一些数据增强
目录
创建一个dataset
CenterCrop:
ToTensor
Normalize
RandomResizedCrop
水平翻转
垂直翻转
ColorJitter
图像旋转
透视变化:
灰度变换
高斯模糊
HSV变化
总结:
创建一个dataset
class TestDataset(torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder):
# 根路径,
def __init__(self, root, imgsz, cache):
super().__init__(root=root)
self.torch_transforms = T.Compose([CenterCrop(size), ToTensor(), T.Normalize(IMAGENET_MEAN, IMAGENET_STD)])
self.cache_ram = cache is True or cache == 'ram'
self.cache_disk = cache == 'disk'
self.samples = [list(x) + [Path(x[0]).with_suffix('.npy'), None] for x in self.samples]
def __getitem__(self, i):
f, j, fn, im = self.samples[i]
if self.cache_ram and im is None:
im = self.samples[i][3] = cv2.imread(f)
elif self.cache_disk:
if not fn.exists(): # load npy
np.save(fn.as_posix(), cv2.imread(f))
im = np.load(fn)
return self.torch_transforms(im)CenterCrop:
CenterCrop图像裁剪原理_3分钟秒懂大数据的博客-CSDN博客_centercrop
class CenterCrop:
# YOLOv5 CenterCrop class for image preprocessing, i.e. T.Compose([CenterCrop(size), ToTensor()])
def __init__(self, size=640):
super().__init__()
self.h, self.w = (size, size) if isinstance(size, int) else size
def __call__(self, im): # im = np.array HWC
imh, imw = im.shape[:2]
m = min(imh, imw) # min dimension
top, left = (imh - m) // 2, (imw - m) // 2
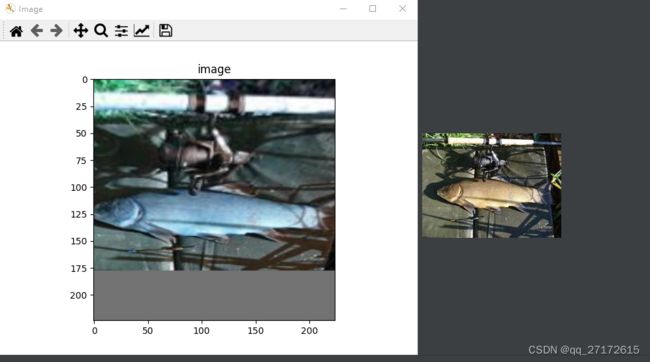
return cv2.resize(im[top:top + m, left:left + m], (self.w, self.h), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)代码解释: 我目前看的都是yolo中的方法 总体就是先裁剪再resize
假设我们输入一个(h, w) = (300, 250) 图片, m 的值就是 250, top, left = 25, 0
所以裁剪的 [25:275, 0:250]
原图高是比较小的,所以没被切掉。就一句话,先剪切再resize.
ToTensor
class ToTensor:
# YOLOv5 ToTensor class for image preprocessing, i.e. T.Compose([LetterBox(size), ToTensor()])
def __init__(self, half=False):
super().__init__()
self.half = half
def __call__(self, im): # im = np.array HWC in BGR order
im = np.ascontiguousarray(im.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1]) # HWC to CHW -> BGR to RGB -> contiguous
im = torch.from_numpy(im) # to torch
im = im.half() if self.half else im.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
im /= 255.0 # 0-255 to 0.0-1.0
return im解释:就一件事, 归一化。和是否设置半精度
Normalize
pytorch个人学习笔记(2)—Normalize()参数详解及用法_吃米的鹰的博客-CSDN博客_pytorch normalize
我的理解:数据大部分符合一个分布,但是总有那么一两个特例会乱窜,所以把那些特例抹掉,所以神经网络只关心总体的特征,关心个别。
yolo选定的参数:
IMAGENET_MEAN = 0.485, 0.456, 0.406 # RGB mean
IMAGENET_STD = 0.229, 0.224, 0.225 # RGB standard deviationRandomResizedCrop
pytorch torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop方法解读_Continue2021的博客-CSDN博客_randomresizedcrop
def forward(self, img):
"""
Args:
img (PIL Image or Tensor): Image to be cropped and resized.
