widerface数据集转成YOLO格式
原文章链接在这里,在实际操作中发现文件夹命名可以改进,所以自己修改了一下Widerface数据集 | widerface数据集转成YOLO格式_Liaojiajia-2020的博客-CSDN博客_widerface转yolo
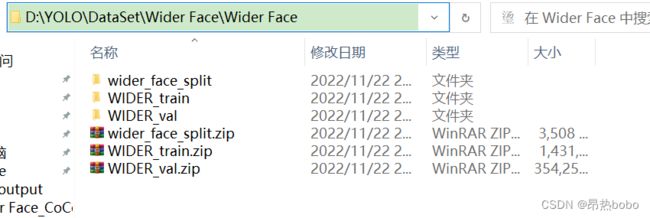
原始数据集
一、原始数据格式转为VOC格式
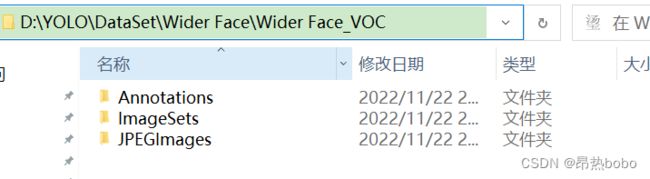
1、首先应该创建Wider Face_VOC文件夹,在里面创建三个文件夹:Annotations, ImageSets\Main, JPEGImages
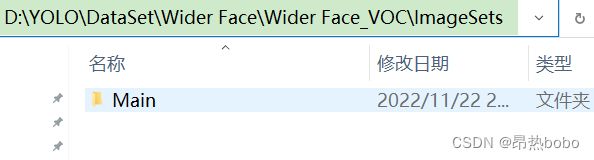
2、在 ImageSets\Main 文件夹下创建train.txt, val.txt
3、将rootdir,gtfile,im_folder,fwrite换成你自己的路径
下面代码段命名为face2voc.py
!!!注意需要执行两次,一次train,一次val
# coding:utf-8
from xml.dom.minidom import Document
import cv2
# 本程序可以将widerface转为VOC格式的数据
def writexml(filename, saveimg, bboxes, xmlpath):
doc = Document()
annotation = doc.createElement('annotation')
doc.appendChild(annotation)
folder = doc.createElement('folder')
folder_name = doc.createTextNode('widerface')
folder.appendChild(folder_name)
annotation.appendChild(folder)
filenamenode = doc.createElement('filename')
filename_name = doc.createTextNode(filename)
filenamenode.appendChild(filename_name)
annotation.appendChild(filenamenode)
source = doc.createElement('source')
annotation.appendChild(source)
database = doc.createElement('database')
database.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('wider face Database'))
source.appendChild(database)
annotation_s = doc.createElement('annotation')
annotation_s.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('PASCAL VOC2007'))
source.appendChild(annotation_s)
image = doc.createElement('image')
image.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('flickr'))
source.appendChild(image)
flickrid = doc.createElement('flickrid')
flickrid.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('-1'))
source.appendChild(flickrid)
owner = doc.createElement('owner')
annotation.appendChild(owner)
flickrid_o = doc.createElement('flickrid')
flickrid_o.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('muke'))
owner.appendChild(flickrid_o)
name_o = doc.createElement('name')
name_o.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('muke'))
owner.appendChild(name_o)
size = doc.createElement('size')
annotation.appendChild(size)
width = doc.createElement('width')
width.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(saveimg.shape[1])))
height = doc.createElement('height')
height.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(saveimg.shape[0])))
depth = doc.createElement('depth')
depth.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(saveimg.shape[2])))
size.appendChild(width)
size.appendChild(height)
size.appendChild(depth)
segmented = doc.createElement('segmented')
segmented.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('0'))
annotation.appendChild(segmented)
for i in range(len(bboxes)):
bbox = bboxes[i]
objects = doc.createElement('object')
annotation.appendChild(objects)
object_name = doc.createElement('name')
object_name.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('face'))
objects.appendChild(object_name)
pose = doc.createElement('pose')
pose.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('Unspecified'))
objects.appendChild(pose)
truncated = doc.createElement('truncated')
truncated.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('0'))
objects.appendChild(truncated)
difficult = doc.createElement('difficult')
difficult.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('0'))
objects.appendChild(difficult)
bndbox = doc.createElement('bndbox')
objects.appendChild(bndbox)
xmin = doc.createElement('xmin')
xmin.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(bbox[0])))
bndbox.appendChild(xmin)
ymin = doc.createElement('ymin')
ymin.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(bbox[1])))
bndbox.appendChild(ymin)
xmax = doc.createElement('xmax')
xmax.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(bbox[0] + bbox[2])))
