CenterNet论文学习解读
文章目录
- 资源
- 原理
-
- 简介
- 相关研究
-
- 使用anchor的目标检测
-
- 优势
- 使用关键点的目标检测
-
- 优势
- 单目3D目标检测
-
- 优势
- 网络结构
-
- 预备知识
- 损失函数
- 推理
-
- 2D检测
- 3D检测:
- 人体姿态估计
- backbone
- 代码解读
-
- 创建模型
- resnet_dcn
- dla34_dcn
资源
论文题目: Objects as Points
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.07850.pdf
发布时间:2019.4.16
机构:UT Austin,UC Berkeley
代码:https://github.com/xingyizhou/CenterNet
相关解读:(本文是基于这两篇文章的学习整理)
https://blog.csdn.net/c20081052/article/details/89358658
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/66048276
原理
简介
此检测器采用关键点估计来找到中心点,并回归到其他目标属性,例如尺寸,3D位置,方向,甚至姿态。
- 对于2D BBox检测, 先生成热力图找到关键点,再回归关键点在特征图和原图间的偏移,再回归宽高
- 对于3D BBox检测,我们直接回归得到目标的深度信息,3D框的尺寸,目标朝向
- 对于人姿态估计,我们将关节点(2D joint)位置作为中心点的偏移量,直接在中心点位置回归出这些偏移量的值
相关研究
使用anchor的目标检测
- fast-rcnn
一组候选框中枚举出目标框,再对每个对象进行卷积分类
- faster-rcnn
卷积网络中生成候选区域区域, IOU > 0.7作为前景,否则为背景,再进行分类
优势
- 仅在目标位置设置关键点,没有了全图枚举或区域提案RPN生成检测框,不用设置阈值做前后框分类
- 不需要NMS后处理来去除重复检测框。
- 使用更大的分辨率(缩放4倍),传统目标检测缩放16倍
总体来说,CenterNet结构优雅简单,直接检测目标的中心点和大小,是真anchor-free。比其他方法更简单,更快。
使用关键点的目标检测
- ExtremeNet
检测所有目标的 最上,最下,最左,最右,中心点
- CornerNet
将bbox的两个角作为关键点
优势
它们都需要经过一个关键点grouping阶段(对关键点以人为单位分组,具体没去看),这会降低算法整体速度,centernet仅仅提取每个目标的中心点,无需对关键点进行grouping 或者是后处理
单目3D目标检测
- Deep3Dbox
使用一个 slow-RCNN 风格的框,该网络先检测2D目标,然后将目标送到3D 估计网络
- 3D RCNN
在Faster-RCNN上添加了额外的head来做3D projection
- Deep Manta
使用一个 coarse-to-fine的Faster-RCNN ,在多任务中训练
优势
同one-stage版本的Deep3Dbox 或3D RCNN相似,同样,CenterNet比它们都更简洁,更快。
网络结构
预备知识
令 I ∈ R W × H × 3 I \in R^{W×H×3} I∈RW×H×3为输出图像,其宽W,高H。
- 关键点热力图定义, R 是输出stride(即尺寸缩放比例),默认为4, C是关键点类型数(即输出特征图通道数),C=80,则为COCO目标类别,C=17,则为COCO姿态点.
