【AlgorithmStar机器学习】AS机器学习库特征工程使用说明文档
目录
Algorithm Star介绍
概述
AS库的一般处理流程
数据采集与清洗
向量生成与特征提取选择
机器学习
后续处理
Algorithm Star使用
数据类型-操作数
浮点类型操作数
整数类型操作数
复数
特征提取
字典特征提取
词频特征提取
特征选择
基于冗余排名比例去除
基于相关系数去除
机器学习
聚合计算
分类计算
差异计算
路径计算
数据预处理(标准化/归一化)
概率计算
决策计算
模型预测
Algorithm Star开源协议
Algorithm Star介绍
概述
Algorithm Star,简称“AS”,中文名为算法之星,由Ling Yu Zhao开发,是针对机器学习过程中的Java库,其具有良好的Java与Scala兼容性,于1.14版本开始重大改动,其中包含样本洗牌随机分布,特征选择,特征提取,度量计算,差异计算,路径推断,分类等计算组件,同时也具有运算符风格的复数,坐标,向量,矩阵等操作数,开发者Ling Yu Zhao于2022年发布的一款开源库,能够将复杂的机器学习简单化。
Algorithm Star采用apache2.0版本开源协议。支持通过maven坐标获取到框架本身,目前在GitHub中进行托管(GitHub - BeardedManZhao/algorithmStar: Toolkits for various algorithms, support vector computing and other functions, machine learning and mathematics, medicine, artificial intelligence and other fields of high practicality. | 用于各种算法、支持向量计算等功能,机器学习和数学、医学、人工智能等领域具有很高的实用性。)。
AS库的一般处理流程
数据采集与清洗
指的是数据的获取操作,在这一步获取到的数据是各种类型的原始数据,往往需要使用到各种大数据技术来采集到我们需要的数据,是整个工程中的第一项任务,在这一项任务中获取到的数据往往是具有噪音的数据,其中包含许多的冗余,因此要进行第二步,针对采集到的数据进行简单清洗。
数据清洗的方式有多种,例如去除空值与不合法的行等,使得其能够被按照预期转换,第一层过滤之后开始进行特征提取,将数据本身转换成为向量或矩阵等。
向量生成与特征提取选择
针对数据样本以及我们的目的和需求,对文本使用合适的特征提取操作,将获取到的数据转换成为AS中的向量/矩阵对象,使得其具有运算功能。
值得注意的是,多行数据的特征提取往往都是提取成为一个矩阵,那么矩阵中如果有一些没有特征的行向量,这将会影响最终的模型误差,因此对于这些行向量应进行特征选择操作,去除掉。
机器学习
作为整个特征工程中的核心操作,是需要频繁与AS库进行交互的一项任务,此任务中,需要涉及到AS库中的各种计算组件,通过这些计算组件达到最终的特征处理需求,目前库中有诸多函数,其中支持8种以上距离算法,3种以上的聚合算法,两种分类算法,5种差异算法等诸多机器学习算法,每一种算法在AS库中都是一个计算组件对象,且可以支持诸多操作组件,例如计算坐标之间的距离,计算矩阵中多个向量之间的类别等。
在计算过程中,AS库将遵循不拷贝原则,能不拷贝出一个新的对象就不拷贝,尽量在不修改原数据的基础上针对结果进行计算,当然,其中作为被计算矩阵与向量对象,允许用户直接获取到正在维护中的只读数组,也允许用户直接将正在维护中的数组拷贝出来一份新数据对象。
后续处理
在经过复杂的机器学习之后,我们应该会得到一种数据模型与数据结果,在这里的结果可以进行校验与后续的数据使用操作等,通过AS库,会使得Java中的机器学习不再困难与痛苦,多个重载函数的配合,使得Java中原生的基本数据类型也可以传递给计算组件进行机器学习的任务。
Algorithm Star使用
数据类型-操作数
操作数是AS库中的被计算对象,例如向量等,这类对象在AS库中能够实现加减乘除等基本运算,在AS库中每一个对象都在维护一个数组,这些数组在向量对象中的表现形式是一个基元的基本数据类型数组,因此在计算的时候具有良好的性能与原生支持。
操作数接口中的常用通用函数
Vector
|
|
方法和说明 |
| Object |
clone |
|
|
copyToNewArray |
|
|
expand |
|
|
getNumberOfDimensions |
|
|
innerProduct 计算两个向量的内积,也称之为数量积,具体实现请参阅api说明 Calculate the inner product of two vectors, also known as the quantity product, please refer to the api node for the specific implementation |
|
|
moduleLength 计算该向量的模长,具体实现请参阅api说明 Calculate the modulo length of the vector, please refer to the api node for the specific implementation |
|
|
multiply 两个向量相乘,同时也是两个向量的外积,具体实现请参阅api说明 The multiplication of two vectors is also the outer product of the two vectors. |
|
|
shuffle 将本对象中的所有数据进行洗牌打乱,随机分布数据行的排列。 |
| String |
toString |
ASVector
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
|
|
add 在两个向量对象之间进行计算的函数,自从1.13版本开始支持该函数的调用,该函数中的计算并不会产生一个新的向量,而是将计算操作作用于原操作数中 The function that calculates between two vector objects supports the call of this function since version 1.13. |
|
|
diff 在两个向量对象之间进行计算的函数,自从1.13版本开始支持该函数的调用,该函数中的计算并不会产生一个新的向量,而是将计算操作作用于原操作数中 The function that calculates between two vector objects supports the call of this function since version 1.13. |
|
|
multiply 在两个向量对象之间进行计算的函数,自从1.13版本开始支持该函数的调用,该函数中的计算并不会产生一个新的向量,而是将计算操作作用于原操作数中 The function that calculates between two vector objects supports the call of this function since version 1.13. |
|
|
reFresh 刷新操作数对象的所有字段 |
|
|
toArray 获取到本向量对象正在维护中的数组对象,注意,这里不会进行拷贝操作。 |
RangeVector
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
|
|
copyToNewArray |
|
|
expand |
|
|
forEach 区间内元素迭代器 Element iterator in interval |
|
|
getRangeEnd |
|
|
getRangeStart |
|
|
getRangeSum |
|
|
moduleLength 计算该向量的模长,具体实现请参阅api说明 Calculate the modulo length of the vector, please refer to the api node for the specific implementation |
|
|
shuffle 将本对象中的所有数据进行洗牌打乱,随机分布数据行的排列。 |
|
|
size |
|
|
toVector 将本区间的向量转换成具体向量。 |
Matrix
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
| ImplementationType |
add 在两个向量对象之间进行计算的函数,自从1.13版本开始支持该函数的调用,该函数中的计算并不会产生一个新的向量,而是将计算操作作用于原操作数中 The function that calculates between two vector objects supports the call of this function since version 1.13. |
|
|
copyToNewArray |
|
|
copyToNewArrays 该方法将会获取到矩阵中的二维数组,值得注意的是,在该函数中获取到的数组是一个新的数组,不会有任何的关系。 |
| ImplementationType |
diff 在两个向量对象之间进行计算的函数,自从1.13版本开始支持该函数的调用,该函数中的计算并不会产生一个新的向量,而是将计算操作作用于原操作数中 The function that calculates between two vector objects supports the call of this function since version 1.13. |
|
|
get 获取到矩阵中指定坐标点的数值 |
|
|
getColCount |
|
|
getRowCount |
| ElementType |
innerProduct |
|
|
isUnlock |
| ImplementationType |
multiply 在两个向量对象之间进行计算的函数,自从1.13版本开始支持该函数的调用,该函数中的计算并不会产生一个新的向量,而是将计算操作作用于原操作数中 The function that calculates between two vector objects supports the call of this function since version 1.13. |