bndbox.appendChild(xmax)
ymax = doc.createElement('ymax')
ymax.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(bbox[1] + bbox[3])))
bndbox.appendChild(ymax)
f = open(xmlpath, "w")
f.write(doc.toprettyxml(indent=''))
f.close()
rootdir = "D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face_VOC"
gtfile = "D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\wider_face_split\\wider_face_train_bbx_gt.txt"
im_folder = "D:\\YOLO\DataSet\\Wider Face\\WIDER_train\\WIDER_train\\images"
fwrite = open("D:\\YOLO\DataSet\\Wider Face_VOC\\ImageSets\\Main\\val.txt", "w")
# wider_face_train_bbx_gt.txt的文件内容
# 第一行为名字
# 第二行为头像的数量 n
# 剩下的为n行人脸数据
# 以下为示例
# 0--Parade/0_Parade_marchingband_1_117.jpg
# 9
# 69 359 50 36 1 0 0 0 0 1
# 227 382 56 43 1 0 1 0 0 1
# 296 305 44 26 1 0 0 0 0 1
# 353 280 40 36 2 0 0 0 2 1
# 885 377 63 41 1 0 0 0 0 1
# 819 391 34 43 2 0 0 0 1 0
# 727 342 37 31 2 0 0 0 0 1
# 598 246 33 29 2 0 0 0 0 1
# 740 308 45 33 1 0 0 0 2 1
with open(gtfile, "r") as gt:
while (True):
gt_con = gt.readline()[:-1]
if gt_con is None or gt_con == "":
break
im_path = im_folder + "/" + gt_con
print(im_path)
im_data = cv2.imread(im_path)
if im_data is None:
continue
# 可视化的部分
# cv2.imshow(im_path, im_data)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
numbox = int(gt.readline())
# 获取每一行人脸数据
bboxes = []
if numbox == 0: # numbox 为0 的情况处理
gt.readline()
else:
for i in range(numbox):
line = gt.readline()
infos = line.split(" ") # 用空格分割
# x y w h .....
bbox = (int(infos[0]), int(infos[1]), int(infos[2]), int(infos[3]))
# 绘制人脸框
# cv2.rectangle(im_data, (int(infos[0]), int(infos[1])),
# (int(infos[0]) + int(infos[2]), int(infos[1]) + int(infos[3])),
# color=(0, 0, 255), thickness=1)
bboxes.append(bbox) # 将一张图片的所有人脸数据加入bboxes
# cv2.imshow(im_path, im_data)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
filename = gt_con.replace("/", "_") # 将存储位置作为图片名称,斜杠转为下划线
fwrite.write(filename.split(".")[0] + "\n")
cv2.imwrite("{}/JPEGImages/{}".format(rootdir, filename), im_data)
xmlpath = "{}/Annotations/{}.xml".format(rootdir, filename.split(".")[0])
writexml(filename, im_data, bboxes, xmlpath)
fwrite.close()
二、VOC格式转为COCO格式
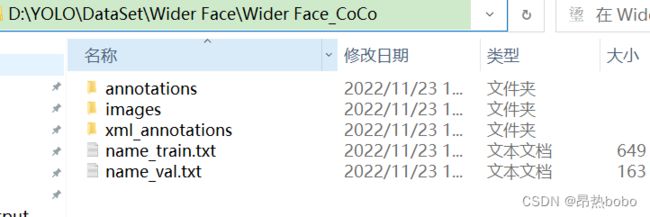
1、创建Wider Face_CoCo文件夹,在里面创建annotations, images, xml_annotations 这三个文件夹,第一个用于保存json文件,第二个用于保存图片,第三个用于保存已经分成train和val的xml的文件。创建两个文件name_train.txt,name_train.txt
2、创建Wider Face_YOLO文件夹,在里面创建images,labels文件夹,images_train.txt,
images_val.txt两个文件
第一步:转成COCO格式
文件名:I_voc2coco.py
# coding:utf-8
import os
import shutil
from tqdm import tqdm
# 根据/data/data/UAV2017/ImageSets/Layout里面的trainval.txt和test.txt挑选出训练集和测试集
SPLIT_PATH = "D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_VOC\\ImageSets\Main"
IMGS_PATH = "D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_VOC\\JPEGImages"
TXTS_PATH = "D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_VOC\\Annotations"
TO_IMGS_PATH = 'D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\images'
TO_TXTS_PATH = 'D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\xml_annotations'
data_split = ['train.txt', 'val.txt']
to_split = ['train', 'val']
train_file = 'D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_YOLO\\images_train.txt'
val_file = 'D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_YOLO\\images_val.txt'
train_file_txt = ''
val_file_txt = ''
for index, split in enumerate(data_split):
split_path = os.path.join(SPLIT_PATH, split)
# import pdb; pdb.set_trace()
to_imgs_path = os.path.join(TO_IMGS_PATH, to_split[index])
if not os.path.exists(to_imgs_path):
os.makedirs(to_imgs_path)
to_txts_path = os.path.join(TO_TXTS_PATH, to_split[index])
if not os.path.exists(to_txts_path):
os.makedirs(to_txts_path)
f = open(split_path, 'r')
count = 1
for line in tqdm(f.readlines(), desc="{} is copying".format(to_split[index])):
