elmo(BiLSTM-CRF+elmo)(Conll-2003 命名实体识别NER)
文章目录
- elmo(BiLSTM-CRF+elmo)(Conll-2003 命名实体识别NER)
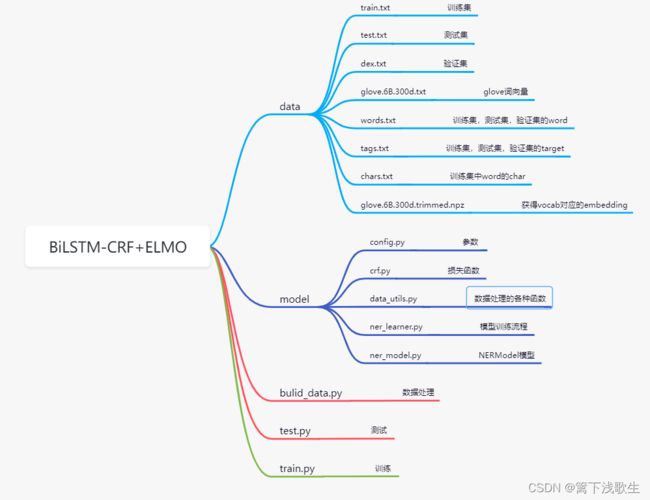
- 一、文件目录
- 二、语料集
- 三、数据处理(bulid_data.py)(data_utils.py)
- 四、NERModel模型(ner_model.py)
- 五、BiLSTM-CRF+ELMO模型训练流程(ner_learner.py)
- 六、计算loss值(CRF)
- 七、训练(train.py)
- 八、测试(test.py)
- 实验结果
elmo(BiLSTM-CRF+elmo)(Conll-2003 命名实体识别NER)
一、文件目录
二、语料集
CoNLL 2003 NER :
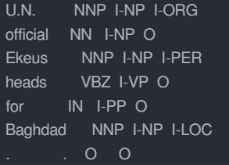
数据集第一列是单词,第二列是词性,第三列是语法,第四列是实体标签。在NER任务中,只关心第一列和第四列。
三、数据处理(bulid_data.py)(data_utils.py)
bulid_data.py——数据处理
from model.config import Config
from model.data_utils import CoNLLDataset, get_vocabs, UNK, NUM, \
get_glove_vocab, write_vocab, load_vocab, get_char_vocab, \
export_trimmed_glove_vectors, get_processing_word
def main():
"""Procedure to build data
You MUST RUN this procedure. It iterates over the whole dataset (train,
dev and test) and extract the vocabularies in terms of words, tags, and
characters. Having built the vocabularies it writes them in a file. The
writing of vocabulary in a file assigns an id (the line #) to each word.
It then extract the relevant GloVe vectors and stores them in a np array
such that the i-th entry corresponds to the i-th word in the vocabulary.
Args:
config: (instance of Config) has attributes like hyper-params...
"""
# 1. get config and processing of words
config = Config(load=False)
#2. Get processing word generator
# 获取预训练词embedding
processing_word = get_processing_word(lowercase=True)
# 3. Generators
# 获得dev,test,train的word和target
dev = CoNLLDataset(config.filename_dev, processing_word)
test = CoNLLDataset(config.filename_test, processing_word)
train = CoNLLDataset(config.filename_train, processing_word)
# 4. Build Word and Tag vocab
# 建立word和target的词库
vocab_words, vocab_tags = get_vocabs([train, dev, test])
# 处理glove:建里glove词库
vocab_glove = get_glove_vocab(config.filename_glove)
# 5. Get a vocab set for words in both vocab_words and vocab_glove
# vocab 为既存在vocab_words又存在vocab_glove的词
vocab = vocab_words & vocab_glove
# vocab 中添加UNK,NUM
vocab.add(UNK)
vocab.add(NUM)
# 6. Save vocab
# 保存words.txt和tags.txt
write_vocab(vocab, config.filename_words)
write_vocab(vocab_tags, config.filename_tags)
# 7. Trim GloVe Vectors
# 下载vocab
vocab = load_vocab(config.filename_words)
# 获得词对应的词向量
export_trimmed_glove_vectors(vocab, config.filename_glove,
config.filename_trimmed, config.dim_word)
# Build and save char vocab
# 获得train的word和target
train = CoNLLDataset(config.filename_train)
# 获得训练集中word的char
vocab_chars = get_char_vocab(train)
# 保存chars.txt
write_vocab(vocab_chars, config.filename_chars)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
data_utils.py——数据处理的各种函数
" Data utils from https://github.com/guillaumegenthial/sequence_tagging "
import numpy as np
import torch
import os
# shared global variables to be imported from model also
UNK = "$UNK$"
NUM = "$NUM$"
NONE = "O"
# special error message
class MyIOError(Exception):
def __init__(self, filename):
# custom error message
message = """
ERROR: Unable to locate file {}.
FIX: Have you tried running python build_data.py first?
This will build vocab file from your train, test and dev sets and
trimm your word vectors.
""".format(filename)
super(MyIOError, self).__init__(message)
# 训练数据预处理
# 函数调用:train = CoNLLDataset(config.filename_train, processing_word)
class CoNLLDataset(object):
"""Class that iterates over CoNLL Dataset
__iter__ method yields a tuple (words, tags)
words: list of raw words
tags: list of raw tags
If processing_word and processing_tag are not None,
optional preprocessing is appplied
Example:
```python
data = CoNLLDataset(filename)
for sentence, tags in data:
pass
```
"""
def __init__(self, filename, processing_word=None, processing_tag=None,
max_iter=None, use_crf=True):
"""
Args:
filename: path to the file
processing_words: (optional) function that takes a word as input
processing_tags: (optional) function that takes a tag as input
max_iter: (optional) max number of sentences to yield
"""
self.filename = filename
# 预处理词
self.processing_word = processing_word
# 处理标签
self.processing_tag = processing_tag
# 迭代次数
self.max_iter = max_iter
# 是否使用crf
self.use_crf = use_crf
self.length = None
def __iter__(self):
niter = 0
with open(self.filename) as f:
words, tags = [], []
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
# 一句结束
if (len(line) == 0 or line.startswith("-DOCSTART-")):
if len(words) != 0:
niter += 1
if self.max_iter is not None and niter > self.max_iter:
break
# 保存 words, tags
yield words, tags
# 清空 words, tags
words, tags = [], []
else:
ls = line.split(' ')
# 获取第一列(词)和第四列(标签)
word, tag = ls[0],ls[-1]
if self.processing_word is not None:
word = self.processing_word(word)
if self.processing_tag is not None:
if self.use_crf:
tag = self.processing_tag(tag)
words += [word]
tags += [tag]
def __len__(self):
"""Iterates once over the corpus to set and store length"""
if self.length is None:
self.length = 0
for _ in self:
self.length += 1
return self.length
# 获得词和标签
# 函数调用:vocab_words, vocab_tags = get_vocabs([train, dev, test])
def get_vocabs(datasets):
"""Build vocabulary from an iterable of datasets objects
Args:
datasets: a list of dataset objects
Returns:
a set of all the words in the dataset
"""
print("Building vocab...")
