分类问题的评价指标:多标签分类【基于标签度量(同多分类一样):准确率(Accuracy)、精确率(Precision)、召回率(Recall)、F1】【基于样本度量:Hamming Loss...】
![]()
多标签分类的分类评价指标分为两大类:
- 基于标签上的度量:同多分类一样,在每一个标签上计算 Accuray、P、R、F……
- 基于样本上的度量:又分为基于分类的度量、基于排序的度量
- 基于分类的度量:Subset Accuracy、Hamming Loss、Accuracy exam、Precision exam、Recall exam、 F β F_{\beta} Fβ exam……
- 基于排序的度量:one-error、Coverage、Ranking Loss、Average precision……
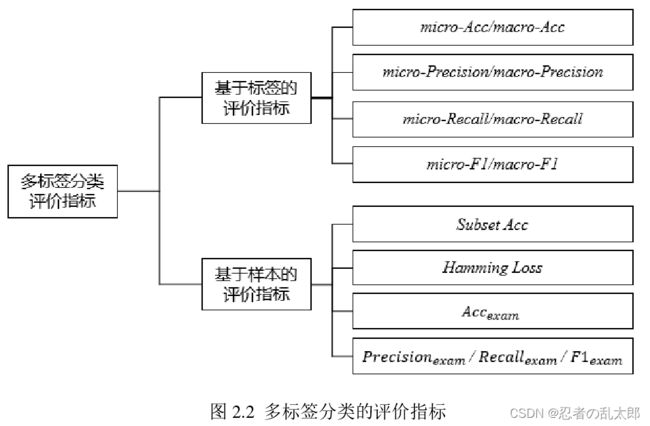
多标签分类的评价指标可以划分为基于标签的评价指标和基于样本的评价指标,区别在于:
- ① 基于标签的评价指标首先计算分类器在标签空间中每一个标签上的指标值,然后通过对全部标签上的评价值取宏观或微观平均得到最终指标值;
- ② 基于样本的评价指标首先评估分类器在每个样本上的表现,然后通过对测试集全部样本的指标值取平均来评估分类器在整个测试集上的表现。
一、基于标签上的度量(同多分类一样)
1、Precision
Precision、 micro-P、macro-P、weighted-P
2、Recall
Recall、micro-Recall、macro-Recall、weighted-Recall
3、F1
F1、 micro-F1、macro-F1、weighted-F1
二、基于样本上的度量
1、基于分类的度量
1.1 Hamming Loss(Hamming Distance)
h l o s s h_{loss} hloss 可能是最直观也是最容易理解的一个loss,它直接统计了被误分类label的个数(不属于这个样本的标签被预测,或者属于这个样本的标签没有被预测)。 h l o s s = 0 h_{loss}=0 hloss=0表示所有的每一个data的所有label都被分对了。
h l o s s = 1 p ∑ i = 1 p h ( x i ) Δ Y i , 其 中 p = N × L h_{loss}= \frac{1}{p}∑_{i=1}^ph(x_{i})ΔY_{i},其中 p=N\times L hloss=p1i=1∑ph(xi)ΔYi,其中p=N×L
图示:
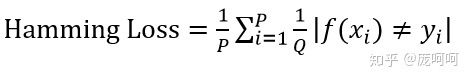
P:样本数 、Q:标签数 、 | ……|:错误样本的个数
例:
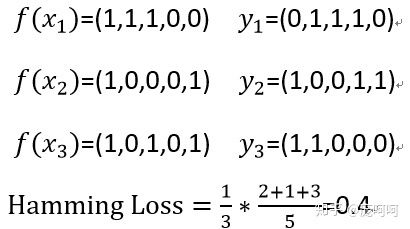
HammingLoss用于考察样本在单个标记上的误分类情况,即相关标记未出现在预测的标记集合中或无关标记出现在预测的标记集合中(预测结果中,错误数/总数)。该指标取值越小则系统性能越优。
#computing hammingLoss
def HammingLossClass(preLabels,test_targets):
num_class,num_instance = np.mat(test_targets).shape
temp = sum((preLabels != test_targets))
miss_pairs = sum(temp)
hammingLoss = miss_pairs/(num_class*num_instance)
return hammingLoss
2、基于排序的度量
2.1 查准率- Average precision
Intuitively, precision is the ability of the classifier not to label as positive a sample that is negative, and recall is the ability of the classifier to find all the positive samples(查准率是分类器不把阴性样本标记为阳性的能力,而召回率是分类器找到所有阳性样本的能力。)2者都是越高越好.
