(1) Stream是什么
Redis 从 5.0 版本开始支持提供 Stream 数据类型,它可以用来保存消息数据,能帮助我们实现一个带有消息读写基本功能的消息队列,并用于日常的分布式程序通信当中。
(1.1) Stream 消息数据的特征
Stream 作为消息队列,它保存的消息通常具有以下两个特征:
一条消息由一个或多个键值对组成;
每插入一条消息,这条消息都会对应一个消息 ID。
一般会让 Redis 服务器自动生成递增的消息 ID。此时,消息 ID 由时间戳和序号组成。其中,时间戳是消息插入时,以毫秒为单位的服务器当时时间,序号是插入消息在当前毫秒内的序号。
(2) 为什么使用Stream
如果要用消息队列,用比较流行的mq 比如:Kafka、RocketMq,为什么要用Redis Stream呢?
Kafka等MQ使用起来比较重,如果仅仅是简单使用的话,成本比较高。而Redis Stream是对消息队列的完美实现,可以快速上手使用,成本也比较低。
(3) Stream原理
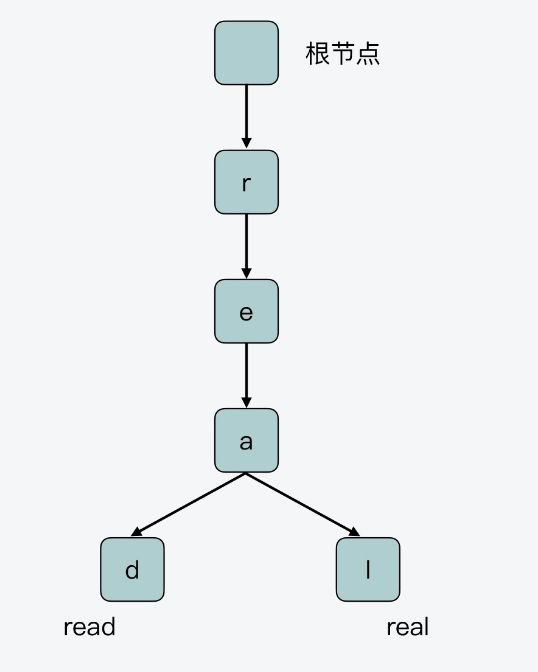
Radix Tree 是属于前缀树的一种类型。
前缀树也称为 Trie Tree,它的特点是,保存在树上的每个 key 会被拆分成单字符,然后逐一保存在树上的节点中。
前缀树的根节点不保存任何字符,而除了根节点以外的其他节点,每个节点只保存一个字符。
当我们把从根节点到当前节点的路径上的字符拼接在一起时,就可以得到相应 key 的值了。
前缀树是把保存的 key 的公共前缀(即 r、e、a)独立出来共享使用的。这样一来,就可以避免在树中对相同的字符做重复存储。
前缀树相比于哈希表,节省了重复字符的内存开销
(3.1) Redix tree的改进
前缀树的不足
前缀树在每个节点中只保存一个字符,这样做的好处就是可以尽可能地共享不同 key 的公共前缀。
但是,这也会导致 key 中的某些字符串,虽然不再被共享,可仍然会按照每个节点一个字符的形式来保存,这样反而会造成空间的浪费和查询性能的降低。
如果我们还是按照前缀树的方式,为每一个字符创建一个节点进行保存的话,一是会浪费内存空间,二是在进行查询时,还需要逐一匹配每个节点表示的字符,对查询性能也会造成影响。
如果一系列单字符节点之间的分支连接是唯一的,那么这些单字符节点就可以合并成一个节点,而这种结构的树,就正是 Radix Tree,也被称为基数树。相比前缀树来说,Radix Tree 既可以节约内存的使用,同时还可以提高查询访问的效率。
(3.2) Stream 如何组合使用 Radix Tree 和 listpack?