Y ^ ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] W R × H R × C \hat Y \in [0,1]^{ \frac{W}{R} ×\frac{H}{R}×C} Y^∈[0,1]RW×RH×C
-
Y ^ x , y , c = 1 \hat Y _{x,y,c} = 1 Y^x,y,c=1 表示检测到的关键点
-
Y ^ x , y , c = 0 \hat Y _{x,y,c} = 0 Y^x,y,c=0 表示背景
-
将真实关键点分布到特征图上, 真实关键点 p ∈ R 2 p \in R^2 p∈R2 对于下采样后的坐标,我们设为 p ~ = ∣ p R ∣ \tilde p = |\frac{p}{R}| p~=∣Rp∣,通过高斯核分散到热力图 Y ^ \hat Y Y^上,如果对于同个类 c (同个关键点或是目标类别)有两个高斯函数发生重叠,我们选择元素级最大的。
Y x y c = e x p ( − ( x − p ~ x ) 2 + ( y − p ~ y ) 2 2 σ p 2 ) Y _{xyc} = exp(-\frac{(x- \tilde p_x)^2 + (y- \tilde p_y)^2}{2\sigma^2_p}) Yxyc=exp(−2σp2(x−p~x)2+(y−p~y)2)

高斯生成的中心点
损失函数
- 中心点损失函数,像素级逻辑回归的focal loss
L k = − 1 N ∑ { ( 1 − Y ^ x y c ) α l o g ( Y ^ x y c ) , i f Y x y c = 1 ( 1 − Y x y c ) β ( Y ^ x y c ) α l o g ( 1 − Y ^ x y c ) , o t h e r w i s e L_k = \frac{-1}{N}\sum \begin{cases}(1 - \hat Y_{xyc})^\alpha log(\hat Y_{xyc}), \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ ifY_{xyc}=1 \\ \\ (1-Y_{xyc})^\beta(\hat Y_{xyc})^\alpha log(1-\hat Y_{xyc}), \ \ otherwise \end{cases} Lk=N−1∑⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧(1−Y^xyc)αlog(Y^xyc), ifYxyc=1(1−Yxyc)β(Y^xyc)αlog(1−Y^xyc), otherwise
其中 α \alpha α 和 β \beta β是focal loss的超参数,实验中两个数分别设置为2和4, N是图像 I 中的关键点个数,除以N主要为了将所有focal loss归一化。
解读:
如果预测的中心点真值为1,那该点为易学目标,更加减小预测正确的损失值,增大错误的损失值。
如果预测的中心点真值不为1,真值中心点很少,正负样本不均衡,通过 ( 1 − Y x y c ) β (1-Y_{xyc})^\beta (1−Yxyc)β加大远离真值为1的中心点损失值,减小靠近真值1的中心点损失值。靠近真实点的地方为易学点通过 ( Y ^ x y c ) α (\hat Y_{xyc})^\alpha (Y^xyc)α增大靠近真实点预测错误的损失值, ( 1 − Y x y c ) β (1-Y_{xyc})^\beta (1−Yxyc)β和 ( Y ^ x y c ) α (\hat Y_{xyc})^\alpha (Y^xyc)α在靠近真实点处相互牵制
- 目标中心的偏置损失,下采样4倍的真实关键点可能为小数,而预测点为整数,映射到原始图像,会有精度误差,这个偏置值用L1 loss来训练
L o f f = 1 N ∑ p ∣ O ^ p ~ − ( P R − p ~ ) ∣ L_{off} = \frac{1}{N}\sum_{p}|\hat O_{\tilde p} - (\frac{P}{R} - \tilde p)| Loff=N1p∑∣O^p~−(RP−p~)∣
O ^ p ~ \hat O_{\tilde p} O^p~ 是我们预测出来的偏置, ( P R − p ~ ) (\frac{P}{R} - \tilde p) (RP−p~)则是在训练过程中提前计算出来的实际误差
- 目标大小的损失,对每个目标的size进行回归,最终回归到 s k = ( x 2 ( 2 ) − x 1 ( 2 ) , y 2 ( 2 ) − y 1 ( 2 ) ) s_k = ( x_2^{(2)} - x_1^{(2)}, y_2^{(2)} - y_1^{(2)}) sk=(x2(2)−x1(2),y2(2)−y1(2)),使用L1 loss来训练
L s i z e = 1 N ∑ k = 1 N ∣ S ^ p k − s k ∣ L_{size} = \frac{1}{N}\sum_{k=1}^N|\hat S_{p_k} - s_k| Lsize=N1k=1∑N∣S^pk−sk∣
- 整体的损失函数为物体损失、大小损失与偏置损失的和,每个损失都有相应的权重
L d e t = L k + λ s i z e L s i z e + λ o f f L o f f L_{det} = L_k + \lambda_{size}L_{size} + \lambda_{off}L_{off} Ldet=Lk+λsizeLsize+λoffLoff
推理
2D检测
找到关键点:
在推理的时候,我们分别提取热力图上每个类别的峰值点。如何得到这些峰值点呢?做法是将热力图上的所有响应点与其连接的8个临近点进行比较,如果该点响应值大于或等于其八个临近点值则保留,最后我们保留所有满足之前要求的前100个峰值点
产生bbox: ( δ x ^ i , δ y ^ i ) (\delta \hat x_i,\delta \hat y_i) (δx^i,δy^i)为偏移预测结果, ( w ^ i , h ^ i ) (\hat w_i, \hat h_i) (w^i,h^i)为宽高预测结果