个人关于查准率和召回率简记(都是基于多分类为背景),最好结合一个混淆矩阵读下面例子:
查准率:字面意思,希望查的越准越好,识别模型查的准不准。举个极端例子,模型预测该类99个样本为真(99/100, 100个样本下),但实际只有5个样本。此时prec= 5/99, 查准率就非常小了。说明模型查的不准,因为它把很多阴性样本标记为阳性样本。
召回率:字面意思,召回,希望召回产品越来越少(比如说,研制了A产品,公司觉得是好产品(你的模型预测为真),但是,消费者一使用,发现很多是坏的(实际是假),此时需要重新召回产品,重新修理,然后在给消费者。)。 召回率越高,说明公司真正召回产品的概率越低,即1-recall。
2.2 召回率 -avgRecall
2.3 收敛 -coverage
2.4 秩损失 -ranking_loss
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Sep 6 20:38:38 2020
"""
#from sklearn import datasets
import sklearn
#import torch
import numpy as np
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
from scipy.sparse.csgraph import laplacian
from scipy.sparse.linalg import eigs
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score
from sklearn.metrics import hamming_loss
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score, recall_score,auc
# np.set_printoptions(threshold='nan')
class Metric(object):
def __init__(self,output,label):
self.output = output #prediction label matric
self.label = label #true label matric
def accuracy_subset(self,threash=0.5):
y_pred =self.output
y_true = self.label
y_pred=np.where(y_pred>threash,1,0)
accuracy=accuracy_score(y_true,y_pred)
return accuracy
def accuracy_mean(self,threash=0.5):
y_pred =self.output
y_true = self.label
y_pred=np.where(y_pred>threash,1,0)
accuracy=np.mean(np.equal(y_true,y_pred))
return accuracy
def accuracy_multiclass(self):
y_pred =self.output
y_true = self.label
accuracy=accuracy_score(np.argmax(y_pred,1),np.argmax(y_true,1))
return accuracy
def micfscore(self,threash=0.5,type='micro'):
y_pred =self.output
y_true = self.label
y_pred=np.where(y_pred>threash,1,0)
return f1_score(y_pred,y_true,average=type)
def macfscore(self,threash=0.5,type='macro'):
y_pred =self.output
y_true = self.label
y_pred=np.where(y_pred>threash,1,0)
return f1_score(y_pred,y_true,average=type)
def hamming_distance(self,threash=0.5):
y_pred =self.output
y_true = self.label
y_pred=np.where(y_pred>threash,1,0)
return hamming_loss(y_true,y_pred)
def fscore_class(self,type='micro'):
y_pred =self.output
y_true = self.label
return f1_score(np.argmax(y_pred,1),np.argmax(y_true,1),average=type)
def auROC(self):
y_pred =self.output
y_true = self.label
row,col = label.shape
temp = []
ROC = 0
for i in range(col):
sigle_ROC = roc_auc_score(y_true[:,i], y_pred[:,i], average='macro', sample_weight=None)
#print("%d th AUROC: %f"%(i,ROC))
temp.append(sigle_ROC)
ROC += sigle_ROC
return ROC/(col)
def MacroAUC(self):
y_pred =self.output #num_instance*num_label
y_true = self.label #num_instance*num_label
num_instance,num_class = y_pred.shape
count = np.zeros((num_class,1)) # store the number of postive instance'score>negative instance'score
num_P_instance = np.zeros((num_class,1)) #number of positive instance for every label
num_N_instance = np.zeros((num_class,1))
AUC = np.zeros((num_class,1)) # for each label
count_valid_label = 0
for i in range(num_class): #第i类
num_P_instance[i,0] = sum(y_true[:,i] == 1) #label,,test_target
num_N_instance[i,0] = num_instance - num_P_instance[i,0]
# exclude the label on which all instances are positive or negative,
# leading to num_P_instance(i,1) or num_N_instance(i,1) is zero
if num_P_instance[i,0] == 0 or num_N_instance[i,0] == 0:
AUC[i,0] = 0
count_valid_label = count_valid_label + 1
else:
