数据结构与算法之二叉排序(查找)树
前言
前面介绍学习的大多是线性表相关的内容,把指针搞懂后其实也没有什么难度。规则相对是简单的。
再数据结构中树、图才是数据结构标志性产物,(线性表大多都现成api可以使用),因为树的难度相比线性表大一些并且树的拓展性很强,你所知道的树、二叉树、二叉排序树,AVL树,线索二叉树、红黑树、B数、线段树等等高级数据结构。然而二叉排序树是所有的基础,所以彻底搞懂二叉排序树也是非常重要的。
树
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-l2N9eCfF-1588738639653)(https://s2.ax1x.com/2020/03/01/32PwHH.png)]
二叉树也是树的一种,而二叉排序树又是二叉树的一种。
树是递归的,将树的任何一个节点以及节点下的节点都能组合成一个新的树。并且很多操作基于递归完成。
根节点: 最上面的那个节点(root),根节点没有前驱节点,只有子节点(0个或多个都可以)
层数: 一般认为根节点是第1层(有的也说第0层)。而树的高度就是层数最高(上图层数开始为1)节点的层数
节点关系: 父节点:就是链接该节点的上一层节点,孩子节点:和父节点对应,上下关系。而祖先节点是父节点的父节点(或者祖先)节点。兄弟节点:拥有同一个父节点的节点们!
度: 节点的度就是节点拥有孩子节点的个数(是孩子不是子孙).而树的度(最大)节点的度。同时,如果度大于0就成为分支节点,度等于0就成为叶子节点(没有子孙)。
相关性质:
~树的节点数=所有节点度数+1.
度为m的树第i层最多有mi-1个节点。(i>=1)
高度而h的m叉树最多(mh-1)/(m-1)个节点(等比数列求和)
n个节点的m叉树最小高度[logm(n(m-1)+1)]
二叉树
二叉树是一树的一种,但应用比较多,所以需要深入学习。二叉树的每个节点最多只有两个节点。
二叉树与度为2的树的区别:
度为2的的树必须有三个节点以上,二叉树可以为空。
二叉树的度不一定为2:比如说斜树。
二叉树有左右节点区分,而度为2的树没有左右节点的区分。
几种特殊二叉树:
满二叉树。高度为n的满二叉树有2n-1个节点
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-VqIZLmwD-1588738639660)(https://s2.ax1x.com/2020/03/01/32PNjO.png)]
完全二叉树:上面一层全部满,最下一层从左到右顺序排列
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-OMAsTB0Y-1588738639665)(https://s2.ax1x.com/2020/03/01/32PdDe.png)]
二叉排序树:树按照一定规则插入排序(本文详解)。
平衡二叉树:树上任意节点左子树和右子树深度差距不超过1.
二叉树性质:
相比树,二叉树的性质就是树的性质更加具体化。
非空二叉树叶子节点数=度为2的节点树+1.本来一个节点如果度为1.那么一直延续就一个叶子,但如果出现一个度为2除了延续原来的一个节点,会多出一个节点需要维系。所以到最后会多出一个叶子。
非空第i层最多有2i-1个节点。
高为h的树最多有2h-1个节点(等比求和)。
完全二叉树若从左往右,从上到下编号如图:

二叉排序(搜索)树
概念
前面铺垫那么多,咱们言归正传,详细实现一个二叉排序树。首先要了解二叉排序树的规则:
从任意节点开始,节点左侧节点值总比节点右侧值要小。
例如。一个二叉排序树依次插入15,6,23,7,4,71,5,50会形成下图顺序
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-6G59Yo52-1588738639668)(https://s2.ax1x.com/2020/03/01/32PY36.png)]
构造
首先二叉排序树是由若干节点构成。
对于node需要这些属性:left,right,和value。其中left和right是左右指针,而value是储存的数据,这里用*int *类型。
node类构造为:
class node {//结点
public int value;
public node left;
public node right;
public node()
{
}
public node(int value)
{
this.value=value;
this.left=null;
this.right=null;
}
public node(int value,node l,node r)
{
this.value=value;
this.left=l;
this.right=r;
}
}
~既然节点构造好了,那么就需要节点等其他信息构造成树。有了链表构造经验,很容易得知一棵树最主要的还是root根节点。
所以树的构造为:
public class BinarySortTree {
node root;//根
public BinarySortTree()
{root=null;}
public void makeEmpty()//变空
{root=null;}
public boolean isEmpty()//查看是否为空
{return root==null;}
//各种方法
}
主要方法
既然已经构造号一棵树,那么就需要实现主要的方法。因为二叉排序树中每个节点都能看作一棵树。所以我们创建方法的是时候加上节点参数(也就是函数对每一个节点都能有效)
findmax(),findmin()
findmin()找到最小节点:
因为所有节点的最小都是往左插入,所以只需要找到最左侧的返回即可。
findmax()找到最大节点:
因为所有节点大的都是往右面插入,所以只需要找到最右侧的返回即可。
代码使用递归函数
public node findmin(node t)//查找最小返回值是node,调用查看结果时需要.value
{
if(t==null) {return null;}
else if(t.left==null) {return t;}
else return(findmin(t.left));
}
public node findmax(node t)//查找最大
{
if(t==null) {return null;}
else if(t.right==null) {return t;}
else return(findmax(t.right));
}
isContains(int x)
这里的意思是查找二叉查找树中是否存在x。
假设我们我们插入x,那么如果存在x我们一定会在查找插入路径的过程中遇到x。因为你可以如果已经存在的点,再它的前方会走一次和它相同的步骤。也就是说前面固定,我来1w次x,那么x都会到达这个位置。那么我们直接进行查找比较即可!
