ROS入门七 机器人建模——URDF
ROS入门七 机器人建模——URDF
- urdf
-
- ufdf介绍
- 语法
- 创建机器人URDF模型
-
- 创建机器人描述功能包
- 创建URDF模型
- 在rviz中显示模型
- 改进URDF模型
-
- 添加物理和碰撞属性
- 使用xacro优化URDF
- xacro文件引用
- 显示优化后的模型
urdf
ufdf介绍
用于描述机器人结构的格式。根据该格式的设计者所言,设计这一格式的目的在于提供一种尽可能通用(as general as possible)的机器人描述规范。(度娘解释)
在使用URDF文件构建机器人模型之前有必要先梳理一下URDF文件中常用的XML标签对URDF有一个大概的了解。
语法
- 标签
标签用于描述机器人某个刚体部分的外观和物理属性包括尺寸size、颜色color、形状shape、惯性矩阵inertial matrix、碰撞参数collision properties等。
<link name="">
<inertial> . . . . . . </ inertial>
<visual> . . . . . . </visual>
<collision> . . . . . . </coll ision>
</link>
标签
标签用于描述机器人关节的运动学和动力学属性包括关节运动的位置和速度限制。与人的关节一样机器人关节的主要作用是连接两个刚体link这两个link分别称为parent link和child link。
<joint name="" >
<parent link="parent_link"/>
<child link="child_link"/>
<calibration .... />
<dynamics damping .. ../>
<limit effort .... />
....
</joint>
标签
是完整机器人模型的最顶层标签和 标签都必须包含在 标签内。
<robot name="" >
<link> ....... </link>
<link> ....... </link>
<joint> ....... </join t>
<joint> ....... </joint>
</robot>
标签
标签用于描述机器人模型在Gazebo中仿真所需要的参数包括机器人材料的属性、Gazebo插件等。该标签不是机器人模型必需的部分只有在Gazebo仿真时才需加入。
<gazebo reference="link_1">
<material>Gazebo/Black< /material>
</gazebo>
创建机器人URDF模型
创建机器人描述功能包
$ catkin_create_pkg mrobot_description urdf xacro
创建URDF模型
打开工作空间catkin_ws下的src文件
$ cd ~/catkin_ws/src/
创建名为mrobot_description的功能包
$ catkin_create_pkg mrobot_description urdf xacro
在功能包mrobot_description下新建一个名为urdf的文件夹,在新建文件下创建一个mrobot_chassis.urdf文件
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<robot name="mrobot_chassis">
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<origin xyz=" 0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="0.005" radius="0.13"/>
</geometry>
<material name="yellow">
<color rgba="1 0.4 0 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
</link>
<joint name="base_left_motor_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="-0.055 0.075 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="left_motor" />
</joint>
<link name="left_motor">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="1.5707 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="0.02" length = "0.08"/>
</geometry>
<material name="gray">
<color rgba="0.75 0.75 0.75 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
</link>
<joint name="left_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="0 0.0485 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<parent link="left_motor"/>
<child link="left_wheel_link"/>
<axis xyz="0 1 0"/>
</joint>
<link name="left_wheel_link">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="1.5707 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="0.033" length = "0.017"/>
</geometry>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 0.9"/>
</material>
</visual>
</link>
URDF提供了一些命令行工具可以帮助我们检查、梳理模型文件需要在终端中独立安装
$ sudo apt-get install liburdfdom-tools
然后使用check_urdf命令对mrobot_chassis.urdf文件进行检查
$ check_urdf mrobot_chassis.urdf
在rviz中显示模型
在mrobot_description 功能包launch文件夹下创建用于显示mrobot_chassis 模型的launch 文件display_mrobot_chassis_urdf.launch
unch>
<param name="robot_description" textfile="$(find mrobot_description)/urdf/mrobot_chassis.urdf" />
<!-- 设置GUI参数,显示关节控制插件 -->
<param name="use_gui" value="true"/>
<!-- 运行joint_state_publisher节点,发布机器人的关节状态 -->
<node name="joint_state_publisher" pkg="joint_state_publisher" type="joint_state_publisher" />
<!-- 运行robot_state_publisher节点,发布tf -->
<node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="state_publisher" />
<!-- 运行rviz可视化界面 -->
<node name="rviz" pkg="rviz" type="rviz" args="-d $(find mrobot_description)/config/mrobot_urdf.rviz" required="true" />
</launch>
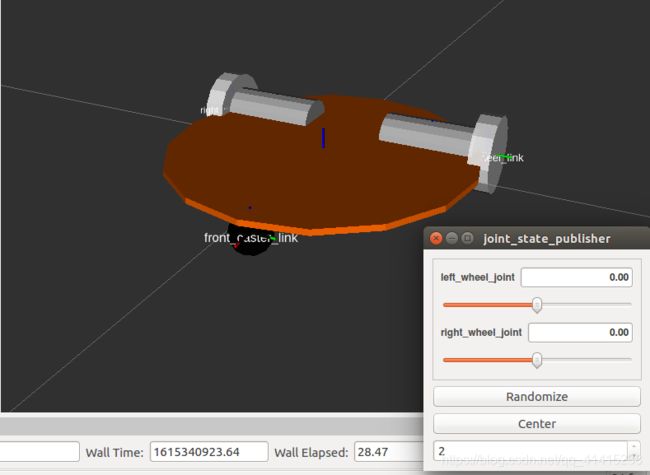
打开终端运行该launch文件如果一切正常可以在打开的rviz中看到机器人模型。
$ roslaunch mrobot_description display_mrobot_chassis_urdf.launch
改进URDF模型
添加物理和碰撞属性
这里以机器人底盘base_link为例介绍如何添加这些属性。在base_link中加入和标签描述机器人的物理惯性属性和碰撞属性。
<link name="base_link">
<inertial>
<mass value="2" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0 .0" />
<inertia ixx="0.01" ixy= "0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.01" iyz="0.0" izz="0.5" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<ori gin xyz=" 0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylin der length="${base_link_length}" radius="${base_link_radius}"/>
</geometry>
<material n ame="yellow" />
</visual>