vocab_words = set()
vocab_tags = set()
for dataset in datasets:
for words, tags in dataset:
vocab_words.update(words)
vocab_tags.update(tags)
print("- done. {} tokens".format(len(vocab_words)))
return vocab_words, vocab_tags
# 获得训练集中的char
# 函数调动:vocab_chars = get_char_vocab(train)
def get_char_vocab(dataset):
"""Build char vocabulary from an iterable of datasets objects
Args:
dataset: a iterator yielding tuples (sentence, tags)
Returns:
a set of all the characters in the dataset
"""
print("Building char vocab...")
vocab_char = set()
for words, _ in dataset:
for word in words:
vocab_char.update(word)
print("- done. {} tokens".format(len(vocab_char)))
return vocab_char
# 处理glove:建里glove词库
# 函数调用:vocab_glove = get_glove_vocab(config.filename_glove)
def get_glove_vocab(filename):
"""Load vocab from file
Args:
filename: path to the glove vectors
Returns:
vocab: set() of strings
"""
print("Building vocab...")
vocab = set()
with open(filename, encoding="utf8") as f:
for line in f:
word = line.strip().split(' ')[0]
#glove的第一个单词存入vocab中
vocab.add(word)
print("- done. {} tokens".format(len(vocab)))
return vocab
def write_vocab(vocab, filename):
"""Writes a vocab to a file
Writes one word per line.
Args:
vocab: iterable that yields word
filename: path to vocab file
Returns:
write a word per line
"""
print("Writing vocab...")
with open(filename, "w") as f:
for i, word in enumerate(vocab):
if i != len(vocab) - 1:
f.write("{}\n".format(word))
else:
f.write(word)
print("- done. {} tokens".format(len(vocab)))
# 获得词典 word和id
# 函数调用: self.vocab_words = load_vocab(self.filename_words)
def load_vocab(filename):
"""Loads vocab from a file
Args:
filename: (string) the format of the file must be one word per line.
Returns:
d: dict[word] = index
"""
try:
d = dict()
with open(filename) as f:
for idx, word in enumerate(f):
word = word.strip()
d[word] = idx
except IOError:
raise MyIOError(filename)
return d
# 获得词对应的词向量
# 函数调用:export_trimmed_glove_vectors(vocab, config.filename_glove,config.filename_trimmed, config.dim_word)
def export_trimmed_glove_vectors(vocab, glove_filename, trimmed_filename, dim):
"""Saves glove vectors in numpy array
Args:
vocab: dictionary vocab[word] = index
glove_filename: a path to a glove file
trimmed_filename: a path where to store a matrix in npy
dim: (int) dimension of embeddings
"""
embeddings = np.zeros([len(vocab), dim])
with open(glove_filename, encoding="utf8") as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip().split(' ')
word = line[0]
embedding = [float(x) for x in line[1:]]
if word in vocab:
word_idx = vocab[word]
embeddings[word_idx] = np.asarray(embedding)
np.savez_compressed(trimmed_filename, embeddings=embeddings)
def get_trimmed_glove_vectors(filename):
"""
Args:
filename: path to the npz file
Returns:
matrix of embeddings (np array)
"""
try:
with np.load(filename) as data:
return data["embeddings"]
except IOError:
raise MyIOError(filename)
# 获得预训练词
# 初始化函数调用:processing_word = get_processing_word(lowercase=True)
# 函数调用:self.processing_word = get_processing_word(self.vocab_words,self.vocab_chars, lowercase=True, chars=self.use_chars)
def get_processing_word(vocab_words=None, vocab_chars=None,
lowercase=False, chars=False, allow_unk=True):
"""Return lambda function that transform a word (string) into list,
or tuple of (list, id) of int corresponding to the ids of the word and
its corresponding characters.
Args:
vocab: dict[word] = idx
Returns:
f("cat") = ([12, 4, 32], 12345)
= (list of char ids, word id)
"""
def f(word):
# 0. get chars of words
#chars == False
if vocab_chars is not None and chars == True:
char_ids = []
for char in word:
# ignore chars out of vocabulary
if char in vocab_chars:
char_ids += [vocab_chars[char]]
# 1. preprocess word
# lowercase=True
if lowercase:
word = word.lower()
# 如果word是数字,转成特殊符号NUM
if word.isdigit():
word = NUM
# 2. get id of word
# vocab_words=None
if vocab_words is not None:
if word in vocab_words:
word = vocab_words[word]
else:
if allow_unk:
word = vocab_words[UNK]
else:
raise Exception("Unknow key is not allowed. Check that "\
"your vocab (tags?) is correct")
# 3. return tuple char ids, word id
if vocab_chars is not None and chars == True:
return char_ids, word
else:
return word
return f
def _pad_sequences(sequences, pad_tok, max_length):
"""
Args:
sequences: a generator of list or tuple
pad_tok: the char to pad with
Returns:
a list of list where each sublist has same length
"""
sequence_padded, sequence_length = [], []
for seq in sequences:
seq = list(seq)
seq_ = seq[:max_length] + [pad_tok]*max(max_length - len(seq), 0)
sequence_padded += [seq_]
sequence_length += [min(len(seq), max_length)]
return sequence_padded, sequence_length
def pad_sequences(sequences, pad_tok, nlevels=1):
"""
Args:
sequences: a generator of list or tuple
pad_tok: the char to pad with
nlevels: "depth" of padding, for the case where we have characters ids
Returns:
a list of list where each sublist has same length
"""
if nlevels == 1:
max_length = max(map(lambda x : len(x), sequences))
sequence_padded, sequence_length = _pad_sequences(sequences,
pad_tok, max_length)
elif nlevels == 2:
max_length_word = max([max(map(lambda x: len(x), seq))
for seq in sequences])
sequence_padded, sequence_length = [], []
for seq in sequences:
# all words are same length now
sp, sl = _pad_sequences(seq, pad_tok, max_length_word)
