目标检测学习笔记——map概念、IoU汇总Iou、Giou、Ciou、Diou
目标检测学习笔记——map概念、IoU汇总Iou、Giou、Ciou、Diou
文章目录
- 目标检测学习笔记——map概念、IoU汇总Iou、Giou、Ciou、Diou
- 前言
- 一、什么是map值?
-
-
- Precision:查准率、精度
- Recall:查全率、召回率
-
- 二、IoU汇总Iou、Giou、Ciou、Diou
-
- 2.1 Iou
- 2.2 Giou
- 2.3Diou
- 2.4 Ciou
- 2.5 代码
-
- 图片以左上角为中心点
- 以h,w中心为中心点
- 总结
前言
一、什么是map值?
map是Mean Average Precision 的缩写(均值平均精度)
介绍map之前,先了解以下概念
TP:True Positive,分类器预测结果为正样本,实际也为正样本,即正样本被正确识别的数量。
FP:False Positive,分类器预测结果为正样本,实际为负样本,即误报的负样本数量。
TN:True Negative,分类器预测结果为负样本,实际为负样本,即负样本被正确识别的数量。
FN:False Negative,分类器预测结果为负样本,实际为正样本,即漏报的正样本数量。
TP+FN:真实正样本的总和,正确分类的正样本数量+漏报的正样本数量。
FP+TN:真实负样本的总和,负样本被误识别为正样本数量+正确分类的负样本数量。
TP+TN:正确分类的样本总和,正确分类的正样本数量+正确分类的负样本数量。
Precision:查准率、精度
Precision表征的是预测正确的正样本的准确度,查准率等于预测正确的正样本数量/所有预测为正样本数量。Precision越大说明误检的越少,Precision越小说明误检的越多。
Precision=TP/(TP+FP)
Recall:查全率、召回率
Recall表征的是预测正确的正样本的覆盖率,查全率等于预测正确的正样本数量/所有正样本的总和,TP+FN实际就是Ground Truth的数量。Recall越大说明漏检的越少,Recall越小说明漏检的越多。
Recall=TP/(TP+FN)
对于目标检测来说,每一个类都可以计算出Precision和Recall,每个类都可以得到一条P-R曲线(P-R曲线,顾名思义,就是P-R的关系曲线图,表示了召回率和准确率之间的关系),曲线下的面积就是AP(平均精确度)的值。对所有AP的值求平均就是map。
二、IoU汇总Iou、Giou、Ciou、Diou
2.1 Iou
Iou通俗来说也就是交并比,计算不同图像相互重叠比例。
I o U = A ∩ B A ∪ B IoU = \frac{A\cap B}{A\cup B} IoU=A∪BA∩B
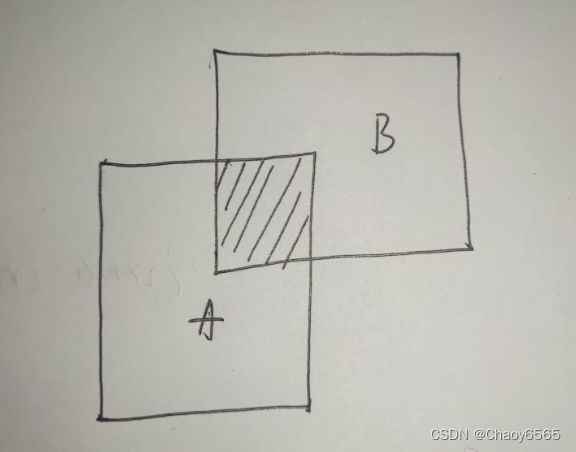
IoU Loss具有非负性、尺度不变性、同一性、对称性、三角不等性等特点,但是如果|A∩B|=0,也就是两个图像没有相交时,无法比较两个图像的距离远近,无法体现两个图像到底是如何相交的。
2.2 Giou
GIoU比IoU多了一个‘Generalized’,能在更广义的层面上计算IoU,解决了两个图像没有相交时,无法比较两个图像的距离远近的问题。
G I O U = I o U − ∣ C − A ∪ B ∣ C GIOU = IoU- \frac{\left | C-A\cup B \right | }{C} GIOU=IoU−C∣C−A∪B∣
其中C代表两个图像的最小包庇面积,也可以理解为这两个图像的最小外接矩形的面积。GIoU不仅关注重叠区域,还关注其他的非重合区域,能更好的反映两者的重合度。GIoU完善了图像重叠度的计算功能,但仍无法对图形距离以及长宽比的相似性进行很好的表示。
2.3Diou
DIoU(Distance-IoU)将两个框之间的重叠度、距离、尺度都考虑了进来。
D i o u = I o u − ρ 2 ( b , b g t ) c 2 Diou = Iou-\frac{\rho ^{2}(b,b^{gt} ) }{c^{2} } Diou=Iou−c2ρ2(b,bgt)
其中b,bgt分别代表两个框的中心点,ρ代表两个中心点之间的欧氏距离,C代表最小包庇矩形的对角线。
预测框和真实框的重叠程度。并且考虑到预测框长和宽的比值问题并以此添加惩罚项,从而使预测框的效果更加稳定
DIoU在完善图像重叠度的计算功能的基础上,实现了对图形距离的考量,但仍无法对图形长宽比的相似性进行很好的表示。
2.4 Ciou

可以看出,CIoU就是在DIoU的基础上,增加了图像相似性的影响因子,因此可以更好的反映两个框之间的差异性。
我们还需要注意的一点是,在使用CIoU作为Loss的时候,v的梯度同样会参与反向传播的计算。
2.5 代码
图片以左上角为中心点
# 以左上角为中心点
# box:[上, 左, 下, 右]
import numpy as np
import math
