CSAPP(CMU 15-213):Lab4 Cachelab详解
# 前言
本系列文章意在记录答主学习CSAPP Lab的过程,也旨在可以帮助后人一二,欢迎大家指正!
tips:本lab主要是为了深入理解cache的机制!!完成了模拟cache行为的实现以及应用!!
Part A: Writing a Cache Simulator
实现一个有关cache行为的模拟器,一开始不知从何做起,还是要注意看文档啊,CMU15-213是有recition的,里面有一些提示!
准备工作
以下内容来自rec07.pdf
A cache simulator is NOT a cache!
- Memory contents NOT stored
- Block offffsets are NOT used – the b bits in your address don’t matter. //本cache中不涉及数据处理
- Simply count hits, misses, and evictions.
A cache is just 2D array of cache lines: cache_line cache[S] [E]
Each cache_line has:
- valid bit
- tag
- LRU counter (only if you are not using a queue)
代码分析
命令行输入解析
//命令行输入解析: 利用getopt() man 3 getopt
// ./csim -s 4 -E 1 -b 4 -t traces/yi.trace -v
int opt;
FILE* pFile = NULL;
int wrong_arg = 0; //输入错误参数
while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "hvs:E:b:t:")) != -1) {
switch(opt) {
case 'h':
wrong_arg = 1;
break;
case 'v':
printTraceInfo = 1;
break;
case 's':
s = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'E':
E = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'b':
b = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 't':
pFile = fopen(optarg, "r");
break;
default:
usage();
break;
}
}
if (s <= 0 || E <= 0 || b <= 0 || wrong_arg == 1 || pFile == NULL) {
usage();
return 0;
}
构建cache
//构建cache 使用calloc动态分配cache
typedef struct cache_line {
int validBit; //valid bit
int tag; //tag bit
int lru; //LRU counter
}cache;
cache** initCache() {
int S = (int)pow(2, s); //set num
cache** myCache = (cache**)calloc(S, sizeof(cache*));
for (int i = 0; i < S; i++) {
myCache[i] = (cache*)calloc(E, sizeof(cache));
}
return myCache;
}
void freeCache() { //free cache memory
int S = (int)pow(2, s);
for (int i = 0; i < S; i++) {
free(myCache[i]);
}
free(myCache);
}
读入输入文件
因为做cache模拟器不设计对cache存储数据的实际处理,故对于load和store,cache的行为一致,对于modify来说,则分别由一次Load与一次Store组合完成。
//读入数据并cache行为
void readTraceFile(FILE* pFile) {
char identifier; //the type of memory access
long unsigned address; //address of memory access
int size; //the number of bytes accessed by the operation
while (fscanf(pFile, " %c %lx,%d", &identifier, &address, &size) != EOF) {
if (printTraceInfo) printf("%c %lx,%d", identifier, address, size);
switch(identifier) {
case 'M':
cacheOperation(address);
case 'L': //no data-operation, so load is idential with store
case 'S':
cacheOperation(address);
break;
}
if (printTraceInfo) printf("\n");
}
fclose(pFile);
}
模拟cache行为
void cacheOperation(long unsigned address) {
int setIndex = (address>>b)%((int)pow(2, s)); // * and / can use << >> ,
int addressOfTag = address>>(s+b);