|
|
toArray |
| ArraysType |
toArrays 该方法将会获取到矩阵中的二维数组,注意,与toArray一样返回的是正在被维护的数组对象,建议作为只读变量使用。 |
| String |
toString |
|
|
transpose 将现有矩阵的转置矩阵获取到 Get the transpose of an existing matrix into |
NumberMatrix
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
|
|
deleteRelatedDimensions 删除与目标索引维度相关的所有行维度,并返回新矩阵对象。 |
|
|
featureSelection 去除冗余特征维度,将当前矩阵中的每一个维度都进行方差或无向差计算,并将过于稳定的冗余特征去除。 |
Coordinate
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
| ImplementationType |
extend 显式拓展到子类的函数 |
|
|
getNumberOfDimensions 一般是获取到坐标对象中的维度 |
IntegerCoordinates
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
| ImplementationType |
extend 与 父类函数的作用 一样 |
|
|
getNumberOfDimensions 与 父类函数的作用 一样 |
|
|
toArray 获取到坐标的每一个维度的值组成的数组 |
FloatingPointCoordinates
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
| ImplementationType |
extend 与 父类函数的作用 一样 |
|
|
getNumberOfDimensions 与 父类函数的作用 一样 |
|
|
toArray 获取到坐标的每一个维度的值组成的数组 |
浮点类型操作数
能够通过一个浮点数组创建出来其对应的操作数对象,操作数对象中具有强大的计算功能。
package zhao.algorithmMagic;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.matrix.DoubleMatrix;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.vector.DoubleVector;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MAIN1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构建出Java数组
double[] ints1 = new double[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
double[] ints2 = new double[]{10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60};
// 构建出整形向量
DoubleVector parse1 = DoubleVector.parse(ints1);
DoubleVector parse2 = DoubleVector.parse(ints2);
// 对向量进行加减基本运算,并打印结果
System.out.println(">>> 1: =========");
System.out.println(parse2.add(parse1));
System.out.println(parse2.diff(parse1));
// 进行连减
System.out.println(parse2.diff(parse1).diff(parse1).diff(parse1));
// 进行内积与外积计算
System.out.println(">>> 2: =========");
System.out.println(parse2.innerProduct(parse1));
System.out.println(parse2.multiply(parse1));
// 将两个向量对象组合成为矩阵
DoubleMatrix matrix = DoubleMatrix.parse(parse1, parse2);
// 进行特征选择,在这里我们选择清理掉特征突出性较小排名中,前70% 的维度
System.out.println(">>> 3: =========");
DoubleMatrix integerMatrix = matrix.featureSelection(0.7);
// 打印去除结果
System.out.println(integerMatrix);
// 获取到向量中的数组对象
System.out.println(">>> 4: =========");
double[] ints3 = parse1.copyToNewArray();
double[] ints4 = parse2.copyToNewArray();
double[] ints5 = parse1.toArray();
double[] ints6 = parse2.toArray();
// 修改 ints5 ints6 两个数组的数值
// 会导致ints1 ints2 以及其所有对象发生变化,这是因为AS允许用户直接从对象中获取到数组
ints5[1] = 1024;
ints6[1] = 1024;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints1));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints2));
// 而修改 ints3 ints4 则不会发生这种情况
// 因此在需要对数组进行修改的时候,建议使用copyToNewArray
ints3[1] = 2048;
ints4[1] = 2048;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints1));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints2));
}
}整数类型操作数
package zhao.algorithmMagic;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.matrix.IntegerMatrix;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.vector.IntegerVector;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MAIN1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构建出Java数组
int[] ints1 = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
int[] ints2 = new int[]{10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60};
// 构建出整形向量
IntegerVector parse1 = IntegerVector.parse(ints1);
IntegerVector parse2 = IntegerVector.parse(ints2);
// 对向量进行加减基本运算,并打印结果
System.out.println(">>> 1: =========");
System.out.println(parse2.add(parse1));
System.out.println(parse2.diff(parse1));
// 进行连减
System.out.println(parse2.diff(parse1).diff(parse1).diff(parse1));
// 进行内积与外积计算
System.out.println(">>> 2: =========");
System.out.println(parse2.innerProduct(parse1));
System.out.println(parse2.multiply(parse1));
// 将两个向量对象组合成为矩阵
IntegerMatrix matrix = IntegerMatrix.parse(parse1, parse2);
// 进行特征选择,在这里我们选择清理掉特征突出性较小排名中,前70% 的维度
System.out.println(">>> 3: =========");
IntegerMatrix integerMatrix = matrix.featureSelection(0.7);
// 打印去除结果
System.out.println(integerMatrix);
// 获取到向量中的数组对象
System.out.println(">>> 4: =========");
int[] ints3 = parse1.copyToNewArray();
int[] ints4 = parse2.copyToNewArray();
int[] ints5 = parse1.toArray();
int[] ints6 = parse2.toArray();
// 修改 ints5 ints6 两个数组的数值
// 会导致ints1 ints2 以及其所有对象发生变化
// 这是因为AS允许用户直接从对象中获取到数组
ints5[1] = 1024;
ints6[1] = 1024;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints1));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints2));