( x ^ i + δ x ^ i − w ^ i / 2 , y ^ i + δ y ^ i − h ^ i / 2 , x ^ i + δ x ^ i + w ^ i / 2 , y ^ i + δ y ^ i + h ^ i / 2 ) (\hat x_i + \delta \hat x_i - \hat w_i/2, \hat y_i + \delta \hat y_i - \hat h_i/2,\\ \hat x_i + \delta \hat x_i + \hat w_i/2, \hat y_i + \delta \hat y_i + \hat h_i/2) (x^i+δx^i−w^i/2,y^i+δy^i−h^i/2,x^i+δx^i+w^i/2,y^i+δy^i+h^i/2)
3D检测:
每个中心点需要3个附加信息:depth, 3D dimension, orientation。我们为每个信息分别添加head.
depth:对于每个中心点,深度值depth是一个维度的, 然后depth很难直接回归, 在特征点估计网络上添加了一个深度计算通道 D ^ ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] W R × H R \hat D \in [0,1]^{\frac{W}{R}\times \frac{H}{R}} D^∈[0,1]RW×RH, 该通道使用了两个卷积层,然后做ReLU 。输出为 d = 1 / σ ( d ^ ) − 1 d=1/ \sigma (\hat d)-1 d=1/σ(d^)−1,$ \sigma$为sigmoid函数,我们用L1 loss来训练深度估计器。
3D维度:目标的3D维度是三个标量值。我们直接回归出它们(长宽高)的绝对值,单位为米,用的是一个独立的head,和L1 loss
方向:方向默认是单标量的值,然而其也很难回归。用两个bins来呈现方向,且i做n-bin回归。特别地,方向用8个标量值来编码的形式,每个bin有4个值。对于一个bin,两个值用作softmax分类,其余两个值回归到在每个bin中的角度。
人体姿态估计
设人体关键点为 k k k
- 通过中心点,回归出 k k k个关节点的偏移 J ^ ∈ R W R × H R × k × 2 \hat J \in R^{\frac{W}{R} \times \frac{H}{R} \times k \times 2} J^∈RRW×RH×k×2,得到关节点 l j = ( x ^ , y ^ ) + J ^ x ^ y ^ j f o r j ∈ 1... k l_j = (\hat x, \hat y)+ \hat J_{\hat x \hat y j} \ for j \in 1...k lj=(x^,y^)+J^x^y^j forj∈1...k用到了L1 loss,我们通过给loss添加mask方式来无视那些不可见的关键点(关节点)。此处参照了slow-RCNN。
- 估计 k k k个人体关节点热力图,检测出所有人体关键点(热力图上值小于0.1的直接略去)。使用focal loss和像素偏移量。
- 分配关节点到人,将第一步的中心偏移 J ^ \hat J J^ 作为一个grouping的线索,来为每个关键点(关节点)分配其最近的人,回归得到的位置 l j l_j lj与最近的检测关节点进行分配 a r g min l ∈ L j ( l − l j ) 2 arg\,\min_{l \in L_j }(l-l_j)^2 argminl∈Lj(l−lj)2 ,只对检测到的目标框中的关节点进行关联。
backbone
我们实验了4个结构:ResNet-18, ResNet-101, DLA-34, Hourglass-104. 我们用deformable卷积层来更改ResNets和DLA-34,按照原样使用Hourglass 网络
- Resnet-18 with up-convolutional layers : 28.1% coco and 142 FPS
Xiao et al. [55]等人对标准的ResNet做了3个up-convolutional网络来得到更高的分辨率输出(最终stride为4)。为了节省计算量,我们改变这3个up-convolutional的输出通道数分别为256,128,64。up-convolutional核初始为双线性插值。
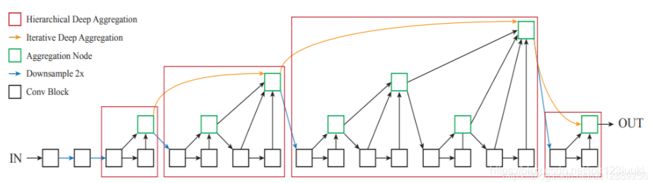
- DLA-34 : 37.4% COCOAP and 52 FPS
即Deep Layer Aggregation (DLA),是带多级跳跃连接的图像分类网络,我们采用全卷积上采样版的DLA,用deformable卷积来跳跃连接低层和输出层;将原来上采样层的卷积都替换成3x3的deformable卷积。在每个输出head前加了一个3x3x256的卷积,然后做1x1卷积得到期望输出。
- Hourglass-104 : 45.1% COCOAP and 1.4 FPS
堆叠的Hourglass网络,通过两个连续的hourglass 模块对输入进行了4倍的下采样,每个hourglass 模块是个对称的5层 下和上卷积网络,且带有skip连接。该网络较大,但通常会生成最好的关键点估计。
(b):使用反卷积的ResNet
(c ):DLA-34
(d):DLA-34,底层添加了更多的跳转连接,并对每个卷积层替换为可变形卷积层的上采样阶段
代码解读
创建模型
model = get_model(num_layers=num_layers, heads=heads, head_conv=head_conv)
-
num_layers 为选择num_layers层的resnet网络
-
heads 为需要输出的特征有哪些,比如coco目标检测模型,输出80类热力图,宽高,偏移
if opt.task == 'exdet':