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
if (myCache[setIndex][i].tag == addressOfTag && myCache[setIndex][i].validBit == 1) { //cache hit
hits++;
myCache[setIndex][i].lru = time++;
if (printTraceInfo) printf(" hit");
return;
}
}
// cache miss
misses++;
if (printTraceInfo) printf(" miss");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
if (myCache[setIndex][i].validBit == 0) { //no eviction
myCache[setIndex][i].validBit = 1;
myCache[setIndex][i].tag = addressOfTag;
myCache[setIndex][i].lru = time++;
return;
}
}
// cache miss && eviction
evictions++;
if (printTraceInfo) printf(" eviction");
int min_time = INT_MAX, min_index;
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
if (myCache[setIndex][i].lru < min_time) {
min_time = myCache[setIndex][i].lru;
min_index = i;
}
}
myCache[setIndex][min_index].validBit = 1;
myCache[setIndex][min_index].tag = addressOfTag;
myCache[setIndex][min_index].lru = time++;
}
帮助信息函数usage()
void usage() {
printf("Usage: ./csim-ref [-hv] -s -E -b -t \n" );
printf("Options:\n");
printf(" -h Print this help message.\n");
printf(" -v Optional verbose flag.\n");
printf(" -s Number of set index bits.\n" );
printf(" -E Number of lines per set.\n" );
printf(" -b Number of block offset bits.\n" );
printf(" -t Trace file.\n\n" );
printf("Examples:\n");
printf(" linux> ./csim-ref -s 4 -E 1 -b 4 -t traces/yi.trace\n");
printf(" linux> ./csim-ref -v -s 8 -E 2 -b 4 -t traces/yi.trace\n");
}
Part A 测试结果
Part A: Testing cache simulator
Running ./test-csim
Your simulator Reference simulator
Points (s,E,b) Hits Misses Evicts Hits Misses Evicts
3 (1,1,1) 9 8 6 9 8 6 traces/yi2.trace
3 (4,2,4) 4 5 2 4 5 2 traces/yi.trace
3 (2,1,4) 2 3 1 2 3 1 traces/dave.trace
3 (2,1,3) 167 71 67 167 71 67 traces/trans.trace
3 (2,2,3) 201 37 29 201 37 29 traces/trans.trace
3 (2,4,3) 212 26 10 212 26 10 traces/trans.trace
3 (5,1,5) 231 7 0 231 7 0 traces/trans.trace
6 (5,1,5) 265189 21775 21743 265189 21775 21743 traces/long.trace
27
途遇BUG (数据格式错误-边界条件)
最一开始遇到因为碰到7ff000390 用的是unsigned int型接收,这样会将数据截断为ff000390,而我在函数传参的过程中变成了int型,如下图代码所示,导致在cacheOperation函数中的address被解释为负数,继而在后续的处理过程发生内存越界。
void cacheOperation(int address) {}
void readTraceFile(char* tracefile) {
unsigned address;
while (fscanf(pFile, " %c %x,%d", &identifier, &address, &size) != EOF) {}
}
将有关参数address的类型全部改为unsigned后,因为int为4B,所以还是存在数据被阶段现象,造成tag不完整,但因为测试案例较为保守,所以还是通过了全部测试。
继而正确代码参数address应为unsigned long型,即 scanf()的输入格式中也改为%lx
void cacheOperation(unsigned long address) {}
void readTraceFile(char* tracefile) {
unsigned long address;