// 而修改 ints3 ints4 则不会发生这种情况
// 因此在需要对数组进行修改的时候,建议使用copyToNewArray
ints3[1] = 2048;
ints4[1] = 2048;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints1));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints2));
}
}复数
package zhao.algorithmMagic;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.ComplexNumber;
public class MAIN1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建2个复数对象
ComplexNumber complexNumber1 = ComplexNumber.parse("1 + 2i");
ComplexNumber complexNumber2 = ComplexNumber.parse(2, 1);
// 打印两个复数对象
System.out.println(">>> 1: =========");
System.out.println(complexNumber1);
System.out.println(complexNumber2);
System.out.println(
"complexNumber1 的实部 = " + complexNumber1.getReal() +
"\tcomplexNumber1 的虚部 = " + complexNumber1.getImaginary()
);
// 对两个复数对象进行基本运算
System.out.println(">>> 2: =========");
System.out.println(complexNumber1.add(complexNumber2));
System.out.println(complexNumber1.diff(complexNumber2));
System.out.println(complexNumber1.multiply(complexNumber2));
System.out.println(complexNumber1.divide(complexNumber2));
// 获取到两个复数的共轨
System.out.println(">>> 3: =========");
System.out.println(complexNumber1.conjugate());
System.out.println(complexNumber2.conjugate());
}
}特征提取
特征提取的本质就是将一份计算机中并不认识的数据,转换成为向量或矩阵这种计算机可以用来计算的对象,使得后续的数据处理流程不会因此受挫,AS库中的特征提取主要针对字符串类的数据,接下来就进行一下演示!
字典特征提取
字典特征提取是将每一个数据作为矩阵中的一个行向量,AS库中采用one-hot编码的形式将数据进行转换,接下来看一个实际的例子。
代码与运行结果
package zhao.algorithmMagic;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.featureExtraction.DictFeatureExtraction;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.matrix.ColumnIntegerMatrix;
public class MAIN1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取到字典特征提取组件
DictFeatureExtraction dict = DictFeatureExtraction.getInstance("dict");
// 构造一个需要被提取的数组,其中每一个元素都会作为一个行向量,每一个行内数据会作为一个列字段
String[] strings = {
"cat", "dog", "turtle", "fish", "cat"
};
// 开始提取特征矩阵
ColumnIntegerMatrix extract = dict.extract(strings);
// 打印矩阵
System.out.println(extract);
// 打印矩阵的hashMap形式
extract.toHashMap().forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(value.toString() + '\t' + key));
}
}接下来是运行结果,在运行结果中可以看到,针对所有的行数据都构建成为了一个数组,每一个数组都是一个向量对象,可以看到其中数据对应的值在每一列都是对应的,其中1代表所属标记,0代表不属于。
简单来说就是在进行字典特征提取之前将每一个行数据作为了一种类别,在构造的时候,为对应类别打上属于标记!
通过toHashMap函数可以获取到不同行数据对应的向量值。
词频特征提取
词频特征提取,顾名思义就是词频统计,一句话中的词频往往可以体现出这句话要表达的意义,本次就进行AS库中的词频特征向量提取实现。
代码与运行结果
package zhao.algorithmMagic;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.featureExtraction.WordFrequency;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.matrix.ColumnIntegerMatrix;
public class MAIN1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取到词频特征提取组件
WordFrequency word = WordFrequency.getInstance("word");
// 构建一些被统计的文本
String[] data = {
"I love you, Because you are beautiful.",
"I need you. Because I'm trapped"
};
// 开始统计
ColumnIntegerMatrix extract1 = word.extract(data);
// 打印结果
System.out.println(extract1);
}
}下面是运行结果,可以看到它返回的是一个具有行列的整形矩阵,在矩阵中,列字段代表每一个被提取的文本,在矩阵中的行字段代表每一种词,其中矩阵的数值就是代表的对应词的出现频率。
特征选择
基于冗余排名比例去除
代码与运行结果
特征选择是所有矩阵中都可以使用的一个函数,其于1.14版本后开始支持,特征选择能够将诸多的冗余特征去除掉,AS库中的矩阵进行的特征选择都是基于行向量的操作,接下来是矩阵冗余特征去除实现!
package zhao.algorithmMagic;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.matrix.DoubleMatrix;
public class MAIN1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个矩阵对象,其中包含一些不具有特征突出行的向量
DoubleMatrix doubleMatrix = DoubleMatrix.parse(
new double[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6},
new double[]{1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 1}, // 过于稳定,缺少特征突出性
new double[]{10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60}
);
System.out.println(doubleMatrix);
// 开始调用特征去除函数,去除其中百分之40的行,并返回新矩阵
DoubleMatrix doubleMatrix1 = doubleMatrix.featureSelection(0.4);
System.out.println(doubleMatrix1);
}
}基于相关系数去除
代码与运行结果
package zhao.algorithmMagic;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.matrix.ColumnDoubleMatrix;
public class MAIN1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个矩阵对象,其中包含一些相关联的数据,本次要求将与年龄相关联的数据全部删掉
ColumnDoubleMatrix columnDoubleMatrix = ColumnDoubleMatrix.parse(
new String[]{"人员编号", "人员年龄", "人员工资(k)", "幸福指数"},
new String[]{"N1", "N2", "N3", "N4", "N5"},
new double[]{1, 25, 14, 16},
new double[]{2, 45, 12, 10},
new double[]{3, 33, 13, 12},
new double[]{4, 42, 16, 17},
new double[]{5, 25, 12, 10}
);
System.out.println(columnDoubleMatrix);
// 转置矩阵
columnDoubleMatrix = columnDoubleMatrix.transpose();
System.out.println(columnDoubleMatrix);
// 开始去除与第3行正相关的所有维度数据 TODO 需要保证相关维度的值接近!