# 复制图片
src_img_path = os.path.join(IMGS_PATH, line.strip() + '.jpg')
# import pdb; pdb.set_trace()
dst_img_path = os.path.join(to_imgs_path, line.strip() + '.jpg')
if os.path.exists(src_img_path):
shutil.copyfile(src_img_path, dst_img_path)
else:
print("error file: {}".format(src_img_path))
if to_split[index] == 'train':
train_file_txt = train_file_txt + dst_img_path + '\n'
elif to_split[index] == 'val':
val_file_txt = val_file_txt + dst_img_path + '\n'
# 复制txt标注文件
src_txt_path = os.path.join(TXTS_PATH, line.strip() + '.xml')
dst_txt_path = os.path.join(to_txts_path, line.strip() + '.xml')
if os.path.exists(src_txt_path):
shutil.copyfile(src_txt_path, dst_txt_path)
else:
print("error file: {}".format(src_txt_path))
with open(train_file, 'w') as out_train:
out_train.write(train_file_txt)
with open(val_file, 'w') as out_val:
out_val.write(val_file_txt)
第二步:从原来打乱的XML标注文件中提取出train和val
文件名:II_voc2coco.py
!!!注意该文件也是执行两次,一次train,一次val
#### customized for crack detection dataset
#### usage : python3 voc2coco.py xml_dir ./data/xml --json_file ./val.json
import sys
import os
import json
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import glob
START_BOUNDING_BOX_ID = 1
PRE_DEFINE_CATEGORIES = {"face": 0}
def get(root, name):
vars = root.findall(name)
return vars
def get_and_check(root, name, length):
vars = root.findall(name)
if len(vars) == 0:
raise ValueError("Can not find %s in %s." % (name, root.tag))
if length > 0 and len(vars) != length:
raise ValueError(
"The size of %s is supposed to be %d, but is %d."
% (name, length, len(vars))
)
if length == 1:
vars = vars[0]
return vars
def get_filename_as_int(filename):
try:
# print(filename,filename[6:])
filename = filename.replace("\\", "/")
filename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(filename))[0]
if filename[:5] == "India":
return int("2" + filename[6:])
elif filename[:5] == "Japan":
return int("3" + filename[6:])
else:
return int("1" + filename[6:])
# return int(filename[6:])
except:
raise ValueError("Filename %s is supposed to be an integer." % (filename))
def get_categories(xml_files):
"""Generate category name to id mapping from a list of xml files.
Arguments:
xml_files {list} -- A list of xml file paths.
Returns:
dict -- category name to id mapping.
"""
acceptable_classes = ["car", "truck", "bus"]
classes_names = []
for xml_file in xml_files:
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
for member in root.findall("object"):
classes_names.append(member[0].text)
classes_names = list(set(classes_names))
# for item in classes_names :
# if item not in acceptable_classes :
# classes_names.remove(item)
# print("removed{}".format(item))
# classes_names.sort()
# print("clsnames : {}".format(classes_names))
return {name: i for i, name in enumerate(classes_names)}
def convert(xml_files, json_file):
json_dict = {"images": [], "type": "instances", "annotations": [], "categories": []}
if PRE_DEFINE_CATEGORIES is not None:
categories = PRE_DEFINE_CATEGORIES
else:
categories = get_categories(xml_files)
bnd_id = START_BOUNDING_BOX_ID
for xml_file in xml_files:
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
path = get(root, "path")
if len(path) == 1:
filename = os.path.basename(path[0].text)
elif len(path) == 0:
filename = get_and_check(root, "filename", 1).text
else:
raise ValueError("%d paths found in %s" % (len(path), xml_file))
## The filename must be a number
# import pdb; pdb.set_trace()
# image_id = get_filename_as_int(filename)
image_id = filename[:-4]
size = get_and_check(root, "size", 1)
width = int(get_and_check(size, "width", 1).text)
height = int(get_and_check(size, "height", 1).text)
image = {
"file_name": filename,
"height": height,
"width": width,
"id": filename[:-4],
}
json_dict["images"].append(image)