while (fscanf(pFile, " %c %lx,%d", &identifier, &address, &size) != EOF) {}
}
Part B: Optimizing Matrix Transpose
目的: 充分利用Cache的能力,尽量不访存
- 主要利用blocking技术提高矩阵的时间局部性/空间局部性,尽可能让载入cache的数据块得到利用,1. 此块数据载入被替换后不再使用,即不再二次载入 2. 将此块的数据存入寄存器,以避免此块因为冲突替换后二次载入(即,局部变量,注意局部变量数目不能太多,否则会被存入栈中,又回到了内存中)
Tips:
-
为了trace文件能够更加纯粹地指示数组的存取,要求局部变量不可超过12个,减少关于栈的引用。
-
题目采用直接映射(E=1),要重点考虑冲突的情况,尤其是对角线上的情况。(因为数组A的起始地址为
0x30a080, 数组B的起始地址为0x34a080,其两个数组在对角线上的元素会被映射到同一块。)
题目要求:(s = 5, E = 1, b = 5)
- 拥有 S = 2 s = s 5 = 32 S = 2^s = s^5 = 32 S=2s=s5=32个高速缓存组,每组只包含一个(E = 1)高速缓存行(cache line)。每个行由一个 B = 2 b = 2 5 = 32 B B = 2^b = 2^5 = 32B B=2b=25=32B的数据块(block)组成,所以总共有
1KB的直接映射高速缓存(direct mapped cache)。 int型数据占4个字节,一个cache行可以存储8B。
1. M = 32, N = 32
对于题目所给的trans()函数来说,misses数高的原因在于,对于数组A是以行来访问,而对于数组B是以列为访问,又由cahce的存储量可知,一整个cache可以存储的数组的前8行所有元素(8行填满一个cahce),而在访问数组B第九行的第1个元素之后,又会将之前存储的八行cache全部冲突替换掉,导致没有充分利用cache数据(只用到每个块的1个元素),只能重新加载之前的cache,造成大量的misses。
故我们为了提高cache的利用率,即,在cache载入后,将cache包含的元素全部操作后再替换cache,保证不会二次载入相同的cache,即设置子块大小为 8 × 8 8\times8 8×8。
//按分块8*8处理
int bi, bj, i, j, tmp;
for (bi = 0; bi < M; bi += 8) {
for (bj = 0; bj < N; bj += 8) {
for (i = bi; i < bi + 8; i++) {
for (j = bj; j < bj + 8; j++) {
tmp = A[i][j];
B[j][i] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
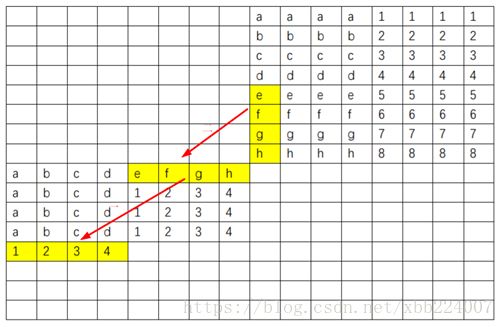
运行结果会发现会有343次的misses,而我们理论上的研究则为 16 块 × 8 次 × 2 = 256 次 16块 \times 8次 \times 2 = 256次 16块×8次×2=256次,显然有很大的差距,而且满分的操作为misses < 300。再次分析trace文件就会发现数组A(0x30a080)和B(0x34a080)的起始地址所映射的cache块相同,即在数组A和B的对角块上的元素会发生冲突不命中,而且在对角块上时数组B的缓存会将刚才缓存的数组A丢弃掉,故我们只需将A中缓存的值用变量保存起来,就可以减少misses数。

(上图转自网络,出处见水印。显然可以看出对角块上数组A和B的缓存会存在冲突。)
可以利用trace文件查看cache块信息(对角块与蓝块)。
//针对第一个蓝块的cache数据(数组A和B的cache不会相互冲突丢掉)
//左列 蓝块第一行 B的8个cache块都miss,即首次填充好
//右列 蓝块第二行 所有的B数据都命中,因为第一次已填充好
L 30a0a0,4 miss eviction L 30a120,4 miss
S 34a480,4 miss eviction S 34a484,4 hit
L 30a0a4,4 hit L 30a124,4 hit
S 34a500,4 miss eviction S 34a504,4 hit
L 30a0a8,4 hit L 30a128,4 hit
S 34a580,4 miss eviction S 34a584,4 hit
L 30a0ac,4 hit L 30a12c,4 hit
S 34a600,4 miss eviction S 34a604,4 hit
L 30a0b0,4 hit L 30a130,4 hit
S 34a680,4 miss eviction S 34a684,4 hit
L 30a0b4,4 hit L 30a134,4 hit
S 34a700,4 miss eviction S 34a704,4 hit
L 30a0b8,4 hit L 30a138,4 hit
S 34a780,4 miss eviction S 34a784,4 hit
L 30a0bc,4 hit L 30a13c,4 hit
S 34a800,4 miss eviction S 34a804,4 hit
// ./csim-ref -v -s 5 -E 1 -b 5 -t trace.f0 > trace_details.f0
//针对第一个对角块的cache数据(读取A的第一行)(数组A和B的cache会相互冲突丢掉)
L 30a080,4 miss eviction //第一次未命中,存放数组A的前8个元素,Load A[第一行][0]
S 34a080,4 miss eviction //B数组的cache映射地址与刚刚所属数组A的cache冲突,故替换