ColumnDoubleMatrix columnDoubleMatrix1 = columnDoubleMatrix.deleteRelatedDimensions(2, 0.5, 1);
// 打印新矩阵
System.out.println(columnDoubleMatrix1);
}
}机器学习
是特征工程中及其重要的一部分,A库中有诸多的算法计算组件,通过不同的计算组件实现不同的计算需求与学习目的,每一个计算组件采用惰性加载,不会将所有的计算组件全都实例化到内存中,减少冗余内存占用。度量计算
能够将两个坐标或其它操作数之间的距离计算出来,并将计算出来的结果作为函数的返回值,接下来看一些与之相关的所有函数。
度量计算函数说明
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
|
|
getTrueDistance 获取两个序列之间的距离 Get the Canberra distance between two sequences (note that there is no length check function here, if you need to use this method, please configure the array length check outside) |
|
|
getTrueDistance 计算一个路线的起始点与终止点的真实距离。 |
|
|
getTrueDistance 计算一个路线的起始点与终止点的真实距离。 |
|
|
getTrueDistance 获取两个序列之间的距离 Get the Canberra distance between two sequences (note that there is no length check function here, if you need to use this method, please configure the array length check outside) |
|
|
getTrueDistance 计算一个路线的起始点与终止点的真实距离。 |
|
|
getTrueDistance 计算一个路线的起始点与终止点的真实距离。 |
度量计算组件列表
| 计算组件类型 |
支持版本 |
功能 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.distanceAlgorithm.EuclideanMetric |
v1.0 |
计算欧几里得距离 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.distanceAlgorithm.CanberraDistance |
v1.0 |
计算堪培拉距离 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.distanceAlgorithm.ChebyshevDistance |
v1.0 |
计算切比雪夫距离 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.distanceAlgorithm.CosineDistance |
v1.0 |
计算向量余弦度量 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.distanceAlgorithm.HausdorffDistance |
v1.0 |
计算豪斯多夫距离 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.distanceAlgorithm.ManhattanDistance |
v1.0 |
计算曼哈顿距离 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.distanceAlgorithm.MinkowskiDistance |
v1.0 |
计算闵可夫斯基距离 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.distanceAlgorithm.StandardizedEuclideanDistance |
v1.0 |
计算标准化欧几里得度量 |
度量计算API实现
本次我们使用欧几里得进行度量计算的API相关示例调用。
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.distanceAlgorithm.EuclideanMetric;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.coordinate.FloatingPointCoordinates;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.coordinate.IntegerCoordinateMany;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取到德氏距离计算组件对象
EuclideanMetric> euclideanMetric = EuclideanMetric.getInstance("zhao");
// 创建需要计算的向量数组(也可以是坐标)
double[] v1 = new double[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
double[] v2 = new double[]{1, 2, 3, 1, 5};
double[] v3 = new double[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 开始进行计算
System.out.println("v1 与 v2 之间的德式距离:" + euclideanMetric.getTrueDistance(v1, v2));
System.out.println("v1 与 v3 之间的德式距离:" + euclideanMetric.getTrueDistance(v1, v3));
System.out.println("v2 与 v3 之间的德式距离:" + euclideanMetric.getTrueDistance(v2, v3));
}
} 聚合计算
在AS库中,聚合计算组件是专用于向量这一类多数值转换成为少量甚至1个数值任务的计算组件,能够实现多种需求的计算与操作。接下来展示与之相关的API介绍。
聚合计算函数说明
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
|
|
calculation 计算函数,将某个数组中的所有元素按照某个规则进行聚合 Compute function to aggregate all elements in an array according to a certain rule |
|
|
calculation 计算函数,将某个数组中的所有元素按照某个规则进行聚合 Compute function to aggregate all elements in an array according to a certain rule |
聚合计算组件列表
| 计算组件类型 |
支持版本 |
功能 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.aggregationAlgorithm.ExtremumAggregation |
v1.14 |
计算一些数值的极值 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.aggregationAlgorithm.WeightedAverage |
v1.14 |
计算一些数值的加权平均数 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.aggregationAlgorithm.ModularOperation |
v1.14 |
计算一个序列或多个序列聚合之后的模长 |
聚合计算API实现
接下来使用AS库中的聚合计算组件,计算一个向量中的极值,AS库中的极值计算组件是一个聚合计算组件的实现类,其包含强大的数据过滤与极值计算功能,接下来就进行该组件的一个演示。
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.aggregationAlgorithm.ExtremumAggregation;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取到德氏距离计算组件对象
// 创建需要计算的向量数组(也可以是坐标)
double[] v1 = new double[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5,10, 1024, -1};
// 获取到极值计算组件对象
ExtremumAggregation ex = ExtremumAggregation.getInstance("ex");
// 设置计算模式 - 计算向量中的最大值
ex.setMode(ExtremumAggregation.MAX);
System.out.println("最大值 = " + ex.calculation(v1));
// 设置计算模式 - 计算向量中的最小值
ex.setMode(ExtremumAggregation.MIN);
System.out.println("最小值 = " + ex.calculation(v1));
// 设置计算模式 - 计算向量中所有偶数的最大值(如果存在偶数的话就会返回预期结果)
ex.setMode(ExtremumAggregation.EVEN_MAX);
System.out.println("偶数中的最大值 = " + ex.calculation(v1));
// 设置计算模式 - 计算向量中所有偶数的最小值(如果存在偶数的话就会返回预期结果)
ex.setMode(ExtremumAggregation.EVEN_MIN);
System.out.println("偶数中的最小值 = " + ex.calculation(v1));
// 设置计算模式 - 计算向量中所有奇数的最大值(如果存在奇数的话就会返回预期结果)
ex.setMode(ExtremumAggregation.ODD_MAX);
System.out.println("奇数中的最大值 = " + ex.calculation(v1));
// 设置计算模式 - 计算向量中所有奇数的最小值(如果存在奇数的话就会返回预期结果)
ex.setMode(ExtremumAggregation.ODD_MIN);
System.out.println("奇数中的最小值 = " + ex.calculation(v1));
}
}分类计算
专注于样本中某些未知类别的数据推断工作的计算组件,在AS库中常用的就是自定义距离计算组件的分类计算函数,能够通过用户所设设置的距离计算组件来进行样本之间的相似度分析等操作,在诸多支持自定义距离计算组件的分类组件中,默认的距离计算组件往往都是欧几里得计算,接下来就展示与之相关的一些信息!
