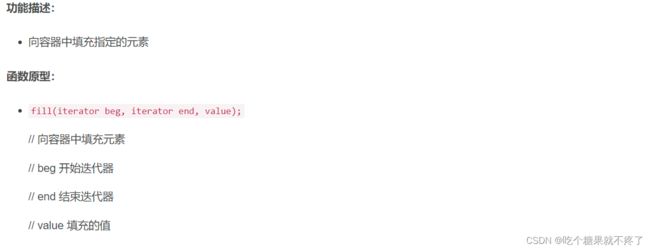STL-常用算法手册 | <algorithm> | <functional> | <numeric>
目录
- STL常用算法
-
- 概述
- 遍历算法
-
- for_each
- transform
- 常见查找算法
-
- find
- find_if
- adjacent_find
- binary_search
- count
- count_if
- 常见排序算法
-
- sort
- random_shuffle
- merge
- reverse
- 常见拷贝和替换算法
-
- copy
- replace
- replace_if
- swap
- 常见算术生成法
-
- accumulate
- fill
- 常见集合算法
-
- set_intersection
- set_union
- set_difference
STL常用算法
概述
遍历算法
for_each
#include transform
#include常见查找算法
find
#include find_if
class Greater20
{
public:
bool operator()(Person &p)
{
return p.m_Age > 20;
}
};
vector<Person>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没有找到!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄: " << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}
adjacent_find
#include binary_search
#include count
#include count_if
#include 常见排序算法
sort
sort属于开发中最常用的算法之一,需熟练掌握
#include random_shuffle
random_shuffle洗牌算法比较实用,使用时记得加随机数种子
#include merge
#include reverse
#include 常见拷贝和替换算法
copy
copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin());
replace
将20改为2000
replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 20,2000);
replace_if
// 自定义伪函数
class ReplaceGreater30
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val >= 30;
}
};
// 将>=30的数字,替换为3000
replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), ReplaceGreater30(), 3000);
swap
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
swap(v1, v2);
常见算术生成法
accumulate
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
// 从零开始累加
int total = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);
fill
vector<int> v;
v.resize(10);
//填充
fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 100); //将元素的值填充为100
常见集合算法
set_intersection
求交集的两个集合必须的有序序列
目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器中取小值
set_intersection返回值既是交集中最后一个元素的位置
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i+5);
}
vector<int> vTarget;
//取两个里面较小的值给目标容器开辟空间
vTarget.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));
//返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址
vector<int>::iterator itEnd =
set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());
cout << endl;
set_union
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i+5);
}
vector<int> vTarget;
//取两个容器的和给目标容器开辟空间
vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
//返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址
vector<int>::iterator itEnd =
set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());
cout << endl;
set_difference
差集的两个集合必须的有序序列
目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器取较大值
vector v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {undefined
v1.push_back(i + 1);
}
vector v2;
v2.resize(v1.size());
copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin());
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint());
cout << endl;