OAuth2认证授权流程解析
在阅读该文章前,需要对oAuth2的使用有一定的了解才能更好的阅读代码和理解对应流程
一、介绍
其实,关于系统认证授权的开源组件有很多,包括Shiro、Security和OAuth2等,这些组件各自有各自的优点,shiro配置比较简单,而OAuth2配置和实现相对而言就比较复杂一些,但是功能更强大,此处,我只讲解OAuth2相关技术,关于OAuth2的使用,我在csdn上已经写过几篇文章,大致已经将所有的流程说的比较明白,但是一直没有出一片比较系统的文章对OAuth2内部认证授权流程进行详细解析,故而静下心来,在工作中做一下总结,目的如下:
- 对前面oauth2系统性使用讲解缺失部分的弥补
- 各个技术网中很难有一篇文章对oauth2的使用有一篇比较全面的讲解,一般仅仅局限于如何使用,而不知道具体原理和实际的代码实现
- 对工作中的自我问题的总结及源码剖析过程中相关技术点的讲解
该课题的目的就是oAuth2源码的认证流程的代码剖析,所以我会将重点定在“流程”二字上。
二、原理
首先我们需要了解的是OAuth2的集中认证方式,然后我们在对各个模式的代码进行一一调试跟踪与剖析。
1、认证模式
我们知道,OAuth2提供了4种认证流程,它包括如下4中认证模式:
密码模式
密码模式,也就是说通过用户名密码的方式进行登录验证。这种方式有如下特点:
- 这种模式是不推荐使用的,因为客户端携带了用户名和密码,存在安全问题
- 主要用来做遗留项目升级为oauth2认证授权的适配方案
- 如果client是自己的平台的应用,这种模式是可以用的
- 该模式是支持刷新更换token的(过期前更换新token,一般是有效期的3倍时间后过期)
请求实例:
请求地址:
http://localhost:7000/oauth/token?grant_type=password&username=lixx&password=dw123456
请求类型: POST
请求参数:
(1)grant_type必须为密码模式(password)
(2)系统用户名:lixx,用户密码:dw123456
(3)HTTP头authorization,值为Basic64加密的client_id:client_secret
授权码模式
授权码模式,可以说是最安全的一种模式,所以,我们多花点时间来讲解一下授权码模式的使用。
例如微信公众号,它的过程简单来讲就是当用户点击访问微信公众号连接的时候,公众号需要获取用户的信息,但是用户的信息获取不是任何人想什么时候获取就什么时候获取的,必须得到用户的授权才行!所以首先会进入腾讯的授权网页(进入该网页也会附带公众号<第三方非腾讯根据腾讯规则开发的应用>的连接地址),用户在腾讯的网页上输入自己的用户名和密码点击确定后,腾讯进行校验,如果通过用户认证(说明用户允许)则腾讯会重定向跳转到第三方应用的公众号中并附带上验证通过之后的授权码(而不是一次性将用户信息推送给第三方,注意code是给了浏览器客户端),公众号服务在通过code换取对应的令牌token(注意token是给了可信的客户的服务端在转给浏览器),最后拿着token去获取用户信息。流程简写如下:
- 微信用户通过微信访问第三方的公众号服务
- 腾讯跳转或弹出授权按钮
- 用户授权允许,腾讯服务器通过后返回一个code给第三方应用
- 第三方应用服务拿着code去腾讯服务器换取token通信令牌
- 第三方应用获取到token之后,在带上token到腾信服务获取用户的基本信息(昵称、头像等)
通过上面的案例,我们可以知道授权码模式有如下特点:
- 授权码模式主要用在一些需要暂时性的获取用户密码的场合,如果直接登录的话安全性什么的会降低。主要原因也就是因为客户端拥有了用户的密码,而且用户无法限制客户端的授权范围和时间,导致一些安全隐患, 授权码就是避免这些问题。
- 这种模式算是正宗的oauth2的授权模式
- 这种模式使用了auth code(授权码),通过这个code再获取token
- 该模式支持刷新token令牌(一般过期为token有效期的3倍时间)
整个流程可能有点拗口,需要仔细理解一番,理解之后,大家这里是否有如下几个问题:
-
为什么不一次性将“用户信息”传递给公众号服务,而是采用返回token的方式
首先,这是授权过程,不知道第三方应用需要获取什么样的信息,只有获取了token之后才可以;其次,返回的是code而不是token,因为如果把token直接返回给浏览器客户端那就没有安全性可言了;再次,如果授权服务直接返回token给第三方服务,第三方服务可能是http的,token可能存在安全问题,而授权服务是https的时候第三方服务主动获取就不存在泄露问题; -
传递过程中的code是否存在泄密的风险,是否安全
回答: 首先,用户的点击同意动作在微信端页面,更可控,而不是在第三方应用;其次,授权码模式最后返回的token一定是返回给第三方应用的服务器,有些简单的客户只有前端静态页面而没有服务器,则只能通过:"简化模式"在web页面进行授权、获取token等一系列动作。

站在OAuth2设计者的角度来理解code
为什么要有授权码模式,以访客为例,比如,朋友到我家访问我的过程如下:
- 朋友找到小区保安,说要去访问我(请求token)
- 安保电话询问我是否同意,朋友等到结果
- 我告诉保安我是否同意,朋友还在等待结果
- 保安哥哥挂完电话,允许朋友进入我家(获取token)
那么OAuth2也完全照抄这个流程是否可行?关键的问题在于,web系统与现实场景是有区别的:
在web系统中,第一步请求token后,网络就关闭了(短连接),无法等待第四步返回结果就断开了连接,Authorization Server就再也无法主动找到OAuth2 Client,更加不可能把token传递到OAuth2 Cilent了。web系统与现实生活例子最大区别就是web系统无法长时间等待:Http协议是单向的无状态协议,只有浏览器主动连接到服务器端,而服务器是无法主动找到浏览端的,web系统的服务端要同时支持无数浏览器高并发,因此常见的Http的请求都是有超时限制的短连接,长时间不响应就会主动断开连接。所有现实中获取token的流程不适合web系统。
那么,OAuth协议是通过怎样的流程来绕过http协议的B/S架构的局限性,从而实现安全而且相对高效的获取token呢? OAuth2把如何获取授权,获取token的这套流程叫做“授权模式”,而其中最通用、最安全的流程叫做“授权码模式”。
OAuth2 Client直接向用户要token?
这样是不行的。用户只有用户名和密码,而且是不能给你的,没有对应的token。
OAuth2 Client在后端直接向AS要token?
这种方式也是不行的,因为AS首先要通知到用户,由用户亲自授权后,AS才能向OAuth2 Client发token。不经过用户授权就随便发token是明显地侵犯他人权益,不被允许的。
OAuth2 Client如何将token传给OAuth2 Client?
AS如何把token给到OAuth2 Client?方式一:直接给前端。虽然此时网络链接已经断开,但是AS仍然可以通过浏览器重定向的方式,将token作为URL参数传给到OAuth2 Client的前端。方式二:直接给后端。AS直接调用OAuth2 Client后端的接口将token给到后端。但是先不说AS是否能直接调用 OAuth2 Client后端接口,就算可以调用, OAuth2 Client的后端也无法简单快捷地把获取token成功的状态通知到 OAuth2 Client前端和用户。token直接暴露在浏览器地址栏了。泄露token意味着直接泄露资源服务器中的数据。换句话说,token不应该出现在前端的任何地方。token只能在OAuth2 Client 、AS 和RS后端之间传递。
OAuth2解决这个问题的方式非常巧妙,那就是引入code,这个code被称作“授权码”,这就是"授权码模式"名称的由来。具体的流程:
- 浏览器重定向不直接传token,而是先传一个code
- OAuth2 Client前端拿到code,传给OAuth2 Client后端
- OAuth2 Client后端携带这个code调用AS后端,AS校验成功后,放心地分发token。
为了安全,每一个code只能使用一次:AS一旦接收到携带这个code的请求,那这个code就作废了,不能使用同一个code再次请求了。同时,携带code交换token时,请求参数中需要携带OAuth2 Client的密钥。对于黑客来说,同一个code只能使用一次(后面的代码解析过程我们会看到验证这一点),还无法获取OAuth2 Client密钥,也就无法做token的暴力碰撞了。最重要的是:token一直在后端之间传递,根本就不给黑客通过浏览器窥视token的机会。
至此这就是完整的授权码模式流程。为什么要引入code来交换token的问题也就迎刃而解了。
安全不是绝对的。假如token真的泄露了,那也比直接泄露用户名和密码强。因为:
- token是有效期的,并且一般有效期很短,几秒钟到几分钟,短期的,到期就自动失效。
- token可以被用户主动撤销而失效
- token可以访问的数据是有权限控制的,是有限的权限。
请求实例:
请求地址:
http://localhost:7010/oauth/authorize?response_type=code&client_id=wx_takeout_client_id&redirect_uri=http://localhost:700/response
请求方式:
GET
请求结果:
http://localhost:7000/response?code=zfmpz
此时返回浏览器客户端一个code,浏览器带着这个code在去请求浏览器客户端后台,在客户端后台获取对应的token。
简化模式
implicit模式(隐式模式)和授权码模式(authorization_code)访问差不多,相比之下,少了一步获取code的步骤,而是直接获取token,它有如下特点:
- 这种模式比授权码模式少了code环节,回调url直接携带token
- 这种模式的使用场景是基于浏览器的应用
- 这种模式基于安全性考虑,建议把token时效设置短一些
- 不支持refresh token
请求实例:
请求地址:
http://localhost:7010/uaa/oauth/authorize?response_type=token&client_id=wx_takeout_client_id&redirect_uri=http://localhost:7010/uaa/login
参数:response_type=token&client_id=wx_takeout_client_id&redirect_uri=http://localhost:7010/uaa/login
响应结果:
http://localhost:7010/uaa/login?access_token=xxx
客户端模式
客户端模式即根据client_id和秘钥即可换取令牌,不需要额外的code或用户名密码。它具有如下特点:
- 这种模式直接根据client的id和密钥即可获取token,无需用户参与
- 这种模式比较合适消费api的后端服务,比如拉取一组用户信息等
- 不支持refresh token,主要是没有必要
请求实例:
请求地址:
http://localhost:7010/oauth/token?grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=dondown_client_id&client_secret=dondown_client_secret
请求方式: POST
二、流程及代码跟踪
1、认证总流程
认识oauth2的4种认证模式之后,接下来我们就需要介入本文章的重点: 认证流程解析
oauth2的认证流程如下所示:
- 安装定义的过滤器
- 过滤器处理过滤请求并生成不同类型的认证token如UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
- 调用注入的AuthenticationManager管理对象的authenticate进行认证
- AuthenticationManager调用所有的AuthenticationProvider(包括你配置的数据库认证Provider类DaoAuthenticationProvider)循环尝试认证,如果Provider支持则进行认证。
- 对应的某Provider认证成功则退出认证并生成对应的认证token认证请求
- 如果认证成功则发布认证成功事件,否则抛出用户名账户异常
- 如果前面认证成功,默认(自定义过滤器实现除外)下一步交由TokenEndpoint或AuthorizationEndpoint控制层端点处理token认证请求
- TokenEndpoint或AuthorizationEndpoint安装的几个端点同样交给AuthenticationProvider进行认证授权处理,流程同上
以上即是OAuth2认证流程的核心处理流程,几个步骤非常受用,我们以后在代码过程中遇到问题,如果了解以上处理流程就可以很快速定位调试相关问题。
2、过滤器介绍
介绍了OAuth2的流程之后,我们第一需要了解的就是过滤器,oauth2是对security的升级,它包含了如下几个过滤器,根据不同的启动服务类型选择性安置了其中几个过滤器,首先我们来了解一下各个过滤器的作用:
- BasicAuthenticationFilter
该过滤器是最基本的过滤器,所有的请求都会经过该过滤器,该过滤器处理的流程是:
(1)获取请求头的授权字段Authorization,如果不包含则不处理该请求(递交给后续过滤器处理)
(2)解析basic加密的客户端client_id和client_secret(案例:Authorization: Basic ZG9uZG93bl9jbGllbnRfaWQ6ZG9uZG93bl9jbGllbnRfc2VjcmV0);
(3)通过以上两个参数创建UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken认证请求。
(4)调用authenticationManager的认证方法进行认证authenticate
(5)更新认证结果到SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication中
(6)更新认证结果到remenberme服务this.rememberMeServices
核心代码如下:
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
final boolean debug = this.logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 获取请求头的Authorization字段
String header = request.getHeader("Authorization");
// 没有Authorization头或不是basic加密交由其他过滤器处理
if (header == null || !header.toLowerCase().startsWith("basic ")) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
try {
// 提取Authorization的client_id和client_secret客户端id和免密
String[] tokens = extractAndDecodeHeader(header, request);
assert tokens.length == 2;
// 获取client_id
String username = tokens[0];
if (debug) {
this.logger
.debug("Basic Authentication Authorization header found for user '"
+ username + "'");
}
// 当前会话全向为匿名或没有登录或用户名发生变化则需要重新授权
if (authenticationIsRequired(username)) {
// 通过客户端id和客户端秘钥创建认证请求
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, tokens[1]);
authRequest.setDetails(
this.authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
// 将认证请求提交给认证管理器进行认证
Authentication authResult = this.authenticationManager
.authenticate(authRequest);
if (debug) {
this.logger.debug("Authentication success: " + authResult);
}
// 更新当前会话的认证信息
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
// 是否记住我
this.rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
onSuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, authResult);
}
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
if (debug) {
this.logger.debug("Authentication request for failed: " + failed);
}
this.rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
onUnsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
// 认证失败端点处理
if (this.ignoreFailure) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
else {
this.authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, failed);
}
return;
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
private boolean authenticationIsRequired(String username) {
// Only reauthenticate if username doesn't match SecurityContextHolder and user
// isn't authenticated
// (see SEC-53)
// 当前会话没有认证信息或没有认证成功
Authentication existingAuth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
.getAuthentication();
if (existingAuth == null || !existingAuth.isAuthenticated()) {
return true;
}
// Limit username comparison to providers which use usernames (ie
// UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)
// (see SEC-348)
// 认证信息无效或用户名发生变化
if (existingAuth instanceof UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
&& !existingAuth.getName().equals(username)) {
return true;
}
// Handle unusual condition where an AnonymousAuthenticationToken is already
// present
// This shouldn't happen very often, as BasicProcessingFitler is meant to be
// earlier in the filter
// chain than AnonymousAuthenticationFilter. Nevertheless, presence of both an
// AnonymousAuthenticationToken
// together with a BASIC authentication request header should indicate
// reauthentication using the
// BASIC protocol is desirable. This behaviour is also consistent with that
// provided by form and digest,
// both of which force re-authentication if the respective header is detected (and
// in doing so replace
// any existing AnonymousAuthenticationToken). See SEC-610.