分类计算函数说明
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
| HashMap |
classification 计算一个矩阵中所有行或列的数据类别,并将计算之后的数据类别样本返回出去。 |
| HashMap |
classification 计算一个矩阵中所有行或列的数据类别,并将计算之后的数据类别样本返回出去。 |
| HashMap |
classification 计算一个矩阵中所有行或列的数据类别,并将计算之后的数据类别样本返回出去。 |
| HashMap |
classification 计算一个矩阵中所有行或列的数据类别,并将计算之后的数据类别样本返回出去。 |
|
|
getInstance 获取到该算法的类对象。 |
支持自定义距离计算组件的分类函数
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
| HashMap |
classification 计算一个矩阵中所有行或列的数据类别,并将计算之后的数据类别样本返回出去。 |
| HashMap |
classification 计算一个矩阵中所有行或列的数据类别,并将计算之后的数据类别样本返回出去。 |
| HashMap |
classification 计算一个矩阵中所有行或列的数据类别,并将计算之后的数据类别样本返回出去。 |
| HashMap |
classification 计算一个矩阵中所有行或列的数据类别,并将计算之后的数据类别样本返回出去。 |
|
|
getInstance 获取到该算法的类对象。 |
分类计算组件列表
| 计算组件类型 |
支持版本 |
功能 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm. classificationAlgorithm.UDFDistanceClassification |
v1.14 |
利用手动传入类别样本的方式,进行距离计算并分类 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm. classificationAlgorithm.KnnClassification |
v1.14 |
利用K 近邻算法将最近的K个特征进行距离 |
分类计算API实现
package zhao.algorithmMagic;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.classificationAlgorithm.KnnClassification;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.distanceAlgorithm.EuclideanMetric;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.matrix.ColumnDoubleMatrix;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.vector.DoubleVector;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.utils.DependentAlgorithmNameLibrary;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MAIN1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个矩阵对象其中包含一些数据
ColumnDoubleMatrix columnDoubleMatrix = new ColumnDoubleMatrix(
new String[]{"会说话", "会工具", "会觅食", "会编程"},
new String[]{"人类", "人类", "?", "小鸟", "小鸟", "?", "人类", "人类"},
new double[]{1, 1, 1, 0}, // 人类
new double[]{1, 1, 1, 1}, // 人类
new double[]{0, 0, 1, 0}, // 小鸟 未知量
new double[]{1, 0, 1, 0}, // 小鸟
new double[]{0, 0, 1, 0}, // 小鸟
new double[]{0, 1, 1, 0}, // 人类 未知量
new double[]{1, 1, 1, 1}, // 人类
new double[]{0, 1, 1, 1} // 人类
);
// 打乱矩阵中的数据 使用 221 作为随机种子
columnDoubleMatrix = columnDoubleMatrix.shuffle(221);
System.out.println(columnDoubleMatrix);
// 开始进行矩阵数据的分类 先获取到knn近邻计算组件
KnnClassification knn = KnnClassification.getInstance("knn");
// 设置分类时需要使用的距离计算组件,这里使用的是欧几里得(如果不设置也是一样的)
knn.setDistanceAlgorithm(
EuclideanMetric.getInstance(DependentAlgorithmNameLibrary.EUCLIDEAN_METRIC_NAME)
); // 设置K近邻计算时候的 近邻阈值 K的具体数值
knn.setK(10);
// 开始进行计算与分类
HashMap> classification = knn.classification(
columnDoubleMatrix.getRowFieldNames(), columnDoubleMatrix.toArrays()
); // 打印分类结果 这里只会将需要分类的数据获取到
classification.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.print("\n种类:");
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println(value);
});
}
} 差异计算
差异计算用于计算两个样本之间的差异数值,其本身与度量计算组件是有关系的,一般来说差异计算组件的结果代表的就是差异系数,系数与样本之间的差异程线性关系,在AS库中,向量之间的距离由度量计算组件实现,而诸多其它类型的差异计算也可以被支持,其专门设立了一个差异计算组件模型,这类计算组件能支持的计算类型是泛型的,不同组件的实现能进行不同类型的数据对象的计算。
差异计算函数说明
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
|
|
getDifferenceRatio 计算两个事物之间的差异系数百分比 Calculate the percentage difference from the coefficient of difference between two things |
差异计算组件列表
| 计算组件类型 |
支持版本 |
功能 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm. differenceAlgorithm.BrayCurtisDistance |
v1.0 |
计算两个数据样本之间的布雷柯蒂斯差异系数 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm. differenceAlgorithm.DiceCoefficient |
v1.0 |
计算两个数据样本之间的Dice差异系数 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm. differenceAlgorithm.EditDistance |
v1.0 |
计算两个数据样本之间的最小编辑次数 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm. differenceAlgorithm.HammingDistance |
v1.0 |
计算两个数据样本之间的汉明差异系数 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm. differenceAlgorithm.JaccardSimilarityCoefficient |
v1.0 |
计算两个数据样本之间的杰卡德相似系数 |
差异计算API实现
package zhao.algorithmMagic;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.differenceAlgorithm.BrayCurtisDistance;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.differenceAlgorithm.HammingDistance;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.coordinate.DoubleCoordinateThree;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.coordinate.IntegerCoordinateThree;
public class MAIN1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取到两个差异计算组件,分别用于计算坐标之间的距离与字符串之间的差异
// 该组件能够接收字符串对象
HammingDistance hammingDistance = HammingDistance.getInstance("HammingDistance");
// 这里指定组件能够计算的坐标数据类型
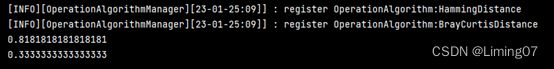
BrayCurtisDistance brayCurtisDistance = BrayCurtisDistance.getInstance("BrayCurtisDistance");
// 开始进行字符串之间的距离计算
System.out.println(hammingDistance.getDifferenceRatio("Hello Zhao!", "Hello Yang!"));
// 开始进行坐标之间的差异计算
System.out.println(brayCurtisDistance.getDifferenceRatio(
new DoubleCoordinateThree(1, 0, 1), new DoubleCoordinateThree(2, 1, 1)
));
}
} 路径计算
路径计算专用于路径网络中的计算,能够在一个网络中快速的计算出我们需要的目标,目前AS库中能够计算出一个路线网络中的最短路径,与生成潜在的路径联系等功能,接下来就是相关信息多少介绍。
路径计算函数说明
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
|
|
addRoute 添加一个需要被算法处理的线路。 |
|
|
addRoute 添加一个需要被算法处理的线路。 |