public boolean isContains(int x)//是否存在
{
node current=root;
if(root==null) {return false;}
while(current.value!=x&¤t!=null)
{
if(x<current.value) {current=current.left;}
if(x>current.value) {current=current.right;}
if(current==null) {return false;}//在里面判断如果超直接返回
}
//如果在这个位置判断是否为空会导致current.value不存在报错
if(current.value==x) {return true;}
return false;
}
insert(int x)
插入的思想和前面isContains类似。找到自己的位置(空位置)插入。但是又不太一样。你可能会疑问为什么不直接找到最后一个空,然后将current赋值过去current=new node(x)。这样的化current就相当于指向一个new node(x)节点。和树就脱离关系,所以要提前判定是否为空,若为空将它的left或者right赋值即可。
public node insert(int x)// 插入 t是root的引用
{
node current = root;
if (root == null) {
root = new node(x);
return root;
}
while (current != null) {
if (x < current.value) {
if (current.left == null) {
return current.left = new node(x);}
else current = current.left;}
else if (x > current.value) {
if (current.right == null) {
return current.right = new node(x);}
else current = current.right;
}
}
return current;//其中用不到
}
delete(int x)
删除操作算是一个相对较难理解的操作了。
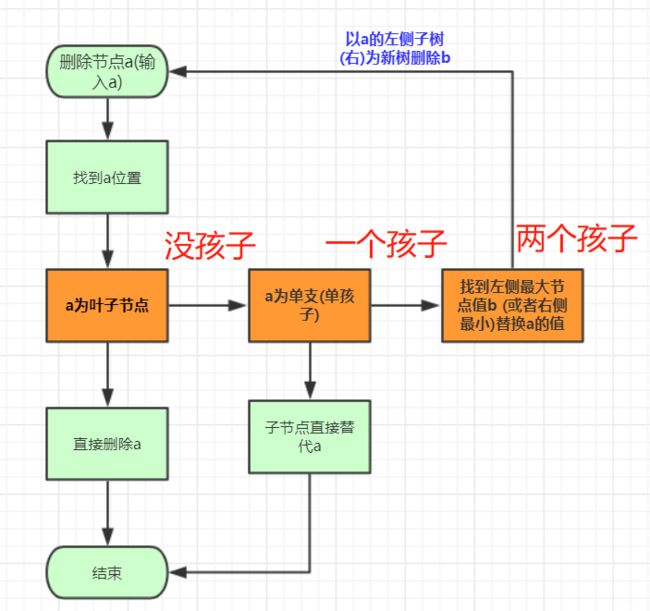
删除节点规则:
先找到这个点。这个点用这个点的子树可以补上的点填充该点,然后在以这个点为头删除替代的子节点(调用递归)然后在添加到最后情况(只有一个分支,等等)。
首先要找到移除的位置,然后移除的那个点分类讨论,如果有两个儿子,就选右边儿子的最左侧那个点替代,然后再子树删除替代的那个点。如果是一个节点,判断是左空还是右空,将这个点指向不空的那个。不空的那个就替代了这个节点。入股左右都是空,那么他自己变空null就删除了。
删除的节点没有子孙:
这种情况不需要考虑,直接删除即可。(途中红色点)。另节点=null即可。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-bHpkAQ1S-1588738639675)(https://s2.ax1x.com/2020/03/01/32k78I.png)]
左节点为空、右节点为空:
左右节点均不空
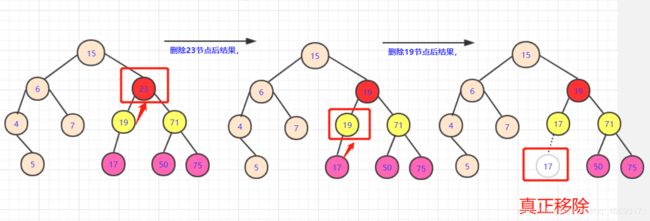
这种情况相对是复杂的。因为这涉及到一个策略问题。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5Ia4CMG7-1588738639679)(https://s2.ax1x.com/2020/03/01/32PDUA.png)]
如果拿19或者71节点填补。虽然可以保证部分侧大于小于该节点,但是会引起合并的混乱.比如你若用71替代23节点。那么你需要考虑三个节点(19,50,75)之间如何处理,还要考虑他们是否满,是否有子女。这是个极其复杂的过程。
首先,我们要分析我们要的这个点的属性:能够继承被删除点的所有属性。如果取左侧节点(例如17)那么首先能满足所有右侧节点都比他大(右侧比左侧大)。那么就要再这边选一个最大的点让左半枝都比它小。我们分析左支最大的点一定是子树最右侧!