Stream 保存的消息数据,按照 key-value 形式来看的话,消息 ID 就相当于 key,而消息内容相当于是 value。
也就是,Stream 会使用 Radix Tree 来保存消息 ID,然后将消息内容保存在 listpack 中,并作为消息 ID 的 value,用 raxNode 的 value 指针指向对应的 listpack。
(4) 源码解读
(4.1) 结构定义
// file: stream.h
typedef struct stream {
rax *rax; // 保存消息的Radix Tree
uint64_t length; // 消息流中的元素个数
streamID last_id; // 当前消息流中最后插入的消息的ID
rax *cgroups; // 当前消息流的消费组信息,也是用Radix Tree保存
} stream;// file: rax.h
/**
* rax结构体
*/
typedef struct rax {
raxNode *head; // 保存消息的 Radix Tree
uint64_t numele; // 元素/key个数
uint64_t numnodes; // raxNode个数
} rax;// file: rax.h
#define RAX_NODE_MAX_SIZE ((1<<29)-1)
/**
*
*/
typedef struct raxNode {
uint32_t iskey:1; // 节点是否包含key
uint32_t isnull:1; // 节点的值是否为NULL
uint32_t iscompr:1; // 节点是否被压缩
uint32_t size:29; // 孩子节点个数 或 压缩字符长度
unsigned char data[];
} raxNode;
/* Stream item ID: a 128 bit number composed of a milliseconds time and
* a sequence counter. IDs generated in the same millisecond (or in a past
* millisecond if the clock jumped backward) will use the millisecond time
* of the latest generated ID and an incremented sequence. */
typedef struct streamID {
uint64_t ms; /* Unix time in milliseconds. */
uint64_t seq; /* Sequence number. */
} streamID;(4.2) 创建stream结构
/**
* 创建一个新的stream数据结构
*/
stream *streamNew(void) {
// 分配内存
stream *s = zmalloc(sizeof(*s));
// 新建
s->rax = raxNew();
s->length = 0;
s->last_id.ms = 0;
s->last_id.seq = 0;
s->cgroups = NULL; /* Created on demand to save memory when not used. */
return s;
}// file: rax.c
/* Allocate a new rax and return its pointer. On out of memory the function
* returns NULL. */
rax *raxNew(void) {
rax *rax = rax_malloc(sizeof(*rax));
if (rax == NULL) return NULL;
rax->numele = 0;
rax->numnodes = 1;
rax->head = raxNewNode(0,0);
if (rax->head == NULL) {
rax_free(rax);
return NULL;
} else {
return rax;
}
}(4.3) 释放Stream
/* Free a stream, including the listpacks stored inside the radix tree. */
void freeStream(stream *s) {
raxFreeWithCallback(s->rax,(void(*)(void*))lpFree);
if (s->cgroups)
raxFreeWithCallback(s->cgroups,(void(*)(void*))streamFreeCG);
zfree(s);
}(4.4) stream新增元素
/* Adds a new item into the stream 's' having the specified number of
* field-value pairs as specified in 'numfields' and stored into 'argv'.
* Returns the new entry ID populating the 'added_id' structure.
*
* If 'use_id' is not NULL, the ID is not auto-generated by the function,
* but instead the passed ID is used to add the new entry. In this case
* adding the entry may fail as specified later in this comment.
*
* The function returns C_OK if the item was added, this is always true
* if the ID was generated by the function. However the function may return
* C_ERR in several cases:
* 1. If an ID was given via 'use_id', but adding it failed since the
* current top ID is greater or equal. errno will be set to EDOM.
* 2. If a size of a single element or the sum of the elements is too big to
* be stored into the stream. errno will be set to ERANGE. */
int streamAppendItem(stream *s, robj **argv, int64_t numfields, streamID *added_id, streamID *use_id) {
/* Generate the new entry ID. */
streamID id;
if (use_id)
id = *use_id;
else
streamNextID(&s->last_id,&id);
/* Check that the new ID is greater than the last entry ID
* or return an error. Automatically generated IDs might
* overflow (and wrap-around) when incrementing the sequence
part. */
if (streamCompareID(&id,&s->last_id) <= 0) {
errno = EDOM;
return C_ERR;
}
/* Avoid overflow when trying to add an element to the stream (listpack
* can only host up to 32bit length sttrings, and also a total listpack size
* can't be bigger than 32bit length. */
size_t totelelen = 0;
for (int64_t i = 0; i < numfields*2; i++) {
sds ele = argv[i]->ptr;
totelelen += sdslen(ele);
}
if (totelelen > STREAM_LISTPACK_MAX_SIZE) {
errno = ERANGE;
return C_ERR;
}
/* Add the new entry. */
raxIterator ri;
raxStart(&ri,s->rax);
raxSeek(&ri,"$",NULL,0);
size_t lp_bytes = 0; /* Total bytes in the tail listpack. */
unsigned char *lp = NULL; /* Tail listpack pointer. */
/* Get a reference to the tail node listpack. */
if (raxNext(&ri)) {
lp = ri.data;
lp_bytes = lpBytes(lp);
}
raxStop(&ri);
/* We have to add the key into the radix tree in lexicographic order,
* to do so we consider the ID as a single 128 bit number written in
* big endian, so that the most significant bytes are the first ones. */
uint64_t rax_key[2]; /* Key in the radix tree containing the listpack.*/
streamID master_id; /* ID of the master entry in the listpack. */
/* Create a new listpack and radix tree node if needed. Note that when
* a new listpack is created, we populate it with a "master entry". This
* is just a set of fields that is taken as references in order to compress
* the stream entries that we'll add inside the listpack.