|
|
clear 一般情况下。该函数用于清理所有被添加的线路 |
路径计算组件列表
| 计算组件类型 |
支持版本 |
功能 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.generatingAlgorithm.Dijkstra |
v1.0 |
计算一个路线网络中的最小距离 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.generatingAlgorithm.Dijkstra2D |
v1.0 |
计算一个路线网络中的最小距离 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.generatingAlgorithm.DirectionalDijkstra2D |
v1.0 |
计算一个路线网络中的最小距离 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.generatingAlgorithm.ZhaoCoordinateNet |
v1.0 |
计算一个路线网络潜在联系,并生成对应的路线对象到路线网中 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.generatingAlgorithm.ZhaoCoordinateNet2D |
v1.0 |
计算一个路线网络潜在联系,并生成对应的路线对象到路线网中 |
路径计算组件API实现
路径计算组件中最常用的同时也是现有计算算法中比较熟悉的dijkstra 计算组件,在AS的实现中,其可以计算出一个复杂路线网络中的最短线路对象,并将其在网络中进行标记,接下来就是与之相关的API实现。
package zhao.algorithmMagic;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.distanceAlgorithm.EuclideanMetric;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.generatingAlgorithm.Dijkstra;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.coordinate.IntegerCoordinateMany;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.coordinateNet.DoubleRouteNet;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.route.DoubleConsanguinityRoute;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.route.IntegerConsanguinityRoute;
public class MAIN1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取到 Dijkstra 算法
Dijkstra dijkstra = Dijkstra.getInstance("Dijkstra");
// 向算法中添加一些线路
IntegerCoordinateMany integerCoordinateMany_B = new IntegerCoordinateMany(1, 2, 8);
dijkstra.addRoute(
IntegerConsanguinityRoute.parse(
"A -> B", new IntegerCoordinateMany(1, 2, 3), integerCoordinateMany_B
)
);
dijkstra.addRoute(
IntegerConsanguinityRoute.parse(
"C -> B", new IntegerCoordinateMany(0, 2, 3), integerCoordinateMany_B
)
);
dijkstra.addRoute(
IntegerConsanguinityRoute.parse(
"D -> B", new IntegerCoordinateMany(-1, 2, 3), integerCoordinateMany_B
)
);
// 设置计算时需要的度量计算组件
dijkstra.setDistanceAlgorithm(EuclideanMetric.getInstance("E"));
// 开始计算出以B为中心的最短线路网
DoubleRouteNet doubleRouteNet = dijkstra.getShortestPath("B");
// 打印出网络中的最短线路 最短线路将会被添加到网络中的主标记集合,因此这里获取到主标记集合,并打印最短坐标的名称
doubleRouteNet
// 获取到所有被标记的线路对象 dijkstra 会将最短线路标记出来
.getDoubleConsanguinityRouteHashMap_MasterTag()
// 将所有的线路对象转换成线路路径名字
.values().stream().map(DoubleConsanguinityRoute::getRouteName)
// 开始打印所有的路径名称
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
数据预处理(标准化/归一化)
特征工程中的数据预处理主要包括数据降维与数据维度标准和归一化操作,针对数据降维等相关函数在矩阵中有直接的调用,针对数据的标准化与归一化则需要使用到数据预处理算法,接下来就进行一个相关的介绍与演示。
数据预处理函数说明
注意:在这里的函数统一使用标准化作为函数名,但不影响归一化组件是实现出来的序列归一操作,后期会更改此函数名称。
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
| String |
getAlgorithmName |
|
|
init 算法模块的初始化方法。 The initialization method of the algorithm module. |
|
|
NormalizedSequence 将一个序列进行标准化,具体的标准化有不同的实现 |
|
|
NormalizedSequence 将一个序列进行标准化,具体的标准化有不同的实现 |
|
|
NormalizedSequence 将一个序列进行标准化,具体的标准化有不同的实现 |
|
|
NormalizedSequence 将一个序列进行标准化,具体的标准化有不同的实现 |
数据预处理组件列表
| 计算组件类型 |
支持版本 |
功能 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.normalization.LinearNormalization |
v1.0 |
将一个向量数据样本进行线性归一化 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.normalization.Z_ScoreNormalization |
v1.0 |
将一个向量数据样本进行正负均匀分配的标准化 |
数据预处理API实现
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.normalization.LinearNormalization;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.vector.DoubleVector;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取到一个向量对象
DoubleVector doubleVector = DoubleVector.parse(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1);
// 获取到数据预处理归一化组件
LinearNormalization line = LinearNormalization.getInstance("line");
// 设置归一化区间
line.setMax(3);
line.setMin(-3);
// 开始进行向量归一化
DoubleVector doubleVector1 = line.NormalizedSequence(doubleVector);
// 打印归一化之后的向量数据
System.out.println(doubleVector1);
}
}![]()
概率计算
概率计算是一种以标准系数衡量事件发生可能性的数据计算组件,其具有强大的概率计算体系,能够针对事务期望做出类别预分析等操作。
概率计算函数说明
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
|
|
estimate 计算一个矩阵中的某些条件限制下的联合概率结果 P(A|B) 其中的分子与分母值! |
|
|
estimate 计算一个矩阵中的某些条件限制下的联合概率结果 P(A|B) 其中的分子与分母值! |
|
|
estimateGetFraction 计算一个矩阵中的某些条件限制下的联合概率结果 P(A|B) 其中的分子与分母值! |
|
|
estimateGetFraction 计算一个矩阵中的某些条件限制下的联合概率结果 P(A|B) 其中的分子与分母值! |
| String |
getAlgorithmName |
|
|
init 算法模块的初始化方法,在这里您可以进行组件的初始化方法,当初始化成功之后,该算法就可以处于就绪的状态,一般这里就是将自己添加到算法管理类中 The initialization method of the algorithm module, here you can perform the initialization method of the component, when the initialization is successful, the algorithm can be in a ready state, generally here is to add yourself to the algorithm management class |
概率计算组件列表
| 计算组件类型 |
支持版本 |
功能 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.probabilisticAlgorithm.NaiveBayes |
v1.14 |
通过较小的计算量计算出形如”P(A\B)“事件发生的概率数值 |
概率计算API实现
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.probabilisticAlgorithm.NaiveBayes;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.matrix.ColumnIntegerMatrix;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.utils.filter.ArrayIntegerFiltering;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] strings1 = {"职业", "体型", "喜欢"};