<collisio n>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylin der length="${base_link_length}" radius="${base_link_radius}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
使用xacro优化URDF
xacro是URDF的升级版模型文件的后缀名由.urdf变为.xacro而且在模型
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot name="robot_na me" xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro>"
1.使用常量定义
<xacro:property name="M_PI" value="3.14159"/>
当需要使用该常量时使用如下语法调用即可
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
现在各种参数的定义都可以使用常量定义的方式进行声明
<xacro:property name="wheel_radius" value="0.033"/>
<xacro:property name="wheel_length" value="0.017"/>
<xacro:property name="base_link_radius" value="0.13 "/>
<xacro:property name="base_link_length" value="0.005"/ >
<xacro:property name="motor_radius" value="0.02"/>
<xacro:property name="motor_length" value="0.08"/>
<xacro:property name="motor_x" value="-0.055"/>
<xacro:property name="motor_y" value="0.075"/>
<xacro:property name="plate_height" value="0.0 7"/>
<xacro:property name="standoff_x" value="0.12"/>
<xacro:property name="standoff_y" value="0.10"/>
2.调用数学公式
在“${}”语句中不仅可以调用常量还可以使用一些常用的数学运算包括加、减、乘、除、负号、括号等例如
<origin xyz="0 ${(motor_length+wheel_length)/2} 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
3.使用宏定义
<xacro:macro name="mrobot_standoff_2in" params="parent number x_loc y_loc z_loc">
<joint name="standoff_2in_${number}_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="${x_loc} ${y_loc} ${z_loc}" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="${parent}"/>
<child link="standoff_2in_${number}_link" />
</joint>
<link name="standoff_2in_${number}_link">
<inertial>
<mass value="0.001" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<inertia ixx="0.0001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.0001" iyz="0.0"
izz="0.0001" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz=" 0 0 0 " rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="0.01 0.01 0.07" />
</geometry>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0.16 0.17 0.15 0.9"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="0.01 0.01 0.07" />
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
</xacro:macro>
以上宏定义中包含五个输入参数joint的parent link支撑柱的序号支撑柱在x、y、z三个方向上的偏移。需要该宏模块时使用如下语句调用设置输入参数即可
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="base_link" number="4" x_loc="${standoff_x/2}"
y_loc="${standoff_y}" z_loc="${plate_height/2}"/>
完整的mrobot_body.urdf.xacro文件,在urdf文件夹下创建的
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
<xacro:property name="M_PI" value="3.14159"/>
<xacro:property name="wheel_radius" value="0.033"/>
<xacro:property name="wheel_length" value="0.017"/>
<xacro:property name="base_link_radius" value="0.13"/>
<xacro:property name="base_link_length" value="0.005"/>
<xacro:property name="motor_radius" value="0.02"/>
<xacro:property name="motor_length" value="0.08"/>
<xacro:property name="motor_x" value="-0.055"/>
<xacro:property name="motor_y" value="0.075"/>
<xacro:property name="plate_height" value="0.07"/>
<xacro:property name="standoff_x" value="0.12"/>
<xacro:property name="standoff_y" value="0.10"/>
<!-- 定义MRobot本体的宏 -->
<xacro:macro name="mrobot_standoff_2in" params="parent number x_loc y_loc z_loc">
<joint name="standoff_2in_${number}_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="${x_loc} ${y_loc} ${z_loc}" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="${parent}"/>
<child link="standoff_2in_${number}_link" />
</joint>
<link name="standoff_2in_${number}_link">
<inertial>
<mass value="0.001" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<inertia ixx="0.0001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.0001" iyz="0.0"
izz="0.0001" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz=" 0 0 0 " rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="0.01 0.01 0.07" />
</geometry>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0.16 0.17 0.15 0.9"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="0.01 0.01 0.07" />
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
</xacro:macro>
<xacro:macro name="mrobot_body">
<material name="Green">
<color rgba="0.0 0.8 0.0 1.0"/>
</material>
<material name="yellow">
<color rgba="1 0.4 0 1"/>
</material>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0 0 0 0.95"/>
</material>
<material name="gray">
<color rgba="0.75 0.75 0.75 1"/>