// 当前为匿名用户
if (existingAuth instanceof AnonymousAuthenticationToken) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
- OAuth2ClientAuthenticationProcessingFilter
OAuth2的客户端过滤器,通过该客户端过滤器,处理远程授权客户端的认证授权服务。主要通过ResourceServerTokenServices的实现类RemoteTokenServices从指定的授权服务获取对应的token信息。
核心代码:
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException, IOException, ServletException {
// 通过http从授权服务获取token
OAuth2AccessToken accessToken;
try {
accessToken = restTemplate.getAccessToken();
} catch (OAuth2Exception e) {
BadCredentialsException bad = new BadCredentialsException("Could not obtain access token", e);
publish(new OAuth2AuthenticationFailureEvent(bad));
throw bad;
}
try {
// 获取用户认证信息
OAuth2Authentication result = tokenServices.loadAuthentication(accessToken.getValue());
if (authenticationDetailsSource!=null) {
request.setAttribute(OAuth2AuthenticationDetails.ACCESS_TOKEN_VALUE, accessToken.getValue());
request.setAttribute(OAuth2AuthenticationDetails.ACCESS_TOKEN_TYPE, accessToken.getTokenType());
result.setDetails(authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
}
// 发布认证结果
publish(new AuthenticationSuccessEvent(result));
return result;
}
catch (InvalidTokenException e) {
BadCredentialsException bad = new BadCredentialsException("Could not obtain user details from token", e);
publish(new OAuth2AuthenticationFailureEvent(bad));
throw bad;
}
}
这里的tokenServices的接口为ResourceServerTokenServices,实现包括
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-66ADrJDE-1596353355814)(./img2/1.png)]
(1) RemoteTokenServices通过远程地址配置获取token
(2) UserInfoTokenServices通过远程地址获取用户认证信息
所以,如果是资源服务与授权服务分离项目,我们需要使用oauth2 client验证模式进行验证,此时需要配置对应的token获取地址或者用户信息获取地址,如下所示:
security:
oauth2:
resource:
filter-order: 3
id: gate_way_server
tokenInfoUri: http://127.0.0.1:7006/oauth/check_token
preferTokenInfo: true
#user-info-uri: http://127.0.0.1:7006/user/principal
#prefer-token-info: false
#如下可暂时不用配置-仅做保留
client:
accessTokenUri: http://127.0.0.1:7006/oauth/token
userAuthorizationUri: http://127.0.0.1:7006/oauth/authorize
clientId: dondown_client_id
clientSecret: dondown_client_secret
- ClientCredentialsTokenEndpointFilter
该过滤器主要拦截的url是"/oauth/token",产生认证请求token,最后交给AuthorizationToken端点进行处理,它核心处理流程是:
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException, IOException, ServletException {
// 验证是否是POST请求方式
if (allowOnlyPost && !"POST".equalsIgnoreCase(request.getMethod())) {
throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(request.getMethod(), new String[] { "POST" });
}
// 获取请求参数client_id和client_secret
String clientId = request.getParameter("client_id");
String clientSecret = request.getParameter("client_secret");
// If the request is already authenticated we can assume that this
// filter is not needed
// 获取当前上下文的认证信息:已经认证成功则不再重新认证
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication != null && authentication.isAuthenticated()) {
return authentication;
}
// client_id是必填字段
if (clientId == null) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("No client credentials presented");
}
if (clientSecret == null) {
clientSecret = "";
}
clientId = clientId.trim();
// 通过client_id和client_secret创建用户名密码认证请求
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(clientId,
clientSecret);
// 最后交给认证管理器进行认证
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
(1)首先获取请求参数中的client_id和client_secret
(2)通过id和秘钥创建UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken认证请求
(3)调用authenticationManager认证管理器进行认证
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
该过滤器主要针对的是web端用户名密码授权认证时候使用的,拦截地址为"/login",处理过程如下
(1)从请求中获取用户名和密码
(2)通过用户名和密码创建用户名密码请求UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
(3)调用authenticationManager认证管理器进行认证
核心处理代码如下:
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
// POST请求方式验证
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
// 获取用户名密码模式中请求参数username和password
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
// 创建用户名密码认证请求token
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
// 交给认证管理器进行认证
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
TokenEndpoint端点
oauth2中在默认过滤器SecurityContextPersistenceFilter、LogoutFilter、ClientCredentialsTokenEndpointFilter、BasicAuthenticationFilter、AnonymousAuthenticationFilter等过滤器以及自定义过滤器,手机登录过滤器、邮箱认证过滤器、二维码认证过滤器等处理之后依旧没有对应处理器,最后交由TokenEndpoint的端点进行认证。它提供了一下几个端点的处理(/oauth/token的GET和POST处理),我们可以看到对应源码如下:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2011 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.endpoint;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.InsufficientAuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.OAuth2AccessToken;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.exceptions.BadClientCredentialsException;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.exceptions.InvalidClientException;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.exceptions.InvalidGrantException;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.exceptions.InvalidRequestException;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.exceptions.OAuth2Exception;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.exceptions.UnsupportedGrantTypeException;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.util.OAuth2Utils;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.ClientDetails;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.ClientRegistrationException;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.OAuth2Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.OAuth2RequestValidator;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.TokenRequest;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.request.DefaultOAuth2RequestValidator;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import java.security.Principal;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
*
* Endpoint for token requests as described in the OAuth2 spec. Clients post requests with a grant_type
* parameter (e.g. "authorization_code") and other parameters as determined by the grant type. Supported grant types are
* handled by the provided {@link #setTokenGranter(org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.TokenGranter) token
* granter}.
*
*
*
* Clients must be authenticated using a Spring Security {@link Authentication} to access this endpoint, and the client
* id is extracted from the authentication token. The best way to arrange this (as per the OAuth2 spec) is to use HTTP
* basic authentication for this endpoint with standard Spring Security support.
*
*
* @author Dave Syer
*
*/
@FrameworkEndpoint
public class TokenEndpoint extends AbstractEndpoint {
// 默认的请求验证器
private OAuth2RequestValidator oAuth2RequestValidator = new DefaultOAuth2RequestValidator();
// 只允许POST请求
private Set allowedRequestMethods = new HashSet(Arrays.asList(HttpMethod.POST));
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/token", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity getAccessToken(Principal principal, @RequestParam
Map parameters) throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException {
// 如果允许GET方式请求
if (!allowedRequestMethods.contains(HttpMethod.GET)) {
throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException("GET");
}
// 转向POST请求处理
return postAccessToken(principal, parameters);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/token", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity postAccessToken(Principal principal, @RequestParam
Map parameters) throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException {
// 由上一层filter处理生成的认证请求token
if (!(principal instanceof Authentication)) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"There is no client authentication. Try adding an appropriate authentication filter.");
}
// 获取client_id
String clientId = getClientId(principal);
// 从数据库获取客户端信息
ClientDetails authenticatedClient = getClientDetailsService().loadClientByClientId(clientId);
// 通过请求参数、客户段信息生成token请求信息
TokenRequest tokenRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createTokenRequest(parameters, authenticatedClient);
// 验证clientId有效性
if (clientId != null && !clientId.equals("")) {
// Only validate the client details if a client authenticated during this
// request.
// 注册的client_id与请求参数client_id不一致
if (!clientId.equals(tokenRequest.getClientId())) {
// double check to make sure that the client ID in the token request is the same as that in the
// authenticated client
throw new InvalidClientException("Given client ID does not match authenticated client");
}
}
// 验证客户端请求范围是否有效
if (authenticatedClient != null) {
oAuth2RequestValidator.validateScope(tokenRequest, authenticatedClient);
}
// 授权类型不能为空
if (!StringUtils.hasText(tokenRequest.getGrantType())) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("Missing grant type");
}
// TokenEndpoint不支持简化模式(见AuthorizationEndpoint)
if (tokenRequest.getGrantType().equals("implicit")) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Implicit grant type not supported from token endpoint");
}
// 授权码模式的请求范围不能为空
if (isAuthCodeRequest(parameters)) {
// The scope was requested or determined during the authorization step
if (!tokenRequest.getScope().isEmpty()) {
logger.debug("Clearing scope of incoming token request");
tokenRequest.setScope(Collections. emptySet());
}
}
// 如果是刷新模式获取scope
if (isRefreshTokenRequest(parameters)) {
// A refresh token has its own default scopes, so we should ignore any added by the factory here.