// 准备一个数据矩阵
// 职业:1-程序员 2-产品 3-美工
ColumnIntegerMatrix parse = ColumnIntegerMatrix.parse(
strings1,
new String[]{"N1", "N2", "N3", "N4", "N5", "N6", "N7", "N8", "N9", "N10"},
new int[]{1, 1, 0},
new int[]{2, 0, 1},
new int[]{1, 0, 1},
new int[]{1, 1, 1},
new int[]{3, 0, 0},
new int[]{3, 1, 0},
new int[]{2, 0, 1},
new int[]{2, 1, 1},
new int[]{2, 1, 0},
new int[]{2, 1, 0}
);
System.out.println(parse);
// 打乱样本 删除原先的矩阵,并打印新矩阵
parse = parse.shuffle(22);
System.out.println(parse);
// 开始获取朴素贝叶斯算法 计算目标:在自己是产品同时超重的情况下,被喜欢的概率 P(被喜欢|产品,超重)
NaiveBayes bayes = NaiveBayes.getInstance("bayes");
// 构造事件A 自己被喜欢
ArrayIntegerFiltering arrayIntegerFilteringA = v -> v[2] == 1;
// 构造事件B 自己是产品,同时超重
ArrayIntegerFiltering arrayIntegerFilteringB = v -> v[0] == 2 && v[1] == 1;
// 开始计算结果 这个结果是一个条件概率值 P(A|B) 在B事件的前提下,A事件发生的概率
System.out.println(bayes.estimate(parse, arrayIntegerFilteringA, arrayIntegerFilteringB));
}
}![]()
决策计算
决策计算函数说明
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
|
|
estimate 计算一个矩阵中的某些条件限制下的联合概率结果 P(A|B) 其中的分子与分母值! |
|
|
estimate 计算一个矩阵中的某些条件限制下的联合概率结果 P(A|B) 其中的分子与分母值! |
|
|
estimateGetFraction 计算一个矩阵中的某些条件限制下的联合概率结果 P(A|B) 其中的分子与分母值! |
|
|
estimateGetFraction 计算一个矩阵中的某些条件限制下的联合概率结果 P(A|B) 其中的分子与分母值! |
| String |
getAlgorithmName |
|
|
init 算法模块的初始化方法,在这里您可以进行组件的初始化方法,当初始化成功之后,该算法就可以处于就绪的状态,一般这里就是将自己添加到算法管理类中 The initialization method of the algorithm module, here you can perform the initialization method of the component, when the initialization is successful, the algorithm can be in a ready state, generally here is to add yourself to the algorithm management class |
决策计算组件列表
| 计算组件类型 |
支持版本 |
功能 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.schemeAlgorithm.DecisionTree |
v1.14 |
决策树计算组件,计算出最有效率的筛选路径,并按照路径将传递进来的事件处理函数进行排列 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.schemeAlgorithm.RandomForest |
v1.15 |
随机森林计算组件,随机分布样本自动选择最优秀解 |
决策计算API实现
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.schemeAlgorithm.DecisionTree;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.matrix.ColumnIntegerMatrix;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.utils.filter.ArrayIntegerFiltering;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取到决策树计算组件
DecisionTree decisionTree = DecisionTree.getInstance("DecisionTree");
String[] strings1 = {"职业", "体型", "喜欢"};
// 准备一个数据矩阵
// 职业:1-程序员 2-产品 3-美工
ColumnIntegerMatrix parse = ColumnIntegerMatrix.parse(
strings1,
new String[]{"N1", "N2", "N3", "N4", "N5", "N6", "N7", "N8", "N9", "N10"},
new int[]{1, 1, 0},
new int[]{2, 0, 1},
new int[]{1, 0, 1},
new int[]{1, 1, 1},
new int[]{3, 0, 0},
new int[]{3, 1, 0},
new int[]{2, 0, 1},
new int[]{2, 1, 1},
new int[]{2, 1, 0},
new int[]{2, 1, 0}
);
System.out.println(parse);
// 使用22作为随机种子,打乱样本 删除原先的矩阵,并打印新矩阵
parse = parse.shuffle(22);
System.out.println(parse);
// 开始进行筛选,要去获取到 职业=3 体型=1 喜欢=0 的行数据,并将其处理过程展示出来
// 先将事件对象准备出来
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加职业=3的事件
arrayList.add(v -> v[0] == 3);
// 添加体型=1的事件
arrayList.add(v -> v[1] == 1);
// 添加喜欢=0的是啊金
arrayList.add(v -> v[2] == 0);
String s = decisionTree.executeGetString(parse.toArrays(), arrayList);
// 打印结果
System.out.println(s);
}
} 模型预测
在机器学习中的预测部分经常是使用的模型对数据的趋势进行的数据预测,在我们的已知的这些计算组件中,常用的就是线性回归计算组件,在该组件这种,您可以使用一个预先设置好的线性模型,来对数据模型中的未知回归参数进行推断与计算。
模型预测
在机器学习中的预测部分经常是使用的模型对数据的趋势进行的数据预测,在我们的已知的这些计算组件中,常用的就是线性回归计算组件,在该组件这种,您可以使用一个预先设置好的线性模型,来对数据模型中的未知回归参数进行推断与计算。
模型预测函数说明
| 限定符和类型 |
方法和说明 |
|
|
getAlgorithmName |
|
|
init 算法模块的初始化方法,在这里您可以进行组件的初始化方法,当初始化成功之后,该算法就可以处于就绪的状态,一般这里就是将自己添加到算法管理类中 The initialization method of the algorithm module, here you can perform the initialization method of the component, when the initialization is successful, the algorithm can be in a ready state, generally here is to add yourself to the algorithm management class |
|
|
modelInference 通过给定的一个模型,不断修正模型中的参数或其它方式,最终返回在最接近样本本身时所有参数组成的数组 Through a given model, continuously modify the parameters in the model or other ways, and finally return the array of all parameters when they are closest to the sample itself. |
|
|
modelInference 通过给定的一个模型,不断修正模型中的参数或其它方式,最终返回在最接近样本本身时所有参数组成的数组 Through a given model, continuously modify the parameters in the model or other ways, and finally return the array of all parameters when they are closest to the sample itself. |
概率预测组件列表
| 计算组件类型 |
支持版本 |
功能 |
| zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm. modelAlgorithm.LinearRegression |
v1.15 |
该计算组件能够实现快速的一元线性回归计算 |
概率预测API实现
package zhao.algorithmMagic;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.algorithm.modelAlgorithm.LinearRegression;
import zhao.algorithmMagic.operands.matrix.ColumnDoubleMatrix;
public class MAIN1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
// 创建一个矩阵对象,其中包含一些数据,现在需要找到最块的筛选路线,并使用此路线将数据进行一次获取
ColumnDoubleMatrix columnDoubleMatrix = ColumnDoubleMatrix.parse(
new String[]{"x", "y"},
null,
new double[]{1, 50},
new double[]{2, 100},
new double[]{3, 150},
new double[]{4, 200}
);
// 获取到线性回归