L 30a084,4 miss eviction //load A[1],因被替换,故只能重新二次载入相同的cache块
S 34a100,4 miss
L 30a088,4 hit
S 34a180,4 miss
L 30a08c,4 hit
S 34a200,4 miss
L 30a090,4 hit
S 34a280,4 miss
L 30a094,4 hit
S 34a300,4 miss
L 30a098,4 hit
S 34a380,4 miss
L 30a09c,4 hit
S 34a400,4 miss
//经过这次操作后,cache第一行为A的,第二行-第八行都为B的
//读取A的第二行
L 30a100,4 miss eviction //替换cache第二行为A的
S 34a084,4 miss eviction //替换cache第一行为B的
L 30a104,4 hit
S 34a104,4 miss eviction //替换cache第二行为B的
L 30a108,4 miss eviction //替换cache第二行为A的
S 34a184,4 hit
L 30a10c,4 hit
S 34a204,4 hit
L 30a110,4 hit
S 34a284,4 hit
L 30a114,4 hit
S 34a304,4 hit
L 30a118,4 hit
S 34a384,4 hit
L 30a11c,4 hit
S 34a404,4 hit
故改进代码如下:
int bj, bi, i;
int a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h; //8 local variables
for (bi = 0; bi < M; bi += 8) {
for (bj = 0; bj < N; bj += 8) {
for (i = bi; i < bi + 8; i++) {
a = A[i][0+bj]; b = A[i][1+bj]; c = A[i][2+bj]; d = A[i][3+bj];
e = A[i][4+bj]; f = A[i][5+bj]; g = A[i][6+bj]; h = A[i][7+bj]; //除第一个A,其他都是利用cache命中存入
B[0+bj][i] = a; B[1+bj][i] = b; B[2+bj][i] = c; B[3+bj][i] = d;
B[4+bj][i] = e; B[5+bj][i] = f; B[6+bj][i] = g; B[7+bj][i] = h;
}
}
}
//对角块情况
//左列为第一行情况 右列为第二行情况 可以未改进代码的对角块情况进行对比,此次无二次载入相同的cache块,因为已经将需要的原数据放入了局部变量(寄存器)中
L 30b080,4 miss eviction L 30b100,4 miss eviction
L 30b084,4 hit L 30b104,4 hit
L 30b088,4 hit L 30b108,4 hit
L 30b08c,4 hit L 30b10c,4 hit
L 30b090,4 hit L 30b110,4 hit
L 30b094,4 hit L 30b114,4 hit
L 30b098,4 hit L 30b118,4 hit
L 30b09c,4 hit L 30b11c,4 hit
S 34b080,4 miss eviction S 34b084,4 hit
S 34b100,4 miss S 34b104,4 miss eviction
S 34b180,4 miss S 34b184,4 hit
S 34b200,4 miss S 34b204,4 hit
S 34b280,4 miss S 34b284,4 hit
S 34b300,4 miss S 34b304,4 hit
S 34b380,4 miss S 34b384,4 hit
S 34b400,4 miss S 34b404,4 hit
此时misses数已降为287,符合满分标准(misses < 300)。
2. M = 64, N = 64
如果我们采用刚才同样的分析,可以得到子块为 8 × 4 8\times4 8×4,可以保证数组B每四个cache块( 4 × 8 4\times8 4×8),不会发生二次载入的情况。而对于数组A来说,四个cahce块为( 8 × 4 8\times4 8×4),这样的配置会导致每一个A的cache块只有四个int数据会被利用到,而其余四个数据需要下次载入才可利用,这样的代码如下:
//8*4
int bj, bi, i;
int a, b, c, d;
for (bj = 0; bj < 64; bj += 4) {
for (bi = 0; bi < 64; bi += 8) {
for (i = bi; i < bi + 8; i++) {
a = A[i][0+bj]; b = A[i][1+bj]; c = A[i][2+bj]; d = A[i][3+bj];
B[0+bj][i] = a; B[1+bj][i] = b; B[2+bj][i] = c; B[3+bj][i] = d;
}
}
}
misses数为1651,很显然不符合满分要求。(misses < 1300)
所以为了能够充分利用cache块,我们只能在 8 × 8 8\times8 8×8的框架下具体分析操作。(将 8 × 8 8\times8 8×8分为4个 4 × 4 4\times4 4×4)
思路:为了能够将前文浪费的四个int数据有效利用起来,因为局部变量数目的限制,所以可以考虑将多的数据暂时放入数组B的cache中,以待后续的操作,这样就可以避免二次载入相同的cache块。
tips:此处思路以及下面所用的图片参考引用了深入理解计算机系统-cachelab才得以做下去,感谢作者大大!