</material>
<link name="base_footprint">
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<box size="0.001 0.001 0.001" />
</geometry>
</visual>
</link>
<link name="base_link">
<inertial>
<mass value="2" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0.0" />
<inertia ixx="0.01" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.01" iyz="0.0" izz="0.5" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz=" 0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${base_link_length}" radius="${base_link_radius}"/>
</geometry>
<material name="yellow" />
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${base_link_length}" radius="${base_link_radius}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<joint name="base_footprint_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="0 0 ${wheel_radius}" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_footprint"/>
<child link="base_link" />
</joint>
<link name="left_motor">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0.0 0 0"/>
<mass value="0.1" />
<inertia ixx="0.001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.001" iyz="0.0" izz="0.001" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${motor_radius}" length = "${motor_length}"/>
</geometry>
<material name="gray" />
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${motor_radius}" length = "${motor_length}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<joint name="base_left_motor_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="${motor_x} ${motor_y} 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="left_motor" />
</joint>
<link name="left_wheel_link">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0"/>
<mass value="0.01" />
<inertia ixx="0.001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.001" iyz="0.0" izz="0.001" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length = "${wheel_length}"/>
</geometry>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 0.9"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length = "${wheel_length}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<joint name="left_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="0 ${(motor_length+wheel_length)/2} 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<parent link="left_motor"/>
<child link="left_wheel_link"/>
<axis xyz="0 1 0"/>
</joint>
<link name="right_motor">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0.0 0 0"/>
<mass value="0.1" />
<inertia ixx="0.001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.001" iyz="0.0" izz="0.001" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${motor_radius}" length = "${motor_length}" />
</geometry>
<material name="gray" />
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${motor_radius}" length = "${motor_length}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<joint name="base_right_motor_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="${motor_x} -${motor_y} 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="right_motor" />
</joint>
<link name="right_wheel_link">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0"/>
<mass value="0.01" />
<inertia ixx="0.001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.001" iyz="0.0" izz="0.001" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length = "${wheel_length}"/>
</geometry>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 0.9"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length = "${wheel_length}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<joint name="right_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="0 -${(motor_length+wheel_length)/2} 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<parent link="right_motor"/>
<child link="right_wheel_link"/>
<axis xyz="0 1 0"/>
</joint>
<link name="front_caster_link">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0"/>
<mass value="0.001" />
<inertia ixx="0.0001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.0001" iyz="0.0" izz="0.0001" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="${wheel_radius/2}" />
</geometry>
<material name="black" />
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0.01" rpy="${M_PI/2} 0 0" />
<geometry>
<sphere radius="${wheel_radius/2}" />