LinearRegression line = LinearRegression.getInstance("line");
// 开始计算线性回归 计算x 与 y 之间的关系 其中 x 为自变量 y 为因变量
// 设置自变量的列编号
line.setFeatureIndex(0);
// 设置因变量的列编号
line.setTargetIndex(1);
// 计算出回归系数与结果值
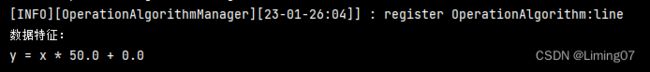
double[] doubles = line.modelInference(columnDoubleMatrix);
// 获取到线性回归计算之后的权重数组,并将权重数组插入到公式打印出来
System.out.println("数据特征:");
System.out.println("y = x * " + doubles[0] + " + " + doubles[1]);
}
}
Algorithm Star开源协议
| Apache License Version 2.0, January 2004 http://www.apache.org/licenses/ TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION 1. Definitions. "License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction, and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document. "Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by the copyright owner that is granting the License. "Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition, "control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity. "You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity exercising permissions granted by this License. "Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications, including but not limited to software source code, documentation source, and configuration files. "Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical transformation or translation of a Source form, including but not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation, and conversions to other media types. "Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work (an example is provided in the Appendix below). "Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of, the Work and Derivative Works thereof. "Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted" means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems, and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution." "Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and subsequently incorporated within the Work. 2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual, worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of, publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form. 3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual, worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable (except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made, use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work, where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s) with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You institute patent litigation against any entity (including a cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate as of the date such litigation is filed. 4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You meet the following conditions: (a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or Derivative Works a copy of this License; and (b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices stating that You changed the files; and (c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and attribution notices from the Source form of the Work, excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of the Derivative Works; and (d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or, within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed as modifying the License. You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and may provide additional or different license terms and conditions for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use, reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with the conditions stated in this License. 5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise, any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of this License, without any additional terms or conditions. Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed with Licensor regarding such Contributions. 6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor, except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file. 7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License. 8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory, whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise, unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill, work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor has been advised of the possibility of such damages. 9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer, and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity, or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify, defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability. END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work. To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "[]" replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a file or class name and description of purpose be included on the same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier identification within third-party archives. Copyright [yyyy] [name of copyright owner] Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. |