temp_P_Outputs = np.zeros((int(num_P_instance[i,0]), num_class))
temp_N_Outputs = np.zeros((int(num_N_instance[i,0]), num_class))
#
temp_P_Outputs[:,i] = y_pred[y_true[:,i]==1,i]
temp_N_Outputs[:,i] = y_pred[y_true[:,i]==0,i]
for m in range(int(num_P_instance[i,0])):
for n in range(int(num_N_instance[i,0])):
if(temp_P_Outputs[m,i] > temp_N_Outputs[n,i] ):
count[i,0] = count[i,0] + 1
elif(temp_P_Outputs[m,i] == temp_N_Outputs[n,i]):
count[i,0] = count[i,0] + 0.5
AUC[i,0] = count[i,0]/(num_P_instance[i,0]*num_N_instance[i,0])
macroAUC1 = sum(AUC)/(num_class-count_valid_label)
return float(macroAUC1),AUC
def avgPrecision(self):
y_pred =self.output
y_true = self.label
num_instance,num_class = y_pred.shape
precision_value = 0
precisions = []
for i in range(num_instance):
p = precision_score(y_true[i,:], y_pred[i,:])
precisions.append(p)
precision_value += p
#print(precision_value)
pre_list = np.array([1.0] + precisions + [0.0] )#for get AUPRC
#print(pre_list)
return float(precision_value/num_instance), pre_list
def avgRecall(self):
y_pred =self.output
y_true = self.label
num_instance,num_class = y_pred.shape
recall_value = 0
recalls = []
for i in range(num_instance):
p = recall_score(y_true[i,:], y_pred[i,:])
recalls.append(p)
recall_value += p
rec_list = np.array([0.0] + recalls + [1.0]) #for get AUPRC
sorting_indices = np.argsort(rec_list)
#print(rec_list)
return float(recall_value/num_instance),rec_list,sorting_indices
def getAUPRC(self):
avgPrecision,precisions = self.avgPrecision()
avfRecall,recalls, sorting_indices = self.avgRecall()
#x is either increasing or decreasing
#such as recalls[sorting_indices]
auprc = auc(recalls[sorting_indices], precisions[sorting_indices])
return auprc
def cal_single_label_micro_auc(self,x, y):
idx = np.argsort(x) # 升序排列
y = y[idx]
m = 0
n = 0
auc = 0
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
if y[i] == 1:
m += 1
auc += n
if y[i] == 0:
n += 1
auc /= (m * n)
return auc
def get_micro_auc(self):
"""
:param x: the predicted outputs of the classifier, the output of the ith instance for the jth class is stored in x(i,j)
:param y: the actual labels of the instances, if the ith instance belong to the jth class, y(i,j)=1, otherwise y(i,j)=0
:return: the micro auc
"""
x =self.output
y = self.label
n, d = x.shape
if x.shape[0] != y.shape[0]:
print("num of instances for output and ground truth is different!!")
if x.shape[1] != y.shape[1]:
print("dim of output and ground truth is different!!")
x = x.reshape(n * d)
y = y.reshape(n * d)
auc = self.cal_single_label_micro_auc(x, y)
return auc
def cal_single_instance_coverage(self,x, y):
idx = np.argsort(x) # 升序排列
y = y[idx]
loc = x.shape[0]
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
if y[i] == 1:
loc -= i
break
return loc
def get_coverage(self):
"""
:param x: the predicted outputs of the classifier, the output of the ith instance for the jth class is stored in x(i,j)
:param y: the actual labels of the test instances, if the ith instance belong to the jth class, y(i,j)=1, otherwise y(i,j)=0
:return: the coverage
"""
x =self.output
y = self.label
n, d = x.shape
if x.shape[0] != y.shape[0]:
print("num of instances for output and ground truth is different!!")
if x.shape[1] != y.shape[1]:
print("dim of output and ground truth is different!!")