如果这个节点是最底层我们很好考虑,可以直接替换值,然后将最底层的点删除即可。但是如果这个节点有左枝。我们该怎么办?
这个分析起来也不难,用递归的思想啊。我们删除这个节点,用可以满足的节点替换了。会产生什么样的后果?
多出个用过的19节点,转化一下,在左子树中删除19的点!那么这个问题又转化为删除节点的问题,查找左子树中有没有能够替代19这个点的。
所以整个删除算法流程为:
代码为:
public node remove(int x, node t)// 删除节点
{
if (t == null) {
return null;
}
if (x < t.value) {
t.left = remove(x, t.left);
} else if (x > t.value) {
t.right = remove(x, t.right);
} else if (t.left != null && t.right != null)// 左右节点均不空
{
t.value = findmin(t.right).value;// 找到右侧最小值替代
t.right = remove(t.value, t.right);
} else // 左右单空或者左右都空
{
if (t.left == null && t.right == null) {
t = null;
} else if (t.right != null) {
t = t.right;
} else if (t.left != null) {
t = t.left;
}
return t;
}
return t;
}
完整代码
二叉排序树完整代码为:
package 二叉树;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class BinarySortTree {
class node {// 结点
public int value;
public node left;
public node right;
public node() {
}
public node(int value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
public node(int value, node l, node r) {
this.value = value;
this.left = l;
this.right = r;
}
}
node root;// 根
public BinarySortTree() {
root = null;
}
public void makeEmpty()// 变空
{
root = null;
}
public boolean isEmpty()// 查看是否为空
{
return root == null;
}
public node findmin(node t)// 查找最小返回值是node,调用查看结果时需要.value
{
if (t == null) {
return null;
} else if (t.left == null) {
return t;
} else
return (findmin(t.left));
}
public node findmax(node t)// 查找最大
{
if (t == null) {
return null;
} else if (t.right == null) {
return t;
} else
return (findmax(t.right));
}
public boolean isContains(int x)// 是否存在
{
node current = root;
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
while (current.value != x && current != null) {
if (x < current.value) {
current = current.left;
}
if (x > current.value) {
current = current.right;
}
if (current == null) {
return false;
} // 在里面判断如果超直接返回
}
// 如果在这个位置判断是否为空会导致current.value不存在报错
if (current.value == x) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public node insert(int x)// 插入 t是root的引用
{
node current = root;
if (root == null) {
root = new node(x);
return root;
}
while (current != null) {
if (x < current.value) {
if (current.left == null) {
return current.left = new node(x);}
else current = current.left;}
else if (x > current.value) {
if (current.right == null) {
return current.right = new node(x);}
else current = current.right;
}
}
return current;//其中用不到
}
public node remove(int x, node t)// 删除节点
{
if (t == null) {
return null;
}
if (x < t.value) {
t.left = remove(x, t.left);
} else if (x > t.value) {
t.right = remove(x, t.right);
} else if (t.left != null && t.right != null)// 左右节点均不空
{
t.value = findmin(t.right).value;// 找到右侧最小值替代
t.right = remove(t.value, t.right);
} else // 左右单空或者左右都空
{
if (t.left == null && t.right == null) {
t = null;
} else if (t.right != null) {
t = t.right;
} else if (t.left != null) {
t = t.left;
}
return t;
}
return t;
}
}