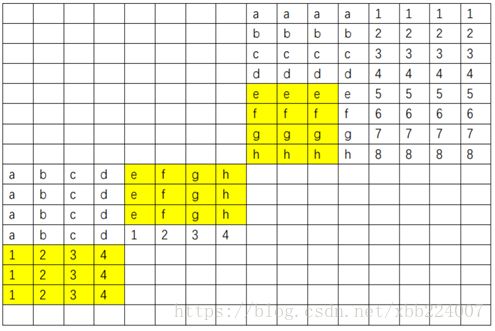
1. 观察以下两个对应的 8 × 8 8\times8 8×8区域。我们要将区域一的元素转置到区域二。

2.将区域一的黄色区域元素转置至对应位置,将区域一的蓝色区域暂时转置存放在区域二的蓝色区域(即数组B此时cache块的右半部分)

至此这个 8 × 8 8\times8 8×8的区域全部转置完成,理论上每一块中不命中一次,即 8 块 / 行 × 64 行 × 2 = 1024 次 8块/行\times64行\times2 = 1024次 8块/行×64行×2=1024次。
代码如下:
int bi, bj, i, j;
int a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h; //8 local variables
for (bi = 0; bi < N; bi += 8) {
for (bj = 0; bj < M; bj += 8) {
for (i = bi; i < bi + 4; i++) {
a = A[i][0+bj]; b = A[i][1+bj]; c = A[i][2+bj]; d = A[i][3+bj]; //store a a a a
e = A[i][4+bj]; f = A[i][5+bj]; g = A[i][6+bj]; h = A[i][7+bj]; //store 1 1 1 1
B[0+bj][i] = a; B[1+bj][i] = b; B[2+bj][i] = c; B[3+bj][i] = d; //assign a a a a
B[0+bj][4+i] = e; B[1+bj][4+i] = f; B[2+bj][4+i] = g; B[3+bj][4+i] = h; //assign 1 1 1 1
}
for (j = bj; j < bj + 4; j++) {
a = A[4+bi][j]; b = A[5+bi][j]; c = A[6+bi][j]; d = A[7+bi][j]; //store e f g h
e = B[j][4+bi]; f = B[j][5+bi]; g = B[j][6+bi]; h = B[j][7+bi]; //store 1 2 3 4
B[j][4+bi] = a; B[j][5+bi] = b; B[j][6+bi] = c; B[j][7+bi] = d; //assign e f g h
B[4+j][0+bi] = e; B[4+j][1+bi] = f; B[4+j][2+bi] = g; B[4+j][3+bi] = h; //assign 1 2 3 4
}
for (i = bi + 4; i < bi + 8; i++) {
a = A[i][4+bj]; b = A[i][5+bj]; c = A[i][6+bj]; d = A[i][7+bj];
B[4+bj][i] = a; B[5+bj][i] = b; B[6+bj][i] = c; B[7+bj][i] = d;
}
}
}
通过测试,结果为misses = 1179,与理论数值相差在于对于对角块会存在冲突,而我们只处理了一部分。
3.M = 61, N = 67
此时所给的M和N对于cache块来说已经无法像前面的情况一样,可以对齐处理,如果要分析的话比较复杂,题目的满分要求也比较低misses < 2000。故我们采用变换分块大小来观察。
代码如下:
int bi, bj, i, j, tmp;
int block_size = 16; //子块大小:block_size * block_size
for (bi = 0; bi < N; bi += block_size) {
for (bj = 0; bj < M; bj += block_size) {
for (i = bi; i < N && i < bi + block_size; i++) {
for (j = bj; j < M && j < bj + block_size; j++) {
tmp = A[i][j];
B[j][i] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
结果如下:(此图引用同一位博主的数据,谢谢博主大大!)