def IoU(box1, box2):
# 计算中间矩形的宽高
in_h = min(box1[2], box2[2]) - max(box1[0], box2[0])
in_w = min(box1[3], box2[3]) - max(box1[1], box2[1])
# 计算交集、并集面积
inter = 0 if in_h < 0 or in_w < 0 else in_h * in_w
union = (box1[2] - box1[0]) * (box1[3] - box1[1]) + \
(box2[2] - box2[0]) * (box2[3] - box2[1]) - inter
# 计算IoU
iou = inter / union
return iou
def GIoU(box1, box2):
# 计算最小包庇面积
y1,x1,y2,x2 = box1
y3,x3,y4,x4 = box2
area_C = (max(x1,x2,x3,x4)-min(x1,x2,x3,x4)) * \
(max(y1,y2,y3,y4)-min(y1,y2,y3,y4))
# 计算IoU
in_h = min(box1[2], box2[2]) - max(box1[0], box2[0])
in_w = min(box1[3], box2[3]) - max(box1[1], box2[1])
inter = 0 if in_h < 0 or in_w < 0 else in_h * in_w
union = (box1[2] - box1[0]) * (box1[3] - box1[1]) + \
(box2[2] - box2[0]) * (box2[3] - box2[1]) - inter
iou = inter / union
# 计算空白部分占比
end_area = (area_C - union)/area_C
giou = iou - end_area
return giou
def CIoU(box1, box2):
y1,x1,y2,x2 = box1
y3,x3,y4,x4 = box2
iou = IoU(box1, box2)
diou = DIoU(box1, box2)
v = 4 / math.pi**2 * (math.atan((x2-x1)/(y2-y1)) - \
math.atan((x4-x3)/(y4-y3)))**2 + 1e-5
alpha = v / ((1-iou) + v)
ciou = diou - alpha * v
return ciou
def DIoU(box1, box2):
# 计算对角线长度
y1,x1,y2,x2 = box1
y3,x3,y4,x4 = box2
C = np.sqrt((max(x1,x2,x3,x4)-min(x1,x2,x3,x4))**2 + \
(max(y1,y2,y3,y4)-min(y1,y2,y3,y4))**2)
# 计算中心点间距
point_1 = ((x2+x1)/2, (y2+y1)/2)
point_2 = ((x4+x3)/2, (y4+y3)/2)
D = np.sqrt((point_2[0]-point_1[0])**2 + \
(point_2[1]-point_1[1])**2)
# 计算IoU
iou = IoU(box1, box2)
# 计算空白部分占比
lens = D**2 / C**2
diou = iou - lens
return diou
输出
# box:[上, 左, 下, 右]
box1 = [0,0,8,6]
box2 = [2,3,10,9]
print('Iou',IoU(box1, box2))
print('GIou',GIoU(box1, box2))
print('DIou',DIoU(box1, box2))
print('CIou',CIoU(box1, box2))
以h,w中心为中心点
import numpy as np
import torch
import math
def Iou(box1, box2, wh=False):
if wh == False:
xmin1, ymin1, xmax1, ymax1 = box1
xmin2, ymin2, xmax2, ymax2 = box2
else:
xmin1, ymin1 = int(box1[0]-box1[2]/2.0), int(box1[1]-box1[3]/2.0)
xmax1, ymax1 = int(box1[0]+box1[2]/2.0), int(box1[1]+box1[3]/2.0)
xmin2, ymin2 = int(box2[0]-box2[2]/2.0), int(box2[1]-box2[3]/2.0)
xmax2, ymax2 = int(box2[0]+box2[2]/2.0), int(box2[1]+box2[3]/2.0)