sequence_padded += [sp]
sequence_length += [sl]
max_length_sentence = max(map(lambda x : len(x), sequences))
sequence_padded, _ = _pad_sequences(sequence_padded,
[pad_tok]*max_length_word, max_length_sentence)
sequence_length, _ = _pad_sequences(sequence_length, 0,
max_length_sentence)
return sequence_padded, sequence_length
def minibatches(data, minibatch_size, use_crf=True):
"""
Args:
data: generator of (sentence, tags) tuples
minibatch_size: (int)
Yields:
list of tuples
"""
x_batch, y_batch = [], []
for (x, y) in data:
if len(x_batch) == minibatch_size:
yield x_batch, y_batch
x_batch, y_batch = [], []
if type(x[0]) == tuple:
x = zip(*x)
x_batch += [x]
if use_crf:
y_batch += [y]
else:
if any([x.isdigit() for x in y]):
y_batch.append([int(x) for x in y if x.isdigit()])
else:
y_batch.append([0,0,0,0,0])
if len(x_batch) != 0:
yield x_batch, y_batch
def get_chunk_type(tok, idx_to_tag):
"""
Args:
tok: id of token, ex 4
idx_to_tag: dictionary {4: "B-PER", ...}
Returns:
tuple: "B", "PER"
"""
if isinstance(tok, torch.Tensor): tok = tok.item()
tag_name = idx_to_tag[tok]
tag_class = tag_name.split('-')[0]
tag_type = tag_name.split('-')[-1]
return tag_class, tag_type
def get_chunks(seq, tags):
"""Given a sequence of tags, group entities and their position
Args:
seq: [4, 4, 0, 0, ...] sequence of labels
tags: dict["O"] = 4
Returns:
list of (chunk_type, chunk_start, chunk_end)
Example:
seq = [4, 5, 0, 3]
tags = {"B-PER": 4, "I-PER": 5, "B-LOC": 3}
result = [("PER", 0, 2), ("LOC", 3, 4)]
"""
default = tags[NONE]
idx_to_tag = {idx: tag for tag, idx in tags.items()}
chunks = []
chunk_type, chunk_start = None, None
for i, tok in enumerate(seq):
# End of a chunk 1
if tok == default and chunk_type is not None:
# Add a chunk.
chunk = (chunk_type, chunk_start, i)
chunks.append(chunk)
chunk_type, chunk_start = None, None
# End of a chunk + start of a chunk!
elif tok != default:
tok_chunk_class, tok_chunk_type = get_chunk_type(tok, idx_to_tag)
if chunk_type is None:
chunk_type, chunk_start = tok_chunk_type, i
elif tok_chunk_type != chunk_type or tok_chunk_class == "B":
chunk = (chunk_type, chunk_start, i)
chunks.append(chunk)
chunk_type, chunk_start = tok_chunk_type, i
else:
pass
# end condition
if chunk_type is not None:
chunk = (chunk_type, chunk_start, len(seq))
chunks.append(chunk)
return chunks
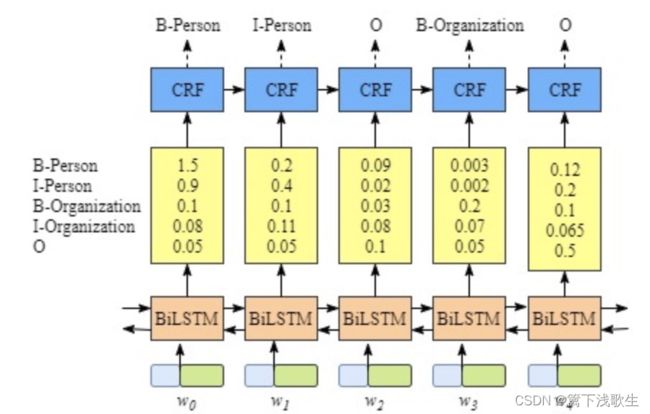
四、NERModel模型(ner_model.py)
#from fastai.text import *
from .core import *
# NERModel
# 函数调用:model = NERModel(config)
class NERModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
self.use_elmo = config.use_elmo
# config.use_elmo=True
if not self.use_elmo:
self.emb = nn.Embedding(self.config.nwords, self.config.dim_word, padding_idx=0)
self.char_embeddings = nn.Embedding(self.config.nchars, self.config.dim_char, padding_idx=0)
self.char_lstm = nn.LSTM(self.config.dim_char, self.config.hidden_size_char, bidirectional=True)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=self.config.dropout)
# BiLSTM 1024*600
self.word_lstm = nn.LSTM(self.config.dim_elmo if self.use_elmo else self.config.dim_word+2*self.config.hidden_size_char,
self.config.hidden_size_lstm, bidirectional=True)#dim_elmo = 1024 , hidden_size_lstm = 300
# 输出的线性层:[600,9]
self.linear = LinearClassifier(self.config, layers=[self.config.hidden_size_lstm*2, self.config.ntags], drops=[0.5])#self.ntags = len(self.vocab_tags)=9
def forward(self, input):
# Word_dim = (batch_size x sent_length)
# char_dim = (batch_size x sent_length x word_length)
# self.use_elmo=True
if self.use_elmo:
# [5, 31, 1024]->[31,5,1024]
word_emb = self.dropout(input.transpose(0,1))
else:
word_input, char_input = input[0], input[1]
word_input.transpose_(0,1)
# Word Embedding
word_emb = self.emb(word_input) #shape= S*B*wnh
# Char LSTM
char_emb = self.char_embeddings(char_input.view(-1, char_input.size(2))) #https://stackoverflow.com/questions/47205762/embedding-3d-data-in-pytorch
char_emb = char_emb.view(*char_input.size(), -1) #dim = BxSxWxE
_, (h, c) = self.char_lstm(char_emb.view(-1, char_emb.size(2), char_emb.size(3)).transpose(0,1)) #(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size) = 2*BS*cnh
char_output = torch.cat((h[0], h[1]), 1) #shape = BS*2cnh
char_output = char_output.view(char_emb.size(0), char_emb.size(1), -1).transpose(0,1) #shape = S*B*2cnh
# Concat char output and word output
word_emb = torch.cat((word_emb, char_output), 2) #shape = S*B*(wnh+2cnh)
word_emb = self.dropout(word_emb)
# 进入BiLSTM [31,5,600]
output, (h, c) = self.word_lstm(word_emb) #shape = S,B,hidden_size_lstm
output = self.dropout(output)
# 进入线性层[31,5,9]
output = self.linear(output)
return output #shape = S*B*ntags
# 被LinearClassifier()函数调用,用于线性层
class LinearBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ni, nf, drop):
super().__init__()
self.lin = nn.Linear(ni, nf)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(ni)
def forward(self, x):
return self.lin(self.drop(self.bn(x)))
# 输出的线性层:[600,9]
# 函数调用: self.linear = LinearClassifier(self.config, layers=[self.config.hidden_size_lstm*2, self.config.ntags], drops=[0.5])
class LinearClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config, layers, drops):
self.config = config
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([
LinearBlock(layers[i], layers[i + 1], drops[i]) for i in range(len(layers) - 1)])