*
* Note that while we use the first added entry fields to create
* the master entry, the first added entry is NOT represented in the master
* entry, which is a stand alone object. But of course, the first entry
* will compress well because it's used as reference.
*
* The master entry is composed like in the following example:
*
* +-------+---------+------------+---------+--/--+---------+---------+-+
* | count | deleted | num-fields | field_1 | field_2 | ... | field_N |0|
* +-------+---------+------------+---------+--/--+---------+---------+-+
*
* count and deleted just represent respectively the total number of
* entries inside the listpack that are valid, and marked as deleted
* (deleted flag in the entry flags set). So the total number of items
* actually inside the listpack (both deleted and not) is count+deleted.
*
* The real entries will be encoded with an ID that is just the
* millisecond and sequence difference compared to the key stored at
* the radix tree node containing the listpack (delta encoding), and
* if the fields of the entry are the same as the master entry fields, the
* entry flags will specify this fact and the entry fields and number
* of fields will be omitted (see later in the code of this function).
*
* The "0" entry at the end is the same as the 'lp-count' entry in the
* regular stream entries (see below), and marks the fact that there are
* no more entries, when we scan the stream from right to left. */
/* First of all, check if we can append to the current macro node or
* if we need to switch to the next one. 'lp' will be set to NULL if
* the current node is full. */
if (lp != NULL) {
size_t node_max_bytes = server.stream_node_max_bytes;
if (node_max_bytes == 0 || node_max_bytes > STREAM_LISTPACK_MAX_SIZE)
node_max_bytes = STREAM_LISTPACK_MAX_SIZE;
if (lp_bytes + totelelen >= node_max_bytes) {
lp = NULL;
} else if (server.stream_node_max_entries) {
int64_t count = lpGetInteger(lpFirst(lp));
if (count >= server.stream_node_max_entries) lp = NULL;
}
}
int flags = STREAM_ITEM_FLAG_NONE;
if (lp == NULL || lp_bytes >= server.stream_node_max_bytes) {
master_id = id;
streamEncodeID(rax_key,&id);
/* Create the listpack having the master entry ID and fields. */
lp = lpNew();
lp = lpAppendInteger(lp,1); /* One item, the one we are adding. */
lp = lpAppendInteger(lp,0); /* Zero deleted so far. */
lp = lpAppendInteger(lp,numfields);
for (int64_t i = 0; i < numfields; i++) {
sds field = argv[i*2]->ptr;
lp = lpAppend(lp,(unsigned char*)field,sdslen(field));
}
lp = lpAppendInteger(lp,0); /* Master entry zero terminator. */
raxInsert(s->rax,(unsigned char*)&rax_key,sizeof(rax_key),lp,NULL);
/* The first entry we insert, has obviously the same fields of the
* master entry. */
flags |= STREAM_ITEM_FLAG_SAMEFIELDS;
} else {
serverAssert(ri.key_len == sizeof(rax_key));
memcpy(rax_key,ri.key,sizeof(rax_key));
/* Read the master ID from the radix tree key. */
streamDecodeID(rax_key,&master_id);
unsigned char *lp_ele = lpFirst(lp);
/* Update count and skip the deleted fields. */
int64_t count = lpGetInteger(lp_ele);
lp = lpReplaceInteger(lp,&lp_ele,count+1);
lp_ele = lpNext(lp,lp_ele); /* seek deleted. */
lp_ele = lpNext(lp,lp_ele); /* seek master entry num fields. */
/* Check if the entry we are adding, have the same fields
* as the master entry. */
int64_t master_fields_count = lpGetInteger(lp_ele);
lp_ele = lpNext(lp,lp_ele);
if (numfields == master_fields_count) {
int64_t i;
for (i = 0; i < master_fields_count; i++) {
sds field = argv[i*2]->ptr;
int64_t e_len;
unsigned char buf[LP_INTBUF_SIZE];
unsigned char *e = lpGet(lp_ele,&e_len,buf);
/* Stop if there is a mismatch. */
if (sdslen(field) != (size_t)e_len ||
memcmp(e,field,e_len) != 0) break;
lp_ele = lpNext(lp,lp_ele);
}
/* All fields are the same! We can compress the field names
* setting a single bit in the flags. */
if (i == master_fields_count) flags |= STREAM_ITEM_FLAG_SAMEFIELDS;
}
}
/* Populate the listpack with the new entry. We use the following
* encoding:
*
* +-----+--------+----------+-------+-------+-/-+-------+-------+--------+
* |flags|entry-id|num-fields|field-1|value-1|...|field-N|value-N|lp-count|
* +-----+--------+----------+-------+-------+-/-+-------+-------+--------+
*
* However if the SAMEFIELD flag is set, we have just to populate
* the entry with the values, so it becomes:
*
* +-----+--------+-------+-/-+-------+--------+
* |flags|entry-id|value-1|...|value-N|lp-count|
* +-----+--------+-------+-/-+-------+--------+
*
* The entry-id field is actually two separated fields: the ms
* and seq difference compared to the master entry.
