31/doc-ikyakumx7537811.shtml','https://news.sina.com.cn/w/2021-12-30/doc-ikyamrmz2171966.shtml','https://news.sina.com.cn/c/2022-01-01/doc-ikyakumx7666807.shtml',
'https://news.sina.com.cn/c/xl/2021-12-30/doc-ikyakumx7357600.shtml']
url_163 = ['https://www.163.com/dy/article/GSG29CEJ05346RC6.html',
'https://www.163.com/dy/article/GSIEC0U70514R9OJ.html', 'https://www.163.com/dy/article/GSGOQOQE05346RC6.html','https://www.163.com/dy/article/GSK18CJD0514R9OJ.html'
'https://www.163.com/news/article/GSIBLSAH000189FH.html','https://www.163.com/dy/article/GSKR7DJ60514R9M0.html','https://www.163.com/dy/article/GSH9FIT90514R9M0.html?clickfrom=w_yw','https://www.163.com/gov/article/GD3TBM6R002399RB.html'
'https://www.163.com/dy/article/GA4CC6I20512D3VJ.html','https://www.163.com/dy/article/GSKP64C80514R9OJ.html']
url_ifeng = ['https://news.ifeng.com/c/8CRYT9RnXii', 'https://news.ifeng.com/c/8CQQcdns5Jg','https://news.ifeng.com/c/8CRl1IGC2vG','https://news.ifeng.com/c/8CRE4AyY0NX','https://finance.ifeng.com/c/8CRE4AyY0P0',
'https://news.ifeng.com/c/8CCxj8nMaVl','https://news.ifeng.com/c/8CQKzempy4j','https://news.ifeng.com/c/8CRa0Nir1bc','https://news.ifeng.com/c/8CRYT9RnXkL','https://news.ifeng.com/c/8CRU98XbWBp']
url.append(url_sina);url.append(url_163);url.append(url_ifeng)
class UIPython:
def __init__(self):
# 从文件中加载UI定义
qfile = QFile("UI.ui")
qfile.open(QFile.ReadOnly)
qfile.close()
# 从 UI 定义中动态 创建一个相应的窗口对象
self.ui = QUiLoader().load(qfile)
self.ui.ciyunButton.clicked.connect(self.ciyun)
# 将爬取内容写入html文件 使用异常处理防止反爬导致程序崩溃停止
def writetext(self, url_name, address):
with open(address, mode='w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write('')
for j in url_name:
try:
r = request.Request(j)
r.add_header('User-agent', 'PyMOTW(https://pymotw.com/)')
responce = request.urlopen(r)
except Exception as e:
print("页面加载失败{0}\n".format(j))
data = responce.read().decode('utf-8', 'ignore')
with open('try.html', mode='a', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(data)
data = BeautifulSoup(data, 'lxml')
data_title = list(data.find_all('title'))
data_content = list(data.find_all('content'))
data_page = list(data.find_all('p'))
with open(address, mode='a', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for i in data_title:
f.write(str(i.text) + '\n')
for i in data_content:
f.write(str(i.text) + '\n')
for i in data_page:
f.write(str(i.text) + '\n')
# 定义词云格式
def definewc(self):
# 获取UI.ui界面内容
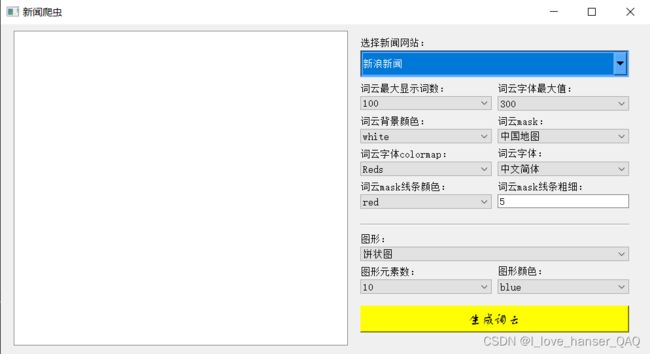
max_words = self.ui.max_words.currentText()
max_font_size = self.ui.max_font_size.currentText()
colormap = self.ui.colormap.currentText()
background_color = self.ui.background_color.currentText()
font_path = self.ui.font_path.currentText()
mask = self.ui.maskname.currentText()
contour_color = self.ui.contour_color.currentText()
contour_width =self.ui.contour_width.text()
# 获取字体
if font_path == '中文简体':
font_path = 'fonts\simfang.ttf'
elif font_path == '方正舒体':
font_path='fonts\FZSTK.TTF'
elif font_path == '华文行楷':
font_path='fonts\STXINGKA.TTF'
# 获取mask
if mask == '中国地图':
mask = np.array(Image.open('E://语音包//ChinaMap.png')) # 定义词频背景
elif mask == '爱丽丝':
mask = np.array(Image.open('E://语音包//alice_mask.png'))
# 设置词云格式
wc = wordcloud.WordCloud(
font_path=str(font_path), # 设置字体格式
background_color=str(background_color),
mask=mask, # 设置背景图
colormap=str(colormap),
max_words=int(max_words), # 最多显示词数
max_font_size=int(max_font_size), # 字体最大值