def forward(self, input):
# [31,5,600]
output = input
sl,bs,_ = output.size()
x = output.view(-1, 2*self.config.hidden_size_lstm)#[155,600]
# [155,9]
for l in self.layers:
l_x = l(x)
x = F.relu(l_x)
return l_x.view(sl, bs, self.config.ntags)# [31,5,9]
五、BiLSTM-CRF+ELMO模型训练流程(ner_learner.py)
""" Works with pytorch 0.4.0 """
from .core import *
from .data_utils import pad_sequences, minibatches, get_chunks
from .crf import CRF
from .general_utils import Progbar
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import StepLR
# allennlp中的elmo
if os.name == "posix": from allennlp.modules.elmo import Elmo, batch_to_ids # AllenNLP is currently only supported on linux
# model = NERModel(config)
# 函数调用:learn = NERLearner(config, model)
class NERLearner(object):
"""
NERLearner class that encapsulates a pytorch nn.Module model and ModelData class
Contains methods for training a testing the model
"""
def __init__(self, config, model):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
self.logger = self.config.logger
self.model = model
self.model_path = config.dir_model
self.use_elmo = config.use_elmo
# 构建id_to_tag
self.idx_to_tag = {idx: tag for tag, idx in
self.config.vocab_tags.items()}
self.criterion = CRF(self.config.ntags)
# 优化器
self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.model.parameters())
# use_elmo = True
if self.use_elmo:
options_file = "https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/allennlp/models/elmo/2x4096_512_2048cnn_2xhighway/elmo_2x4096_512_2048cnn_2xhighway_options.json"
weight_file = "https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/allennlp/models/elmo/2x4096_512_2048cnn_2xhighway/elmo_2x4096_512_2048cnn_2xhighway_weights.hdf5"
self.elmo = Elmo(options_file, weight_file, 2, dropout=0)
else:
self.load_emb()
if USE_GPU:
self.use_cuda = True
self.logger.info("GPU found.")
self.model = model.cuda()
self.criterion = self.criterion.cuda()
if self.use_elmo:
self.elmo = self.elmo.cuda()
print("Moved elmo to cuda")
else:
self.model = model.cpu()
self.use_cuda = False
self.logger.info("No GPU found.")
def get_model_path(self, name):
return os.path.join(self.model_path,name)+'.h5'
def get_layer_groups(self, do_fc=False):
return children(self.model)
def freeze_to(self, n):
c=self.get_layer_groups()
for l in c:
set_trainable(l, False)
for l in c[n:]:
set_trainable(l, True)
def unfreeze(self):
self.freeze_to(0)
def save(self, name=None):
if not name:
name = self.config.ner_model_path
save_model(self.model, self.get_model_path(name))
self.logger.info(f"Saved model at {self.get_model_path(name)}")
def load_emb(self):
self.model.emb.weight = nn.Parameter(T(self.config.embeddings))
self.model.emb.weight.requires_grad = False
self.logger.info('Loading pretrained word embeddings')
def load(self, fn=None):
if not fn: fn = self.config.ner_model_path
fn = self.get_model_path(fn)
load_ner_model(self.model, fn, strict=True)
self.logger.info(f"Loaded model from {fn}")
# 根据batch_size整理数据集
# 函数调用:nbatches_train, train_generator = self.batch_iter(train, batch_size, return_lengths=True)
def batch_iter(self, train, batch_size, return_lengths=False, shuffle=False, sorter=False):
"""
Builds a generator from the given dataloader to be fed into the model
Args:
train: DataLoader
batch_size: size of each batch
return_lengths: if True, generator returns a list of sequence lengths for each
sample in the batch
ie. sequence_lengths = [8,7,4,3]
shuffle: if True, shuffles the data for each epoch
sorter: if True, uses a sorter to shuffle the data
Returns:
nbatches: (int) number of batches
data_generator: batch generator yielding
dict inputs:{'word_ids' : np.array([[padded word_ids in sent1], ...])
'char_ids': np.array([[[padded char_ids in word1_sent1], ...],
[padded char_ids in word1_sent2], ...],
...])}
labels: np.array([[padded label_ids in sent1], ...])
sequence_lengths: list([len(sent1), len(sent2), ...])
"""
nbatches = (len(train) + batch_size - 1) // batch_size
def data_generator():
while True:
if shuffle: train.shuffle()
elif sorter==True and train.sorter: train.sort()
for i, (words, labels) in enumerate(minibatches(train, batch_size)):
# perform padding of the given data
if self.config.use_chars:
char_ids, word_ids = zip(*words)
word_ids, sequence_lengths = pad_sequences(word_ids, 1)
char_ids, word_lengths = pad_sequences(char_ids, pad_tok=0,
nlevels=2)
else:
word_ids, sequence_lengths = pad_sequences(words, 0)
if self.use_elmo:
word_ids = words
if labels:
labels, _ = pad_sequences(labels, 0)
# if categorical
## labels = [to_categorical(label, num_classes=len(train.tag_itos)) for label in labels]
# build dictionary
inputs = {
"word_ids": np.asarray(word_ids)
}
if self.config.use_chars:
inputs["char_ids"] = np.asarray(char_ids)
if return_lengths:
yield(inputs, np.asarray(labels), sequence_lengths)
else:
yield (inputs, np.asarray(labels))
return (nbatches, data_generator())
def fine_tune(self, train, dev=None):
"""
Fine tune the NER model by freezing the pre-trained encoder and training the newly
instantiated layers for 1 epochs
"""
self.logger.info("Fine Tuning Model")
self.fit(train, dev, epochs=1, fine_tune=True)
# 函数调用:learn.fit(train, dev)
def fit(self, train, dev=None, epochs=None, fine_tune=False):
"""
Fits the model to the training dataset and evaluates on the validation set.