## Currently we do not support segmentation.
# segmented = get_and_check(root, 'segmented', 1).text
# assert segmented == '0'
for obj in get(root, "object"):
category = get_and_check(obj, "name", 1).text
if category not in categories:
continue
new_id = len(categories)
categories[category] = new_id
category_id = categories[category]
bndbox = get_and_check(obj, "bndbox", 1)
xmin = int(get_and_check(bndbox, "xmin", 1).text) - 1
ymin = int(get_and_check(bndbox, "ymin", 1).text) - 1
xmax = int(get_and_check(bndbox, "xmax", 1).text)
ymax = int(get_and_check(bndbox, "ymax", 1).text)
assert xmax > xmin
assert ymax > ymin
o_width = abs(xmax - xmin)
o_height = abs(ymax - ymin)
ann = {
"area": o_width * o_height,
"iscrowd": 0,
"image_id": image_id,
"bbox": [xmin, ymin, o_width, o_height],
"category_id": category_id,
"id": bnd_id,
"ignore": 0,
"segmentation": [],
}
json_dict["annotations"].append(ann)
bnd_id = bnd_id + 1
for cate, cid in categories.items():
cat = {"supercategory": "none", "id": cid, "name": cate}
json_dict["categories"].append(cat)
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(json_file), exist_ok=True)
json_fp = open(json_file, "w")
json_str = json.dumps(json_dict, indent=4)
json_fp.write(json_str)
json_fp.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description="Convert Pascal VOC annotation to COCO format."
)
# parser.add_argument("xml_dir", help="Directory path to xml files.", type=str)
# parser.add_argument("json_file", help="Output COCO format json file.", type=str)
# args = parser.parse_args()
xml_path = 'D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\xml_annotations\\val' # 这是xml文件所在的地址
json_file = 'D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\annotations\\val.json' # 这是你要生成的json文件
xml_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(xml_path, "*.xml"))
# If you want to do train/test split, you can pass a subset of xml files to convert function.
print("Number of xml files: {}".format(len(xml_files)))
convert(xml_files, json_file)
print("Success: {}".format(json_file))
三、VOC格式转成YOLO格式
!!!注意下面步骤需要执行两次,一次train,一次val
1、提取标注文件夹里面的文件名
文件名:extrace.py
# P02 批量读取文件名(不带后缀)
import os
file_path = "D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\xml_annotations\\val\\"
path_list = os.listdir(file_path) # os.listdir(file)会历遍文件夹内的文件并返回一个列表
# print(path_list)
path_name = [] # 把文件列表写入save.txt中
def saveList(pathName):
for file_name in pathName:
with open("D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\name_val.txt", "a") as f:
f.write(file_name.split(".")[0] + "\n")
def dirList(path_list):
for i in range(0, len(path_list)):
path = os.path.join(file_path, path_list[i])
if os.path.isdir(path):
saveList(os.listdir(path))
dirList(path_list)
saveList(path_list)
2、将xml格式转成yolo格式
文件名:voc_label.py
# 缺陷坐标xml转txt
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
classes = ['face'] # 输入缺陷名称,必须与xml标注名称一致
train_file = 'D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_YOLO\\images_val.txt'
train_file_txt = ''
wd = os.getcwd()
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / size[0]
dh = 1. / size[1]
box = list(box)
box[1] = min(box[1], size[0]) # 限制目标的范围在图片尺寸内
box[3] = min(box[3], size[1])
x = ((box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0) * dw
y = ((box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0) * dh
w = (box[1] - box[0]) * dw
h = (box[3] - box[2]) * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open(
'D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\xml_annotations\\val\\%s.xml' % (image_id)) # 读取xml文件路径
out_file = open('D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_YOLO\\labels\\val\\%s.txt' % (image_id),
'w') # 需要保存的txt格式文件路径
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes: # 检索xml中的缺陷名称
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
# if cls_id == 0 or cls_id == 11:
# continue
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
image_ids_train = open(
'D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\name_val.txt').read().strip().split() # 读取xml文件名索引
for image_id in image_ids_train:
convert_annotation(image_id)
anns = os.listdir('D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\xml_annotations\\val\\')
for ann in anns:
ans = ''
outpath = 'D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_YOLO\\labels\\val\\' + ann
if ann[-3:] != 'xml':
continue