tokenRequest.setScope(OAuth2Utils.parseParameterList(parameters.get(OAuth2Utils.SCOPE)));
}
// 交给端点的granter进行一一授权
OAuth2AccessToken token = getTokenGranter().grant(tokenRequest.getGrantType(), tokenRequest);
if (token == null) {
throw new UnsupportedGrantTypeException("Unsupported grant type: " + tokenRequest.getGrantType());
}
// 返回token信息
return getResponse(token);
}
/**
* @param principal the currently authentication principal
* @return a client id if there is one in the principal
*/
protected String getClientId(Principal principal) {
Authentication client = (Authentication) principal;
if (!client.isAuthenticated()) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException("The client is not authenticated.");
}
String clientId = client.getName();
if (client instanceof OAuth2Authentication) {
// Might be a client and user combined authentication
clientId = ((OAuth2Authentication) client).getOAuth2Request().getClientId();
}
return clientId;
}
@ExceptionHandler(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class)
public ResponseEntity handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException e) throws Exception {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Handling error: " + e.getClass().getSimpleName() + ", " + e.getMessage());
}
return getExceptionTranslator().translate(e);
}
// 普通异常处理器
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity handleException(Exception e) throws Exception {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Handling error: " + e.getClass().getSimpleName() + ", " + e.getMessage());
}
return getExceptionTranslator().translate(e);
}
@ExceptionHandler(ClientRegistrationException.class)
public ResponseEntity handleClientRegistrationException(Exception e) throws Exception {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Handling error: " + e.getClass().getSimpleName() + ", " + e.getMessage());
}
return getExceptionTranslator().translate(new BadClientCredentialsException());
}
// 认证异常处理器
@ExceptionHandler(OAuth2Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity handleException(OAuth2Exception e) throws Exception {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Handling error: " + e.getClass().getSimpleName() + ", " + e.getMessage());
}
return getExceptionTranslator().translate(e);
}
private ResponseEntity getResponse(OAuth2AccessToken accessToken) {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.set("Cache-Control", "no-store");
headers.set("Pragma", "no-cache");
headers.set("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8");
return new ResponseEntity(accessToken, headers, HttpStatus.OK);
}
private boolean isRefreshTokenRequest(Map parameters) {
return "refresh_token".equals(parameters.get("grant_type")) && parameters.get("refresh_token") != null;
}
private boolean isAuthCodeRequest(Map parameters) {
return "authorization_code".equals(parameters.get("grant_type")) && parameters.get("code") != null;
}
public void setOAuth2RequestValidator(OAuth2RequestValidator oAuth2RequestValidator) {
this.oAuth2RequestValidator = oAuth2RequestValidator;
}
public void setAllowedRequestMethods(Set allowedRequestMethods) {
this.allowedRequestMethods = allowedRequestMethods;
}
}
@frameworkendpoint注解的端点是Spring框架的端点,@Controller的同义词,但仅用于框架提供的端点(因此它永远不会与用@Controller定义的用户自己的端点冲突)
以密码模式登录为例,假如我们配置的token存储方式为数据库存储,WebSecurityConfigurerAdapters实现类配置类如下所示:
@Bean
public DaoAuthenticationProvider daoAuthenticationProvider(){
DaoAuthenticationProvider provider = new DaoAuthenticationProvider();
// 设置userDetailsService
provider.setUserDetailsService(usernameUserDetailService);
// 禁止隐藏用户未找到异常
provider.setHideUserNotFoundExceptions(false);
// 使用BCrypt进行密码的hash
provider.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
return provider;
}
数据库设置的UserDetailService服务为自己实现的通过用户名密码获取用户详情服务:
package com.dondown.login.service;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import com.dondown.model.Right;
import com.dondown.service.RightService;
/**
* @文件名称: BaseUserDetailService.java
* @功能描述: 用户详情查询接口实现基类,提供基础的功能骨架,用户实现getUser接口提供用户查询实现即可
* @版权信息: www.dondown.com
* @编写作者: [email protected]
* @开发日期: 2020年4月8日
* @历史版本: V1.0
*/
public abstract class BaseUserDetailService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private RightService rightService; // 权限服务
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String userName) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 查找用户
com.dondown.model.User user = getUser(userName);
if (null == user) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户:" + userName + ",不存在!");
}
// 设置用户权限
Set grantedAuthorities = new HashSet();
List rights = rightService.findByUsername(user.getUsername());
for(Right right : rights) {
GrantedAuthority authority = new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_" + right.getDescription());
grantedAuthorities.add(authority);
}
// 标识位设置
boolean enabled = user.getEnabled() == 0 ? false : true; // 可用性 :true:可用 false:不可用
boolean accountNonExpired = user.getExpired() == 0 ? true : false; // 过期性 :true:没过期 false:过期
boolean credentialsNonExpired = true; // 有效性 :true:凭证有效 false:凭证无效
boolean accountNonLocked = user.getLocked() == 0 ? true : false; // 锁定性 :true:未锁定 false:已锁定
// 扩展security的用户信息
AccsUser accsUser = new AccsUser(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), enabled, accountNonExpired, credentialsNonExpired, accountNonLocked, grantedAuthorities);
if (null != accsUser) {
accsUser.setId(user.getId());
accsUser.setUserType(user.getUserType());
accsUser.setEmail(user.getEmail());
accsUser.setMobile(user.getMobile());
}
return accsUser;
}
/**
* @功能描述: 用户信息查询抽象接口实现
* @编写作者: [email protected]
* @开发日期: 2020年4月8日
* @历史版本: V1.0
* @参数说明:
*/
protected abstract com.dondown.model.User getUser(String var) ;
}
@Service
public class UsernameUserDetailService extends BaseUserDetailService {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Override
protected com.dondown.model.User getUser(String userName) {
return userService.findByUsername(userName);
}
}
3、认证流程解析
用户名密码登录流程
首先,我们介绍的一种认证模式:用户名密码登录认证,此时,通过浏览器用户名密码认证,请求实例地址:
http://localhost:15003/oauth/token?username=admin&password=dd123456&grant_type=password
认识了TokenEndpoint之后,我们知道TokenEndpoint端点处理的就是以上地址(/oauth/token), 它前期经过了BasicAuthenticationFilter的过滤处理器(包含Authorization头字段就会交给它处理)生成了认证UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,最后交给servlet处理交给TokenEndpoint,通过TokenEndpoint的处理流程知道,endPoint最终通过ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter的grant返回创建OAuth2AccessToken返回前端
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
if (!this.grantType.equals(grantType)) {
return null;
}
// 获取请求客户端id
String clientId = tokenRequest.getClientId();
// 从数据库中加载客户端id
ClientDetails client = clientDetailsService.loadClientByClientId(clientId);
// 验证grantType是否正确
validateGrantType(grantType, client);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Getting access token for: " + clientId);
}
// 生成认证token
return getAccessToken(client, tokenRequest);
}
创建OAuth2AccessToken是通过tokenServices(实现类DefaultTokenServices)createAccessToken方法实现的,它是一个数据库服务层类,实现如下:
@Transactional
public OAuth2AccessToken createAccessToken(OAuth2Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
// 通过认证id从数据库获取认证token(如果之前已经认证通过则会存储)
OAuth2AccessToken existingAccessToken = tokenStore.getAccessToken(authentication);
OAuth2RefreshToken refreshToken = null;
// 之前认证通过
if (existingAccessToken != null) {
// 当前认证是否过期了
if (existingAccessToken.isExpired()) {
// 过期删除刷新token
if (existingAccessToken.getRefreshToken() != null) {
refreshToken = existingAccessToken.getRefreshToken();
// The token store could remove the refresh token when the
// access token is removed, but we want to
// be sure...
tokenStore.removeRefreshToken(refreshToken);
}
// 然后删除认证token(第二列包含OAuth2AccessToken序列化后的对象里面有过期信息等)
tokenStore.removeAccessToken(existingAccessToken);
}
// 没有过期则更新认证信息并返回
else {
// Re-store the access token in case the authentication has changed
tokenStore.storeAccessToken(existingAccessToken, authentication);
return existingAccessToken;
}
}
// Only create a new refresh token if there wasn't an existing one
// associated with an expired access token.
// Clients might be holding existing refresh tokens, so we re-use it in
// the case that the old access token
// expired.
// 重新创建刷新token
if (refreshToken == null) {
refreshToken = createRefreshToken(authentication);
}
// But the refresh token itself might need to be re-issued if it has
// expired.
// 刷新token过期则更新
else if (refreshToken instanceof ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken) {
ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken expiring = (ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken) refreshToken;
if (System.currentTimeMillis() > expiring.getExpiration().getTime()) {
refreshToken = createRefreshToken(authentication);
}
}
// 创建新的令牌并存储到数据库
OAuth2AccessToken accessToken = createAccessToken(authentication, refreshToken);
tokenStore.storeAccessToken(accessToken, authentication);
// 创建新的刷新token
// In case it was modified
refreshToken = accessToken.getRefreshToken();
if (refreshToken != null) {
tokenStore.storeRefreshToken(refreshToken, authentication);
}
return accessToken;
}
通过上面的步骤,我们可以看到他经过如下几个步骤:
- 查询数据库表oauth_access_token检查用户是否登录,查询返回OAuth2AccessToken(第二列二进制序列化后字段)
- 如果查询到,说明之前登录过,检查token是否过期,过期则移除该记录和刷新token记录,未过期则更新
- 如果没有查询到则查询到client_id对应用户details的过期时间并创建刷新token和认证token
private OAuth2AccessToken createAccessToken(OAuth2Authentication authentication, OAuth2RefreshToken refreshToken) {
DefaultOAuth2AccessToken token = new DefaultOAuth2AccessToken(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
int validitySeconds = getAccessTokenValiditySeconds(authentication.getOAuth2Request());
if (validitySeconds > 0) {
token.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + (validitySeconds * 1000L)));
}
token.setRefreshToken(refreshToken);
token.setScope(authentication.getOAuth2Request().getScope());
return accessTokenEnhancer != null ? accessTokenEnhancer.enhance(token, authentication) : token;
}
- 创建成功之后,存储OAuth2AccessToken和OAuth2RefreshToken到数据库中并返回access_token到前端
刷新token
认证之后,我们获取到token,但是token始终会过期的,在过期之前,我们必须通过刷新token换取新的token,通过对endpoint端点的认知,我们知道它实现了/oauth/token端点的get和post方法,刷新token也是请求的改地址,由它前期经过了BasicAuthenticationFilter的过滤处理器(包含Authorization头字段就会交给它处理)生成了认证UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken, 最终由端点进行处理,请求实例地址如下:
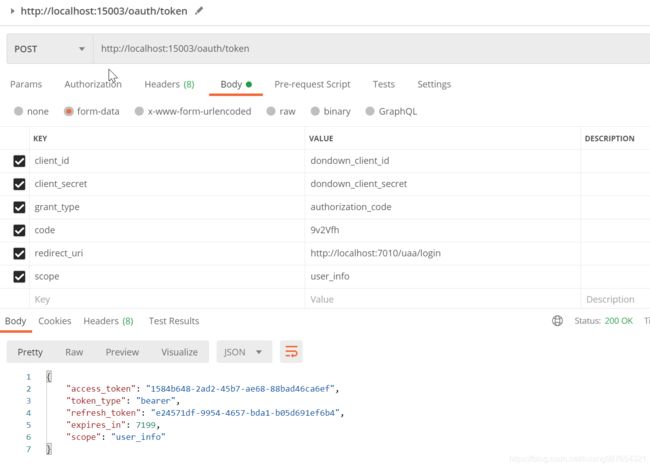
http://localhost:15003/oauth/token?grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=0395184b-5a50-45c9-b812-ba64e8602f15&client_id=dondown_client_id&client_secret=dondown_client_secret
具体如下:
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/token", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity postAccessToken(Principal principal, @RequestParam
Map parameters) throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException {
// 由上一层filter处理生成的认证请求token
if (!(principal instanceof Authentication)) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"There is no client authentication. Try adding an appropriate authentication filter.");
}
// 获取client_id
String clientId = getClientId(principal);
// 从数据库获取客户端信息
ClientDetails authenticatedClient = getClientDetailsService().loadClientByClientId(clientId);
// 通过请求参数、客户段信息生成token请求信息
TokenRequest tokenRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createTokenRequest(parameters, authenticatedClient);
// 验证clientId有效性
if (clientId != null && !clientId.equals("")) {
// Only validate the client details if a client authenticated during this
// request.
// 注册的client_id与请求参数client_id不一致
if (!clientId.equals(tokenRequest.getClientId())) {
// double check to make sure that the client ID in the token request is the same as that in the
// authenticated client
throw new InvalidClientException("Given client ID does not match authenticated client");
}
}
// 验证客户端请求范围是否有效
if (authenticatedClient != null) {
oAuth2RequestValidator.validateScope(tokenRequest, authenticatedClient);
}
// 授权类型不能为空
if (!StringUtils.hasText(tokenRequest.getGrantType())) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("Missing grant type");
}
// TokenEndpoint不支持简化模式(见AuthorizationEndpoint)
if (tokenRequest.getGrantType().equals("implicit")) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Implicit grant type not supported from token endpoint");
}
// 授权码模式的请求范围不能为空
if (isAuthCodeRequest(parameters)) {
// The scope was requested or determined during the authorization step
if (!tokenRequest.getScope().isEmpty()) {
logger.debug("Clearing scope of incoming token request");
tokenRequest.setScope(Collections. emptySet());
}
}
// 如果是刷新模式获取scope
if (isRefreshTokenRequest(parameters)) {
// A refresh token has its own default scopes, so we should ignore any added by the factory here.