contour_color=contour_color,
contour_width=int(contour_width)
)
return wc
# 展示词云
def showwordcloud(self, address):
with open(address, mode='r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
string_data = f.read()
# 文本预处理
for i in Englishpunctuation:
string_data = string_data.replace(i, '') # 删除标点符号
for i in zhonpunctuation:
string_data = string_data.replace(i, '')
string_data = re.sub('[a-zA-Z]', '', string_data) # 删除英文
string_data = re.sub('[\d]', '', string_data) # 删除数字
# 文本分词
seg_list_exact = jieba.cut(string_data, cut_all=False) # 精确模式分词
object_list = []
remove_words = [u'的', u'和', u'是', u'随着', u'对于', u'对', u'等', u'能', u'都', u'中', u'在', u'了',u'通常', u'如果', u'我们', u'需要', u'他', u'要', u"\u3000", u'年', u'月', u'也', u'你'
, u'\n', u' ', u'▎'] # 自定义去除词库
for word in seg_list_exact: # 循环读出每个分词
if word not in remove_words: # 如果不在去除词库中
object_list.append(word) # 分词追加到列表
# 词频统计
word_counts = collections.Counter(object_list) # 对分词做词频统计
maxword_number = self.ui.number.currentText()
word_counts_top = word_counts.most_common(int(maxword_number)) # 获取前10最高频的词
word_counts_topall = word_counts.most_common()
print(word_counts_top) # 输出检查
# 词频展示
wc = self.definewc()
wc.generate_from_frequencies(word_counts) # 从字典生成词云
wc.to_file('wc.png')
# 将词云图加载到UI.ui界面
self.ui.GraphView.scene_img = QGraphicsScene()
self.imgShow = QPixmap()
self.imgShow.load('wc.png')
self.imgShowItem = QGraphicsPixmapItem()
self.imgShowItem.setPixmap(QPixmap(self.imgShow))
self.ui.GraphView.scene_img.addItem(self.imgShowItem)
self.ui.GraphView.setScene(self.ui.GraphView.scene_img)
self.ui.GraphView.fitInView(QGraphicsPixmapItem(QPixmap(self.imgShow)))
# 将词云结果插入MySQL数据库
数据库.insertdb(word_counts_topall)
# 写入“word_counts_topALL.text”文本
with open("word_counts_topALL.text", mode='w', encoding='utf8') as f:
for i in word_counts_topall:
f.write(i[0]+'\t'+str(i[1])+'\n')
# 写入.csv和.xls
CSV.writecsv(word_counts_topall)
CSV.openxls()
# 获取选择的图形颜色
colour = self.ui.colour.currentText()
if colour == 'blue':colour = '#abddff'
elif colour == 'yellow':colour = '#ffff7f'
elif colour == 'green':colour = '#7cff9d'
elif colour == 'red':colour = '#ff0000'
# 生成分析图形
word = []
for i in word_counts_top:
word.append(list(i))
tuxing = self.ui.tuxing.currentText()
if tuxing == '饼状图':
showpie.pietu(word, colour)
elif tuxing == '柱状图':
showpie.Bartu(word, colour)
elif tuxing == '散点图':
showpie.Scatter(word, colour)
# 设置显示图片守护线程
thread1 = threading.Thread(target=self.keepdriver)
thread1.setDaemon(True)
thread1.start()
# 使html在游览器上循环出现
def keepdriver(self):
driver = webdriver.Edge()
while(True):
driver.get('file://C://Users//hp//Desktop//Python//课设//Lib//customized.html')
driver.maximize_window()
time.sleep(1000)
# 词云主程序
def ciyun(self):
url_address=self.ui.news_address.currentText()
if url_address == '新浪新闻':
url_address = url[0]
address = 'news_sina.html'
elif url_address == '网易新闻':
url_address = url[1]
address = 'news_163.html'
elif url_address == '凤凰新闻':
url_address = url[2]
address = 'news_ifeng.html'
self.writetext(url_address, address)
self.showwordcloud(address)
# 登陆界面
class Denlu:
def __init__(self):
# 从文件中加载UI定义
qfile = QFile("denlu.ui")
qfile.open(QFile.ReadOnly)
qfile.close()
# 从 UI 定义中动态 创建一个相应的窗口对象
self.ui = QUiLoader().load(qfile)
self.ui.acknowledge.clicked.connect(self.acknowledge)
self.ui.delete_2.clicked.connect(self.ui.close)
self.ui.zhuce.clicked.connect(self.zhuce)