# assert opt.dataset in ['coco']
num_hm = 1 if opt.agnostic_ex else opt.num_classes
opt.heads = {'hm_t': num_hm, 'hm_l': num_hm,
'hm_b': num_hm, 'hm_r': num_hm,
'hm_c': opt.num_classes}
if opt.reg_offset:
opt.heads.update({'reg_t': 2, 'reg_l': 2, 'reg_b': 2, 'reg_r': 2})
elif opt.task == 'ddd':
# assert opt.dataset in ['gta', 'kitti', 'viper']
opt.heads = {'hm': opt.num_classes, 'dep': 1, 'rot': 8, 'dim': 3}
if opt.reg_bbox:
opt.heads.update(
{'wh': 2})
if opt.reg_offset:
opt.heads.update({'reg': 2})
elif opt.task == 'ctdet':
# assert opt.dataset in ['pascal', 'coco']
opt.heads = {'hm': opt.num_classes,
'wh': 2 if not opt.cat_spec_wh else 2 * opt.num_classes}
if opt.reg_offset:
opt.heads.update({'reg': 2})
elif opt.task == 'multi_pose':
# assert opt.dataset in ['coco_hp']
# opt.flip_idx = dataset.flip_idx
opt.flip_idx = False
opt.heads = {'hm': opt.num_classes, 'wh': 2, 'hps': 34}
if opt.reg_offset:
opt.heads.update({'reg': 2})
if opt.hm_hp:
opt.heads.update({'hm_hp': 17})
if opt.reg_hp_offset:
opt.heads.update({'hp_offset': 2})
- head_conv 输出通道数
if opt.head_conv == -1: # init default head_conv
opt.head_conv = 256 if 'dla' in opt.arch else 64
resnet_dcn
-
resnet是由多个block构成一个layer,再有多个layer组成的残差网络,残差结构是下图的dawnsample
-
resnet18的block结构
- BasicBlock前向传播
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
- layper网络定义
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
- deconv_layers x 3
DCN部分是cuda代码,我看不懂,之后会专门开一篇文章将DCN
- 可变形卷积+反卷积网络定义
def _make_deconv_layer(self, num_layers, num_filters, num_kernels):
assert num_layers == len(num_filters), \
'ERROR: num_deconv_layers is different len(num_deconv_filters)'
assert num_layers == len(num_kernels), \
'ERROR: num_deconv_layers is different len(num_deconv_filters)'
layers = []
for i in range(num_layers):
kernel, padding, output_padding = \
self._get_deconv_cfg(num_kernels[i], i)
planes = num_filters[i]
fc = DCN(self.inplanes, planes,
kernel_size=(3,3), stride=1,
padding=1, dilation=1, deformable_groups=1)
# fc = nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes,
# kernel_size=3, stride=1,
# padding=1, dilation=1, bias=False)
# fill_fc_weights(fc)
up = nn.ConvTranspose2d(
in_channels=planes,
out_channels=planes,
kernel_size=kernel,
stride=2,
padding=padding,
output_padding=output_padding,
bias=self.deconv_with_bias)
fill_up_weights(up)
layers.append(fc)
layers.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM))
layers.append(nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
layers.append(up)
layers.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM))
layers.append(nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
self.inplanes = planes