tokenRequest.setScope(OAuth2Utils.parseParameterList(parameters.get(OAuth2Utils.SCOPE)));
}
// 交给端点的granter进行一一授权
OAuth2AccessToken token = getTokenGranter().grant(tokenRequest.getGrantType(), tokenRequest);
if (token == null) {
throw new UnsupportedGrantTypeException("Unsupported grant type: " + tokenRequest.getGrantType());
}
// 返回token信息
return getResponse(token);
}
我们可以看到不论是授权模式或刷新模式,都进行如下处理:
// 获取授权器进行授权认证
OAuth2AccessToken token = getTokenGranter().grant(tokenRequest.getGrantType(), tokenRequest);
if (token == null) {
throw new UnsupportedGrantTypeException("Unsupported grant type: " + tokenRequest.getGrantType());
}
return getResponse(token);
最终调用组合授权组件CompositeTokenGranter,它包含了oauth2支持的多种granter列表:

- AuthorizationCodeTokenGranter 授权码授权组件
- RefreshTokenGranter 刷新token授权组件
- ImplicitTokenGranter 简化模式授权组件
- ClientCredentialsTokenGranter 客户端模式授权组件
- ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter 资源所有者密码授权组件
通过遍历所有组件,最终由RefreshTokenGranter处理该请求
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
if (!this.grantType.equals(grantType)) {
return null;
}
String clientId = tokenRequest.getClientId();
ClientDetails client = clientDetailsService.loadClientByClientId(clientId);
validateGrantType(grantType, client);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Getting access token for: " + clientId);
}
return getAccessToken(client, tokenRequest);
}
该组件首先通过数据库表oauth_client_details查询客户端详情,查询是否具有refresh_token权限,如果有则创建对应token, 创建token同上实现类DefaultTokenServices的createAccessToken方法。
授权码模式认证
根据授权码模式的介绍,我们知道,首先是通过请求换取授权码,这时候需要用户授权干预,所以我们请求授权服务地址并指定授权code获取完成后重定向回来的地址,打开浏览器输入一下地址并回车(注意这里必须是浏览器发送GET请求,postman是不会响应重定向的,这里要千万留意):
http://localhost:15003/oauth/authorize?response_type=code&client_id=dondown_client_id&redirect_uri=http://localhost:7010/uaa/login
在说明一下,我们这里指定了响应类型为code授权码,并指定了客户id以及用户认证成功之后携带code重定向的地址。
此时,授权服务器会让请求的浏览器重定向到授权服务器的用户登录页面以便用户输入用户名密码进行登录授权访问。那么,**授权服务如何重定向到登录页面的呢?**肯定是发现访问授权服务没有对应权限才重定向到对应地址的,我们还是回到BasicAuthenticationFilter,请求头中没有Authorization字段则交由其他处理器处理:
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
final boolean debug = this.logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 处理http请求头Authorization进行认证
String header = request.getHeader("Authorization");
if (header == null || !header.toLowerCase().startsWith("basic ")) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
...
其处理路径:
BasicAuthenticationFilter.doFilterInternal=>
SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter.doFilter=>
VirtualFilterChain.doFilter=>
AnonymousAuthenticationFilter.doFilter=>
SessionManagementFilter.doFilter
ExceptionTranslationFilter.doFilter=>
FilterSecurityInterceptor.doFilter=>
FilterSecurityInterceptor.invoke=>
AbstractSecurityInterceptor.beforeInvocation=>
**org.springframework.security.access.vote.AffirmativeBased.decide **
关键点就是在AffirmativeBased.decide的权限验证处理。 FilterSecurityInterceptor.invoke处理流程如下:
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
if ((fi.getRequest() != null)
&& (fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null)
&& observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
else {
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
if (fi.getRequest() != null && observeOncePerRequest) {
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
// 调用前验证
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}
// 调用前验证处理
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
Assert.notNull(object, "Object was null");
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (!getSecureObjectClass().isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Security invocation attempted for object "
+ object.getClass().getName()
+ " but AbstractSecurityInterceptor only configured to support secure objects of type: "
+ getSecureObjectClass());
}
// 配置的安全属性,我这里配置的为[authenticated],也就是需要认证,后面代码的HTTPSecurity访问配置有对应代码
Collection attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource()
.getAttributes(object);
if (attributes == null || attributes.isEmpty()) {
if (rejectPublicInvocations) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Secure object invocation "
+ object
+ " was denied as public invocations are not allowed via this interceptor. "
+ "This indicates a configuration error because the "
+ "rejectPublicInvocations property is set to 'true'");
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Public object - authentication not attempted");
}
publishEvent(new PublicInvocationEvent(object));
return null; // no further work post-invocation
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Secure object: " + object + "; Attributes: " + attributes);
}
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
credentialsNotFound(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractSecurityInterceptor.authenticationNotFound",
"An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext"),
object, attributes);
}
// 进行认证:当前没有任何认证信息,所以认证返回AnonymousAuthenticationToken
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
// 尝试授权
try {
// 使用accessDecisionManager访问控制管理器决定是否访问资源是否有对应的访问权限
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
}
catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {
// 通过投票验证该资源不能访问则抛出异常
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,
accessDeniedException));
throw accessDeniedException;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authorization successful");
}
if (publishAuthorizationSuccess) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizedEvent(object, attributes, authenticated));
}
// Attempt to run as a different user
Authentication runAs = this.runAsManager.buildRunAs(authenticated, object,
attributes);
if (runAs == null) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("RunAsManager did not change Authentication object");
}
// no further work post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(), false,
attributes, object);
}
else {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Switching to RunAs Authentication: " + runAs);
}
SecurityContext origCtx = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext());
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(runAs);
// need to revert to token.Authenticated post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(origCtx, true, attributes, object);
}
}
这里有一个地方是获取安全配置参数,进行访问地址验证:
Collection attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource()
.getAttributes(object);
这里配置的安全属性为“[authenticated]”,也就是当前访问地址需要用户验证,验证交由this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);处理,这的accessDecisionManager就是AffirmativeBased(继承了AbstractAccessDecisionManager抽象类)。
一下代码就是获取当前用户的认证信息,如果已经认证则使用对应认证信息,否则返回匿名认证信息。
private Authentication authenticateIfRequired() {
// 获取前期认证信息
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
.getAuthentication();
// 如果已经认证且不必须每次都认证则返回认证信息
if (authentication.isAuthenticated() && !alwaysReauthenticate) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Previously Authenticated: " + authentication);
}
return authentication;
}
// 交给认证管理器进行认证返回认证结果
authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(authentication);
// We don't authenticated.setAuthentication(true), because each provider should do
// that
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Successfully Authenticated: " + authentication);
}
// 将认证结果设置到当前的会话中
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
return authentication;
}
具体该用户是否有访问该资源的权限则由投票选举详情代码(说白了就是你在httpsecurity中的权限设置验证,根据你配置的权限验证该用户是否有该资源的访问权限):
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object,
Collection configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException {
int deny = 0;
// 所有的访问控制投票
for (AccessDecisionVoter voter : getDecisionVoters()) {
int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configAttributes);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Voter: " + voter + ", returned: " + result);
}
// 投票结果:拒绝或允许
switch (result) {
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_GRANTED:
return;
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_DENIED:
deny++;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
// 如果拒绝数量大于0说明不允许访问该资源
if (deny > 0) {
throw new AccessDeniedException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractAccessDecisionManager.accessDenied", "Access is denied"));
}
// 允许访问
// To get this far, every AccessDecisionVoter abstained
checkAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions();
}
认证投票过程如上所示,其中包含了WebExpressionVoter处理器, 其投票处理流程如下所示:
public int vote(Authentication authentication, FilterInvocation fi,
Collection attributes) {
assert authentication != null;
assert fi != null;
assert attributes != null;
// 通过属性获取对应的属性类
WebExpressionConfigAttribute weca = findConfigAttribute(attributes);
if (weca == null) {
return ACCESS_ABSTAIN;
}
// 创建评估上下文
EvaluationContext ctx = expressionHandler.createEvaluationContext(authentication,fi);
ctx = weca.postProcess(ctx, fi);
// 评估是否可以访问
return ExpressionUtils.evaluateAsBoolean(weca.getAuthorizeExpression(), ctx) ? ACCESS_GRANTED
: ACCESS_DENIED;
}
通过配置属性WebExpressionConfigAttribute(这里是[authenticated])el表达式验证是否允许授权或拒绝访问:
public final class ExpressionUtils {
public static boolean evaluateAsBoolean(Expression expr, EvaluationContext ctx) {
try {
return ((Boolean) expr.getValue(ctx, Boolean.class)).booleanValue();
}
catch (EvaluationException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Failed to evaluate expression '"
+ expr.getExpressionString() + "'", e);
}
}
}
如果访问的url需要授权认证[authenticated], 那么会抛出AccessDeniedException访问拒绝异常。抛出异常后就会在ExceptionTranslationFilter过滤器的方法中捕获处理:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
logger.debug("Chain processed normally");
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace
Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
// 转化为拒绝访问异常
if (ase == null) {
ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(
AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
}
// 处理Spring的Security安全异常,这是重点
if (ase != null) {
if (response.isCommitted()) {
throw new ServletException("Unable to handle the Spring Security Exception because the response is already committed.", ex);
}
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase);
}
else {
// Rethrow ServletExceptions and RuntimeExceptions as-is
if (ex instanceof ServletException) {
throw (ServletException) ex;
}
else if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
// Wrap other Exceptions. This shouldn't actually happen
// as we've already covered all the possibilities for doFilter
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
该过程就会在此处被处理:
if (ase != null) {
if (response.isCommitted()) {
throw new ServletException("Unable to handle the Spring Security Exception because the response is already committed.", ex);
}
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase);
}
我们看看handleSpringSecurityException到底在用户无权的访问的时候做了什么处理?!
private void handleSpringSecurityException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, RuntimeException exception)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// 如果是权限认证异常则发送权限认证错误
if (exception instanceof AuthenticationException) {
logger.debug(
"Authentication exception occurred; redirecting to authentication entry point",
exception);
sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain,
(AuthenticationException) exception);
}
// 如果是拒绝访问或用户无资源访问权限
else if (exception instanceof AccessDeniedException) {
// 匿名用户访问
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) || authenticationTrustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication)) {
logger.debug(
"Access is denied (user is " + (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) ? "anonymous" : "not fully authenticated") + "); redirecting to authentication entry point",
exception);
// 发送权限不足异常
sendStartAuthentication(
request,
response,
chain,
new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
messages.getMessage(
"ExceptionTranslationFilter.insufficientAuthentication",
"Full authentication is required to access this resource")));
}
else {
logger.debug(
"Access is denied (user is not anonymous); delegating to AccessDeniedHandler",
exception);
accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response,
(AccessDeniedException) exception);
}
}
}
可以通过上面代码知道如果异常时认证异常,则发送开始认证并附带认证异常,如果是拒绝访问且是匿名用户表示权限不足则发送开始认证并附带一个“无足够权限异常”,如果不是匿名用户而被拒绝访问则交由accessDeniedHandler进行处理,我们进一步跟着代码尝试查看匿名处理代码:
protected void sendStartAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
AuthenticationException reason) throws ServletException, IOException {
// SEC-112: Clear the SecurityContextHolder's Authentication, as the
// existing Authentication is no longer considered valid
// 清空当前用户权限为null
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(null);
requestCache.saveRequest(request, response);
logger.debug("Calling Authentication entry point.");
// 调用认证端点处理
authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, reason);
}
那么问题又来了,如果是没有足够的权限,我们跳转到什么页面?根据我们的使用规则就会知道,会跳转到登录页面,我们继续跟进,验证是否会重定向到登录页面,首先,我们配置的WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的安全策略如下,除了login和logout其他页面都需要用户认证后才能访问(authenticated):
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// 注册各类型的登录认证过滤器
http
.addFilterBefore(openIdLoginAuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.addFilterBefore(accessTokenAuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.addFilterBefore(phoneLoginAuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.addFilterBefore(qrLoginAuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
// 自定义开放url过滤器配置--无需鉴权
ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer.ExpressionInterceptUrlRegistry registry = http.authorizeRequests();
if(filter != null){
List urls = filter.getUrls();
if(urls != null){
for(String url: urls){
registry = registry.antMatchers(url.trim()).permitAll();
}
}
}
registry.anyRequest().authenticated().and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login").permitAll()
.and()
.logout().permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable()
.httpBasic();
/**
* 老版本遗留参考保留--请勿删除
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/door/toolReader/start").hasRole("DOOR_TOOLREADER_START")
.anyRequest().denyAll()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login").permitAll()
.and()
.logout().permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable()
.httpBasic();*/
}
accessDeniedHandler交由authenticationEntryPoint处理:
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 匹配所的访问端点
for (RequestMatcher requestMatcher : entryPoints.keySet()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Trying to match using " + requestMatcher);
}
// 如果匹配到访问端点
if (requestMatcher.matches(request)) {
// 通过matcher获取到对应的AuthenticationEntryPoint端点(如LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint)
AuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = entryPoints.get(requestMatcher);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Match found! Executing " + entryPoint);
}
// 交给该认证进行处理
entryPoint.commence(request, response, authException);
return;
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No match found. Using default entry point " + defaultEntryPoint);
}
// No EntryPoint matched, use defaultEntryPoint
defaultEntryPoint.commence(request, response, authException);
}
这里entryPoints有多个,包括AndRequestMatcher(map映射值为LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint)、OrRequestMatcher(map映射值为DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint)
这有多个enpoint请求端点匹配,其中第一个匹配规则如下,正好与我们的请求/oauth/authorize相匹配:
{
AndRequestMatcher [
requestMatchers=[
NegatedRequestMatcher [
requestMatcher=RequestHeaderRequestMatcher [
expectedHeaderName=X-Requested-With,
expectedHeaderValue=XMLHttpRequest
]
],
MediaTypeRequestMatcher [
contentNegotiationStrategy=org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManager@1d6b94f2,
matchingMediaTypes=[application/xhtml+xml, image/*, text/html, text/plain],
useEquals=false,
ignoredMediaTypes=[*/*]
]
]
]=org.springframework.security.web.authentication.LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint@27a717a7,
OrRequestMatcher [
requestMatchers=[
RequestHeaderRequestMatcher [
expectedHeaderName=X-Requested-With,
expectedHeaderValue=XMLHttpRequest
],
AndRequestMatcher [
requestMatchers=[
NegatedRequestMatcher [
requestMatcher=MediaTypeRequestMatcher [
contentNegotiationStrategy=org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManager@1d6b94f2,
matchingMediaTypes=[text/html],
useEquals=false,
ignoredMediaTypes=[]
]
],
MediaTypeRequestMatcher [
contentNegotiationStrategy=org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManager@1d6b94f2,
matchingMediaTypes=[application/atom+xml, application/x-www-form-urlencoded, application/json, application/octet-stream, application/xml, multipart/form-data, text/xml],
useEquals=false,
ignoredMediaTypes=[*/*]
]
]
],
MediaTypeRequestMatcher [
contentNegotiationStrategy=org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManager@1d6b94f2,
matchingMediaTypes=[*/*],
useEquals=true,
ignoredMediaTypes=[]
]
]
]=org.springframework.security.web.authentication.DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint@59ffb0af
}
也就是说通过匹配的规则requestMatcher,我们匹配的entryPoint对应的endpoint处理类为:
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint@27a717a7
它的处理逻辑如下所示:
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
String redirectUrl = null;
// 如果使用转发模式
if (useForward) {
// 请求协议http且强制转发到https中
if (forceHttps && "http".equals(request.getScheme())) {
// First redirect the current request to HTTPS.