Saves the model to disk
"""
if not epochs:
epochs = self.config.nepochs
# batch_size = 5
batch_size = self.config.batch_size
# 根据batch_size整理训练数据集
nbatches_train, train_generator = self.batch_iter(train, batch_size,
return_lengths=True)
# 根据batch_size整理验证数据集
if dev:
nbatches_dev, dev_generator = self.batch_iter(dev, batch_size,
return_lengths=True)
# 优化器
scheduler = StepLR(self.optimizer, step_size=1, gamma=self.config.lr_decay)
if not fine_tune: self.logger.info("Training Model")
f1s = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
scheduler.step()
# 将句子中的word生成elmo中的id,进入NERModel模型中训练
self.train(epoch, nbatches_train, train_generator, fine_tune=fine_tune)
if dev:
f1 = self.test(nbatches_dev, dev_generator, fine_tune=fine_tune)
# Early stopping
if len(f1s) > 0:
if f1 < max(f1s[max(-self.config.nepoch_no_imprv, -len(f1s)):]): #if sum([f1 > f1s[max(-i, -len(f1s))] for i in range(1,self.config.nepoch_no_imprv+1)]) == 0:
print("No improvement in the last 3 epochs. Stopping training")
break
else:
f1s.append(f1)
if fine_tune:
self.save(self.config.ner_ft_path)
else :
self.save(self.config.ner_model_path)
# 将句子中的word生成elmo中的id,进入NERModel模型中训练
# 函数调用; self.train(epoch, nbatches_train, train_generator, fine_tune=fine_tune)
def train(self, epoch, nbatches_train, train_generator, fine_tune=False):
self.logger.info('\nEpoch: %d' % epoch)
self.model.train()
if not self.use_elmo: self.model.emb.weight.requires_grad = False
train_loss = 0
correct = 0
total = 0
total_step = None
#打印进度条
prog = Progbar(target=nbatches_train)
# inputs:batch输入数据,targets:数据对应target,
for batch_idx, (inputs, targets, sequence_lengths) in enumerate(train_generator):
if batch_idx == nbatches_train: break
if inputs['word_ids'].shape[0] == 1:
self.logger.info('Skipping batch of size=1')
continue
total_step = batch_idx
targets = T(targets, cuda=self.use_cuda).transpose(0,1).contiguous()
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
# self.use_elmo=True
if self.use_elmo:
sentences = inputs['word_ids']#list(['EU', 'rejects', 'German', 'call', 'to', 'boycott', 'British', 'lamb', '.']
# 将句子中的word生成elmo中的id
character_ids = batch_to_ids(sentences)
if self.use_cuda:
character_ids = character_ids.cuda()
# 将句子送入到elmo中
embeddings = self.elmo(character_ids)
# 获得emlo第一层的embedding[5,31,1024]
word_input = embeddings['elmo_representations'][0]
# word_input(batch_size x sent_length x dim_elmo):[5,31,1024] , targets:[31,5]
word_input, targets = Variable(word_input, requires_grad=False), \
Variable(targets)
inputs = (word_input)
else:
word_input = T(inputs['word_ids'], cuda=self.use_cuda)
char_input = T(inputs['char_ids'], cuda=self.use_cuda)
word_input, char_input, targets = Variable(word_input, requires_grad=False), \
Variable(char_input, requires_grad=False),\
Variable(targets)
inputs = (word_input, char_input)
# 送入到NERModel模型中,输出为[31,5,9]
outputs = self.model(inputs)
# Create mask
if self.use_elmo:
mask = Variable(embeddings['mask'].transpose(0,1))
if self.use_cuda:
mask = mask.cuda()
else:
mask = create_mask(sequence_lengths, targets, cuda=self.use_cuda)
# Get CRF Loss
# CRF损失函数
loss = -1*self.criterion(outputs, targets, mask=mask)
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
# Callbacks
train_loss += loss.item()
# 反向查找最优路径
predictions = self.criterion.decode(outputs, mask=mask)
masked_targets = mask_targets(targets, sequence_lengths)
t_ = mask.type(torch.LongTensor).sum().item()
total += t_
c_ = sum([1 if p[i] == mt[i] else 0 for p, mt in zip(predictions, masked_targets) for i in range(len(p))])
correct += c_
prog.update(batch_idx + 1, values=[("train loss", loss.item())], exact=[("Accuracy", 100*c_/t_)])
self.logger.info("Train Loss: %.3f, Train Accuracy: %.3f%% (%d/%d)" %(train_loss/(total_step+1), 100.*correct/total, correct, total) )
def test(self, nbatches_val, val_generator, fine_tune=False):
self.model.eval()
accs = []
test_loss = 0
correct_preds = 0
total_correct = 0
total_preds = 0
total_step = None
for batch_idx, (inputs, targets, sequence_lengths) in enumerate(val_generator):
if batch_idx == nbatches_val: break
if inputs['word_ids'].shape[0] == 1:
self.logger.info('Skipping batch of size=1')
continue
total_step = batch_idx
targets = T(targets, cuda=self.use_cuda).transpose(0,1).contiguous()
if self.use_elmo:
sentences = inputs['word_ids']
character_ids = batch_to_ids(sentences)
if self.use_cuda:
character_ids = character_ids.cuda()
embeddings = self.elmo(character_ids)
word_input = embeddings['elmo_representations'][1]
word_input, targets = Variable(word_input, requires_grad=False), \
Variable(targets)
inputs = (word_input)
else:
word_input = T(inputs['word_ids'], cuda=self.use_cuda)
char_input = T(inputs['char_ids'], cuda=self.use_cuda)
word_input, char_input, targets = Variable(word_input, requires_grad=False), \
Variable(char_input, requires_grad=False),\
Variable(targets)
inputs = (word_input, char_input)
outputs = self.model(inputs)
# Create mask
if self.use_elmo:
mask = Variable(embeddings['mask'].transpose(0,1))
if self.use_cuda:
mask = mask.cuda()
else:
mask = create_mask(sequence_lengths, targets, cuda=self.use_cuda)
# Get CRF Loss
loss = -1*self.criterion(outputs, targets, mask=mask)
# Callbacks
test_loss += loss.item()
predictions = self.criterion.decode(outputs, mask=mask)
masked_targets = mask_targets(targets, sequence_lengths)
# 衡量实体准确率
for lab, lab_pred in zip(masked_targets, predictions):
accs += [1 if a==b else 0 for (a, b) in zip(lab, lab_pred)]