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
- resnet18_dcn
- resnet18_dcn前向传播
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.deconv_layers(x)
ret = {}
for head in self.heads:
ret[head] = self.__getattr__(head)(x)
return [ret]
- 输出head网络定义
for head in self.heads:
classes = self.heads[head]
if head_conv > 0:
fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, head_conv,
kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(head_conv, classes,
kernel_size=1, stride=1,
padding=0, bias=True))
if 'hm' in head:
fc[-1].bias.data.fill_(-2.19)
else:
fill_fc_weights(fc)
else:
fc = nn.Conv2d(64, classes,
kernel_size=1, stride=1,
padding=0, bias=True)
if 'hm' in head:
fc.bias.data.fill_(-2.19)
else:
fill_fc_weights(fc)
self.__setattr__(head, fc)
dla34_dcn
-
dla34_dcn包含dla34以及dlaup解码(上采样)两部分
-
dla34_dcn
- dla34_dcn前向传播
def forward(self, x):
x = self.base(x)
x = self.dla_up(x)
y = []
for i in range(self.last_level - self.first_level):
y.append(x[i].clone())
self.ida_up(y, 0, len(y))
z = {}
for head in self.heads:
z[head] = self.__getattr__(head)(y[-1])
return [z]
- dla34 网络结构
- dla34前向传播
def forward(self, x):
y = []
x = self.base_layer(x)
for i in range(6):
x = getattr(self, 'level{}'.format(i))(x)
y.append(x)
return y
- dla34网络定义
def __init__(self, levels, channels, num_classes=1000,
block=BasicBlock, residual_root=False, linear_root=False):
super(DLA, self).__init__()
self.channels = channels
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.base_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, channels[0], kernel_size=7, stride=1,
padding=3, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channels[0], momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
self.level0 = self._make_conv_level(
channels[0], channels[0], levels[0])
self.level1 = self._make_conv_level(
channels[0], channels[1], levels[1], stride=2)
self.level2 = Tree(levels[2], block, channels[1], channels[2], 2,
level_root=False,
root_residual=residual_root)
self.level3 = Tree(levels[3], block, channels[2], channels[3], 2,
level_root=True, root_residual=residual_root)
self.level4 = Tree(levels[4], block, channels[3], channels[4], 2,
level_root=True, root_residual=residual_root)
self.level5 = Tree(levels[5], block, channels[4], channels[5], 2,
level_root=True, root_residual=residual_root)
- tree前向传播
def forward(self, x, residual=None, children=None):
children = [] if children is None else children
bottom = self.downsample(x) if self.downsample else x
residual = self.project(bottom) if self.project else bottom
if self.level_root:
children.append(bottom)
x1 = self.tree1(x, residual)
if self.levels == 1:
x2 = self.tree2(x1)