# 获取矩形框交集对应的左上角和右下角的坐标(intersection)
xx1 = np.max([xmin1, xmin2])
yy1 = np.max([ymin1, ymin2])
xx2 = np.min([xmax1, xmax2])
yy2 = np.min([ymax1, ymax2])
# 计算两个矩形框面积
area1 = (xmax1-xmin1) * (ymax1-ymin1)
area2 = (xmax2-xmin2) * (ymax2-ymin2)
inter_area = (np.max([0, xx2-xx1])) * (np.max([0, yy2-yy1])) # 计算交集面积
iou = inter_area / (area1+area2-inter_area+1e-6) # 计算交并比
return iou
def Giou(rec1,rec2):
#分别是第一个矩形左右上下的坐标
x1,x2,y1,y2 = rec1
x3,x4,y3,y4 = rec2
iou = Iou(rec1,rec2)
area_C = (max(x1,x2,x3,x4)-min(x1,x2,x3,x4))*(max(y1,y2,y3,y4)-min(y1,y2,y3,y4))
area_1 = (x2-x1)*(y1-y2)
area_2 = (x4-x3)*(y3-y4)
sum_area = area_1 + area_2
w1 = x2 - x1 #第一个矩形的宽
w2 = x4 - x3 #第二个矩形的宽
h1 = y1 - y2
h2 = y3 - y4
W = min(x1,x2,x3,x4)+w1+w2-max(x1,x2,x3,x4) #交叉部分的宽
H = min(y1,y2,y3,y4)+h1+h2-max(y1,y2,y3,y4) #交叉部分的高
Area = W*H #交叉的面积
add_area = sum_area - Area #两矩形并集的面积
end_area = (area_C - add_area)/area_C #闭包区域中不属于两个框的区域占闭包区域的比重
giou = iou - end_area
return giou
def Diou(bboxes1, bboxes2):
rows = bboxes1.shape[0]
cols = bboxes2.shape[0]
dious = torch.zeros((rows, cols))
if rows * cols == 0:
return dious
exchange = False
if bboxes1.shape[0] > bboxes2.shape[0]:
bboxes1, bboxes2 = bboxes2, bboxes1
dious = torch.zeros((cols, rows))
exchange = True
# #xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax->[:,0],[:,1],[:,2],[:,3]
w1 = bboxes1[:, 2] - bboxes1[:, 0]
h1 = bboxes1[:, 3] - bboxes1[:, 1]
w2 = bboxes2[:, 2] - bboxes2[:, 0]
h2 = bboxes2[:, 3] - bboxes2[:, 1]
area1 = w1 * h1
area2 = w2 * h2
center_x1 = (bboxes1[:, 2] + bboxes1[:, 0]) / 2
center_y1 = (bboxes1[:, 3] + bboxes1[:, 1]) / 2
center_x2 = (bboxes2[:, 2] + bboxes2[:, 0]) / 2
center_y2 = (bboxes2[:, 3] + bboxes2[:, 1]) / 2
inter_max_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
inter_min_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
out_max_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
out_min_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
inter = torch.clamp((inter_max_xy - inter_min_xy), min=0)
inter_area = inter[:, 0] * inter[:, 1]
inter_diag = (center_x2 - center_x1)**2 + (center_y2 - center_y1)**2
outer = torch.clamp((out_max_xy - out_min_xy), min=0)