lab_chunks = set(get_chunks(lab, self.config.vocab_tags))
lab_pred_chunks = set(get_chunks(lab_pred,
self.config.vocab_tags))
correct_preds += len(lab_chunks & lab_pred_chunks)
total_preds += len(lab_pred_chunks)
total_correct += len(lab_chunks)
p = correct_preds / total_preds if correct_preds > 0 else 0
r = correct_preds / total_correct if correct_preds > 0 else 0
f1 = 2 * p * r / (p + r) if correct_preds > 0 else 0
acc = np.mean(accs)
self.logger.info("Val Loss : %.3f, Val Accuracy: %.3f%%, Val F1: %.3f%%" %(test_loss/(total_step+1), 100*acc, 100*f1))
return 100*f1
def evaluate(self,test):
batch_size = self.config.batch_size
nbatches_test, test_generator = self.batch_iter(test, batch_size,
return_lengths=True)
self.logger.info('Evaluating on test set')
self.test(nbatches_test, test_generator)
def predict_batch(self, words):
self.model.eval()
if len(words) == 1:
mult = np.ones(2).reshape(2, 1).astype(int)
if self.use_elmo:
sentences = words
character_ids = batch_to_ids(sentences)
if self.use_cuda:
character_ids = character_ids.cuda()
embeddings = self.elmo(character_ids)
word_input = embeddings['elmo_representations'][1]
word_input = Variable(word_input, requires_grad=False)
if len(words) == 1:
word_input = ((mult*word_input.transpose(0,1)).transpose(0,1).contiguous()).type(torch.FloatTensor)
word_input = T(word_input, cuda=self.use_cuda)
inputs = (word_input)
else:
#char_ids, word_ids = zip(*words)
char_ids = [[c[0] for c in s] for s in words]
word_ids = [[x[1] for x in s] for s in words]
word_ids, sequence_lengths = pad_sequences(word_ids, 1)
char_ids, word_lengths = pad_sequences(char_ids, pad_tok=0,
nlevels=2)
word_ids = np.asarray(word_ids)
char_ids = np.asarray(char_ids)
if len(words) == 1:
word_ids = mult*word_ids
char_ids = (mult*char_ids.transpose(1,0,2)).transpose(1,0,2)
word_input = T(word_ids, cuda=self.use_cuda)
char_input = T(char_ids, cuda=self.use_cuda)
word_input, char_input = Variable(word_input, requires_grad=False), \
Variable(char_input, requires_grad=False)
inputs = (word_input, char_input)
outputs = self.model(inputs)
predictions = self.criterion.decode(outputs)
predictions = [p[:i] for p, i in zip(predictions, sequence_lengths)]
return predictions
def predict(self, sentences):
"""Returns list of tags
Args:
words_raw: list of words (string), just one sentence (no batch)
Returns:
preds: list of tags (string), one for each word in the sentence
"""
nlp = spacy.load('en')
doc = nlp(sentences)
words_raw = [[token.text for token in sent] for sent in doc.sents]
if self.use_elmo:
words = words_raw
else:
words = [[self.config.processing_word(w) for w in s] for s in words_raw]
# print(words)
# raise NameError('testing')
# if type(words[0]) == tuple:
# words = zip(*words)
pred_ids = self.predict_batch(words)
preds = [[self.idx_to_tag[idx.item() if isinstance(idx, torch.Tensor) else idx] for idx in s] for s in pred_ids]
return preds
def create_mask(sequence_lengths, targets, cuda, batch_first=False):
""" Creates binary mask """
mask = Variable(torch.ones(targets.size()).type(torch.ByteTensor))
if cuda: mask = mask.cuda()
for i,l in enumerate(sequence_lengths):
if batch_first:
if l < targets.size(1):
mask.data[i, l:] = 0
else:
if l < targets.size(0):
mask.data[l:, i] = 0
return mask
def mask_targets(targets, sequence_lengths, batch_first=False):
""" Masks the targets """
if not batch_first:
targets = targets.transpose(0,1)
t = []
for l, p in zip(targets,sequence_lengths):
t.append(l[:p].data.tolist())
return t
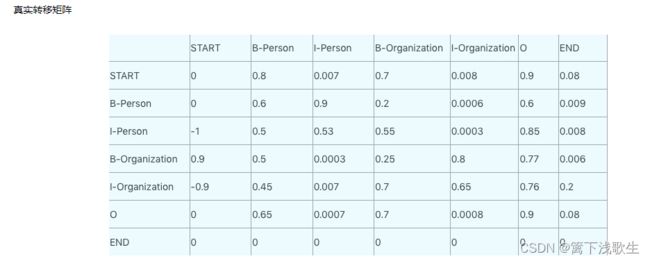
六、计算loss值(CRF)
crf.py
from typing import List, Optional, Union
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# CRF损失函数
# 函数调用:self.criterion = CRF(self.config.ntags)
class CRF(nn.Module):
"""Conditional random field.
This module implements a conditional random field [LMP]. The forward computation
of this class computes the log likelihood of the given sequence of tags and
emission score tensor. This class also has ``decode`` method which finds the
best tag sequence given an emission score tensor using `Viterbi algorithm`_.
Arguments
---------
num_tags : int
Number of tags.
Attributes
----------
num_tags : int
Number of tags passed to ``__init__``.
start_transitions : :class:`~torch.nn.Parameter`
Start transition score tensor of size ``(num_tags,)``.
end_transitions : :class:`~torch.nn.Parameter`
End transition score tensor of size ``(num_tags,)``.
transitions : :class:`~torch.nn.Parameter`
Transition score tensor of size ``(num_tags, num_tags)``.
References
----------
.. [LMP] Lafferty, J., McCallum, A., Pereira, F. (2001).
"Conditional random fields: Probabilistic models for segmenting and
labeling sequence data". *Proc. 18th International Conf. on Machine
Learning*. Morgan Kaufmann. pp. 282–289.
.. _Viterbi algorithm: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Viterbi_algorithm
"""
def __init__(self, num_tags: int) -> None:
if num_tags <= 0:
raise ValueError(f'invalid number of tags: {num_tags}')
super().__init__()
self.num_tags = num_tags
self.start_transitions = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(num_tags))
self.end_transitions = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(num_tags))
self.transitions = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(num_tags, num_tags))
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self) -> None:
"""Initialize the transition parameters.
The parameters will be initialized randomly from a uniform distribution
between -0.1 and 0.1.