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<joint name="front_caster_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="${base_link_radius-wheel_radius/2} 0 -${wheel_radius/2}" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="front_caster_link"/>
</joint>
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="base_link" number="1" x_loc="-${standoff_x/2 + 0.03}" y_loc="-${standoff_y - 0.03}" z_loc="${plate_height/2}"/>
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="base_link" number="2" x_loc="-${standoff_x/2 + 0.03}" y_loc="${standoff_y - 0.03}" z_loc="${plate_height/2}"/>
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="base_link" number="3" x_loc="${standoff_x/2}" y_loc="-${standoff_y}" z_loc="${plate_height/2}"/>
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="base_link" number="4" x_loc="${standoff_x/2}" y_loc="${standoff_y}" z_loc="${plate_height/2}"/>
<joint name="plate_1_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="0 0 ${plate_height}" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="plate_1_link" />
</joint>
<link name="plate_1_link">
<inertial>
<mass value="0.1" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<inertia ixx="0.01" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.01" iyz="0.0" izz="0.01" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz=" 0 0 0 " rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${base_link_length}" radius="${base_link_radius}"/>
</geometry>
<material name="yellow"/>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${base_link_length}" radius="${base_link_radius}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="standoff_2in_1_link" number="5" x_loc="0" y_loc="0" z_loc="${plate_height}"/>
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="standoff_2in_2_link" number="6" x_loc="0" y_loc="0" z_loc="${plate_height}"/>
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="standoff_2in_3_link" number="7" x_loc="0" y_loc="0" z_loc="${plate_height}"/>
<mrobot_standoff_2in parent="standoff_2in_4_link" number="8" x_loc="0" y_loc="0" z_loc="${plate_height}"/>
<joint name="plate_2_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="0 0 ${plate_height}" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="plate_1_link"/>
<child link="plate_2_link" />
</joint>
<link name="plate_2_link">
<inertial>
<mass value="0.01" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<inertia ixx="0.001" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="0.001" iyz="0.0" izz="0.001" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin xyz=" 0 0 0 " rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${base_link_length}" radius="${base_link_radius}"/>
</geometry>
<material name="yellow" />
</visual>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${base_link_length}" radius="${base_link_radius}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
</xacro:macro>
</robot>
xacro文件引用
在urdf文件中新建一个名为mrobot.urdf.xacro文件,引用mrobot_body.urdf.xacro文件
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot name="mrobot" xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
<xacro:include filename="$(find mrobot_description)/urdf/mrobot_body.urdf.xacro" />
<!-- MRobot机器人平台 -->
<mrobot_body/>
</robot>
显示优化后的模型
xacro文件设计完成后可以通过两种方式将优化后的模型显示在rviz中
1.将xacro文件转换成URDF文件
$ rosrun xacro xacro.py mrobot.urdf.xacro > mrobot.urdf
2.直接调用xacro文件解析器
<arg name="model" default="$(find xacro)/xacro --inorder '$(find mrobot_description)/urdf/mrobot.urdf.xacro'" />
<param name="robot_description" command="$(arg model)" />
在launch文件夹下创建一个名为display_mrobot.launch的文件
<launch>
<arg name="model" default="$(find xacro)/xacro --inorder '$(find mrobot_description)/urdf/mrobot.urdf.xacro'" />
<arg name="gui" default="true" />
<param name="robot_description" command="$(arg model)" />
<!-- 设置GUI参数,显示关节控制插件 -->
<param name="use_gui" value="$(arg gui)"/>
<!-- 运行joint_state_publisher节点,发布机器人的关节状态 -->
<node name="joint_state_publisher" pkg="joint_state_publisher" type="joint_state_publisher" />
<!-- 运行robot_state_publisher节点,发布tf -->
<node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher" />
<!-- 运行rviz可视化界面 -->
<node name="rviz" pkg="rviz" type="rviz" args="-d $(find mrobot_description)/config/mrobot.rviz" required="true" />
</launch>
运行launch文件
$ roslaunch mrobot_description display_mrobot.launch
古月《ROS机器人开发实践》