// When that request is received, the forward to the login page will be
// used.
// 创建重定向地址
redirectUrl = buildHttpsRedirectUrlForRequest(request);
}
// 重定向到getLoginFormUrl登录表单URL
if (redirectUrl == null) {
String loginForm = determineUrlToUseForThisRequest(request, response,
authException);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Server side forward to: " + loginForm);
}
// 使用转发模式转发到登录页面
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(loginForm);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
return;
}
}
else {
// redirect to login page. Use https if forceHttps true
// 不使用转发而使用重定向模式重定向到登录页面
redirectUrl = buildRedirectUrlToLoginPage(request, response, authException);
}
// 发送重定向地址
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, redirectUrl);
}
这里会走第二个分支,也就是走重定向而不走转发(useForward为false),重定向的URL地址创建过程为:
protected String buildRedirectUrlToLoginPage(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) {
// 获取登录表单地址: /login
String loginForm = determineUrlToUseForThisRequest(request, response,
authException);
if (UrlUtils.isAbsoluteUrl(loginForm)) {
return loginForm;
}
// 获取请求端口
int serverPort = portResolver.getServerPort(request);
// 获取请求协议
String scheme = request.getScheme();
// 使用RedirectUrlBuilder创建重定向地址
RedirectUrlBuilder urlBuilder = new RedirectUrlBuilder();
// 协议http或https
urlBuilder.setScheme(scheme);
// 设置服务名(ip地址):localhost
urlBuilder.setServerName(request.getServerName());
// 服务端口
urlBuilder.setPort(serverPort);
// 项目上下文名:此处为空字符串
urlBuilder.setContextPath(request.getContextPath());
// 子路径地址: /login
urlBuilder.setPathInfo(loginForm);
// 如果强制重定向到https且当前协议为http则更新协议为https
if (forceHttps && "http".equals(scheme)) {
Integer httpsPort = portMapper.lookupHttpsPort(Integer.valueOf(serverPort));
if (httpsPort != null) {
// Overwrite scheme and port in the redirect URL
urlBuilder.setScheme("https");
urlBuilder.setPort(httpsPort.intValue());
}
else {
logger.warn("Unable to redirect to HTTPS as no port mapping found for HTTP port "
+ serverPort);
}
}
// http://localhost:15003/login
return urlBuilder.getUrl();
}
最后发送重定向通知给客户端重定向到**登录页面(/login)**进行登录授权!根据以上过程,我们可以知道,当匿名用户无权访问对应资源的时候默认会重定向登录页面!!!
public void sendRedirect(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
String url) throws IOException {
// 计算重定向地址
String redirectUrl = calculateRedirectUrl(request.getContextPath(), url);
redirectUrl = response.encodeRedirectURL(redirectUrl);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Redirecting to '" + redirectUrl + "'");
}
// 发送重定向到浏览器客户端
response.sendRedirect(redirectUrl);
}
用户授权
当访问的页面需要权限验证,第三方服务就会转向到授权服务器的登录页面,浏览器重定向到登录页面/login之后,用户通过重定向的页面使用用户名密码(或者其他方式)进行授权认证提交到授权服务器,此时我们提到的用户名密码过滤器UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter登场!!!!,我们上面说过,它拦截地址为"/login",而且是POST请求:
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter() {
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/login", "POST"));
}
也就是我们的用户授权登录页面,它核心处理流程如下所示:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
// 是否需要认证
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Request is to process authentication");
}
Authentication authResult;
try {
// 开始认证
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
// authentication
return;
}
// 认证结果
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
logger.error(
"An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.",
failed);
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
// Authentication success
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
// 认证流程
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
可以看到登录/login必须是POST方式写携带username和password参数才可以。通过用户名和密码创建UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken用户名密码认证请求,然后提交给认证授权管理器进行认证。认证管理器会遍历所有的Provider寻找合适的(通过Provider的supports方法进行验证是否支持该认证token)Provider对其进行认证,最终会找到DaoAuthenticationProvider进行认证。
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Assert.isInstanceOf(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class, authentication,
() -> messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.onlySupports",
"Only UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken is supported"));
// Determine username
// 获取用户名
String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED"
: authentication.getName();
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
// 根据用户名提取用户信息
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException notFound) {
logger.debug("User '" + username + "' not found");
// 是否隐藏用户未找到异常
if (hideUserNotFoundExceptions) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
else {
throw notFound;
}
}
Assert.notNull(user,
"retrieveUser returned null - a violation of the interface contract");
}
try {
// 检查用户是否过期、锁定、禁用
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
// 检查用户密码是否相等
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (AuthenticationException exception) {
if (cacheWasUsed) {
// There was a problem, so try again after checking
// we're using latest data (i.e. not from the cache)
cacheWasUsed = false;
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
else {
throw exception;
}
}
// 后期验证
postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
}
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
}
// 成功后创建UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(用户对象,密码,权限)最后交给endpoint处理生成token
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}
retrieveUser这个过程会使用userDetail接口从数据库加载对应用户和权限(这里我配置的为jdbcToken,也可以配置为redis则从redis加载信息)。
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
prepareTimingAttackProtection();
try {
// 用户用户名载入用户信息
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(authentication);
throw ex;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
最终this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username)会调用我们注入的UserDetail首先类从数据库加载用户详情数据。
package com.dondown.login.service;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import com.dondown.model.Right;
import com.dondown.service.RightService;
/**
* @文件名称: BaseUserDetailService.java
* @功能描述: 用户详情查询接口实现基类,提供基础的功能骨架,用户实现getUser接口提供用户查询实现即可
* @版权信息: www.dondown.com
* @编写作者: [email protected]
* @开发日期: 2020年4月8日
* @历史版本: V1.0
*/
public abstract class BaseUserDetailService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private RightService rightService; // 权限服务
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String userName) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 查找用户
com.dondown.model.User user = getUser(userName);
if (null == user) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户:" + userName + ",不存在!");
}
// 设置用户权限
Set grantedAuthorities = new HashSet();
List rights = rightService.findByUsername(user.getUsername());
for(Right right : rights) {
GrantedAuthority authority = new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_" + right.getDescription());
grantedAuthorities.add(authority);
}
// 标识位设置
boolean enabled = user.getEnabled() == 0 ? false : true; // 可用性 :true:可用 false:不可用
boolean accountNonExpired = user.getExpired() == 0 ? true : false; // 过期性 :true:没过期 false:过期
boolean credentialsNonExpired = true; // 有效性 :true:凭证有效 false:凭证无效
boolean accountNonLocked = user.getLocked() == 0 ? true : false; // 锁定性 :true:未锁定 false:已锁定
// 扩展security的用户信息
AccsUser accsUser = new AccsUser(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), enabled, accountNonExpired, credentialsNonExpired, accountNonLocked, grantedAuthorities);
if (null != accsUser) {
accsUser.setId(user.getId());
accsUser.setUserType(user.getUserType());
accsUser.setEmail(user.getEmail());
accsUser.setMobile(user.getMobile());
}
return accsUser;
}
/**
* @功能描述: 用户信息查询抽象接口实现
* @编写作者: [email protected]
* @开发日期: 2020年4月8日
* @历史版本: V1.0
* @参数说明:
*/
protected abstract com.dondown.model.User getUser(String var) ;
}
我这里注入的是UsernameUserDetailService,它实现了通过用户名查找用户的方式,具体如下:
@Service
public class UsernameUserDetailService extends BaseUserDetailService {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Override
protected com.dondown.model.User getUser(String userName) {
return userService.findByUsername(userName);
}
}
假如所有的过滤器认证成功之后如何处理呢?最终与换取code的流程和认证流程(/oauth/token或/oauth/check_token)一样的,交给RequestMappingHandlerAdapter处理在转ServletInvocableHandlerMethod,ServletInvocableHandlerMethod通过注册的“controller”处理该请求地址,spring security注册了一个与之对应的SpringFrameworkEndpoint端点(org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.endpoint.AuthorizationEndpoint)对这个请求路径进行处理。
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/authorize")
public ModelAndView authorize(Map model, @RequestParam Map parameters,
SessionStatus sessionStatus, Principal principal) {
// Pull out the authorization request first, using the OAuth2RequestFactory. All further logic should
// query off of the authorization request instead of referring back to the parameters map. The contents of the
// parameters map will be stored without change in the AuthorizationRequest object once it is created.
// 通过请求参数创建授权请求对象,请求参数为重定向前的参数:
// {response_type=code, client_id=dondown_client_id, redirect_uri=http://localhost:7010/uaa/login}
AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createAuthorizationRequest(parameters);
// 获取需要的响应类型,这里我code
Set responseTypes = authorizationRequest.getResponseTypes();
// 只支持简化模式和授权码模式
if (!responseTypes.contains("token") && !responseTypes.contains("code")) {
throw new UnsupportedResponseTypeException("Unsupported response types: " + responseTypes);
}
// 必须包含clientid
if (authorizationRequest.getClientId() == null) {
throw new InvalidClientException("A client id must be provided");
}
try {
// UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
if (!(principal instanceof Authentication) || !((Authentication) principal).isAuthenticated()) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"User must be authenticated with Spring Security before authorization can be completed.");
}
// 通过client_id获取客户信息
ClientDetails client = getClientDetailsService().loadClientByClientId(authorizationRequest.getClientId());
// The resolved redirect URI is either the redirect_uri from the parameters or the one from
// clientDetails. Either way we need to store it on the AuthorizationRequest.
// 获取请求参数中的重定向地址redirect_url: http://localhost:7010/uaa/login
String redirectUriParameter = authorizationRequest.getRequestParameters().get(OAuth2Utils.REDIRECT_URI);
String resolvedRedirect = redirectResolver.resolveRedirect(redirectUriParameter, client);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(resolvedRedirect)) {
throw new RedirectMismatchException(
"A redirectUri must be either supplied or preconfigured in the ClientDetails");
}
// 设置重定向地址
authorizationRequest.setRedirectUri(resolvedRedirect);
// We intentionally only validate the parameters requested by the client (ignoring any data that may have
// been added to the request by the manager).
// 设置用户的scope
oauth2RequestValidator.validateScope(authorizationRequest, client);
// Some systems may allow for approval decisions to be remembered or approved by default. Check for
// such logic here, and set the approved flag on the authorization request accordingly.
// 获取所有自动通过的范围
authorizationRequest = userApprovalHandler.checkForPreApproval(authorizationRequest,
(Authentication) principal);
// TODO: is this call necessary?