"""
nn.init.uniform(self.start_transitions, -0.1, 0.1)
nn.init.uniform(self.end_transitions, -0.1, 0.1)
nn.init.uniform(self.transitions, -0.1, 0.1)
def __repr__(self) -> str:
return f'{self.__class__.__name__}(num_tags={self.num_tags})'
def forward(self,
emissions: Variable,
tags: Variable,
mask: Optional[Variable] = None,
reduce: bool = True,
) -> Variable:
"""Compute the log likelihood of the given sequence of tags and emission score.
Arguments
---------
emissions : :class:`~torch.autograd.Variable`
Emission score tensor of size ``(seq_length, batch_size, num_tags)``.
tags : :class:`~torch.autograd.Variable`
Sequence of tags as ``LongTensor`` of size ``(seq_length, batch_size)``.
mask : :class:`~torch.autograd.Variable`, optional
Mask tensor as ``ByteTensor`` of size ``(seq_length, batch_size)``.
reduce : bool
Whether to sum the log likelihood over the batch.
Returns
-------
:class:`~torch.autograd.Variable`
The log likelihood. This will have size (1,) if ``reduce=True``, ``(batch_size,)``
otherwise.
"""
if emissions.dim() != 3:
raise ValueError(f'emissions must have dimension of 3, got {emissions.dim()}')
if tags.dim() != 2:
raise ValueError(f'tags must have dimension of 2, got {tags.dim()}')
if emissions.size()[:2] != tags.size():
raise ValueError(
'the first two dimensions of emissions and tags must match, '
f'got {tuple(emissions.size()[:2])} and {tuple(tags.size())}'
)
if emissions.size(2) != self.num_tags:
raise ValueError(
f'expected last dimension of emissions is {self.num_tags}, '
f'got {emissions.size(2)}'
)
if mask is not None:
if tags.size() != mask.size():
raise ValueError(
f'size of tags and mask must match, got {tuple(tags.size())} '
f'and {tuple(mask.size())}'
)
if not all(mask[0].data):
raise ValueError('mask of the first timestep must all be on')
if mask is None:
mask = Variable(self._new(tags.size()).fill_(1)).byte()
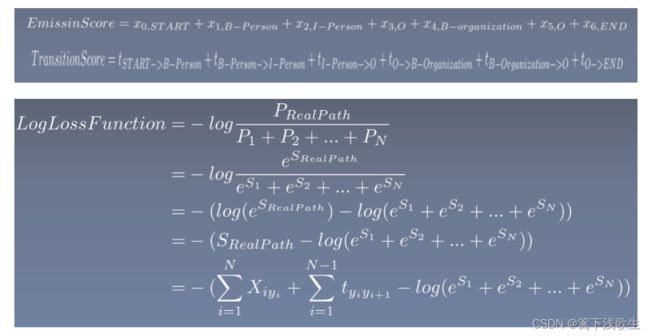
# 计算真实路径的转移矩阵和发射矩阵
numerator = self._compute_joint_llh(emissions, tags, mask)
# 计算其他路径的log值
denominator = self._compute_log_partition_function(emissions, mask)
# 得到loss
llh = numerator - denominator
return llh if not reduce else torch.sum(llh)
def decode(self,
emissions: Union[Variable, torch.FloatTensor],
mask: Optional[Union[Variable, torch.ByteTensor]] = None) -> List[List[int]]:
"""Find the most likely tag sequence using Viterbi algorithm.
Arguments
---------
emissions : :class:`~torch.autograd.Variable` or :class:`~torch.FloatTensor`
Emission score tensor of size ``(seq_length, batch_size, num_tags)``.
mask : :class:`~torch.autograd.Variable` or :class:`torch.ByteTensor`
Mask tensor of size ``(seq_length, batch_size)``.
Returns
-------
list
List of list containing the best tag sequence for each batch.
"""
if emissions.dim() != 3:
raise ValueError(f'emissions must have dimension of 3, got {emissions.dim()}')
if emissions.size(2) != self.num_tags:
raise ValueError(
f'expected last dimension of emissions is {self.num_tags}, '
f'got {emissions.size(2)}'
)
if mask is not None and emissions.size()[:2] != mask.size():
raise ValueError(
'the first two dimensions of emissions and mask must match, '
f'got {tuple(emissions.size()[:2])} and {tuple(mask.size())}'
)
if isinstance(emissions, Variable):
emissions = emissions.data
if mask is None:
mask = self._new(emissions.size()[:2]).fill_(1).byte()
elif isinstance(mask, Variable):
mask = mask.data
return self._viterbi_decode(emissions, mask)
# 函数调用:numerator = self._compute_joint_llh(emissions, tags, mask)
# 计算真实路径的转移矩阵和发射矩阵
def _compute_joint_llh(self,
emissions: Variable,
tags: Variable,
mask: Variable) -> Variable:
# emissions: (seq_length, batch_size, num_tags)
# tags: (seq_length, batch_size)
# mask: (seq_length, batch_size)
assert emissions.dim() == 3 and tags.dim() == 2
assert emissions.size()[:2] == tags.size()
assert emissions.size(2) == self.num_tags
assert mask.size() == tags.size()
assert all(mask[0].data)
seq_length = emissions.size(0)
mask = mask.float()
# Start transition score
llh = self.start_transitions[tags[0]] # (batch_size,)
for i in range(seq_length - 1):
cur_tag, next_tag = tags[i], tags[i+1]
# Emission score for current tag
llh += emissions[i].gather(1, cur_tag.view(-1, 1)).squeeze(1) * mask[i]
# Transition score to next tag
transition_score = self.transitions[cur_tag, next_tag]
# Only add transition score if the next tag is not masked (mask == 1)
llh += transition_score * mask[i+1]
# Find last tag index
last_tag_indices = mask.long().sum(0) - 1 # (batch_size,)
last_tags = tags.gather(0, last_tag_indices.view(1, -1)).squeeze(0)
# End transition score
llh += self.end_transitions[last_tags]
# Emission score for the last tag, if mask is valid (mask == 1)
llh += emissions[-1].gather(1, last_tags.view(-1, 1)).squeeze(1) * mask[-1]
return llh
# 计算其他路径的log值
def _compute_log_partition_function(self,
emissions: Variable,
mask: Variable) -> Variable:
# emissions: (seq_length, batch_size, num_tags)
# mask: (seq_length, batch_size)
assert emissions.dim() == 3 and mask.dim() == 2
assert emissions.size()[:2] == mask.size()
assert emissions.size(2) == self.num_tags
assert all(mask[0].data)
seq_length = emissions.size(0)
mask = mask.float()
# Start transition score and first emission
# 缓存
log_prob = self.start_transitions.view(1, -1) + emissions[0]
# Here, log_prob has size (batch_size, num_tags) where for each batch,
# the j-th column stores the log probability that the current timestep has tag j
for i in range(1, seq_length):
# Broadcast log_prob over all possible next tags
# 缓存矩阵
broadcast_log_prob = log_prob.unsqueeze(2) # (batch_size, num_tags, 1)
# Broadcast transition score over all instances in the batch
# 转移矩阵
broadcast_transitions = self.transitions.unsqueeze(0) # (1, num_tags, num_tags)