| 分块规模 N × N N\times N N×N | miss数 | 分块规模 N × N N\times N N×N | miss数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 × 2 2\times2 2×2 | 3115 | 12 × 12 12\times12 12×12 | 2057 |
| 3 × 3 3\times3 3×3 | 2648 | 13 × 13 13\times13 13×13 | 2048 |
| 4 × 4 4\times4 4×4 | 2425 | 14 × 14 14\times14 14×14 | 1996 |
| 5 × 5 5\times5 5×5 | 2296 | 15 × 15 15\times15 15×15 | 2021 |
| 6 × 6 6\times6 6×6 | 2224 | 16 × 16 16\times16 16×16 | 1992 |
| 7 × 7 7\times7 7×7 | 2152 | 17 × 17 17\times17 17×17 | 1950 |
| 8 × 8 8\times8 8×8 | 2118 | 18 × 18 18\times18 18×18 | 1961 |
| 9 × 9 9\times9 9×9 | 2092 | 19 × 19 19\times19 19×19 | 1979 |
| 10 × 10 10\times10 10×10 | 2076 | 20 × 20 20\times20 20×20 | 2002 |
| 11 × 11 11\times11 11×11 | 2089 | 21 × 21 21\times21 21×21 | 1957 |
基本上 8 × 8 8\times8 8×8之后misses数在2000左右浮动,没有什么规律,在 17 × 17 17\times17 17×17时达到最小1950。
Part B 测试结果
Part B: Testing transpose function
Running ./test-trans -M 32 -N 32
Running ./test-trans -M 64 -N 64
Running ./test-trans -M 61 -N 67
Cache Lab summary:
Points Max pts Misses
Csim correctness 27.0 27
Trans perf 32x32 8.0 8 287
Trans perf 64x64 8.0 8 1179
Trans perf 61x67 10.0 10 1992
Total points 53.0 53
总结
通过这三种不同数据所对应的优化方法来看,这个lab很用心了,层层递进。
对于 M = 32 , N = 32 M = 32, N = 32 M=32,N=32来说,只需分为 8 × 8 8\times8 8×8即可,是最为简单的一种情况,不用什么改动就可完成适配cache,达到目标。
对于 M = 64 , N = 64 M = 64, N = 64 M=64,N=64来说,因为元素增多,导致cache映射的不同,就需要在第一种情况的 8 × 8 8\times8 8×8下进一步的分析,难度递增。而且代码在这种级别的优化下阅读性变差很多。
而对于 M = 61 , N = 64 M = 61, N = 64 M=61,N=64来说,数组的大小对于cache的大小来说已无很好的性质,只能通过 b l o c k i n g blocking blocking技术分块来进行尝试,达到要求。
而第三种情况才是最为常见的情况,也许这也是设计这种lab的良苦用心,现实中更多的情况则只能尝试。。。
Program timed out的解决方法
运行情况如下所示:
leo@masternode:/mnt/hgfs/CMU15-213/lab/4.cachelab-handout$ ./test-trans -M 32 -N 32
Function 0 (2 total)
Step 1: Validating and generating memory traces
Step 2: Evaluating performance (s=5, E=1, b=5)
func 0 (Transpose submission): hits:870, misses:1183, evictions:1151
Function 1 (2 total)
Step 1: Validating and generating memory traces
Error: Program timed out.
TEST_TRANS_RESULTS=0:0
将运行的程序文件夹移动到Linux单独的目录而不是虚拟机共享文件目录里。。。。
Some good habits
1.Warnings are Errors
Add “-Werror” to your compilation flags.
2.Missing Header Files
Use: man function-name