train_file_txt = train_file_txt + 'D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_YOLO\\images\\val\\' + ann[
:-3] + 'jpg\n'
# import pdb
# pdb.set_trace()
with open(train_file, 'w') as outfile:
outfile.write(train_file_txt)
四、在转换过程中查看框是否正确
1、 查看VOC是否转换正确(文件命名为:xml_draw.py)
import os
import os.path
import xml.etree.cElementTree as ET
import cv2
def draw(image_path, xml_path, root_saved_path):
"""
图片根据标注画框
"""
src_img_path = image_path
src_ann_path = xml_path
for file in os.listdir(src_ann_path):
# print(file)
file_name, suffix = os.path.splitext(file)
# import pdb
# pdb.set_trace()
if suffix == '.xml':
# print(file)
xml_path = os.path.join(src_ann_path, file)
image_path = os.path.join(src_img_path, file_name+'.jpg')
img = cv2.imread(image_path)
tree = ET.parse(xml_path)
root = tree.getroot()
# import pdb
# pdb.set_trace()
for obj in root.iter('object'):
name = obj.find('name').text
xml_box = obj.find('bndbox')
x1 = int(xml_box.find('xmin').text)
x2 = int(xml_box.find('xmax').text)
y1 = int(xml_box.find('ymin').text)
y2 = int(xml_box.find('ymax').text)
cv2.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 0, 0), thickness=2)
# 字为绿色
# cv2.putText(img, name, (x1, y1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 255, 0), thickness=2)
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(root_saved_path, file_name+'.jpg'), img)
if __name__ == '__main__':
image_path = "D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\images\\val"
xml_path = "D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\xml_annotations\\val"
root_saved_path = "D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\data\\xml_output"
draw(image_path, xml_path, root_saved_path)
2、 查看COCO是否转换正确(文件命名为:json_draw.py)
import cv2
# import pandas as pd
import json
import os
# ground-truth
def select(json_path, outpath, image_path):
json_file = open(json_path)
infos = json.load(json_file)
images = infos["images"]
annos = infos["annotations"]
assert len(images) == len(images)
# import pdb;pdb.set_trace()
for i in range(len(images)):
im_id = images[i]["id"]
im_path = image_path + images[i]["file_name"]
img = cv2.imread(im_path)
for j in range(len(annos)):
if annos[j]["image_id"] == im_id:
x, y, w, h = annos[j]["bbox"]
x, y, w, h = int(x), int(y), int(w), int(h)
x2, y2 = x + w, y + h
# object_name = annos[j][""]
img = cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), thickness=1)
img_name = outpath + images[i]["file_name"]
# import pdb;pdb.set_trace()
cv2.imwrite(img_name, img)
# continue
# print(i)
print("Done!")
# predict
# def select(json_path, outpath, image_path):
# json_file = open(json_path)
# infos = json.load(json_file)
# for i in range(len(infos)):
# im_id = infos[i]["image_id"]
# im_path = image_path + str(infos[i]["image_id"]) + '.jpg'
# # import pdb;pdb.set_trace()
# img_name = outpath + str(infos[i]["image_id"]) + '.jpg'
# score = str(infos[i]["score"])
# if not os.path.exists(img_name):
# img = cv2.imread(im_path)
# else:
# img = cv2.imread(img_name)
# # if float(score) < 0.5:
# # continue
# # else:
# x, y, w, h = infos[i]["bbox"]
# x, y, w, h = int(x), int(y), int(w), int(h)
# x2, y2 = x + w, y + h
# c_x, c_y = int((x + x2) / 2), int((y + y2) / 2)
# cla = str(infos[i]["category_id"])
# # import pdb;pdb.set_trace()
# # img = cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
# if float(score) <= 0.3:
# cv2.circle(img, (c_x, c_y), 5, (0,0,int(255*float(score))), -1) # red
# continue
# elif float(score) > 0.3 and float(score) <= 0.6:
# cv2.circle(img, (c_x, c_y), 5, (int(255*float(score)),255,0), -1) # green
# elif float(score) > 0.6:
# cv2.circle(img, (c_x, c_y), 5, (0,int(255*float(score)),255), -1) # yellow
# # cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255), thickness=2)
# # cv2.putText(img, score, (x, y + 5), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# # cv2.putText(img, cla,(c_x, c_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (255, 0, 0), 2)
# img_name = outpath + str(infos[i]["image_id"]) + '.jpg'
# # import pdb;pdb.set_trace()
# cv2.imwrite(img_name, img)
# print("Done!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
json_path = "D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\annotations\\val.json"
out_path = "D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\data\\json_output\\"
image_path = "D:\\YOLO\\DataSet\\Wider Face\\Wider Face_CoCo\\images\\val\\"
select(json_path, out_path, image_path)