# Broadcast emission score over all possible current tags
# 发射矩阵
broadcast_emissions = emissions[i].unsqueeze(1) # (batch_size, 1, num_tags)
# Sum current log probability, transition, and emission scores
score = broadcast_log_prob + broadcast_transitions \
+ broadcast_emissions # (batch_size, num_tags, num_tags)
# Sum over all possible current tags, but we're in log prob space, so a sum
# becomes a log-sum-exp
score = self._log_sum_exp(score, 1) # (batch_size, num_tags)
# Set log_prob to the score if this timestep is valid (mask == 1), otherwise
# leave it alone
log_prob = score * mask[i].unsqueeze(1) + log_prob * (1.-mask[i]).unsqueeze(1)
# End transition score
log_prob += self.end_transitions.view(1, -1)
# Sum (log-sum-exp) over all possible tags
return self._log_sum_exp(log_prob, 1) # (batch_size,)
def _viterbi_decode(self, emissions: torch.FloatTensor, mask: torch.ByteTensor) \
-> List[List[int]]:
# Get input sizes
seq_length = emissions.size(0)
batch_size = emissions.size(1)
sequence_lengths = mask.long().sum(dim=0)
# emissions: (seq_length, batch_size, num_tags)
assert emissions.size(2) == self.num_tags
# list to store the decoded paths
best_tags_list = []
# Start transition
viterbi_score = []
viterbi_score.append(self.start_transitions.data + emissions[0])
viterbi_path = []
# Here, viterbi_score is a list of tensors of shapes of (num_tags,) where value at
# index i stores the score of the best tag sequence so far that ends with tag i
# viterbi_path saves where the best tags candidate transitioned from; this is used
# when we trace back the best tag sequence
# Viterbi algorithm recursive case: we compute the score of the best tag sequence
# for every possible next tag
for i in range(1, seq_length):
# Broadcast viterbi score for every possible next tag
broadcast_score = viterbi_score[i - 1].view(batch_size, -1, 1)
# Broadcast emission score for every possible current tag
broadcast_emission = emissions[i].view(batch_size, 1, -1)
# Compute the score matrix of shape (batch_size, num_tags, num_tags) where
# for each sample, each entry at row i and column j stores the score of
# transitioning from tag i to tag j and emitting
score = broadcast_score + self.transitions.data + broadcast_emission
# Find the maximum score over all possible current tag
best_score, best_path = score.max(1) # (batch_size,num_tags,)
# Save the score and the path
viterbi_score.append(best_score)
viterbi_path.append(best_path)
# Now, compute the best path for each sample
for idx in range(batch_size):
# Find the tag which maximizes the score at the last timestep; this is our best tag
# for the last timestep
seq_end = sequence_lengths[idx]-1
_, best_last_tag = (viterbi_score[seq_end][idx] + self.end_transitions.data).max(0)
best_tags = [best_last_tag.item()] #[best_last_tag[0]] #[best_last_tag.item()]
# We trace back where the best last tag comes from, append that to our best tag
# sequence, and trace it back again, and so on
for path in reversed(viterbi_path[:sequence_lengths[idx] - 1]):
best_last_tag = path[idx][best_tags[-1]]
best_tags.append(best_last_tag)
# Reverse the order because we start from the last timestep
best_tags.reverse()
best_tags_list.append(best_tags)
return best_tags_list
@staticmethod
def _log_sum_exp(tensor: Variable, dim: int) -> Variable:
# Find the max value along `dim`
offset, _ = tensor.max(dim)
# Make offset broadcastable
broadcast_offset = offset.unsqueeze(dim)
# Perform log-sum-exp safely
safe_log_sum_exp = torch.log(torch.sum(torch.exp(tensor - broadcast_offset), dim))
# Add offset back
return offset + safe_log_sum_exp
def _new(self, *args, **kwargs) -> torch.FloatTensor:
param = next(self.parameters())
return param.data.new(*args, **kwargs)
七、训练(train.py)
from model.data_utils import CoNLLDataset
from model.config import Config
from model.ner_model import NERModel
from model.ner_learner import NERLearner
def main():
# create instance of config
config = Config()
if config.use_elmo: config.processing_word = None
#build model
# NERModel模型
model = NERModel(config)
# create datasets
# 训练数据预处理
dev = CoNLLDataset(config.filename_dev, config.processing_word,
config.processing_tag, config.max_iter, config.use_crf)
train = CoNLLDataset(config.filename_train, config.processing_word,
config.processing_tag, config.max_iter, config.use_crf)
# 初始化模型训练流程
learn = NERLearner(config, model)
# 1.根据batch_size整理验证数据集
# 2.传入到elmo中获得input
# 3.传入到NERModel模型中
# 4.用CRF求loss值
learn.fit(train, dev)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
八、测试(test.py)
""" Command Line Usage
Args:
eval: Evaluate F1 Score and Accuracy on test set
pred: Predict sentence.
(optional): Sentence to predict on. If none given, predicts on "Peter Johnson lives in Los Angeles"
Example:
> python test.py eval pred "Obama is from Hawaii"
"""
from model.data_utils import CoNLLDataset
from model.config import Config
from model.ner_model import NERModel
from model.ner_learner import NERLearner
import sys
def main():
# create instance of config
config = Config()
if config.use_elmo: config.processing_word = None
#build model
model = NERModel(config)
learn = NERLearner(config, model)
learn.load()
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
print("No arguments given. Running full test")
sys.argv.append("eval")
sys.argv.append("pred")
if sys.argv[1] == "eval":
# create datasets
test = CoNLLDataset(config.filename_test, config.processing_word,
config.processing_tag, config.max_iter)
learn.evaluate(test)
if sys.argv[1] == "pred" or sys.argv[2] == "pred":
try:
sent = (sys.argv[2] if sys.argv[1] == "pred" else sys.argv[3])
except IndexError:
sent = ["Peter", "Johnson", "lives", "in", "Los", "Angeles"]
print("Predicting sentence: ", sent)
pred = learn.predict(sent)
print(pred)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()