// 当前用户认证信息是否可以在指定的范围scope信息(是否可以访问指定scope)
boolean approved = userApprovalHandler.isApproved(authorizationRequest, (Authentication) principal);
authorizationRequest.setApproved(approved);
// Validation is all done, so we can check for auto approval...
// 验证用户scope正确之后
if (authorizationRequest.isApproved()) {
// 如果是简化模式则获取响应的token
if (responseTypes.contains("token")) {
return getImplicitGrantResponse(authorizationRequest);
}
// 如果是授权码模式则获取响应的code
if (responseTypes.contains("code")) {
return new ModelAndView(getAuthorizationCodeResponse(authorizationRequest,
(Authentication) principal));
}
}
// Store authorizationRequest AND an immutable Map of authorizationRequest in session
// which will be used to validate against in approveOrDeny()
model.put(AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_ATTR_NAME, authorizationRequest);
model.put(ORIGINAL_AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_ATTR_NAME, unmodifiableMap(authorizationRequest));
return getUserApprovalPageResponse(model, authorizationRequest, (Authentication) principal);
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
sessionStatus.setComplete();
throw e;
}
}
// DefaultRedirectResolver方法resolveRedirect
public String resolveRedirect(String requestedRedirect, ClientDetails client) throws OAuth2Exception {
// 注册时的允许的授权类型:[authorization_code, refresh_token, implicit, password, client_credentials]
Set authorizedGrantTypes = client.getAuthorizedGrantTypes();
if (authorizedGrantTypes.isEmpty()) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("A client must have at least one authorized grant type.");
}
// 检查配置的授权类型是否包含当前endpoint允许的类型[implicit, authorization_code]
if (!containsRedirectGrantType(authorizedGrantTypes)) {
throw new InvalidGrantException(
"A redirect_uri can only be used by implicit or authorization_code grant types.");
}
// 获取注册多个重定向地址列表:这里我注册的时候是[http://www.baidu.com]
Set registeredRedirectUris = client.getRegisteredRedirectUri();
if (registeredRedirectUris == null || registeredRedirectUris.isEmpty()) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("At least one redirect_uri must be registered with the client.");
}
// 验证请求的重定向地址是否包含在注册地址列表中
return obtainMatchingRedirect(registeredRedirectUris, requestedRedirect);
}
private String obtainMatchingRedirect(Set redirectUris, String requestedRedirect) {
Assert.notEmpty(redirectUris, "Redirect URIs cannot be empty");
if (redirectUris.size() == 1 && requestedRedirect == null) {
return redirectUris.iterator().next();
}
for (String redirectUri : redirectUris) {
if (requestedRedirect != null && redirectMatches(requestedRedirect, redirectUri)) {
return requestedRedirect;
}
}
// 如果请求的redirect_url与注册的重定向地址不一致则抛出异常
throw new RedirectMismatchException("Invalid redirect: " + requestedRedirect
+ " does not match one of the registered values.");
}
如果请求参数的redirect_url与系统注册的url不一致,抛出的异常最终被全局异常处理器处理
@ExceptionHandler(OAuth2Exception.class)
public ModelAndView handleOAuth2Exception(OAuth2Exception e, ServletWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
logger.info("Handling OAuth2 error: " + e.getSummary());
return handleException(e, webRequest);
}
这里说明一下spring处理系统异常有三种方式。
- 第一种,Controller层面的异常处理:在controller层标注了@ExceptionHandler注解的异常处理器处理(一个Controller下多个@ExceptionHandler上的异常类型不能出现一样的,否则运行时抛异常.)@ExceptionHandler的方法入参支持:Exception ;SessionAttribute 、 RequestAttribute注解 ; HttpServletRequest 、HttpServletResponse、HttpSession。@ExceptionHandler方法返回值常见的可以是: ModelAndView 、@ResponseBody注解、ResponseEntity;;
- 第二种,全局级别异常处理器实现HandlerExceptionResolver接口
public class MyHandlerExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
System.out.println("发生全局异常!");
ModelMap mmp=new ModelMap();
mmp.addAttribute("ex",ex.getMessage());
response.addHeader("Content-Type","application/json;charset=UTF-8");
try {
new ObjectMapper().writeValue(response.getWriter(),ex.getMessage());
response.getWriter().flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new ModelAndView();
}
}
释放用法:
只需要将该Bean加入到Spring容器,可以通过Xml配置,也可以通过注解方式加入容器;方法返回值不为null才有意义,如果方法返回值为null,可能异常就没有被捕获.
- 第三种,局部级别异常处理器 @ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler
使用方法很简单如下所示:
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalController {
@ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class)
public ModelAndView fix1(Exception e){
System.out.println("全局的异常处理器");
ModelMap mmp=new ModelMap();
mmp.addAttribute("ex",e);
return new ModelAndView("error",mmp);
}
}
用法说明: 这种情况下@ExceptionHandler与第一种方式用法相同,返回值支持ModelAndView,@ResponseBody等多种形式
** @Controller+@ExceptionHandler、HandlerExceptionResolver接口形式、@ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler优缺点说明**
- 优先级来说,@Controller+@ExceptionHandler优先级最高,其次是@ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler,最后才是HandlerExceptionResolver,说明假设三种方式并存的情况 优先级越高的越先选择,而且被一个捕获处理了就不去执行其他的.
- 三种方式都支持多种返回类型,@Controller+@ExceptionHandler、@ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler可以使用Spring支持的@ResponseBody、ResponseEntity,而HandlerExceptionResolver方法声明返回值类型只能是 ModelAndView,如果需要返回JSON、xml等需要自己实现.
- 缓存利用,@Controller+@ExceptionHandler的缓存信息在ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver的exceptionHandlerCache,@ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler的缓存信息在ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver的exceptionHandlerAdviceCache中, 而HandlerExceptionResolver接口是不做缓存的,在前面两种方式都fail的情况下才会走自己的HandlerExceptionResolver实现类,多少有点性能损耗.
好,知道了redirect_url匹配不上之后,交给了该endpoint的handleOAuth2Exception进行处理
@ExceptionHandler(OAuth2Exception.class)
public ModelAndView handleOAuth2Exception(OAuth2Exception e, ServletWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
logger.info("Handling OAuth2 error: " + e.getSummary());
return handleException(e, webRequest);
}
如果用户名密码正确,那么最终会生成UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken令牌,交由servlet的端点AuthorizationEndpoint进行处理,处理流程如上代码所示,最终交给对应的granter授权认证。
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/authorize")
public ModelAndView authorize(Map model, @RequestParam Map parameters,
SessionStatus sessionStatus, Principal principal) {
// Pull out the authorization request first, using the OAuth2RequestFactory. All further logic should
// query off of the authorization request instead of referring back to the parameters map. The contents of the
// parameters map will be stored without change in the AuthorizationRequest object once it is created.
AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createAuthorizationRequest(parameters);
// 获取响应类型
Set responseTypes = authorizationRequest.getResponseTypes();
// 只支持授权码或简化模式
if (!responseTypes.contains("token") && !responseTypes.contains("code")) {
throw new UnsupportedResponseTypeException("Unsupported response types: " + responseTypes);
}
// client_id不能为空
if (authorizationRequest.getClientId() == null) {
throw new InvalidClientException("A client id must be provided");
}
try {
if (!(principal instanceof Authentication) || !((Authentication) principal).isAuthenticated()) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"User must be authenticated with Spring Security before authorization can be completed.");
}
// 获取client_id
ClientDetails client = getClientDetailsService().loadClientByClientId(authorizationRequest.getClientId());
// The resolved redirect URI is either the redirect_uri from the parameters or the one from
// clientDetails. Either way we need to store it on the AuthorizationRequest.
// 获取成功后重定向的地址
String redirectUriParameter = authorizationRequest.getRequestParameters().get(OAuth2Utils.REDIRECT_URI);
String resolvedRedirect = redirectResolver.resolveRedirect(redirectUriParameter, client);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(resolvedRedirect)) {
throw new RedirectMismatchException(
"A redirectUri must be either supplied or preconfigured in the ClientDetails");
}
authorizationRequest.setRedirectUri(resolvedRedirect);
// We intentionally only validate the parameters requested by the client (ignoring any data that may have
// been added to the request by the manager).
// 获取请求范围
oauth2RequestValidator.validateScope(authorizationRequest, client);
// Some systems may allow for approval decisions to be remembered or approved by default. Check for
// such logic here, and set the approved flag on the authorization request accordingly.
authorizationRequest = userApprovalHandler.checkForPreApproval(authorizationRequest,
(Authentication) principal);
// TODO: is this call necessary?
// 是否自动验证通过,如果不是则弹出用户授权框
boolean approved = userApprovalHandler.isApproved(authorizationRequest, (Authentication) principal);
authorizationRequest.setApproved(approved);
// Validation is all done, so we can check for auto approval...
// 自动验证模式
if (authorizationRequest.isApproved()) {
// 回复类型为token-简化模式,重定向到简化模式地址
if (responseTypes.contains("token")) {
return getImplicitGrantResponse(authorizationRequest);
}
// 回复类型为授权码-授权码模式,重定向到授权码模式地址
if (responseTypes.contains("code")) {
return new ModelAndView(getAuthorizationCodeResponse(authorizationRequest,
(Authentication) principal));
}
}
// Store authorizationRequest AND an immutable Map of authorizationRequest in session
// which will be used to validate against in approveOrDeny()
model.put(AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_ATTR_NAME, authorizationRequest);
model.put(ORIGINAL_AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_ATTR_NAME, unmodifiableMap(authorizationRequest));
return getUserApprovalPageResponse(model, authorizationRequest, (Authentication) principal);
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
sessionStatus.setComplete();
throw e;
}
}
我们看到,当用户名密码输入正确之后,会重定向到之前传递过来的redirect地址中并附带上code或token(授权码附带code,简化模式附带token)

获取授权码过程
有了授权码code给了浏览器客户端,接下来就是需要获取token的时候了,这就要求浏览器将获取到的code发送给客户端自己的服务器,然后服务器再去授权服务换取token,请求地址如下:
http://localhost:15003/oauth/token?grant_type=authorization_code&code=c8rhNC&client_id=dondown_client_id&client_secret=dondown_client_secret&redirect_uri=http://localhost:7010/uaa/login&scope=user_info
请求处理流程经过以上分析,我们只需关注TokenEndpoint调用AuthorizationCodeTokenGranter的granter方法上即可,处理过程如下:
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
if (!this.grantType.equals(grantType)) {
return null;
}
// 获取请求client_id
String clientId = tokenRequest.getClientId();
// 从数据库查询客户信息
ClientDetails client = clientDetailsService.loadClientByClientId(clientId);
validateGrantType(grantType, client);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Getting access token for: " + clientId);
}
// 生成token返回
return getAccessToken(client, tokenRequest);
}
首先验证用户的授权类型知否支持,如果支持则调用getAccessToken,最终调用实现类AuthorizationCodeTokenGranter的getAccessToken方法。
@Override
protected OAuth2Authentication getOAuth2Authentication(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
// 获取请求参数
Map parameters = tokenRequest.getRequestParameters();
// 获取上一次换取的code
String authorizationCode = parameters.get("code");
// 获取换取token后的重定向地址
String redirectUri = parameters.get(OAuth2Utils.REDIRECT_URI);
if (authorizationCode == null) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("An authorization code must be supplied.");
}
// 消费code(消费后就从内存或数据库中删除,下一次不能在使用-返回null,也就是code有且只能使用一次)对应上一次的认证信息
OAuth2Authentication storedAuth = authorizationCodeServices.consumeAuthorizationCode(authorizationCode);
if (storedAuth == null) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Invalid authorization code: " + authorizationCode);
}
// 获取上一次的请求
OAuth2Request pendingOAuth2Request = storedAuth.getOAuth2Request();
// https://jira.springsource.org/browse/SECOAUTH-333
// This might be null, if the authorization was done without the redirect_uri parameter
// 获取上一次的重定向地址
String redirectUriApprovalParameter = pendingOAuth2Request.getRequestParameters().get(
OAuth2Utils.REDIRECT_URI);
// 本次重定向地址与上一次不一致
if ((redirectUri != null || redirectUriApprovalParameter != null)
&& !pendingOAuth2Request.getRedirectUri().equals(redirectUri)) {
throw new RedirectMismatchException("Redirect URI mismatch.");
}
// 本次client_id与上一次不一致
String pendingClientId = pendingOAuth2Request.getClientId();
String clientId = tokenRequest.getClientId();
if (clientId != null && !clientId.equals(pendingClientId)) {
// just a sanity check.
throw new InvalidClientException("Client ID mismatch");
}
// Secret is not required in the authorization request, so it won't be available
// in the pendingAuthorizationRequest. We do want to check that a secret is provided
// in the token request, but that happens elsewhere.