*
* The lp-count field is a number that states the number of listpack pieces
* that compose the entry, so that it's possible to travel the entry
* in reverse order: we can just start from the end of the listpack, read
* the entry, and jump back N times to seek the "flags" field to read
* the stream full entry. */
lp = lpAppendInteger(lp,flags);
lp = lpAppendInteger(lp,id.ms - master_id.ms);
lp = lpAppendInteger(lp,id.seq - master_id.seq);
if (!(flags & STREAM_ITEM_FLAG_SAMEFIELDS))
lp = lpAppendInteger(lp,numfields);
for (int64_t i = 0; i < numfields; i++) {
sds field = argv[i*2]->ptr, value = argv[i*2+1]->ptr;
if (!(flags & STREAM_ITEM_FLAG_SAMEFIELDS))
lp = lpAppend(lp,(unsigned char*)field,sdslen(field));
lp = lpAppend(lp,(unsigned char*)value,sdslen(value));
}
/* Compute and store the lp-count field. */
int64_t lp_count = numfields;
lp_count += 3; /* Add the 3 fixed fields flags + ms-diff + seq-diff. */
if (!(flags & STREAM_ITEM_FLAG_SAMEFIELDS)) {
/* If the item is not compressed, it also has the fields other than
* the values, and an additional num-fileds field. */
lp_count += numfields+1;
}
lp = lpAppendInteger(lp,lp_count);
/* Insert back into the tree in order to update the listpack pointer. */
if (ri.data != lp)
raxInsert(s->rax,(unsigned char*)&rax_key,sizeof(rax_key),lp,NULL);
s->length++;
s->last_id = id;
if (added_id) *added_id = id;
return C_OK;
}(4.5) 查询
/* Return the length of a stream. */
unsigned long streamLength(const robj *subject) {
stream *s = subject->ptr;
return s->length;
}(4.6) 获取下一个id
/* Generate the next stream item ID given the previous one. If the current
* milliseconds Unix time is greater than the previous one, just use this
* as time part and start with sequence part of zero. Otherwise we use the
* previous time (and never go backward) and increment the sequence. */
void streamNextID(streamID *last_id, streamID *new_id) {
// 获取当前时间戳(ms)
uint64_t ms = mstime();
//
if (ms > last_id->ms) {
// 设置 ms 及 该ms内的自增序号
new_id->ms = ms;
new_id->seq = 0;
} else {
// 指针
*new_id = *last_id;
// 序号+1
streamIncrID(new_id);
}
}/* Set 'id' to be its successor streamID */
void streamIncrID(streamID *id) {
if (id->seq == UINT64_MAX) { // 自增序号到64位最大
if (id->ms == UINT64_MAX) { // 时间戳到64位最大
/* Special case where 'id' is the last possible streamID... */
id->ms = id->seq = 0;
} else {
// 增加1ms 重新计数
id->ms++;
id->seq = 0;
}
} else {
// 自增序号+1
id->seq++;
}
}// file: object.c
robj *createStreamObject(void) {
stream *s = streamNew();
robj *o = createObject(OBJ_STREAM,s);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_STREAM;
return o;
}Redis源码剖析与实战 学习笔记 Day7 07 为什么Stream使用了Radix Tree? https://time.geekbang.org/col...