Returns:
PIL Image or Tensor: Randomly cropped and resized image.
"""
i, j, h, w = self.get_params(img, self.scale, self.ratio)
return F.resized_crop(img, i, j, h, w, self.size, self.interpolation, antialias=self.antialias)torch麻烦就是,底层代码都是c++写的,所以看不见怎么实现的,还有一个麻烦的就是必须要plt格式的,yolo用的是 albumentations,不需要进行格式转换,但是我安装了几次都装不上。从效果来说,还是一个剪切, 一个resize。多了一个随机。
水平翻转
np.fliplr(im)
T.RandomHorizontalFlip
def fliplr(m):
m = asanyarray(m)
if m.ndim < 2:
raise ValueError("Input must be >= 2-d.")
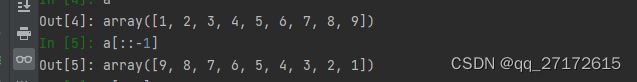
return m[:, ::-1]np.fliplr(im) 的效果,颜色发生了变化,俺也不知道是为什么,第二个方法没试,包安装不起。
::-1作用如图
但是颜色为啥会变呢。搞不懂。
垂直翻转
np.flipud(im)
T.RandomVerticalFlip
def flipud(m):
m = asanyarray(m)
if m.ndim < 1:
raise ValueError("Input must be >= 1-d.")
return m[::-1, ...]ColorJitter
T.Compose(
[T.ColorJitter(brightness=0.5, contrast=0.1, saturation=0.1, hue=0.1)])brightness:亮度
contrast:对比度
saturation:饱和度
hue:色相
都设置0.4要好点
图像旋转
R = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(angle=45, center=(100, 100), scale=1)
sample = cv2.warpAffine(im, R, (im.shape[0], im.shape[1]))angle: 旋转角度
center: 旋转中心,
scale:缩放比例
透视变化:
points1 = np.float32([[50, 0], [150, 0], [0, 200], [200, 200]])
points2 = np.float32([[0, 0], [200, 0], [0, 200], [200, 200]])
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(points1, points2)
sample = cv2.warpPerspective(im, M, dsize=(224, 224), borderValue=(114, 114, 114))OpenCV图像处理--warpPerspective透视变换_C君莫笑的博客-CSDN博客
points1 原图选取的四个坐标 points2需要变化的坐标
灰度变换
T.Compose([T.Grayscale(3)])
Returns:
PIL Image: Grayscale version of the input.
- If ``num_output_channels == 1`` : returned image is single channel
- If ``num_output_channels == 3`` : returned image is 3 channel with r == g == b
"""
def __init__(self, num_output_channels=1):
super().__init__()
_log_api_usage_once(self)
self.num_output_channels = num_output_channels高斯模糊
T.Compose(
[T.GaussianBlur(kernel_size=(3, 3))])
HSV变化
def augment_hsv(im, hgain=0.5, sgain=0.5, vgain=0.5):
# HSV color-space augmentation
if hgain or sgain or vgain:
r = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 3) * [hgain, sgain, vgain] + 1 # random gains
hue, sat, val = cv2.split(cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV))
dtype = im.dtype # uint8
x = np.arange(0, 256, dtype=r.dtype)
lut_hue = ((x * r[0]) % 180).astype(dtype)
lut_sat = np.clip(x * r[1], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
lut_val = np.clip(x * r[2], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
im_hsv = cv2.merge((cv2.LUT(hue, lut_hue), cv2.LUT(sat, lut_sat), cv2.LUT(val, lut_val)))
cv2.cvtColor(im_hsv, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR, dst=im) # no return needed总结:
np.ascontiguousarray
np.ascontiguousarray()详解 - 九叶草 - 博客园
yolo中最后都要调用这个,为了性能更快。PLT显示的图像都有问题,不知道是什么原因,只有最后一张图片是用opencv显