// 获取上一次请求参数
Map combinedParameters = new HashMap(pendingOAuth2Request
.getRequestParameters());
// Combine the parameters adding the new ones last so they override if there are any clashes
// 与本次参数取合集
combinedParameters.putAll(parameters);
// Make a new stored request with the combined parameters
// 创建请求信息
OAuth2Request finalStoredOAuth2Request = pendingOAuth2Request.createOAuth2Request(combinedParameters);
// 获取上一次认证信息
Authentication userAuth = storedAuth.getUserAuthentication();
// 根据请求信息与认证信息创建认证信息
return new OAuth2Authentication(finalStoredOAuth2Request, userAuth);
}
如果我们在客户信息添(客户端注册的时候可以填写多个重定向地址)加上刚才的请求地址(多个以逗号分隔),或者该为注册的地址(http://www.baidu.com): http://localhost:7010/uaa/login

如果重定向地址配置正常且所有的scope验证通过之后,如果响应类型为token(implicit简化模式)则获取生成token信息
// We can grant a token and return it with implicit approval.
private ModelAndView getImplicitGrantResponse(AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest) {
try {
// 创建请求信息
TokenRequest tokenRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createTokenRequest(authorizationRequest, "implicit");
OAuth2Request storedOAuth2Request = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createOAuth2Request(authorizationRequest);
OAuth2AccessToken accessToken = getAccessTokenForImplicitGrant(tokenRequest, storedOAuth2Request);
if (accessToken == null) {
throw new UnsupportedResponseTypeException("Unsupported response type: token");
}
return new ModelAndView(new RedirectView(appendAccessToken(authorizationRequest, accessToken), false, true,
false));
}
catch (OAuth2Exception e) {
return new ModelAndView(new RedirectView(getUnsuccessfulRedirect(authorizationRequest, e, true), false,
true, false));
}
}
此时返回的ModalAndView指向的重定向地址生成规则为:
private String appendAccessToken(AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest, OAuth2AccessToken accessToken) {
Map vars = new LinkedHashMap();
Map keys = new HashMap();
if (accessToken == null) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("An implicit grant could not be made");
}
vars.put("access_token", accessToken.getValue());
vars.put("token_type", accessToken.getTokenType());
String state = authorizationRequest.getState();
if (state != null) {
vars.put("state", state);
}
Date expiration = accessToken.getExpiration();
if (expiration != null) {
long expires_in = (expiration.getTime() - System.currentTimeMillis()) / 1000;
vars.put("expires_in", expires_in);
}
String originalScope = authorizationRequest.getRequestParameters().get(OAuth2Utils.SCOPE);
if (originalScope == null || !OAuth2Utils.parseParameterList(originalScope).equals(accessToken.getScope())) {
vars.put("scope", OAuth2Utils.formatParameterList(accessToken.getScope()));
}
Map additionalInformation = accessToken.getAdditionalInformation();
for (String key : additionalInformation.keySet()) {
Object value = additionalInformation.get(key);
if (value != null) {
keys.put("extra_" + key, key);
vars.put("extra_" + key, value);
}
}
// Do not include the refresh token (even if there is one)
return append(authorizationRequest.getRedirectUri(), vars, keys, true);
}
如果响应类型为code授权码则获取生成code
private View getAuthorizationCodeResponse(AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest, Authentication authUser) {
try {
return new RedirectView(getSuccessfulRedirect(authorizationRequest,
generateCode(authorizationRequest, authUser)), false, true, false);
}
catch (OAuth2Exception e) {
return new RedirectView(getUnsuccessfulRedirect(authorizationRequest, e, false), false, true, false);
}
}
此时重定向url生成规则如下(最终生成http://localhost:7010/uaa/login?code=BTDuF4):
private String getSuccessfulRedirect(AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest, String authorizationCode) {
if (authorizationCode == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No authorization code found in the current request scope.");
}
Map query = new LinkedHashMap();
query.put("code", authorizationCode);
String state = authorizationRequest.getState();
if (state != null) {
query.put("state", state);
}
return append(authorizationRequest.getRedirectUri(), query, false);
}
并通过授权码服务(我这里没配置授权码服务,默认为InMemoryAuthorizationCodeServices)获取授权码:
private String generateCode(AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest, Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
try {
OAuth2Request storedOAuth2Request = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createOAuth2Request(authorizationRequest);
OAuth2Authentication combinedAuth = new OAuth2Authentication(storedOAuth2Request, authentication);
String code = authorizationCodeServices.createAuthorizationCode(combinedAuth);
return code;
}
catch (OAuth2Exception e) {
if (authorizationRequest.getState() != null) {
e.addAdditionalInformation("state", authorizationRequest.getState());
}
throw e;
}
}
如果用户scope自动approve,那么直接重定向到以上对应的url地址,否则没有验证通过或不是autoApprove,那么直接重定向到用户确认地址userApprovalPage让用户进行确认(forward:/oauth/confirm_access)
// Store authorizationRequest AND an immutable Map of authorizationRequest in session
// which will be used to validate against in approveOrDeny()
model.put(AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_ATTR_NAME, authorizationRequest);
model.put(ORIGINAL_AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_ATTR_NAME, unmodifiableMap(authorizationRequest));
return getUserApprovalPageResponse(model, authorizationRequest, (Authentication) principal);
授权码获取成功之后,重定向到请求的redirect_url中, 此时客户端浏览器就可以再次拿着code到服务端去请求换取token了:

授权码换取令牌token
经过上一步的复杂过程,我们知道我们换取的code最终会给到浏览器,浏览器再次拿着这个code给到授权服务再次换取token,接下来我们就用这个code换取对应的token。
换取token的请求地址如下:
http://localhost:15003/oauth/token
根据以上分析经验,我们直接知道spring的TokenEndpoint即可(ctrl+shift+T),该处理逻辑如下:
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/token", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity postAccessToken(Principal principal, @RequestParam
Map parameters) throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException {
if (!(principal instanceof Authentication)) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"There is no client authentication. Try adding an appropriate authentication filter.");
}
String clientId = getClientId(principal);
ClientDetails authenticatedClient = getClientDetailsService().loadClientByClientId(clientId);
TokenRequest tokenRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createTokenRequest(parameters, authenticatedClient);
if (clientId != null && !clientId.equals("")) {
// Only validate the client details if a client authenticated during this
// request.
if (!clientId.equals(tokenRequest.getClientId())) {
// double check to make sure that the client ID in the token request is the same as that in the
// authenticated client
throw new InvalidClientException("Given client ID does not match authenticated client");
}
}
if (authenticatedClient != null) {
oAuth2RequestValidator.validateScope(tokenRequest, authenticatedClient);
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(tokenRequest.getGrantType())) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("Missing grant type");
}
if (tokenRequest.getGrantType().equals("implicit")) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Implicit grant type not supported from token endpoint");
}
if (isAuthCodeRequest(parameters)) {
// The scope was requested or determined during the authorization step
if (!tokenRequest.getScope().isEmpty()) {
logger.debug("Clearing scope of incoming token request");
tokenRequest.setScope(Collections. emptySet());
}
}
if (isRefreshTokenRequest(parameters)) {
// A refresh token has its own default scopes, so we should ignore any added by the factory here.
tokenRequest.setScope(OAuth2Utils.parseParameterList(parameters.get(OAuth2Utils.SCOPE)));
}
OAuth2AccessToken token = getTokenGranter().grant(tokenRequest.getGrantType(), tokenRequest);
if (token == null) {
throw new UnsupportedGrantTypeException("Unsupported grant type: " + tokenRequest.getGrantType());
}
return getResponse(token);
}
最终落在处理authorization_code的granter上授权返回token:
OAuth2AccessToken token = getTokenGranter().grant(tokenRequest.getGrantType(), tokenRequest);
if (token == null) {
throw new UnsupportedGrantTypeException("Unsupported grant type: " + tokenRequest.getGrantType());
}
return getResponse(token);
AuthorizationCodeTokenGranter的授权代码如下:
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
if (!this.grantType.equals(grantType)) {
return null;
}
String clientId = tokenRequest.getClientId();
ClientDetails client = clientDetailsService.loadClientByClientId(clientId);
validateGrantType(grantType, client);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Getting access token for: " + clientId);
}
return getAccessToken(client, tokenRequest);
}
protected OAuth2AccessToken getAccessToken(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
return tokenServices.createAccessToken(getOAuth2Authentication(client, tokenRequest));
}
最后通过tokenServices(DefaultTokenServices)创建对应的token
protected OAuth2AccessToken getAccessToken(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
return tokenServices.createAccessToken(getOAuth2Authentication(client, tokenRequest));
}
授权码模式需要获取并验证(getOAuth2Authentication)之前的验证码在创建token
@Override
protected OAuth2Authentication getOAuth2Authentication(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
Map parameters = tokenRequest.getRequestParameters();
String authorizationCode = parameters.get("code");
String redirectUri = parameters.get(OAuth2Utils.REDIRECT_URI);
if (authorizationCode == null) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("An authorization code must be supplied.");
}
// 通过授权码获取前一次获取code时的认证信息:注意这里获取code之后会被移除(也就是一个code只能使用一次)
OAuth2Authentication storedAuth = authorizationCodeServices.consumeAuthorizationCode(authorizationCode);
if (storedAuth == null) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Invalid authorization code: " + authorizationCode);
}
// 获取前一次换取code请求的是redirec_url,前一次为:http://localhost:7010/uaa/login
OAuth2Request pendingOAuth2Request = storedAuth.getOAuth2Request();
// https://jira.springsource.org/browse/SECOAUTH-333
// This might be null, if the authorization was done without the redirect_uri parameter
String redirectUriApprovalParameter = pendingOAuth2Request.getRequestParameters().get(
OAuth2Utils.REDIRECT_URI);
// 验证前一次换取code的重定向地址和本次的redirect_url是否相同
if ((redirectUri != null || redirectUriApprovalParameter != null)
&& !pendingOAuth2Request.getRedirectUri().equals(redirectUri)) {
throw new RedirectMismatchException("Redirect URI mismatch.");
}
// 前一次的clientid与本次client_id是否一致
String pendingClientId = pendingOAuth2Request.getClientId();
String clientId = tokenRequest.getClientId();
if (clientId != null && !clientId.equals(pendingClientId)) {
// just a sanity check.
throw new InvalidClientException("Client ID mismatch");
}
// Secret is not required in the authorization request, so it won't be available
// in the pendingAuthorizationRequest. We do want to check that a secret is provided
// in the token request, but that happens elsewhere.
// 获取前一次获取code的认证信息的请求参数信息:
// {response_type=code, redirect_uri=http://localhost:7010/uaa/login, client_id=dondown_client_id}
Map combinedParameters = new HashMap(pendingOAuth2Request
.getRequestParameters());
// Combine the parameters adding the new ones last so they override if there are any clashes
// 取所有参数的合集
combinedParameters.putAll(parameters);
// Make a new stored request with the combined parameters
// 通过请求参数创建tokenRequest
OAuth2Request finalStoredOAuth2Request = pendingOAuth2Request.createOAuth2Request(combinedParameters);
Authentication userAuth = storedAuth.getUserAuthentication();
// 通过上一次认证信息与当前创建的tokenRequest和认证信息创建OAuth2Authentication
return new OAuth2Authentication(finalStoredOAuth2Request, userAuth);
}
可以看到授权码依然从authorizationCodeServices(依然为InMemoryAuthorizationCodeServices)获取授权码,验证信息是否与前面请求一致,然后创建token:
{code=9v2Vfh, grant_type=authorization_code, scope=user_info, response_type=code, redirect_uri=http://localhost:7010/uaa/login, client_secret=dondown_client_secret, client_id=dondown_client_id}
org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken@e94a6dba: Principal: AccsUser(id=1, mobile=, email=, userType=1); Credentials: [PROTECTED]; Authenticated: true; Details: org.springframework.security.web.authentication.WebAuthenticationDetails@fffde5d4: RemoteIpAddress: 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1; SessionId: 0F60EA4FCFC48333FCBEF91007E27311; Granted Authorities: ROLE_所有权限
通过code换取token只能使用一次,一次使用之后就失效(不论第一次换取是否成功)。因为获取之后会被移除:
public abstract class RandomValueAuthorizationCodeServices implements AuthorizationCodeServices {
private RandomValueStringGenerator generator = new RandomValueStringGenerator();
protected abstract void store(String code, OAuth2Authentication authentication);
protected abstract OAuth2Authentication remove(String code);
// 创建随机码,这里默认配置存储在内存中
public String createAuthorizationCode(OAuth2Authentication authentication) {
String code = generator.generate();
store(code, authentication);
return code;
}
// 消费一次code(也就是说通过code换取token一次)则会被从队列删除
public OAuth2Authentication consumeAuthorizationCode(String code)
throws InvalidGrantException {
OAuth2Authentication auth = this.remove(code);
if (auth == null) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Invalid authorization code: " + code);
}
return auth;
}
}
public class InMemoryAuthorizationCodeServices extends RandomValueAuthorizationCodeServices {
// 存储的是code=认证OAuth2Authentication
protected final ConcurrentHashMap authorizationCodeStore = new ConcurrentHashMap();
// 随机生成一个code
@Override
protected void store(String code, OAuth2Authentication authentication) {
this.authorizationCodeStore.put(code, authentication);
}
// code换取一次token
@Override
public OAuth2Authentication remove(String code) {
OAuth2Authentication auth = this.authorizationCodeStore.remove(code);
return auth;
}
}
简化模式token
简化模式是授权码模式的一种简化模式,它直接省略了code获取的环节,直接使用客户id、重定向地址和响应类型指定为token即可,请求地址如下所示:
http://localhost:15003/oauth/authorize?response_type=token&client_id=dondown_client_id&redirect_uri=http://localhost:7010/uaa/login
同理,我们熟悉了oAuth2认证流程(先有filter进行认证处理生成对应xxToken在交给endPoint进行处理生成对应token然后返回)之后,我们就可以直接定位到AuthorizationEndpoint(因为该端点处理了对应的Get请求/oauth/authorize),其处理流程与授权码模式一样,只是在不同的分支:
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/authorize")
public ModelAndView authorize(Map model, @RequestParam Map parameters,
SessionStatus sessionStatus, Principal principal) {
// Pull out the authorization request first, using the OAuth2RequestFactory. All further logic should
// query off of the authorization request instead of referring back to the parameters map. The contents of the
// parameters map will be stored without change in the AuthorizationRequest object once it is created.
AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createAuthorizationRequest(parameters);
Set responseTypes = authorizationRequest.getResponseTypes();
if (!responseTypes.contains("token") && !responseTypes.contains("code")) {
throw new UnsupportedResponseTypeException("Unsupported response types: " + responseTypes);
}
if (authorizationRequest.getClientId() == null) {
throw new InvalidClientException("A client id must be provided");
}
try {
if (!(principal instanceof Authentication) || !((Authentication) principal).isAuthenticated()) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"User must be authenticated with Spring Security before authorization can be completed.");
}
ClientDetails client = getClientDetailsService().loadClientByClientId(authorizationRequest.getClientId());
// The resolved redirect URI is either the redirect_uri from the parameters or the one from
// clientDetails. Either way we need to store it on the AuthorizationRequest.
String redirectUriParameter = authorizationRequest.getRequestParameters().get(OAuth2Utils.REDIRECT_URI);
String resolvedRedirect = redirectResolver.resolveRedirect(redirectUriParameter, client);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(resolvedRedirect)) {
throw new RedirectMismatchException(
"A redirectUri must be either supplied or preconfigured in the ClientDetails");
}
authorizationRequest.setRedirectUri(resolvedRedirect);
// We intentionally only validate the parameters requested by the client (ignoring any data that may have
// been added to the request by the manager).
oauth2RequestValidator.validateScope(authorizationRequest, client);
// Some systems may allow for approval decisions to be remembered or approved by default. Check for
// such logic here, and set the approved flag on the authorization request accordingly.
authorizationRequest = userApprovalHandler.checkForPreApproval(authorizationRequest,
(Authentication) principal);
// TODO: is this call necessary?
boolean approved = userApprovalHandler.isApproved(authorizationRequest, (Authentication) principal);
authorizationRequest.setApproved(approved);
// Validation is all done, so we can check for auto approval...
if (authorizationRequest.isApproved()) {
if (responseTypes.contains("token")) {
return getImplicitGrantResponse(authorizationRequest);
}
if (responseTypes.contains("code")) {
return new ModelAndView(getAuthorizationCodeResponse(authorizationRequest,
(Authentication) principal));
}
}
// Store authorizationRequest AND an immutable Map of authorizationRequest in session
// which will be used to validate against in approveOrDeny()
model.put(AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_ATTR_NAME, authorizationRequest);
model.put(ORIGINAL_AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_ATTR_NAME, unmodifiableMap(authorizationRequest));
return getUserApprovalPageResponse(model, authorizationRequest, (Authentication) principal);
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
sessionStatus.setComplete();
throw e;
}
}
我们只需要关注响应类型为token的流程
// Validation is all done, so we can check for auto approval...
if (authorizationRequest.isApproved()) {
if (responseTypes.contains("token")) {
return getImplicitGrantResponse(authorizationRequest);
}
if (responseTypes.contains("code")) {
return new ModelAndView(getAuthorizationCodeResponse(authorizationRequest,
(Authentication) principal));
}
}
该端点处理流程:
// We can grant a token and return it with implicit approval.
private ModelAndView getImplicitGrantResponse(AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest) {
try {
// 创建对应的请求
TokenRequest tokenRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createTokenRequest(authorizationRequest, "implicit");
//
OAuth2Request storedOAuth2Request = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createOAuth2Request(authorizationRequest);
// 生成对应的token
OAuth2AccessToken accessToken = getAccessTokenForImplicitGrant(tokenRequest, storedOAuth2Request);
if (accessToken == null) {
throw new UnsupportedResponseTypeException("Unsupported response type: token");
}
return new ModelAndView(new RedirectView(appendAccessToken(authorizationRequest, accessToken), false, true,
false));
}
catch (OAuth2Exception e) {
return new ModelAndView(new RedirectView(getUnsuccessfulRedirect(authorizationRequest, e, true), false,
true, false));
}
}
private OAuth2AccessToken getAccessTokenForImplicitGrant(TokenRequest tokenRequest,
OAuth2Request storedOAuth2Request) {
OAuth2AccessToken accessToken = null;
// These 1 method calls have to be atomic, otherwise the ImplicitGrantService can have a race condition where
// one thread removes the token request before another has a chance to redeem it.
// 通过授权granter验证权限
synchronized (this.implicitLock) {
accessToken = getTokenGranter().grant("implicit",
new ImplicitTokenRequest(tokenRequest, storedOAuth2Request));
}
return accessToken;
}
最后交给ImplicitTokenGranter进行授权验证:
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
// 授权类型知否是本granter支持,这里为implicit
if (!this.grantType.equals(grantType)) {
return null;
}
// 通过client_id加载用户信息
String clientId = tokenRequest.getClientId();
ClientDetails client = clientDetailsService.loadClientByClientId(clientId);
// 验证用户是否有对应的授权类型
validateGrantType(grantType, client);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Getting access token for: " + clientId);
}
// 创建对应的token
return getAccessToken(client, tokenRequest);
}
protected OAuth2AccessToken getAccessToken(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
return tokenServices.createAccessToken(getOAuth2Authentication(client, tokenRequest));
}
@Override
protected OAuth2Authentication getOAuth2Authentication(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest clientToken) {
Authentication userAuth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (userAuth==null || !userAuth.isAuthenticated()) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException("There is no currently logged in user");
}
Assert.state(clientToken instanceof ImplicitTokenRequest, "An ImplicitTokenRequest is required here. Caller needs to wrap the TokenRequest.");
OAuth2Request requestForStorage = ((ImplicitTokenRequest)clientToken).getOAuth2Request();
return new OAuth2Authentication(requestForStorage, userAuth);
}
最终生成重定向地址:
http://localhost:7010/uaa/login#access_token=ba3563ee-a6d1-46ca-babd-3317d6bd14b9&token_type=bearer&expires_in=6922&scope=user_info
客户端模式换取token
接下来要讲解的最后一种模式就是客户端认证模式,该模式具有如下特点:
- 这种模式直接根据client的id和密钥即可获取token,无需用户参与
- 这种模式比较合适消费api的后端服务,比如拉取一组用户信息等
- 不支持refresh token,主要是没有必要
请求地址:
http://localhost:15003/oauth/token?grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=dondown_client_id&client_secret=dondown_client_secret
根据经验,我们直接打开TokenEndpoint端点处理器的处理端点/oauth/token,代码如下:
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/token", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity postAccessToken(Principal principal, @RequestParam
Map parameters) throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException {
if (!(principal instanceof Authentication)) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"There is no client authentication. Try adding an appropriate authentication filter.");
}
String clientId = getClientId(principal);
ClientDetails authenticatedClient = getClientDetailsService().loadClientByClientId(clientId);
TokenRequest tokenRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createTokenRequest(parameters, authenticatedClient);
if (clientId != null && !clientId.equals("")) {
// Only validate the client details if a client authenticated during this
// request.
if (!clientId.equals(tokenRequest.getClientId())) {
// double check to make sure that the client ID in the token request is the same as that in the
// authenticated client
throw new InvalidClientException("Given client ID does not match authenticated client");
}
}
if (authenticatedClient != null) {
oAuth2RequestValidator.validateScope(tokenRequest, authenticatedClient);
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(tokenRequest.getGrantType())) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("Missing grant type");
}
if (tokenRequest.getGrantType().equals("implicit")) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Implicit grant type not supported from token endpoint");
}
if (isAuthCodeRequest(parameters)) {
// The scope was requested or determined during the authorization step
if (!tokenRequest.getScope().isEmpty()) {
logger.debug("Clearing scope of incoming token request");
tokenRequest.setScope(Collections. emptySet());
}
}
if (isRefreshTokenRequest(parameters)) {
// A refresh token has its own default scopes, so we should ignore any added by the factory here.
tokenRequest.setScope(OAuth2Utils.parseParameterList(parameters.get(OAuth2Utils.SCOPE)));
}
OAuth2AccessToken token = getTokenGranter().grant(tokenRequest.getGrantType(), tokenRequest);
if (token == null) {
throw new UnsupportedGrantTypeException("Unsupported grant type: " + tokenRequest.getGrantType());
}
return getResponse(token);
}
进去以上的跟踪经验,我么直接定位到对应的granter即可,此时的granter实现类为ClientCredentialsTokenGranter:(过程依然是endpoint的AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer调用默认CompositeTokenGranter混合授权器的ClientCredentialsTokenGranter)。
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
for (TokenGranter granter : tokenGranters) {
OAuth2AccessToken grant = granter.grant(grantType, tokenRequest);
if (grant!=null) {
return grant;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
OAuth2AccessToken token = super.grant(grantType, tokenRequest);
if (token != null) {
DefaultOAuth2AccessToken norefresh = new DefaultOAuth2AccessToken(token);
// The spec says that client credentials should not be allowed to get a refresh token
if (!allowRefresh) {
norefresh.setRefreshToken(null);
}
token = norefresh;
}
return token;
}
授权实现:
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
if (!this.grantType.equals(grantType)) {
return null;
}
String clientId = tokenRequest.getClientId();
ClientDetails client = clientDetailsService.loadClientByClientId(clientId);
validateGrantType(grantType, client);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Getting access token for: " + clientId);
}
return getAccessToken(client, tokenRequest);
}
protected OAuth2AccessToken getAccessToken(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
return tokenServices.createAccessToken(getOAuth2Authentication(client, tokenRequest));
}
protected OAuth2Authentication getOAuth2Authentication(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
OAuth2Request storedOAuth2Request = requestFactory.createOAuth2Request(client, tokenRequest);
return new OAuth2Authentication(storedOAuth2Request, null);
}
通过代码可以看到,客户端模式确实是没有刷新token的功能(refreshToken为null),最终换取到token

以上代码介绍了oauth2的4种认证模型以及对应的处理流程,通过以上文档大家应该知道从如何下手调试自己的程序,如有疑问,欢迎通过如下方式进行沟通!
三、自我总结
1、六个常用端点
- /oauth/authorize
授权端点 - /oauth/token
令牌端点 - /oauth/confirm_access
用户确认授权提交端点 - /oauth/error
授权服务错误信息端点 - /oauth/check_token
用于资源服务访问的令牌解析端点 - /oauth/token_key
提供公有密匙的端点,如果使用JWT令牌的话
知道以上几个端点后,我们在开发过程中自己就可以会很容易的调试其源码并解决自己的问题,这里不再多说,重要重要!!!
2、三个核心配置类
- ResourceServerConfiguration
资源服务配置 (配置需要认证的接口) - AuthorizationServerConfiguration
授权认证服务配置 (配置认证方式和token的存储) - WebSecurityConfig
security 配置 (配置oauth2的过滤请求,如/oauth)
源码获取、合作、技术交流请获取如下联系方式:
微信账号:lixiang6153
公众号:IT技术快餐
电子邮箱:[email protected]