outer_diag = (outer[:, 0] ** 2) + (outer[:, 1] ** 2)
union = area1+area2-inter_area
dious = inter_area / union - (inter_diag) / outer_diag
dious = torch.clamp(dious,min=-1.0,max = 1.0)
if exchange:
dious = dious.T
return dious
def Ciou(bboxes1, bboxes2):
rows = bboxes1.shape[0]
cols = bboxes2.shape[0]
cious = torch.zeros((rows, cols))
if rows * cols == 0:
return cious
exchange = False
if bboxes1.shape[0] > bboxes2.shape[0]:
bboxes1, bboxes2 = bboxes2, bboxes1
cious = torch.zeros((cols, rows))
exchange = True
w1 = bboxes1[:, 2] - bboxes1[:, 0]
h1 = bboxes1[:, 3] - bboxes1[:, 1]
w2 = bboxes2[:, 2] - bboxes2[:, 0]
h2 = bboxes2[:, 3] - bboxes2[:, 1]
area1 = w1 * h1
area2 = w2 * h2
center_x1 = (bboxes1[:, 2] + bboxes1[:, 0]) / 2
center_y1 = (bboxes1[:, 3] + bboxes1[:, 1]) / 2
center_x2 = (bboxes2[:, 2] + bboxes2[:, 0]) / 2
center_y2 = (bboxes2[:, 3] + bboxes2[:, 1]) / 2
inter_max_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
inter_min_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
out_max_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
out_min_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
inter = torch.clamp((inter_max_xy - inter_min_xy), min=0)
inter_area = inter[:, 0] * inter[:, 1]
inter_diag = (center_x2 - center_x1)**2 + (center_y2 - center_y1)**2
outer = torch.clamp((out_max_xy - out_min_xy), min=0)
outer_diag = (outer[:, 0] ** 2) + (outer[:, 1] ** 2)
union = area1+area2-inter_area
u = (inter_diag) / outer_diag
iou = inter_area / union
with torch.no_grad():
arctan = torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1)
v = (4 / (math.pi ** 2)) * torch.pow((torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1)), 2)
S = 1 - iou
alpha = v / (S + v)
w_temp = 2 * w1
ar = (8 / (math.pi ** 2)) * arctan * ((w1 - w_temp) * h1)
cious = iou - (u + alpha * ar)
cious = torch.clamp(cious,min=-1.0,max = 1.0)
if exchange:
cious = cious.T
return cious
box_1 = box1 = [0,0,8,6]
box_2 = box2 = [2,3,10,9]
print('Iou',Iou(box1, box2))
print('Giou',Giou(box1, box2))
box1 = torch.unsqueeze(torch.tensor(box1), dim = 0)
box2 = torch.unsqueeze(torch.tensor(box2), dim = 0)
print('Diou',Diou(box1, box2))
print('Ciou',Ciou(box1, box2))