# 确认按钮程序
def acknowledge(self):
name = self.ui.name.text()
password = self.ui.password.text()
if 数据库.searchusername_password(name, password):
self.state = UIPython()
self.state.ui.show()
self.ui.close()
elif name == '' or password == '':
self.ui.Error.setText('Error! Do not enter a user name or password')
else:
self.ui.Error.setText('Error! Incorrect user name or password')
# 注册按钮程序
def zhuce(self):
self.zhuce = Zhuce()
self.zhuce.ui.show()
self.ui.close()
# 注册界面
class Zhuce:
def __init__(self):
# 从文件中加载UI定义
qfile = QFile("zhuce.ui")
qfile.open(QFile.ReadOnly)
qfile.close()
# 从 UI 定义中动态 创建一个相应的窗口对象
self.ui = QUiLoader().load(qfile)
self.ui.submit.clicked.connect(self.submit)
self.ui.delete_2.clicked.connect(self.ui.close)
# 提交按钮————MySQL数据库
def submit(self):
username = self.ui.username.text()
password = self.ui.password.text()
password1 = self.ui.password1.text()
if username == '' or password == '' or password1 == '':
self.ui.Error.setText('Error! Do not enter a user name or password')
elif password != password1:
self.ui.Error.setText('Error! Two times to enter the password do not match')
else:
if 数据库.searchusername(username):
数据库.insertusername(username, password)
self.denlu = Denlu()
self.denlu.ui.show()
self.ui.close()
else:
self.ui.Error.setText('Error! 用户名重复')
app = QApplication([])
denlu=Denlu()
denlu.ui.show()
# 设置守护线程
thread = threading.Thread(target=app.exec_())
thread.setDaemon(True)
thread.start()展示分析图片程序:
import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie,Bar,EffectScatter
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType
# 图形保存为“customized.html”
# 饼图
def pietu(data_pair,colour):
data_pair.sort(key=lambda x: x[1]) # 排序
c = (
# 初始化
Pie(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(
width="900px",
height="600px",
theme=ThemeType.MACARONS))
.add(
series_name="访问来源", # 系列名称
data_pair=data_pair, # 系列数据项,格式为 [(key1, value1), (key2, value2)]
# 是否展示成南丁格尔图,通过半径区分数据大小,有'radius'和'area'两种模式。
# radius:扇区圆心角展现数据的百分比,半径展现数据的大小
# area:所有扇区圆心角相同,仅通过半径展现数据大小
rosetype="radius",
# 饼图的半径
radius="55%",
# 饼图的中心(圆心)坐标,数组的第一项是横坐标,第二项是纵坐标
# 默认设置成百分比,设置成百分比时第一项是相对于容器宽度,第二项是相对于容器高度
center=["50%", "50%"],
# 标签配置项
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False, position="center"),
)
# 全局配置项
.set_global_opts(
# 设置标题
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(
title="Customized Pie",
pos_left="center",
pos_top="20",
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color="#fff"),
),
# 设置图例
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=True),
)
# 系统配置项
.set_series_opts(
# 设置提示框
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(
trigger="item", formatter="{a}
{b}: {c} ({d}%)"
),
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(color=colour),
).render("customized.html")
)
# 柱状图
def Bartu(data_pair, colour):
data_pair.sort(key=lambda x: x[1]) # 排序
x1 = [];y1 = []
for i in data_pair:
x1.append(i[0]);y1.append(i[1])
c = (
Bar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(
width="900px",
height="600px",
theme=ThemeType.MACARONS)).add_xaxis(x1).add_yaxis('频率', y1).set_colors(colour).set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="新闻词出现频率"),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name="频率"),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name="词"))
).render("customized.html")
# 散点图
def Scatter(data_pair, colour):
x1 = [];y1 = []
for i in data_pair:
x1.append(i[0]);y1.append(i[1])