x = self.root(x2, x1, *children)
else:
children.append(x1)
x = self.tree2(x1, children=children)
return x
- tree网络定义
def __init__(self, levels, block, in_channels, out_channels, stride=1,
level_root=False, root_dim=0, root_kernel_size=1,
dilation=1, root_residual=False):
super(Tree, self).__init__()
if root_dim == 0:
root_dim = 2 * out_channels
if level_root:
root_dim += in_channels
if levels == 1:
self.tree1 = block(in_channels, out_channels, stride,
dilation=dilation)
self.tree2 = block(out_channels, out_channels, 1,
dilation=dilation)
else:
self.tree1 = Tree(levels - 1, block, in_channels, out_channels,
stride, root_dim=0,
root_kernel_size=root_kernel_size,
dilation=dilation, root_residual=root_residual)
self.tree2 = Tree(levels - 1, block, out_channels, out_channels,
root_dim=root_dim + out_channels,
root_kernel_size=root_kernel_size,
dilation=dilation, root_residual=root_residual)
if levels == 1:
self.root = Root(root_dim, out_channels, root_kernel_size,
root_residual)
self.level_root = level_root
self.root_dim = root_dim
self.downsample = None
self.project = None
self.levels = levels
if stride > 1:
self.downsample = nn.MaxPool2d(stride, stride=stride)
if in_channels != out_channels:
self.project = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
)
- 解释
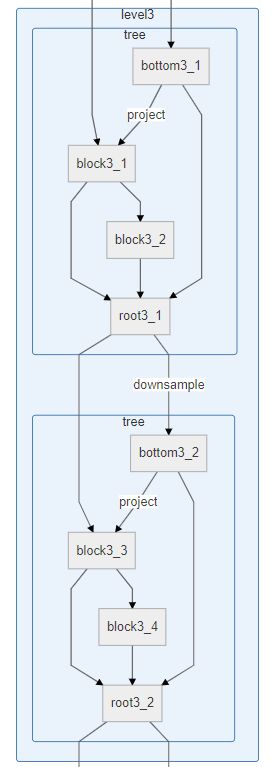
右图为layer3的结构,红圈内为一个tree,黑框为block,绿框为root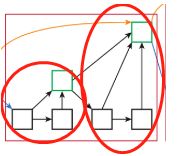
与下图的两个tree相对应,
- block
#残差结构
- block前向传播
def forward(self, x, residual=None):
if residual is None:
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
- DLAUp
- DLAUp前向传播
#执行多个ida
def forward(self, layers):
out = [layers[-1]] # start with 32
for i in range(len(layers) - self.startp - 1):
ida = getattr(self, 'ida_{}'.format(i))
ida(layers, len(layers) -i - 2, len(layers))
out.insert(0, layers[-1])
return out
- ida前向传播
def forward(self, layers, startp, endp):
for i in range(startp + 1, endp):
upsample = getattr(self, 'up_' + str(i - startp))
project = getattr(self, 'proj_' + str(i - startp))
layers[i] = upsample(project(layers[i]))
node = getattr(self, 'node_' + str(i - startp))
layers[i] = node(layers[i] + layers[i - 1])
关键代码 :layers[i] = node(layers[i] + layers[i - 1])
将两个layer的结果相加,对应上图橙色箭头
- ida网络定义
def __init__(self, o, channels, up_f):
super(IDAUp, self).__init__()
for i in range(1, len(channels)):
c = channels[i]
f = int(up_f[i])
proj = DeformConv(c, o)
node = DeformConv(o, o)
up = nn.ConvTranspose2d(o, o, f * 2, stride=f,
padding=f // 2, output_padding=0,
groups=o, bias=False)
fill_up_weights(up)
setattr(self, 'proj_' + str(i), proj)
setattr(self, 'up_' + str(i), up)
setattr(self, 'node_' + str(i), node)