cover = 0
for i in range(n):
cover += self.cal_single_instance_coverage(x[i], y[i])
cover = cover / n - 1
return cover
def cal_single_instance_ranking_loss(self,x, y):
idx = np.argsort(x) # 升序排列
y = y[idx]
m = 0
n = 0
rl = 0
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
if y[i] == 1:
m += 1
if y[i] == 0:
rl += m
n += 1
rl /= (m * n)
return rl
def get_ranking_loss(self):
"""
:param x: the predicted outputs of the classifier, the output of the ith instance for the jth class is stored in x(i,j)
:param y: the actual labels of the test instances, if the ith instance belong to the jth class, y(i,j)=1, otherwise x(i,j)=0
:return: the ranking loss
"""
x =self.output
y = self.label
n, d = x.shape
if x.shape[0] != y.shape[0]:
print("num of instances for output and ground truth is different!!")
if x.shape[1] != y.shape[1]:
print("dim of output and ground truth is different!!")
m = 0
rank_loss = 0
for i in range(n):
s = np.sum(y[i])
if s in range(1, d):
rank_loss += self.cal_single_instance_ranking_loss(x[i], y[i])
m += 1
rank_loss /= m
return rank_loss
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 6行5列,6个样本,5个类别标记
output = np.array([[1,0,0,0,1],
[1,1,0,1,0],
[0,1,0,0,1],
[1,0,1,0,1],
[1,0,1,1,1],
[1,1,0,0,1]
])
label = np.array([[1,0,1,0,1],
[1,1,0,1,0],
[0,1,0,0,1],
[0,1,0,0,1],
[0,0,1,0,1],
[1,1,0,0,1]
])
myMetic = Metric(output,label)
#Macrof1 = myMetic.fscore_class()
ham = myMetic.hamming_distance()
Microf1 = myMetic.micfscore()
Macrof1 = myMetic.macfscore()
AUROC = myMetic.auROC()
MacroAUROC1,AUC_list = myMetic.MacroAUC()
avgPrecision,precisions = myMetic.avgPrecision()
avfRecall,recalls,sorting_indices = myMetic.avgRecall()
auprc = myMetic.getAUPRC()
#!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
micro_auc = myMetic.get_micro_auc()
coverage = myMetic.get_coverage()
ranking_loss = myMetic.get_ranking_loss()
# #print(Macrof1)
print("ham:",ham)
print("Microf1:",Microf1)
print("Macrof1:",Macrof1)
print("AUROC: ",(AUROC))
print("MacroAUC: ",(MacroAUROC1))
# #print(": ",(AUC_list))
print("avgPrecision: ",avgPrecision)
print("avfRecall: ",avfRecall)
print("AUPRC: ",auprc)
print("get_micro_auc _from_KDD2018M3DS:",micro_auc)
print("get_coverage _from_KDD2018M3DS:",coverage)
print("get_ranking_loss _from_KDD2018M3DS:",ranking_loss)
# #iris = datasets.load_iris()
打印结果:
ham: 0.2
Microf1: 0.8125
Macrof1: 0.7547619047619046
AUROC: 0.8133333333333332
MacroAUC: 0.8133333333333332
avgPrecision: 0.8055555555555557
avfRecall: 0.861111111111111
AUPRC: 0.7777777777777778
get_micro_auc _from_KDD2018M3DS: 0.8
get_coverage _from_KDD2018M3DS: 2.3333333333333335
get_ranking_loss _from_KDD2018M3DS: 0.13888888888888887
Process finished with exit code 0
参考资料:
多标记评价指标(一)——HammingLoss
多标记学习指标(一篇博客就够了)
3.3. Metrics and scoring: quantifying the quality of predictions
Multilabel(多标签分类)metrics:hamming loss,F score
多标签分类方法总结——实现方法、评价指标、损失函数
分类问题中的各种评价指标——precision,recall,F1-score,macro-F1,micro-F1
多标签分类的结果评估—macro-average和micro-average介绍
多标签分类(multilabel classification )
[Machine Learning]分类问题的性能度量方法——二分类、多分类、多标签分类
sklearn中 F1-micro 与 F1-macro区别和计算原理
二分类算法评估指标
[Machine Learning]分类问题的性能度量方法——二分类、多分类、多标签分类