c = (
EffectScatter(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(
width="900px",
height="600px",
theme=ThemeType.MACARONS)).add_xaxis(x1).add_yaxis('频率', y1).set_colors(colour).set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="新闻词出现频率"),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name="频率"),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name="词"))
).render("customized.html")数据库登陆方法:localhost:8080 / localhost | phpMyAdmin 4.6.4![]() http://localhost:8080/phpMyAdmin/
http://localhost:8080/phpMyAdmin/
数据库程序:
import pymysql
# 向MySQL服务器插入词云数据
def insertdb(data_pair):
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='12345678', db='DB', charset='utf8')
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS CIYUN")
sql = """CREATE TABLE CIYUN(
NAME CHAR(100) NOT NULL,
NUMBER INT )"""
cursor.execute(sql)
sql = "INSERT INTO CIYUN(NAME,NUMBER) \
VALUES (%s,%s)"
data_pair1 = []
for i in data_pair:
data_pair1.append((i[0], str(i[1])))
data_pair1 = tuple(data_pair1)
for i in data_pair1:
cursor.execute(sql, i)
db.commit()
db.close()
# 在MySQL服务器中搜索用户名和密码
def searchusername_password(usename,usepassword):
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='12345678', db='DB', charset='utf8')
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "SELECT * FROM USERNAME"
cursor.execute(sql)
results = cursor.fetchall()
for row in results:
if row[0] == usename and row[1] == usepassword:
db.close()
return 1
return 0
# 在MySQL服务器中搜索用户名
def searchusername(usename):
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='12345678', db='DB', charset='utf8')
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "SELECT * FROM USERNAME"
cursor.execute(sql)
results = cursor.fetchall()
for row in results:
if row[0] == usename:
db.close()
return 0
return 1
# 注册用户名和密码
def insertusername(username, usepassword):
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='12345678', db='DB', charset='utf8')
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "INSERT INTO USERNAME(NAME,PASSWORD) \
VALUES (%s,%s)"
value = (str(username), str(usepassword))
cursor.execute(sql, value)
db.commit()
db.close()
# 辅助测试用 主程序并未调用 可删除
def creatusername():
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='12345678', db='DB', charset='utf8')
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS USERNAME")
sql = """CREATE TABLE USERNAME(
NAME CHAR(100) NOT NULL,
PASSWORD CHAR(100))"""
cursor.execute(sql)
sql = "INSERT INTO USERNAME(NAME,PASSWORD) \
VALUES (%s,%s)"
value = (('2537148609', '12345678'), ('yangqun', 'kuaile'))
for i in value:
cursor.execute(sql, i)
db.commit()
db.close().csv 文件和和 .xls文件程序:
import csv
import xlwt
# csv文件保存为“ciping.csv”
# xls文件保存为“myexcel.xls”
# 写csv文件
def writecsv(data_pair):
headers = ['词语', '频率']
data_pair1 = []
for i in data_pair:
data_pair1.append((i[0], str(i[1])))
with open('ciping.csv',mode='w',encoding='utf8') as f:
f_csv = csv.writer(f)
f_csv.writerow(headers)
f_csv.writerows(data_pair1)
# 写xls文件
def openxls():
myexcel = xlwt.Workbook()
# 新建sheet页
mysheet = myexcel.add_sheet("testsheet")
# 打开csv文件,事实证明file和open 效果一样的,网上建议用open打开
with open("ciping.csv",mode='r',encoding='utf8') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
l = 0
# 通过循环获取单行信息
for line in reader:
r = 0
# 通过双重循环获取单个单元信息
for i in line:
# 通过双重循环写入excel表格
mysheet.write(l, r, i)
r += 1
l += 1
# 最后保存到excel
myexcel.save("myexcel.xls")